December 04 , 2024.
Iceland : Reykjanes Peninsula :
Eruptive Activity Remains Relatively Stable
Updated 3 December at 16:45 UTC
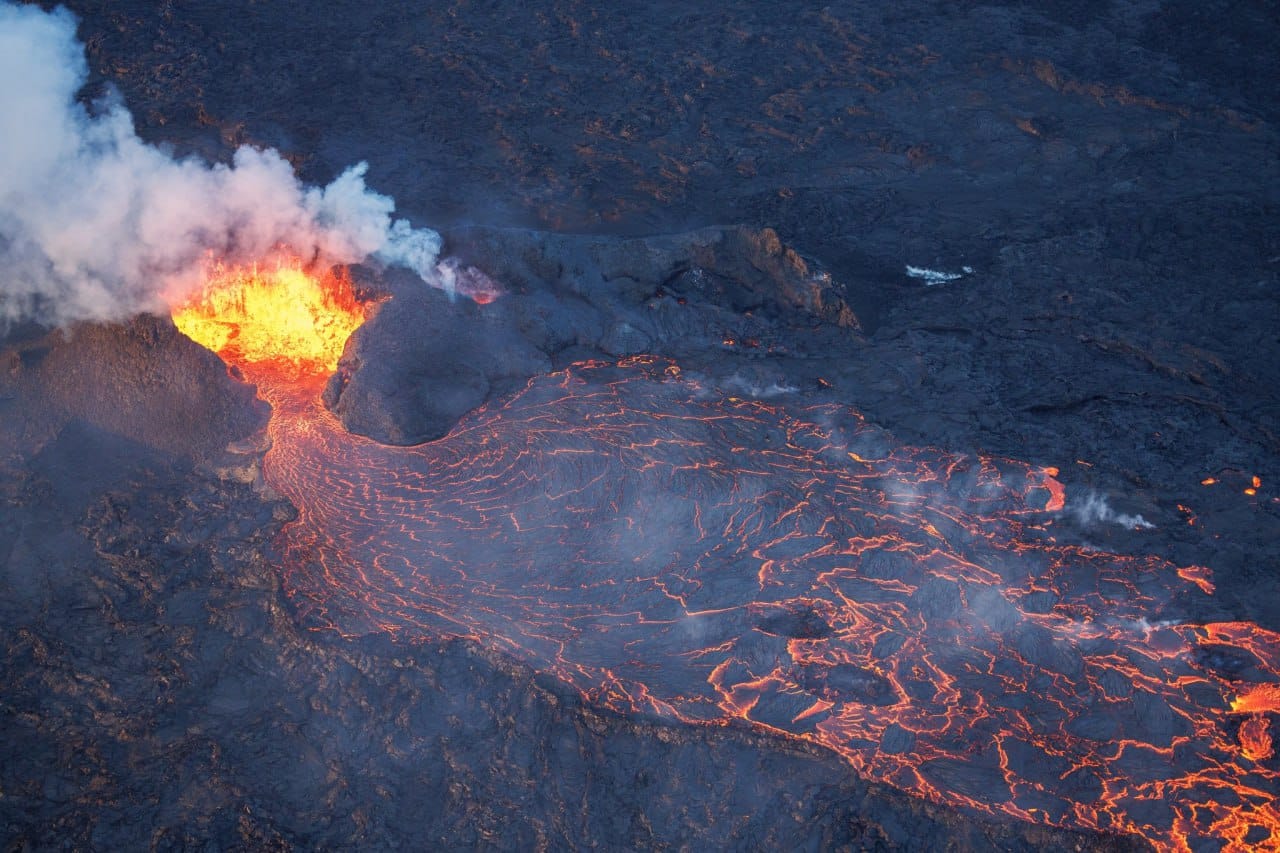
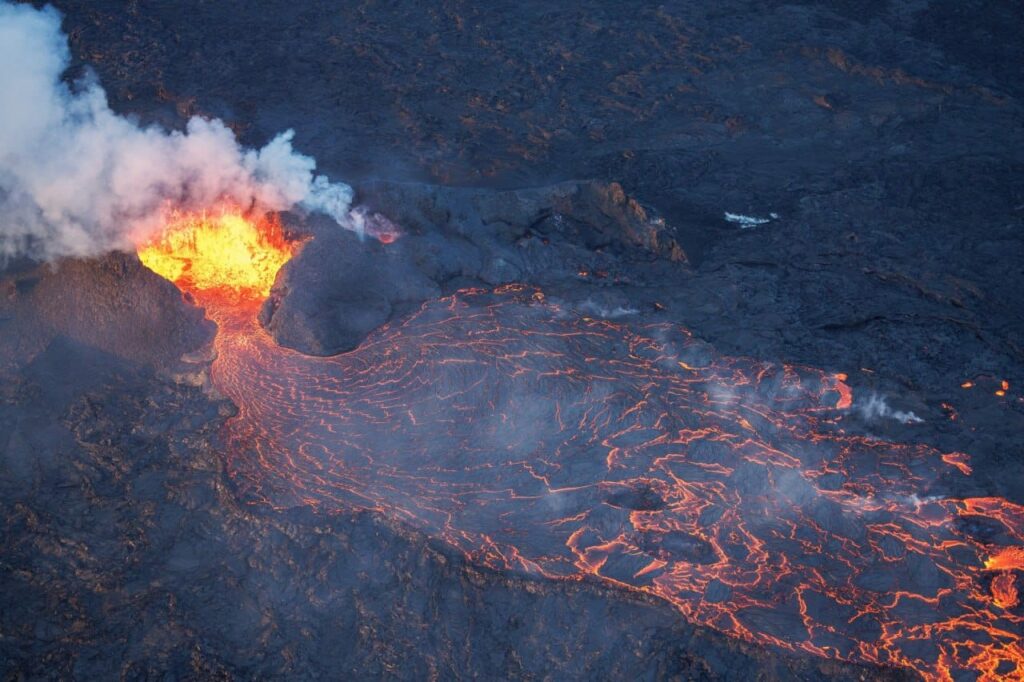
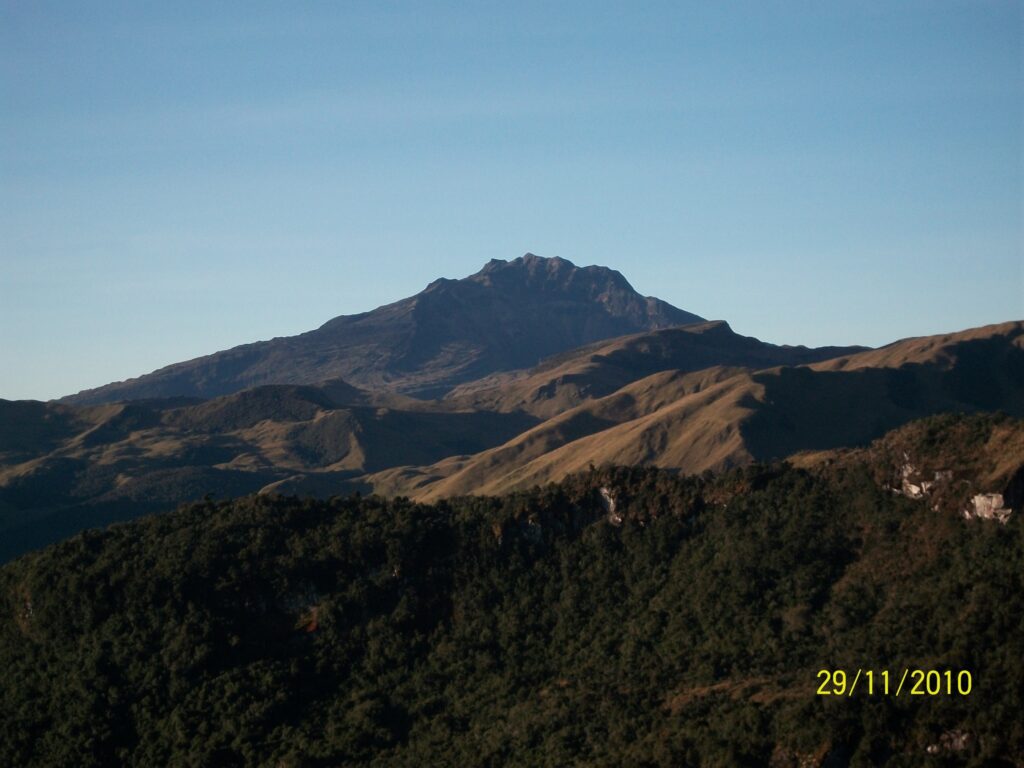
The lava flow from the active crater has been steady in recent days.
Advancement of the lava front is slow and does not threaten infrastructure.
There is a balance between the inflow of magma to the reservoir beneath Svartsengi and the eruption of lava on the surface.
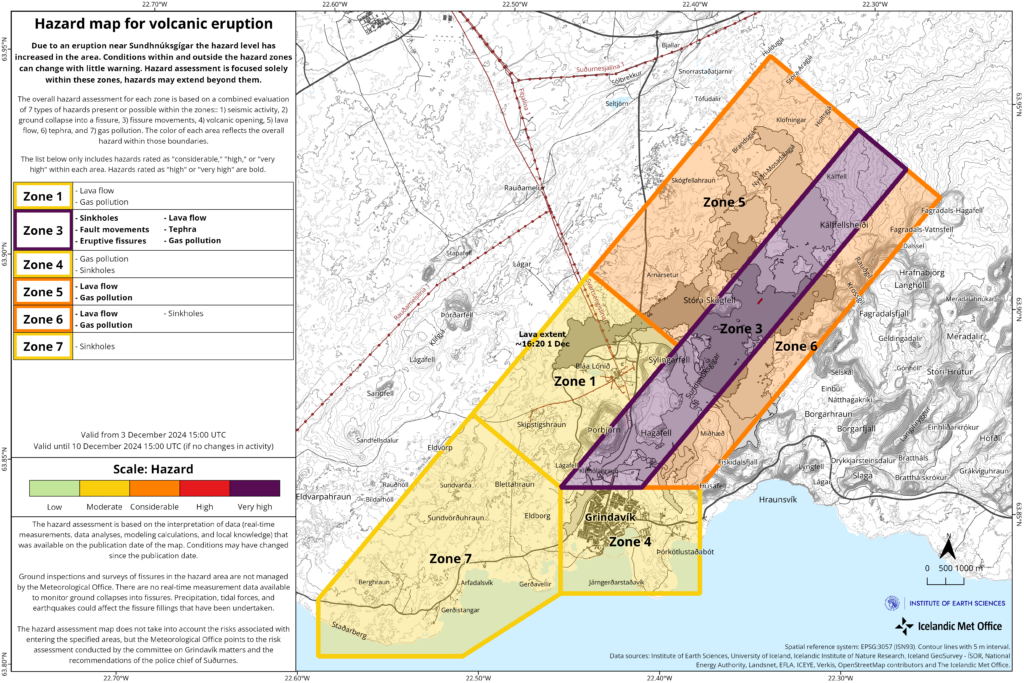
The hazard assessment has been updated.
There has been insignificant change in the eruptive activity of the active vent in recent days, supported by seismic measurements. Lava continues to flow from the active crater, predominantly travelling southeast in the direction of Fagradalsfjall.
Minor changes have occurred at the lava front, but its overall advance has been slow. The crater continues to build up, increasing the risk of structural collapse. If this occurs, the direction of the lava flow could change, but infrastructure is not considered to be at risk due to the crater’s location.
Deformation data indicate that there is a balance between the inflow of magma into the reservoir beneath Svartsengi and the outflow of lava at the surface from the active crater.
Gas pollution was measured at Húsafjall, east of Grindavík, over the weekend. The prevailing northerly winds carried gas southward from the eruption site.
Visitors in the area are advised to monitor the Icelandic Meteorological Office’s gas dispersion forecasts .
Hazard Assessment updated
The hazard assessment has been revised and updated based on the latest measurements and data. Key changes impact Zone 1 (Svartsengi), where the overall risk for the area has decreased from « considerable » (orange) to « moderate » (yellow). This change reflects the lack of lava flow toward Svartsengi in recent days. The hazard in Zone 6 has been lowered from « high » (red) to « considerable » (orange), as the threat from tephra fall is now considered minimal. Gas pollution remains a significant hazard in Zones 5 and 6, and an extreme hazard in Zone 3.
Source : IMO
Photos : Thomas Winstone via Ales Tor /FB , IMO
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from November 25, 2024 to December 01, 2024. (issue date December 03, 2024)
SUMMARY STATUS OF ACTIVITY
In light of the monitoring data, it appears:
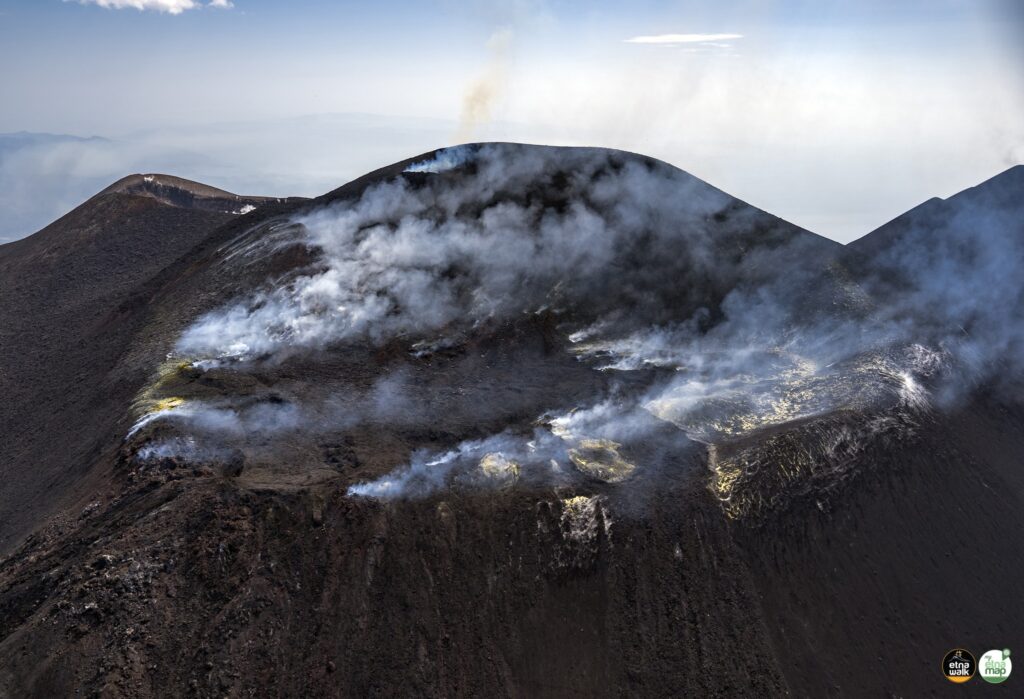
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Degassing activity at the summit craters.
2) SEISMOLOGY: Seismic activity from low-level fracturing. Average amplitude of volcanic tremor at medium and low levels.
3) INFRASOUND: Medium-low level infrasound activity
4) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: Over the past week, ground deformation monitoring networks have not recorded any significant changes.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: Medium-high and increasing SO2 fluxes.
Soil CO2 flux (EtnaGas network): significantly decreasing, on low degassing values.
The partial pressure of dissolved CO2 in groundwater (Ponteferro) shows values in seasonal variability.
Isotope ratio of peripheral sites: there are no updates; latest data on medium-high values (20/11/2024).
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally low.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the week, the monitoring of the volcanic activity of Etna was carried out through the analysis of the images from the surveillance cameras of the INGV, Osservatorio Etneo (INGV-OE). Due to unfavourable weather conditions, the observation of volcanic activity by the cameras was very limited and discontinuous.
On days of visibility, the activity affecting the summit craters was mainly degassing.
VOLCANIC TREMOR:
The average amplitude of the volcanic tremor until 29 November remained confined within the range of average values and reached a low level in the following days. The centroid of the tremor sources is mainly located in an area between the Bocca Nuova crater, the Northeast crater and an area just north of the Southeast crater at altitudes between approximately 2,700 and 3,100 meters above mean sea level.
Source : INGV
Photo : Etna Walk/ Giuseppe Distefano ( 03/08/2024)
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from November 25, 2024 to December 01, 2024. (issue date December 03, 2024)
SUMMARY STATUS OF ACTIVITY
In light of the monitoring data, it emerges:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: During this period, intense eruptive activity with splashes was observed from the northern area of the crater. The total hourly frequency varied between average values (6-15 events/h). The intensity of the explosions was low in the northern crater area and medium to high in the central-southern area.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The monitored seismological parameters do not show significant variations. We report the occurrence of an earthquake of magnitude ML=1.8 on 11/28.
3) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: The ground deformation monitoring networks of the island showed no significant changes to report for the period under review.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux in the plume on 24 November at medium level
The CO2 flux from the soil in the STR02 summit area reaches very high values.
C/S ratio in the plume: is at high values.
Helium isotope ratio in the thermal aquifer at high values.
CO2 flux at Mofeta in the San Bartolo area: values fluctuate at medium-high degassing levels.
CO2 flux at Scari: medium-low values.
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally low to moderate.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
In the observed period, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized by analyzing the images recorded by the INGV-OE surveillance cameras located at an altitude of 190 m (SCT-SCV) and at Punta dei Corvi (SPCT). The explosive activity was mainly produced by 4 eruptive chimneys located in the northern area of the crater and by 3 chimneys located in the central southern area.
Observations of the explosive activity captured by the surveillance cameras
In the area of the northern crater (N), four active vents were observed that produced explosive activity of low intensity (less than 80 m in height) and sometimes medium (less than 150 m in height).
Furthermore, a projection activity was observed at the mouths of the N2 sector, sometimes intense on November 27. The products emitted in eruption were mainly coarse materials (bombs and lapilli). The average frequency of explosions varied between 5 and 10 events/h.
In the Centre-South (CS) area, explosive activity was produced by at least three chimneys, the explosions varied in intensity from medium (less than 150 m in height) to high (more than 250 m in height) emitting fine materials mixed with coarse materials. The average frequency of explosions varied between 1 and 9 events/h
04 December 2024 02:54 (01:54 UTC), Statement on Stromboli activity.
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, reports that from 01:09 UTC, according to surveillance cameras, an overflowing lava flow produced by the North Crater area is observed. The activity is the result of an intensification of the spattering activity since 00:25 UTC; Currently, the lava flow front is located in the upper part of the Sciara del Fuoco.
From a seismic point of view, the average amplitude of the volcanic tremor is currently at very high values. No significant changes have been reported in the frequency of occurrence and amplitude of explosion earthquakes.
Regarding deformations, the GNSS network does not show significant variations, the inclinometric signal of the STDF station is currently being updated.
Further updates will be communicated shortly.
Source : INGV
Photo : Stromboli stati d’animo / Sebastiano Cannavo
Indonesia , Anak Ranakah :
Increase in the activity level of G. Anak Ranakah from level I (normal) to level 2 (Waspada) from 3 December 2024 at 08:00 WITA.
The results of the assessment of volcanic activity of Mount Anak Ranakah, Manggarai Regency, East Nusa Tenggara Province, for the period from 1 November to 2 December 2024, are presented below:
Visual observation
The volcano is clearly visible until it is covered by fog. No crater smoke was observed.
Instrumental observation
The earthquakes recorded during this period were: 18 low-frequency/LF earthquakes, 1 shallow volcanic earthquake, 25 deep volcanic earthquakes. Earthquakes related to tectonic activity were recorded, namely 57 local tectonic earthquakes and 132 distant tectonic earthquakes.
Assessment
Visual observations during the period from 1 November to 2 December 2024 did not show any smoke anomalies from the crater or the main dome. From field observations, smoke was observed coming from under the dome, on its northwest and southwest sides. The smoke activity is thin and white with low intensity.
Seismicity is still dominated by records related to tectonic activity, both in the form of local tectonic and distant tectonic earthquakes, and shows a significant increase. Low frequency/LF earthquakes show a significant increase compared to October 2024. The occurrence of LF earthquakes indicates the presence of fluid flow resonance (magma/gas/water vapor) filling cavities, pipes or fractures beneath Mount Anak Ranakah. Meanwhile, the occurrence of shallow volcanic and deep volcanic earthquakes indicates that there is a rock fissuring process resulting from the supply of shallow and deep magmatics that changes the stress/pressure on the body of Mount Anak Ranakah.
Recommendation
Based on visual and instrumental observation data up to December 2, 2024 and considering the potential threat of hazard, the activity level of G. Anak Ranakah has been raised from Level I (Normal) to Level II (WASPADA) starting December 3, 2024 at 08:00 :00WITA.
At the Level II (Waspada) activity level, the following are recommended:
Communities around Mount Anak Ranakah and visiting tourists/climbers should not approach, enter, and conduct activities within 1 km of the active crater. The regional government, BPBD in the regency always coordinates with the G. Anak Ranakah Observation Post in Waerii Village, Waerii District, Manggarai Regency or the Volcanology and Geological Disaster Mitigation Center in Bandung (West Java Province).
Source : PVMBG
Photos : Antara , Pvmbg.
Colombia , Chiles / Cerro Negro :
San Juan de Pasto, December 3, 2024, 2:45 p.m.
From the monitoring of the activity of the Chiles and Cerro Negro volcanoes, the Colombian Geological Survey (SGC), an entity attached to the Ministry of Mines and Energy, reports that:
During the week of November 26 to December 2, 2024, the activity of the volcanoes showed stable behavior. Compared to the previous week, the main variations in the monitored parameters were:
• While the frequency of earthquakes decreased slightly, the seismic energy released recorded a slight increase.
• Although the seismicity related to the fracture of rocks within the volcanic system continues to be predominant, the recording of earthquakes associated with the movement of fluids within the volcano is also maintained.
• Fracture earthquakes were located in a very concentrated manner in the so-called collapse zone of the Chiles volcano; extending from its summit, in a northerly direction up to about 2 km and from its summit to the south, for about 1.6 km, with depths between 2 and 6 km from its summit (4,700 m) and with a maximum magnitude of 1.9. Some earthquakes were located in a scattered manner near the Chiles volcano about 4 km to the west-southwest and others about 6.5 km to the northeast, at depths between 2 and 5.5 km from its summit; these earthquakes had a maximum magnitude of 0.4.
• Instruments that record cortical deformation and remote satellite sensors continue to show changes related to an inflationary process in the volcanic area.
Based on the above, the SGC recommends to closely monitor the evolution through the weekly bulletins and other information published through our official channels, as well as the instructions of the local and departmental authorities and the National Unit for Disaster Risk Management (UNGRD).
Volcanic activity remains in yellow alert status: active volcano with changes in the behavior of the base level of the monitored parameters and other manifestations.
Source et photo : SGC