April 30 , 2025.
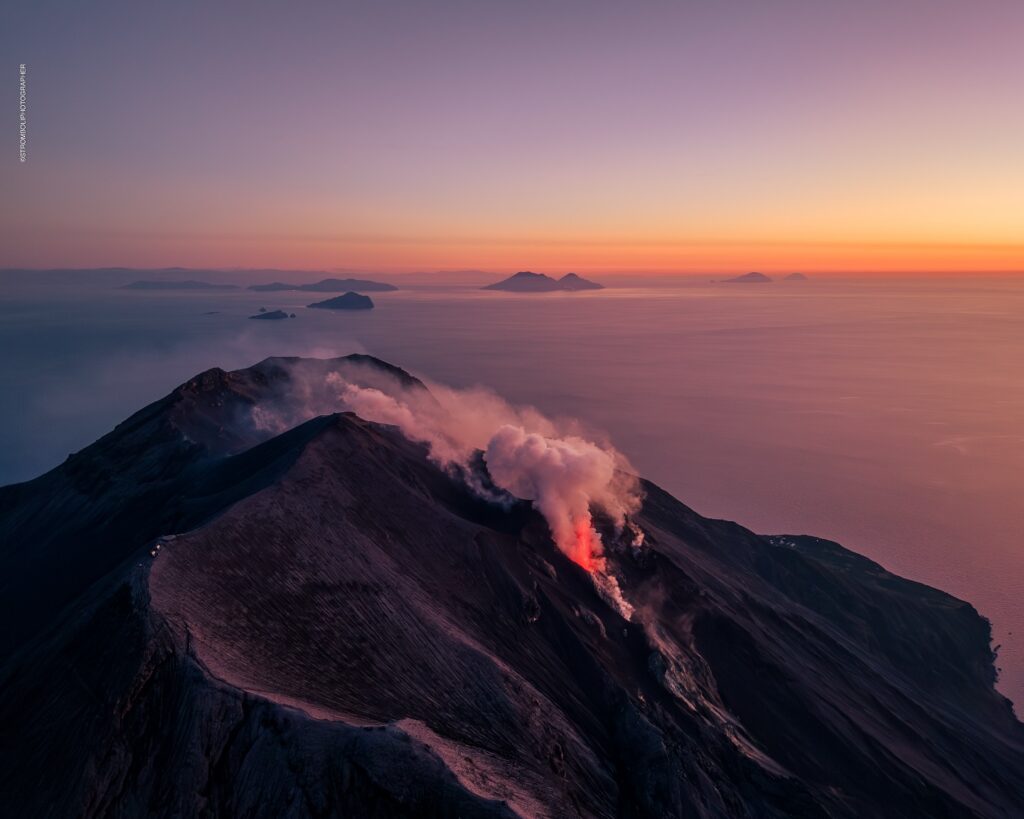
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from April 21, 2025 to April 27, 2025 (publication date April 29, 2025)
SUMMARY OF ACTIVITY STATUS
Based on monitoring data, the following is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: During this period, ordinary Strombolian eruptive activity was observed. The total hourly frequency ranged between average values (9-15 events/h).
The intensity of the explosions was low and medium in the North and South-Central crater areas.
2) SEISMOLOGICAL: The monitored seismic parameters show no significant variations.
3) GROUND DEFORMATION: The ground deformation monitoring networks showed no significant variations. Slight variations have been measured since April 26, 2025.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux: average level.
Soil CO2 flux in the Pizzo area (STR02): no updates.
C/S ratio in the plume: remains at high values.
Helium isotope ratio (R/Ra): no updates.
Soil CO2 flux in the San Bartolo area: average values.
Soil CO2 flux in the Scari area: average values.
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally low.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
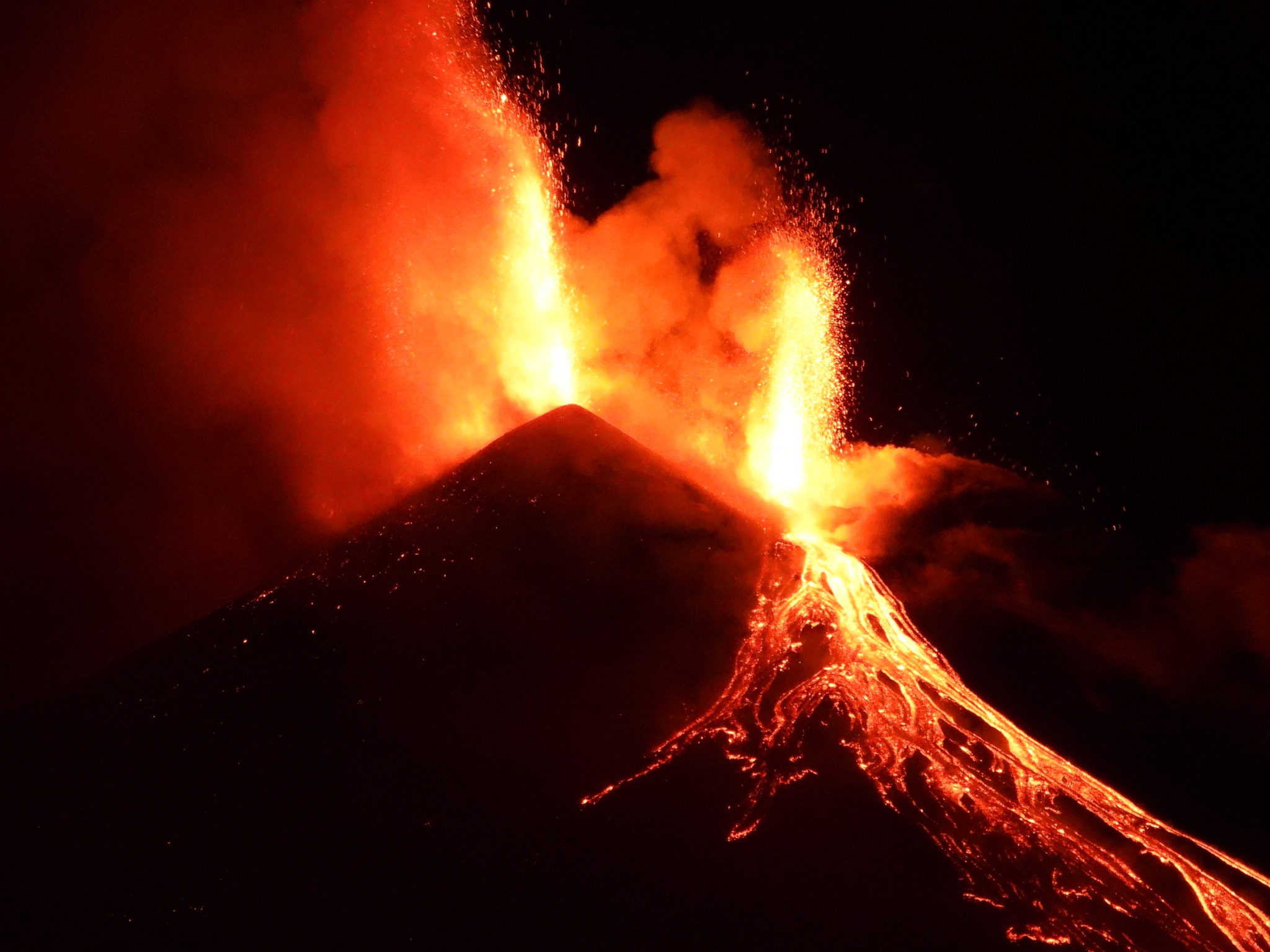
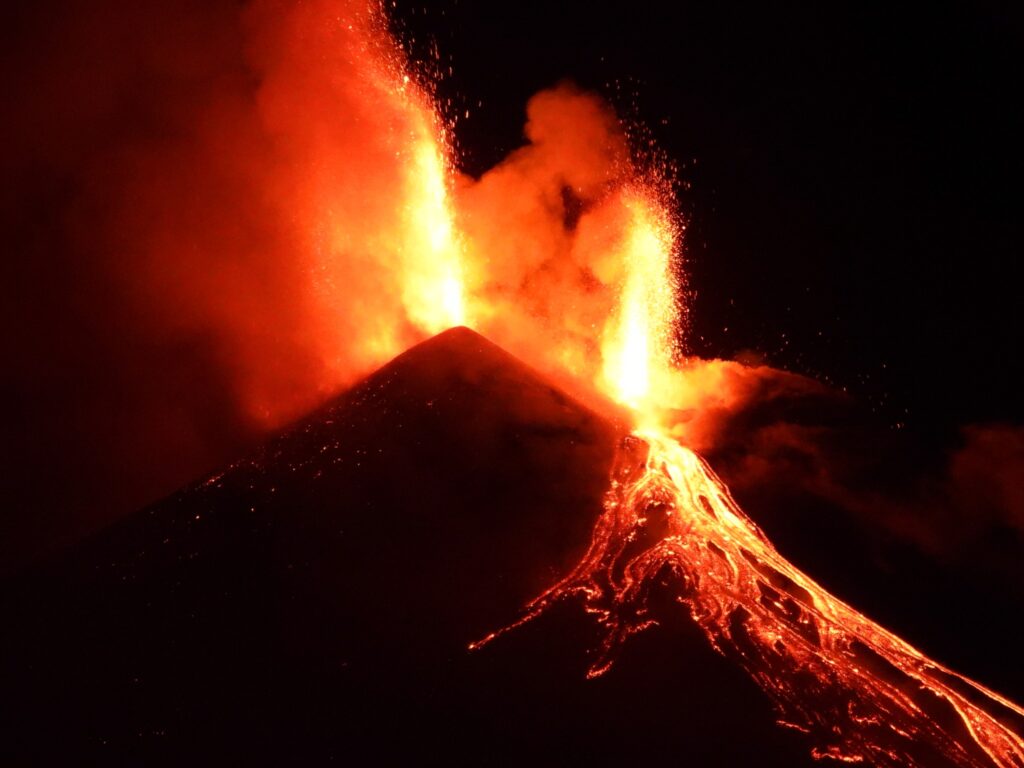
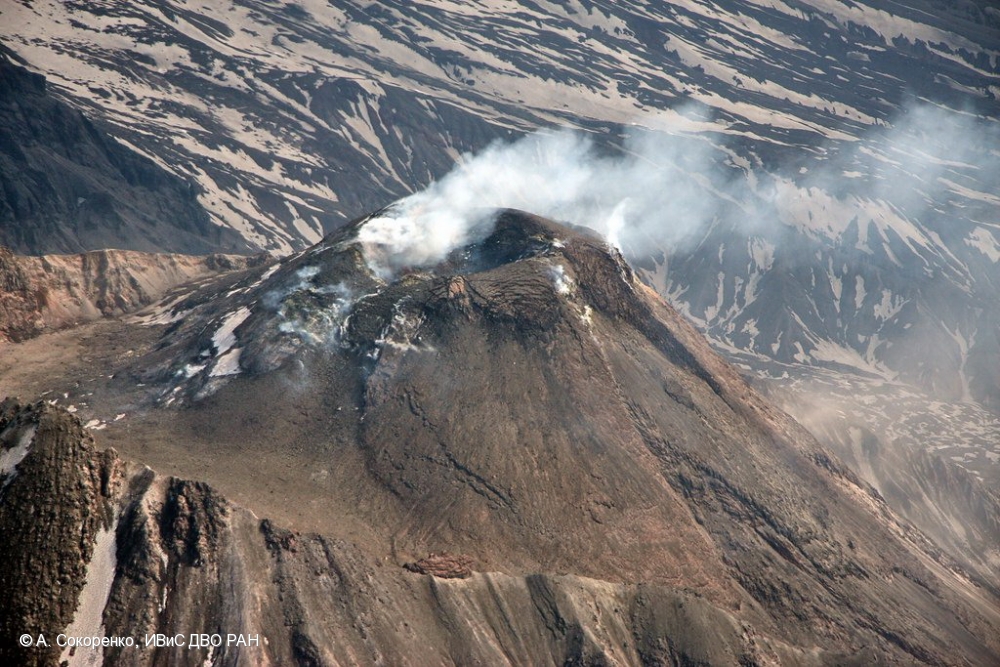
During the observation period, Stromboli’s eruptive activity was characterized by analyzing images recorded by INGV-OE surveillance cameras located at an altitude of 190 m (SCT-SCV) and at Punta dei Corvi (SPCT). The explosive activity was produced mainly by four eruptive vents located in the northern area of the crater and at least two vents located in the central-southern area.
Due to adverse weather conditions, visibility of the crater terrace on April 23, 24, and 25 was insufficient to accurately describe the eruptive activity.
Observations of explosive activity captured by surveillance cameras
In the North (N) crater area, four active vents were observed, producing low-intensity explosive activity (less than 80 m in height) and sometimes medium-intensity explosive activity (less than 150 m in height). The emitted products were mostly coarse (bombs and lapilli). The average explosion frequency ranged from 8 to 11 events/h.
In the South-Central (SC) area, explosive activity was produced by at least two vents. The explosions were mainly low- and medium-intensity, emitting fine materials (ash) sometimes mixed with coarse materials (lapilli and bombs). The average explosion frequency ranged from 2 to 5 events/h.
Source : INGV
Photo : Stromboli stati d’animo / Sebastiano Cannavo
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from April 21, 2025 to April 27, 2025 (publication date April 29, 2025)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
Based on monitoring data, the following is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Strombolian and effusive activity at the Southeast Crater on April 22 and 23. Degassing of the summit craters.
2) SEISMOLOGICAL: No seismic activity due to fracturing with Ml>=2.0. Tremor amplitude at low levels, except for the Strombolian activity episode.
3) INFRASOUND: Infrasound activity is mainly low or moderate; high during the Strombolian activity episode. 4) GROUND DEFORMATION: Ground deformation monitoring networks did not record any significant variations.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux: medium-low level.
Soil CO2 flux: medium-low values.
Partial pressure of dissolved CO2 in groundwater: slightly decreasing values.
Helium isotope ratio at peripheral sites: last updated on 03/04/2025, with medium-high values.
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally low, with high to very high values corresponding to the eruptive activity of the Southeast Crater on April 22, 2025.
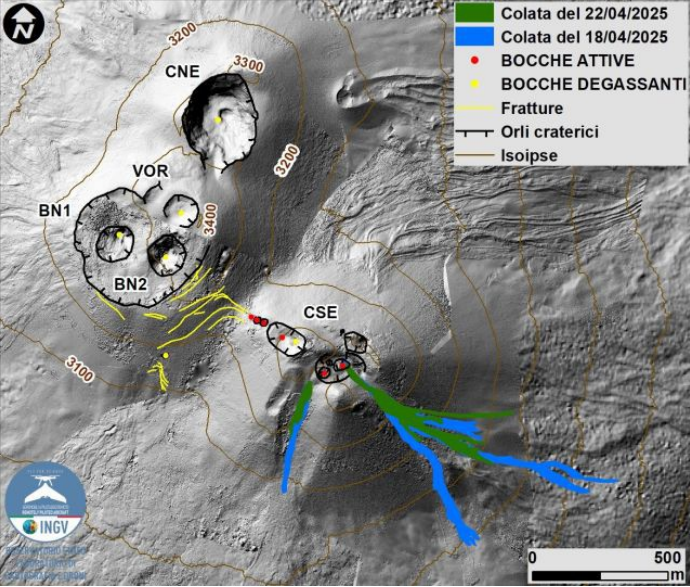
Map of the summit area of Mount Etna and the lava flows of April 18 and 22, superimposed on the shaded terrain relief obtained by processing drone images acquired between February, March, and April 2025 for BN and CSE, and on September 12, 2024 for VOR and CNE. Geoid contours are plotted every 100 m. CSE = Southeast Crater, CNE = Northeast Crater, VOR = Voragine, BN = Bocca Nuova.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the week, monitoring of volcanic activity at Mount Etna was carried out through the analysis of images from the surveillance cameras of the INGV – Etneo Observatory (INGV-OE). In general, during the observation period, Etna was characterized by Strombolian activity with lava overflows from the Southeast Crater (SCC) and degassing of varying intensity from the Bocca Nuova Crater (BN), the Northeast Crater (CNE), and the Voragine Crater (VOR). The eruptive episode fueled by the Southeast Crater (SCC) followed the same pattern as previous ones, with the onset of Strombolian activity that gradually increased in intensity, producing, however, modest emissions of very dilute ash and lava overflows along the southeast and southern slopes of the crater.
In particular, the eruptive episode began around 18:00 UTC on April 22, with the observation of Strombolian activity at the Southeast Crater, fueled by at least three explosive vents and accompanied by the development of lava overflow along the crater’s southeast slope. At 19:45 UTC, the formation of a second lava overflow was observed on the southern slope of the crater. The eruptive activity gradually diminished from 03:00 UTC on April 23, finally ceasing nearly an hour later. The estimated duration of the eruptive episode is about 10 hours.
The April 22 lava outflows were delineated by analysis of a Skysat image from April 26. The overflow that formed in the southeast covered an area of 0.34 x 10^5 m^2, was approximately 0.7 km long, and the most advanced front reached a minimum elevation of 2,940 m above sea level. The overflow, which developed in a southerly direction, had an area of 0.06 x 10^5 m^2, was approximately 0.2 km long, and the front reached a minimum elevation of 3,170 m above sea level.
This bulletin also reports the mapping and derived parameters related to the lava overflows developed during the previous eruptive episode of the Southeast Crater (April 18; Etna Weekly Bulletin of April 22, 2025), which were delineated by analyzing a Skysat image from April 21. In particular, the lava overflow, which was emplaced towards the south, covered an area equal to 0.12 x 10^5 m^2, was about 0.5 km long, and the front reached a minimum height of 3,080 m above sea level. The lava overflow towards the southeast had an area equal to 0.72 x 10^5 m^2, was about 1.1 km long, and the most advanced front reached a minimum height of 2,730 m above sea level.
Etna Activity Update, April 30, 2025, 04:57 (02:57 UTC).
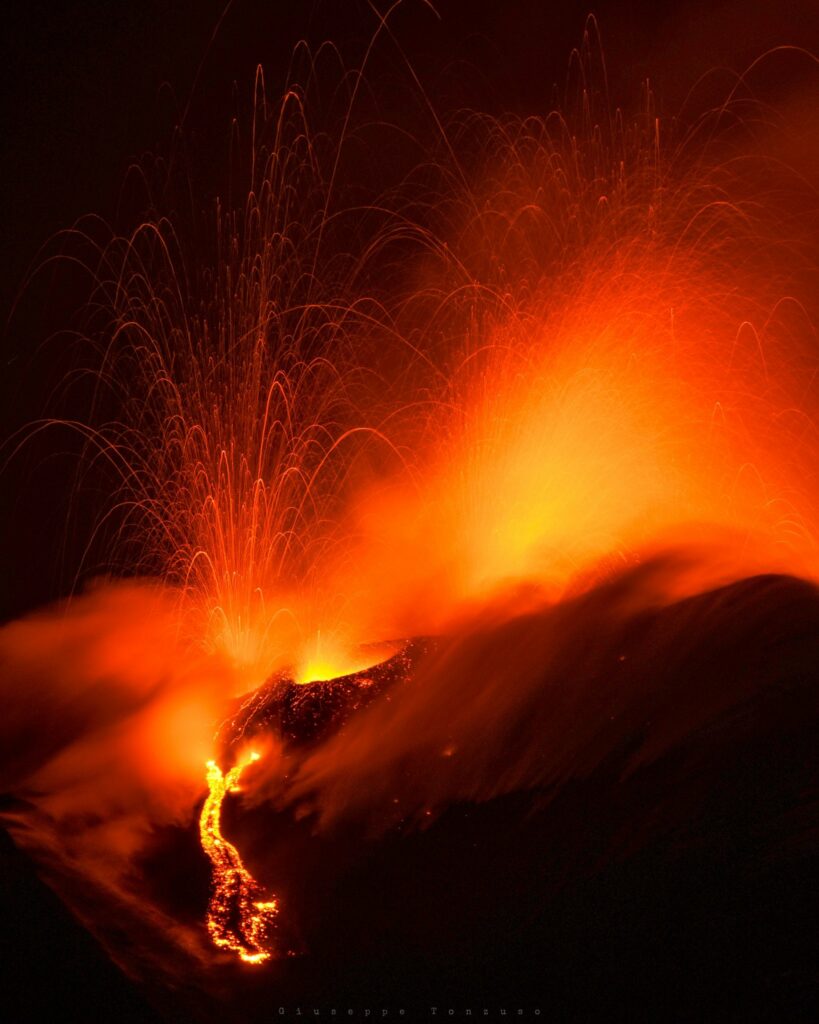
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, reports that eruptive activity at the Southeast Crater intensified in the early hours of April 30, with explosive activity originating from several vents located in the summit area of the crater, and the emission of lava flows towards the southeast and south. Around 00:45 UTC, the Strombolian activity transformed into pulsating lava fountains, which reached heights of 200 to 300 m above the eruptive vents. Around 01:30, a brief fallout of small lapilli was observed in the Piano Vetore area, on the upper southwest slope of the volcano. The forecast model continues to indicate that any eruptive clouds produced by the ongoing activity would disperse in a south-southwest direction and, in the morning, towards the southwest.
From a seismic perspective, the average amplitude of the volcanic tremor reached its maximum value around 00:00 UTC and is currently still at high values. The centroid of the tremor sources is located in the Southeast Crater area at an altitude of approximately 2,700 m above sea level. Infrasound activity is high in terms of both occurrence rate and energy of the events located in correspondence with the Southeast Crater.
From a ground deformation perspective, as of 22:40 GMT, the DRUV dilatometer station shows a decrease of approximately 40 nanostrains.
Further updates will be provided shortly and in any case within 3 hours of this press release.
Source : INGV
Photos : INGV , Giuseppe Tonzuso, Boris Behncke .
Kamchatka , Bezymianny :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Issued: April 29 , 2025
Volcano: Bezymianny (CAVW #300250)
Current aviation colour code: YELLOW
Previous aviation colour code: orange
Source: KVERT
Notice Number: 2025-26
Volcano Location: N 55 deg 58 min E 160 deg 35 min
Area: Kamchatka, Russia
Summit Elevation: 2882 m (9452.96 ft)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
After the explosive eruption on 23 April, an effusive eruption of the volcano continues (viscous lava is extruding onto the dome slopes), which accompanied sometimes by small hot avalanches and powerful gas-steam activity; a bright thermal anomaly over the volcano is noting on satellite images. According to KVERT satellite data, the explosive eruption of the volcano began at 23:10 UTC on 23 April, with ash being carried up to 11 km a.s.l. and pyroclastic flow deposits being formed in the Vostochnaya and Yuzhnaya Valleys. The eruptive cloud moved to the southwest and later southeast for 900 km of the volcano on 23-25 April. KVERT continues to monitor the Bezymianny volcano.
The effusive eruption of the volcano continues. Ongoing activity could affect low-flying aircraft.
Volcanic cloud height: NO ASH CLOUD PRODUSED
Other volcanic cloud information: NO ASH CLOUD PRODUSED
Source : Kvert
Photo : A. Sokorenko, IVS FEB RAS ( 2019)
Philippines , Bulusan :
BULUSAN VOLCANO BULLETIN , 29 April 2025 , 11:00 PM
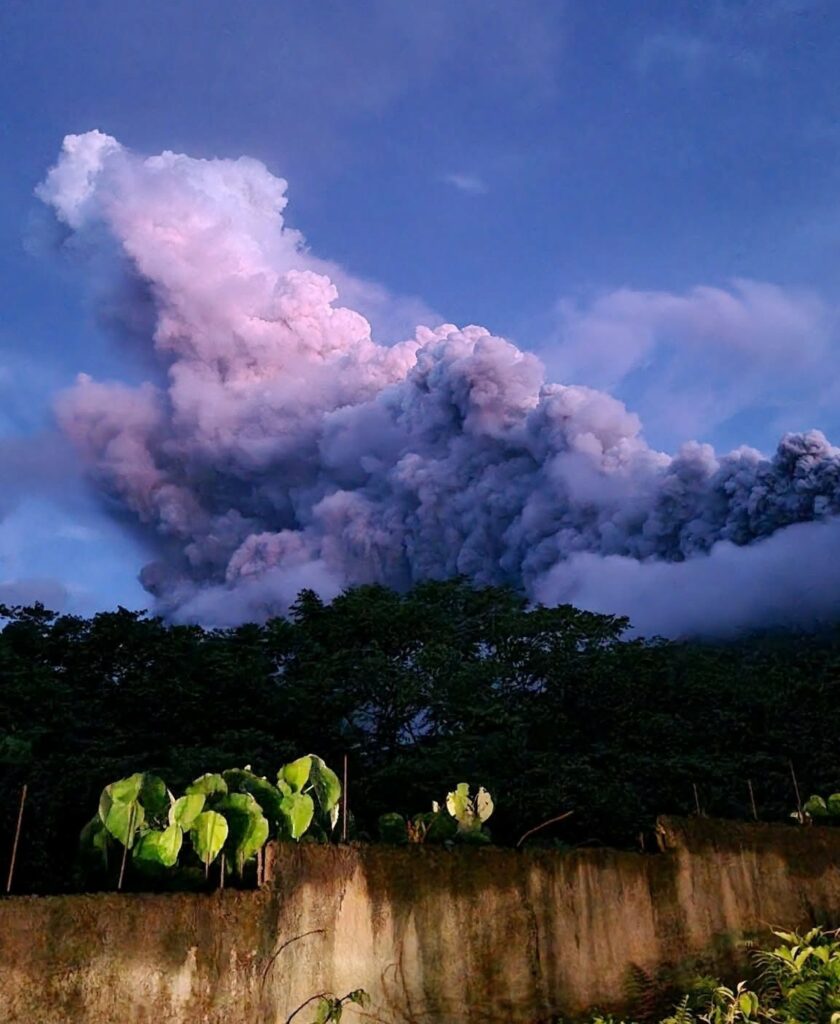
Another phreatic eruption from the summit of Bulusan Volcano occurred at 07:43 PM today, 29 April 2025, and lasted approximately 77 minutes based on seismic and infrasound records. The eruption plume was obscured by clouds but likely drifted to the southwest based on the location of communities affected by ashfall. Significant (~1 centimeter) to trace ashfall was reported in some areas of Sorsogon Province.
Rumbling sounds from the eruption were reported in Brgys. Cogon and Bagsangan, Irosin. As of 8:00 PM, a total of fifty-four (54) volcanic earthquakes were recorded for the day. Sulfur dioxide or SO2 emission for today prior to the eruption was measured at an average of 548 tonnes/day, higher than baseline levels of <200 tonnes/day.
Alert Level 1 (low-level unrest) is maintained over Bulusan Volcano, which means that there are increased chances of phreatic eruptions occurring again after tonight’s eruption. Local government units and the public are reminded that entry into the 4-kilometer radius Permanent Danger Zone (PDZ) must be strictly prohibited and that vigilance in the 2-kilometer Extended Danger Zone (EDZ) on the southeast sector must be exercised due to the possible impacts of volcanic hazards such as pyroclastic density currents or PDCs, ballistic projectiles, rockfall, avalanches, ashfall and others on these danger areas. Communities that experience ashfall must take all necessary precautions and use protective masks or wet cloth to prevent ash inhalation, with special attention given to vulnerable persons including the elderly, persons with respiratory or cardio-vascular diseases, expecting mothers and infants. Civil aviation authorities must also advise pilots to avoid flying close to the volcano’s summit as ash from any sudden phreatic eruption can be hazardous to aircraft. Furthermore, people living within valleys and along river/stream channels especially on the western sectors of the edifice should be vigilant against sediment-laden stream flows and lahars in the event of heavy and prolonged rainfall should phreatic eruption occur.
DOST-PHIVOLCS is closely monitoring Bulusan Volcano’s condition and any new development will be relayed to all concerned.
Source : DOST-PHIVOLCS
Photo : Marcky Ragas/Bulusan MDRRMO
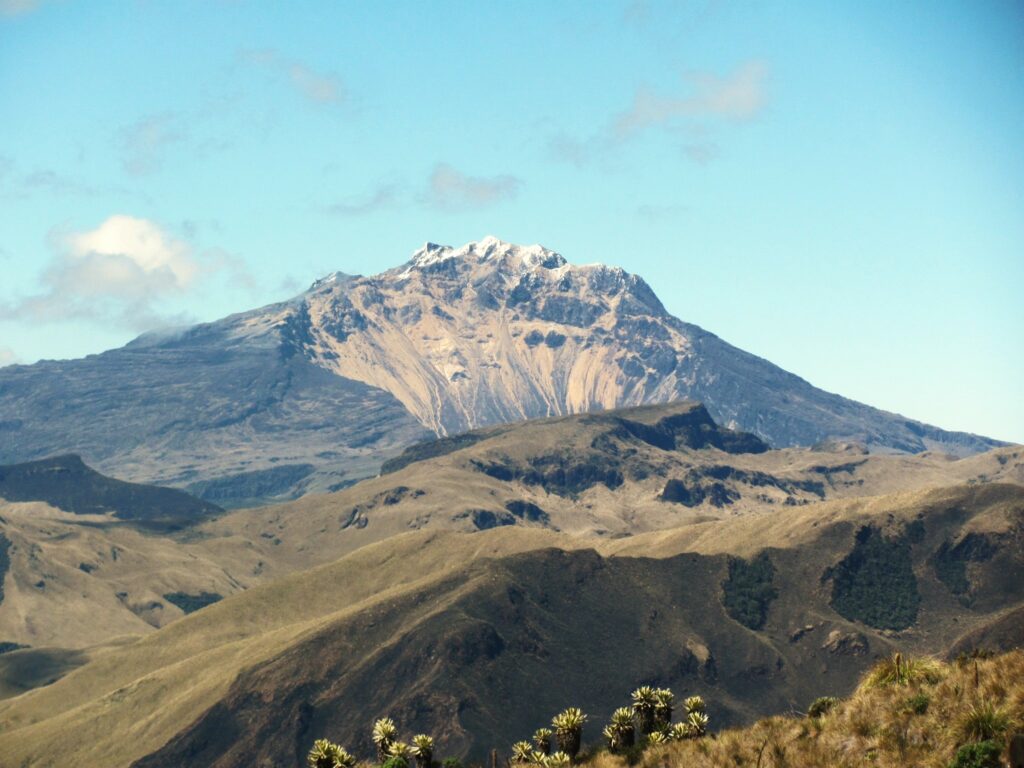
Colombia , Chiles / Cerro Negro :
Monitoring the activity of the Chiles/Cerro Negro volcanoes, the Colombian Geological Survey (SGC), an entity affiliated with the Ministry of Mines and Energy, reports that:
Between April 22 and 28, 2025, seismic activity increased compared to the previous week, within the context of the fluctuating behavior characteristic of recent months. The main variations in the monitored parameters at these volcanoes were:
• An increase in seismic occurrence was recorded, although the energy released showed a decrease. The predominance of seismicity associated with rock fracturing in some areas of the volcanic structures was maintained, as well as the recording of seismic activity related to fluid dynamics, with some very high-frequency low-frequency events.
• Most of the earthquakes were located in the Chiles Volcano collapse zone, at distances less than 2.5 km from its summit (4,700 m above sea level), with depths between 3.0 and 6.0 km and a maximum magnitude of 1.8. Another group of earthquakes was recorded in the southern zone of Chiles Volcano, with depths of up to 8.0 km and a maximum magnitude of 2.3. In addition, other seismic events were evenly distributed throughout the volcanic complex, reaching distances of up to 20 km.
• Analysis of data from satellite sensors and ground stations continues to reveal changes related to deformation processes in the volcanic zone.
Based on the assessment and correlation of monitored parameters, the SGC recommends closely monitoring developments through weekly bulletins and other information published through our official channels, as well as instructions from local and departmental authorities and the National Disaster Risk Management Unit (UNGRD).
Volcanic activity remains on Yellow alert: Active volcano with changes in the baseline behavior of monitored parameters and other manifestations.
Source et photo : SGC