February 18 , 2025.
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
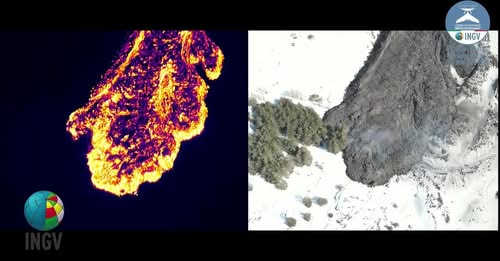
Drone images, both visible and with thermal sensor, collected yesterday by a group of researchers from the Etna Volcano Observatory during an intense day of monitoring and collection of data and samples on the lava flow emitted since February 8.
The monitoring work of the OE group in front of the flow – which had already passed the Altomontana track yesterday – also found that there is an advance of 5m/h (Group of researchers: OE: Cantarero, Corsaro, Debeni, Puglisi).
But still no statement from INGV.
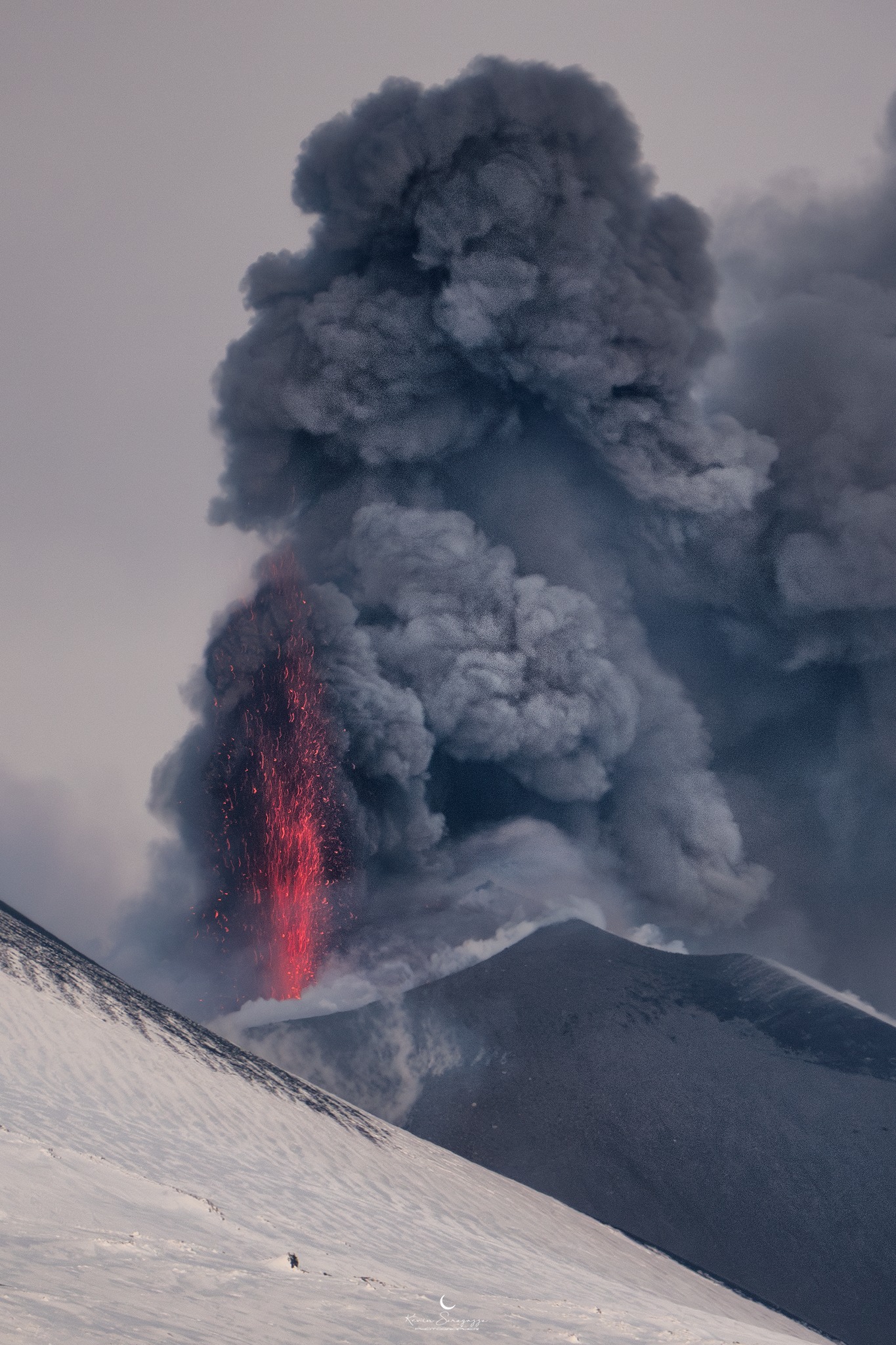
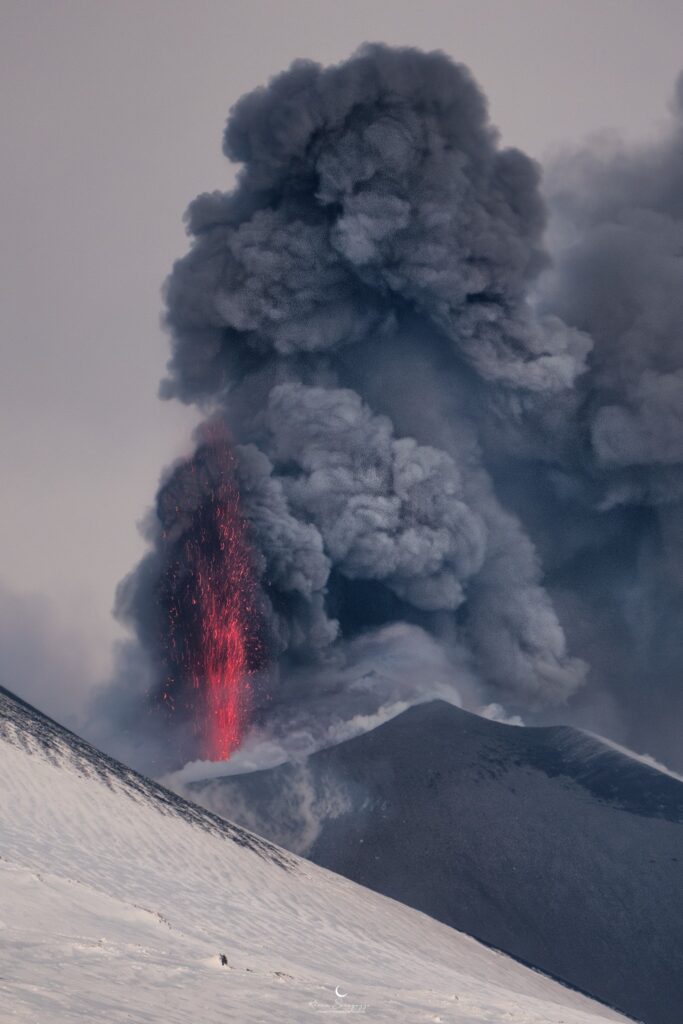
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Issued: February 16 , 2025
Volcano: Etna 211060
Current Color Code: RED
Previous Color Code: orange
Source: Etna Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2025/0011/01E03
Volcano Location: 3744N 01500E
Area: Italy
Summit Elevation: 3300 m
Volcanic Activity Summary:
Strong explosive activity is observed in the summit craters.
Volcanic cloud height:
VOLCANIC CLOUD HEIGHT IS NOT ESTIMABLE
Other volcanic cloud information: N/A
Remarks:
THE PHENOMENON IS OBSERVED BY OBSERVED BY INGV’S PERSONNEL ON THE FIELD
Next Notice:
A new VONA will be issued if conditions change significantly or color code changes.
Source : INGV / FB
Photos : INGV , Kevin Saragozza ( 17/02/2025 ).
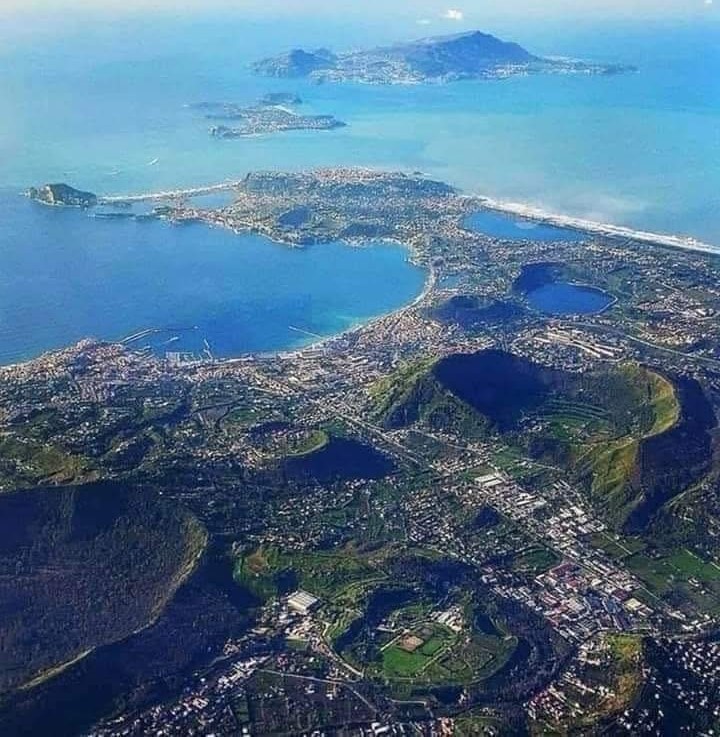
Italy , Campi Flegrei :
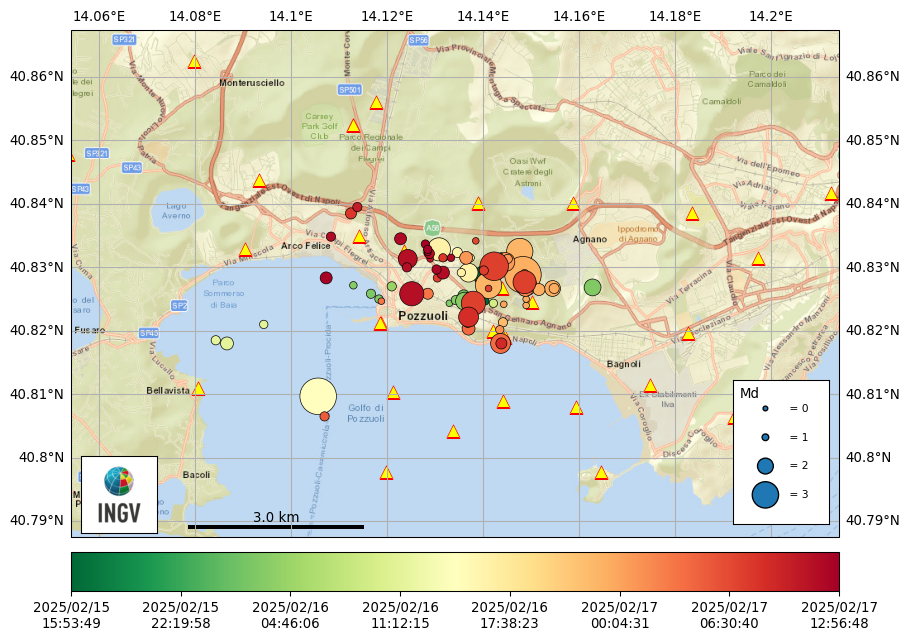
Seismic swarm in the Campi Flegrei: update announcement, 17 February 2025, 14:08
Since 15/02/2025 at 16:53, a seismic swarm has been underway in the Campi Flegrei area. On 17 February at 14:08, 282 earthquakes with a magnitude Md ≥ 0.0 and a maximum magnitude Md = 3.9 ± 0.3 were preliminarily detected.
As can be seen from the map, the two magnitude 3.9 events occurred in two different seismogenic areas where we are currently recording seismicity: yesterday afternoon in the Gulf of Pozzuoli and this evening in the Solfatara-Pisciarelli area.
We are going through a phase of intensification of bradyseism, a phenomenon that has already occurred in the past. For example, on 20 May 2024, a bradyseismic swarm was recorded that lasted less than the current one, but was characterized by events of magnitude 4.4, 3.8 and 3.6. Therefore, the presence of multiple magnitude 3.0 events in particularly energetic swarms is not an anomaly.
Multiparameter monitoring indicates that, for the moment, all parameters other than seismicity do not show significant anomalies, but maintain the usual upward trends. Ground uplift occurs on average at a rate of about 10 millimeters per month. The flow in the main fumaroles has returned to the values recorded two weeks ago, after a slight temporary decrease. Even the concentrations of gases emitted by the fumaroles do not show significant variations compared to the usual anomalies.
As INGV collaborators, we are deeply close to the population. Our advice is to stick to the information provided by the official channels of the bodies responsible for managing the phenomenon.
Source : INGV Vulcani
Photos : INGV , Oibafa
Costa Rica , Poas :
Latitude: 10.20°N;
Longitude: 84.23°W;
Altitude: 2687 m
Current Activity Level: Warning
Following the sequence of shallow proximal volcano-tectonic earthquakes (pVT) last week, a slight increase in tremor amplitude was observed, which remained stable for most of this week. However, between days 11 and 12, a decrease in tremor amplitude was observed, accompanied by some pVTs. Subsequently, since the afternoon of the 12th, 3 episodes of intense, spasmodic and almost monochromatic seismic-acoustic tremor have been recorded. These episodes lasted several hours. The first of these was accompanied by mainly distal, but sometimes proximal, volcano-tectonic seismicity.
Geodetic monitoring has recorded an episode of inflation since November, with the most significant occurring from late December to late January. In recent days, inflation appears to have stopped. The station north of the crater shows stability, while a slight subsidence is observed to the south. However, the extension of the crater continues.
Images of the eruptive activity observed since Friday (left Sunday at 11:45, right today’s eruption at 2:00)
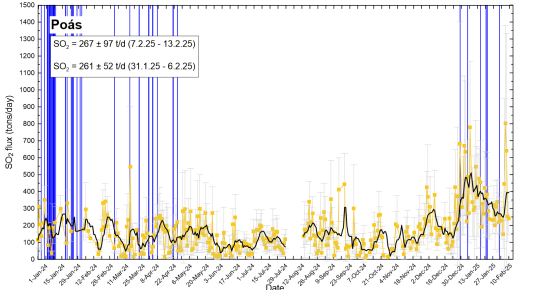
The SO2 flux has remained constant over the last two weeks. The average for the previous week was 267 ± 97 t/d, while the average for the following week was 261 ± 52 t/d. However, yesterday, February 13, a significant increase in the SO2 flux was observed to 445 ± 504 t/d. The MultiGAS station recorded higher SO2 concentrations this week (weekly average of 14 ppm, compared to 5 ppm the previous week). The SO2/CO2 ratio remains relatively stable with an average of 1.0 ± 0.4 this week. A short-term anomaly was observed yesterday with SO2/CO2 up to 2.4. The H2S/SO2 ratio remains low with values close to 0. SO2 concentrations recorded at Mirador increased this week with a maximum of 6.9 ppm this week (two days with concentrations above 5 ppm SO2) compared to 1.5 ppm the previous week. The OMI instruments on the SENTINEL satellite started detecting SO2 in the atmosphere again on 12 February, with high values on 13 February.
The lake level has dropped by about 0.3 m this week and fumarolic convection cells remain underwater.
SO2 flow in tons per day. Weekly averages for the last two weeks are shown. Note the increase in SO2 flux that occurred on February 14.
Updated on February 17, 2025.
Since last week, significant changes in seismic patterns have been observed, notably marked by episodes of intense tremor and larger volcano-tectonic seismicity. Since the night of Friday, February 14, frequent phreatic explosions have been recorded at Boca C with maximum heights of 200 m.
These changes occur after a period of crustal uplift in the northern sector of the crater and an extension of the crater. Over the past week, uplift to the north of the crater has ceased, but extension continues. A significant spike in SO2 degassing was observed this weekend, which decreased yesterday.
We interpret that an intrusion of magmatic fluids has occurred in the last two months that could progressively reach the surface generating an increase in volcanic activity.
Based on the above, two scenarios are envisaged for the next days/weeks, in order of probability:
1. Increased eruptive activity with major phreatic and possibly significant phreato-magmatic eruptions.
2. The pressurized fluids inside the volcano are progressively released and consequently the activity decreases without a major eruption occurring.
The volcano is at the alert level Warning.
Source et photos : Ovsicori
Iceland , Reykjanes Peninsula :
Continued increased risk of eruption at the Sundhnúkur crater row
Updated 11. February at 17:30 UTC
Land uplift and magma accumulation under Svartsengi continues
The period of increased risk of a volcanic eruption risk may last up to a month or longer
Slight increase in seismic activity in recent weeks
Hazard assessment updated but remains unchanged
GPS measurements indicate ongoing land uplift beneath Svartsengi. Although, the rate of uplift has slightly decreased in recent weeks. However, model calculations show continued magma accumulation. The volume of magma has reached the lower threshold believed to be necessary to trigger the next dike intrusion and potential eruption.Past events at the Sundhnúkur crater row suggest that once the magma volume reaches this threshold, eruptions have occurred within a timeframe of a few days to four weeks. This does not guarantee that the next event will happen within a month, but experience suggests this is the most likely scenario.
Seismic activity has slightly increased in recent days. Looking at the number of earthquakes since the last eruption, a gradual increase has been observed since late January. However, stormy weather last week may have affected the sensitivity of the earthquake monitoring system, possibly preventing the detection of the smallest tremors.
The hazard assessment has been updated but remains unchanged and is valid until February 18, unless conditions change.
Source : IMO
Photo : The Icelandic Met Office / Bjarki Kaldalóns Friis.
Indonesia , Lewotobi Laki-laki :
Reduction of the recommended safety distance on Lewotobi Laki-laki, at activity level IV (AWAS) on 18 February 2025 at 06:00 WITA
Visual and seismic observations of Mount Lewotobi Laki-laki on 17 February 2025 until 12:00 WITA are as follows:
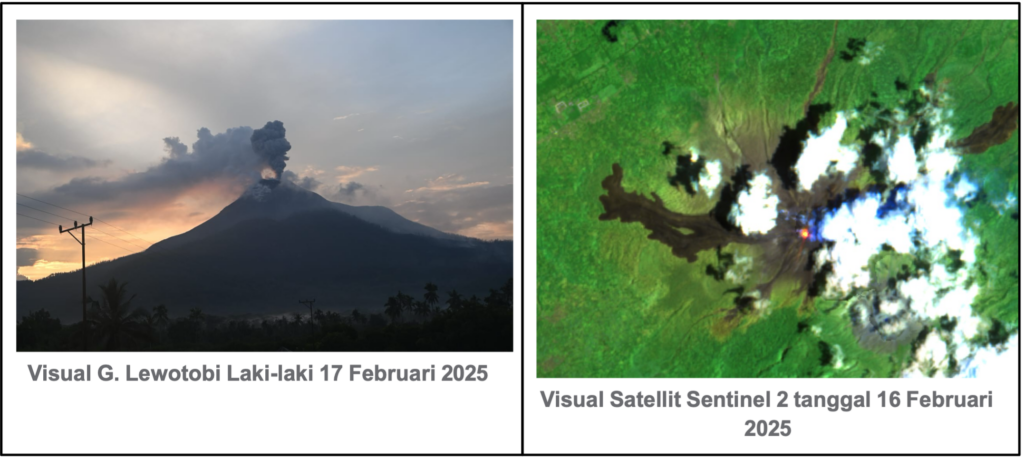
The mountain is clearly visible and sometimes covered with fog. The smoke from the crater, weakly pressurized, was white in color, thick in intensity and 400 to 600 m high above the crater summit. An eruption occurred at 05:58 WITA with an eruption column height of approximately 900 m from the peak.
On February 17, 2025 until 12:00 WITA, 34 emission earthquakes, 5 harmonic tremors, 4 low-frequency earthquakes, 2 deep volcanic earthquakes, and 5 distant tectonic earthquakes were recorded.
Visual observations on February 17, 2025 showed that the mountain could be clearly observed. At night, the incandescence around the summit is clearly visible.
The smoke that is emitted in the area around the peak on the northwest side forms a thin crack. The presence of crater smoke (solfatara) is caused by the presence of an alteration zone (weak zone), so solfatara smoke can be seen coming out of this area. The area has the potential for a « directed explosion » (direct eruption in one direction) that could occur in the northwest/northeast direction from Mount Lewotobi Laki-laki.
The last eruption occurred on February 17, 2025 at 58 WITA.
Earthquake data shows that they are still fluctuating, especially deep volcanic earthquakes that were not recorded before, but were recorded again in the last 24 hours, while shallow volcanic earthquakes were not recorded in the last 24 hours. This indicates that magma movement is still occurring, but there is a decrease in stress/pressure at shallow depths due to reduced magma migration.
Harmonic tremors are still recorded to this day, indicating that there are still vibrations due to fluid movement (magma/gas/water vapor) beneath Lewotobi Laki-laki.
Emission earthquakes were recorded on February 17, 2025, the number has increased quite significantly compared to before.
The Sentinel-5 Tropomi satellite detected on 17 February 2025 a flux of SO2 emitted by Mount Lewotobi Laki-laki of 600.9 x 102 tonnes, an increase compared to the previous period.
The Sentinel-1 satellite showed, during the period from 31 January 2025 to 12 February 2025, a deformation anomaly with indications of inflation around Mount Lewotobi.
Based on the results of a comprehensive analysis and evaluation of visual and instrumental monitoring, it appears that visual and seismic activity on Mount Lewotobi Laki-laki is still fluctuating, so the activity level of Mount Lewotobi Laki-laki is still set at Level IV (AWAS) with a change in the recommended safety distance from a radius of 6 km and a South-West/North-West sector of 7 km to a radius of 6 km.
Source et Photo : PVMBG.