November 10 , 2024.
Indonesia , Lewotobi Laki-laki :
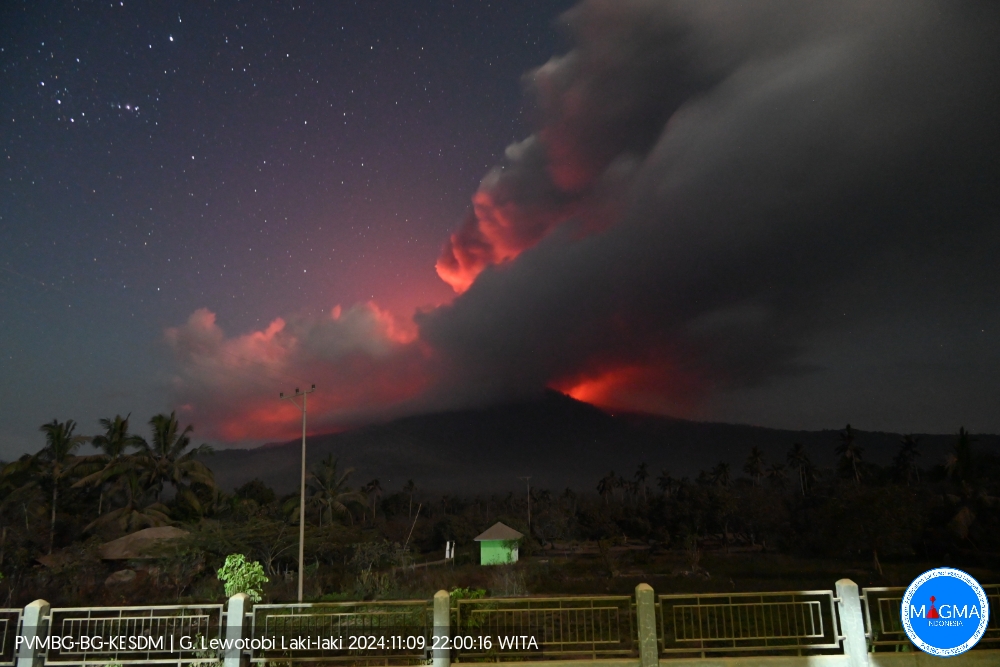
An eruption of Lewotobi Laki-laki occurred on Saturday, 9 November 2024 at 22:00 WITA with the height of the ash column observed at ±5000 m above the summit (±6584 m above sea level). The ash column was observed to be brown with thick intensity, oriented towards the southwest and west. At the time of writing this report, the eruption was still ongoing.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : November 09 , 2024
Volcano : Lewotobi Laki-laki (264180)
Current Aviation Colour Code : RED
Previous Aviation Colour Code : red
Source : Lewotobi Laki-laki Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2024LWK748
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 32 min 20 sec E 122 deg 46 min 06 sec
Area : East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 5069 FT (1584 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 14h00 UTC (22h00 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 21069 FT (6584 M) above sea level or 16000 FT (5000 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving from southwest to west. Volcanic ash is observed to be brown. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 47.3 mm and maximum duration 264 second.
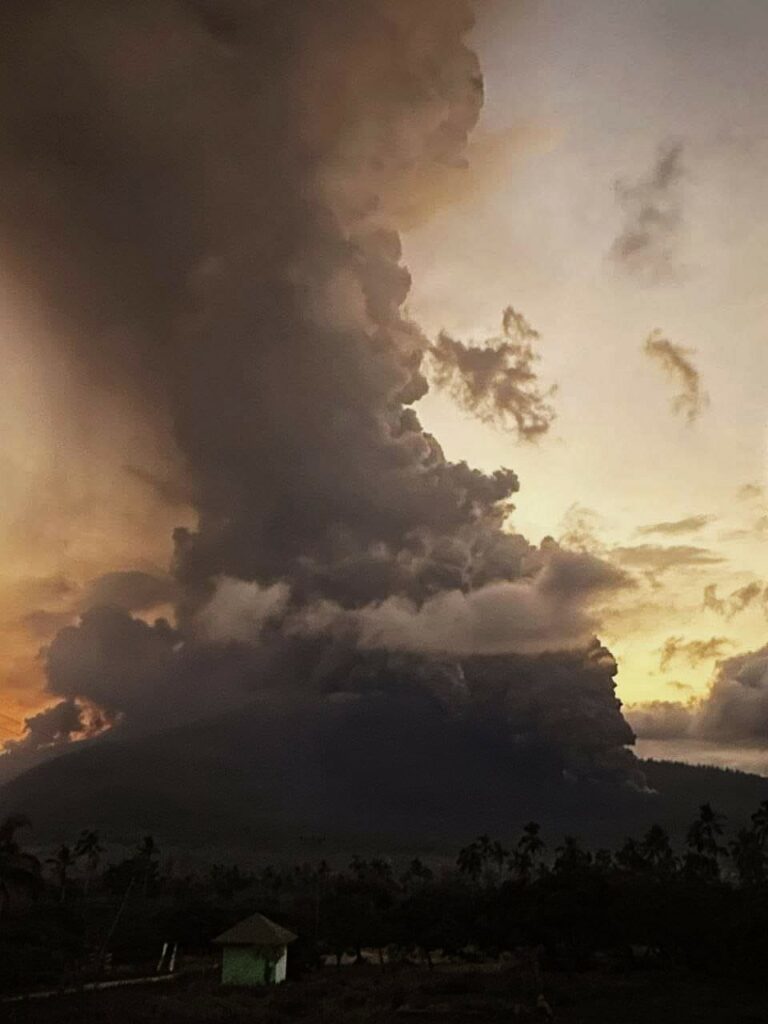
An eruption of Lewotobi Laki-laki occurred on Sunday, 10 November 2024 at 14:49 WITA with the height of the ash column observed at ±1000 m above the summit (±2584 m above sea level). The ash column was observed to be grey in colour with a thick intensity, oriented towards the northwest. At the time of writing this report, the eruption was still ongoing.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : November 10 , 2024 .
Volcano : Lewotobi Laki-laki (264180)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : red
Source : Lewotobi Laki-laki Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2024LWK752
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 32 min 20 sec E 122 deg 46 min 06 sec
Area : East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 5069 FT (1584 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 06h49 UTC (14h49 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 8269 FT (2584 M) above sea level or 3200 FT (1000 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to northwest. Volcanic ash is observed to be gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption and ash emission is continuing. Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 14.8 mm. Tremor recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 7.4 mm.
Source : Magma Indonésie.
Photos : Magma Indonésie , Rizal Muhammad N
Indonesia , Merapi :
MOUNT MERAPI ACTIVITY REPORT, November 1 to November 7, 2024, Published on November 8, 2024
OBSERVATION RESULT
Visual
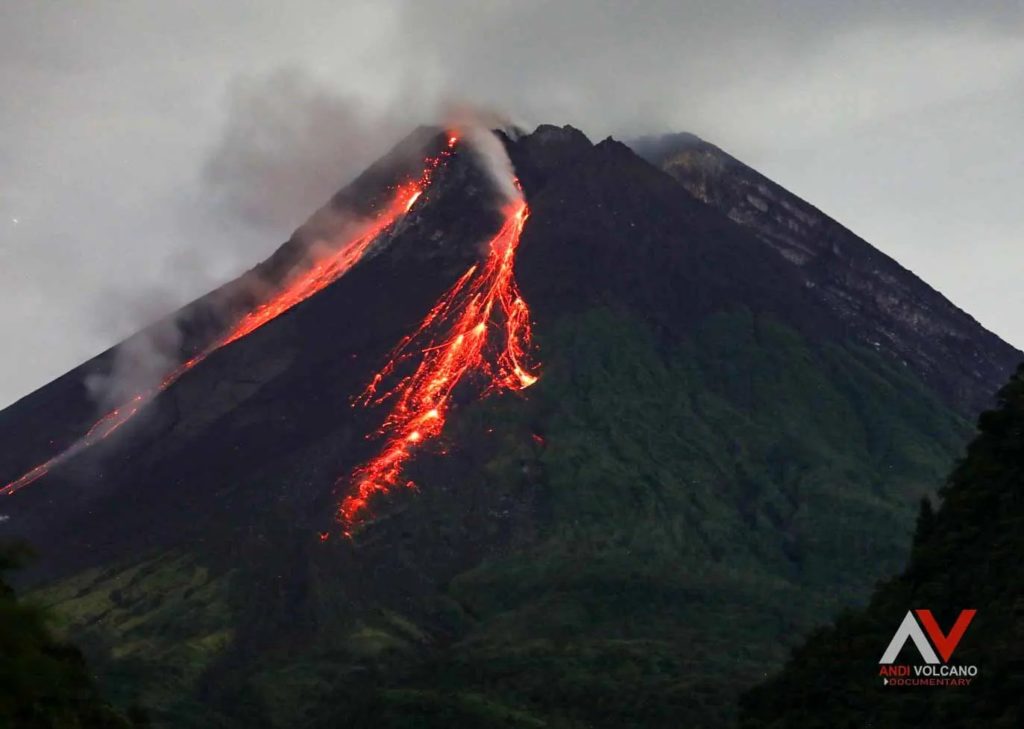
The weather around Mount Merapi is generally clear in the morning and night, while it is foggy from noon to evening. White smoke, thin to thick, low to moderate pressure and 150 m high was observed from the Selo Merapi observation post on November 4, 2024 at 08:20 WIB. This week, a hot cloud avalanche was observed upstream of the Bebeng River up to a maximum of 1000 m. Lava avalanches were observed 271 times upstream of the Bebeng River up to a maximum of 2000 m. The noise of avalanches was heard 5 times from Babadan station with low to moderate intensity.
The morphology of the Southwest dome was observed to change due to dome growth activities, lava avalanches and hot cloud avalanches. Based on the analysis of aerial photos dated October 24, 2024, the volume of the Southwest dome was measured at 3,077,000 m3 and that of the Central dome at 2,361,800 m3.
Seismicity
This week, the seismicity of Mount Merapi recorded:
1 hot cloud avalanche earthquake (WCA)
979 multi-phase earthquakes (MP),
8 low-frequency earthquakes (LF),
1060 avalanche earthquakes (RF),
12 tectonic earthquakes (TT).
The intensity of earthquakes this week is higher than last week.
Deformation
The deformation of Mount Merapi monitored by EDM this week showed a relatively similar average shortening rate to last week.
Rainfall and Lahars
This week, there was rain at the Mount Merapi observation post with a rainfall intensity of 48 mm/hour for 50 minutes at Kaliurang post on 30 October 2024. No additional flows or lahars were reported in the rivers that originate on Mount Merapi.
Conclusion
Based on the results of visual and instrumental observations, it was concluded that:
The volcanic activity of Mount Merapi is still quite high in the form of effusive eruptive activity. The activity status is set at the « SIAGA » level.
Source : BPPTKG Channel
Photo : Andi Volcanist.
Chile , Copahue :
Seismology
The seismological activity of the period was characterized by the recording of:
68 VT-type seismic events, associated with rock fracturing (Volcano-Tectonic). The most energetic earthquake had a Local Magnitude (ML) value equal to 2.4, located 8.1 km to the North-Northeast of the volcanic edifice, at a depth of 4.9 km from the crater.
2 LP-type seismic events, associated with fluid dynamics within the volcanic system (Long Period). The size of the largest earthquake evaluated from the Reduced Displacement (DR) parameter was equal to 1 cm2.
Fluid Geochemistry
The sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions data obtained by the Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy (DOAS) equipment, corresponding to the Mellizas station, installed 6 km east-northeast of the active crater, presented an average value of 661 ± 334 t/d, with a maximum value of 2980 t/d on October 17, considered abnormal and consistent with the increase in activity observed between October 15 and 19.
6 anomalies were reported in sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions into the atmosphere in the area near the volcano, according to data published by the Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) and the sulfur dioxide group of the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) during October 15, 16, 17, 18, 19 and 25.
Thermal anomalies by satellites
During the period, 5 thermal alerts were recorded in the area associated with the volcano, according to the processing of MODIS images by the MIROVA platform, with a maximum volcanic radiative power (VPR) of 10 MW on October 19, consistent with the period of greatest incandescence. According to the analytical processing of Sentinel 2-L2A satellite images, a combination of false color bands identifies an area of anomalous thermal radiation that covers a limited area inside the crater.
Geodesy
Geodetic observations, based on 5 GNSS stations, indicate small displacements, with maximum rates of 0.5 cm/month. The vertical components indicate a low-rate subsidence process, observed mainly at the stations closest to the active crater.
Surveillance cameras
The images provided by the fixed camera installed near the volcano recorded degassing columns with a maximum height of 1220 m and pyroclast emissions between 17 and 22 October, and occasionally on the 26, 27 and 30 of that month. The height associated with these events ranged from 60 to 280 m. On the other hand, the observation of incandescence in the crater area between 15 and 19 October stands out.
Satellite geomorphological analysis
From the photo-interpretation of Planet Scope, Sentinel 2L2A images and Skysat Colect images, a pyroclast fall deposit is observed that reaches an extension of 6.4 km in a southeast direction from the crater. In addition, in the crater area, the absence of the crater lake and the presence of pyroclasts associated with the events described above are observed.
Volcanic activity remained above its base level, as evidenced by the presence of surface anomalies. Pyroclast emission is recorded mainly between October 17 and 22 with variable intensity and columns with a maximum height of up to 280 meters. The pyroclast deposit extended to the southeast. In addition, an incandescence was recorded between October 15 and 20, while from the satellite point of view, an anomalous thermal radiation of moderate intensity was recurrently identified. An important feature present during previous instabilities is the current reduction of the crater lake. The geodetic network data do not suggest any type of relevant variation. The seismic behavior due to this increased activity remains at low levels of occurrence and energy. The presence of surface anomalies favors maintaining the volcanic technical alert at the level:
YELLOW TECHNICAL ALERT: Changes in the behavior of volcanic activity
Observation:
Given the behavior of this volcanic system observed for 8 years, sudden, small explosions without precursors affecting the immediate surroundings of the active crater cannot be ruled out. However, in the context of its base level, this type of event has not been frequent, which is why it is considered to have a low probability of occurrence. The hazards associated with this minor activity consist of the ejection of ballistic pyroclasts, the emission of ash and volcanic gases.
Source : Sernageomin.
Photo : Sernageomin , (04/2018)
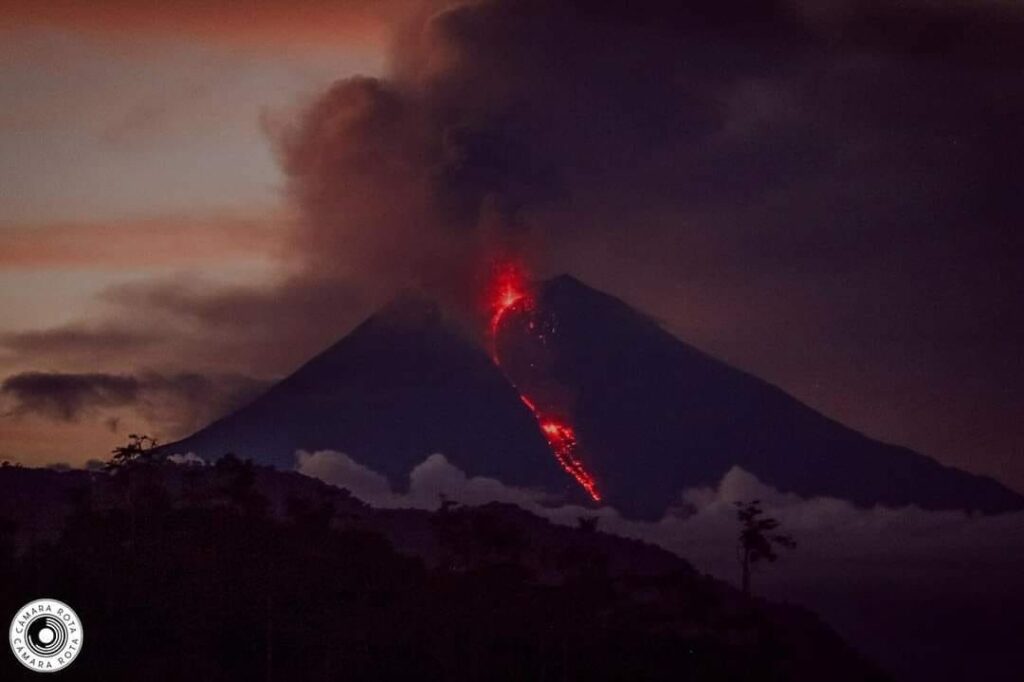
Ecuador , Sangay :
DAILY STATE REPORT OF SANGAY VOLCANO , Sunday, November 09, 2024 .
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface Activity Level: High , Surface Trend: No change
Internal Activity Level: High , Internal Trend: No change
Seismicity: From November 08, 2024, 11:00 a.m. to November 09, 2024, 11:00 a.m. :
Seismicity:
Below is the count of seismic events recorded at the reference station
Explosion (EXP): 193
Rainfall / Lahars:
No rain has been recorded in the volcano area. **In the event of heavy rain, it could remobilize the accumulated materials, generating mud and debris flows that would descend the sides of the volcano and flow into adjacent rivers.
Emissions / Ash Column:
Since this morning, several emissions of gas and ash have been recorded at heights below 1000 meters above the crater level in the Southwest and Southeast directions. In connection with this activity, the VAAC agency in Washington has published two reports on ash clouds, in a Southeast direction, with heights of 900 meters above the crater level.
Observation:
In the early hours of the day, an incandescence was observed at the crater level. Since yesterday afternoon until the closing of this report, the area has remained clear most of the time.
Alert level: yellow
Source : IGEPN
Photo : Camara Rota.
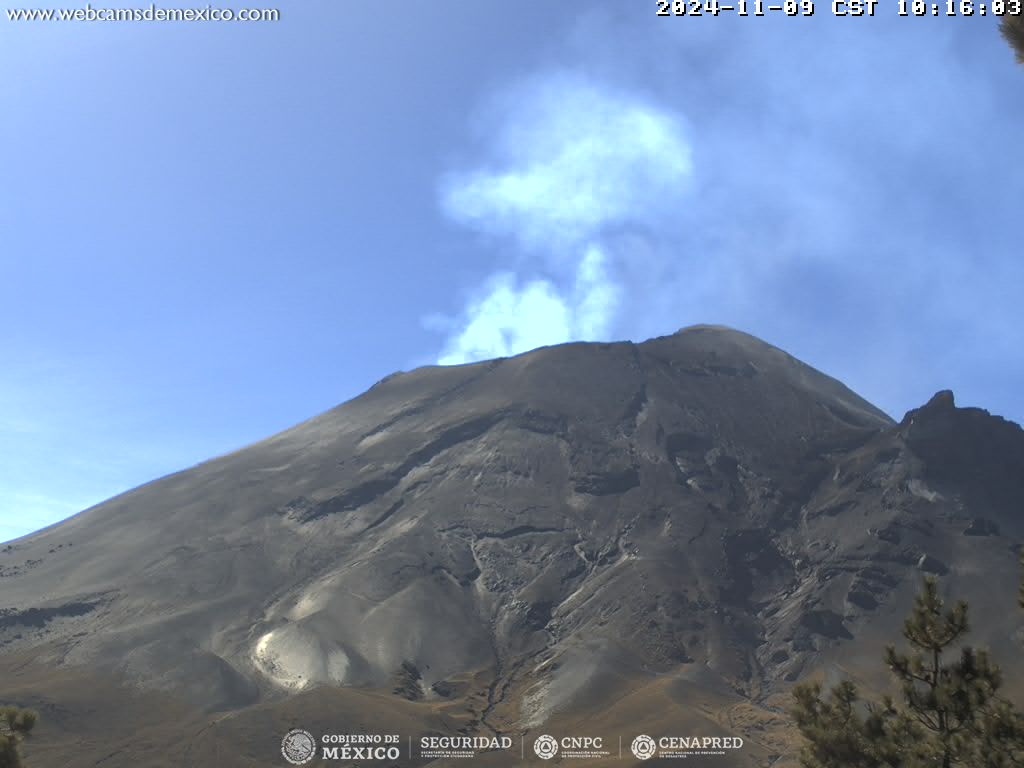
Mexico , Popocatepetl :
November 9, 11:00 (November 9, 17:00 GMT),
Activity in the last 24 hours
53 low intensity exhalations were detected, accompanied by water vapor, other volcanic gases and small amounts of ash.
In addition, 322 minutes of tremor were recorded, of which 35 were high frequency and 287 harmonic.
During the morning and at the time of this report, a continuous emission of water vapor and other volcanic gases is observed, with dispersion towards the West (W).
The Popocatépetl volcanic alert fire is in yellow phase 2.
The scenarios anticipated for this phase are:
A few small to moderate explosions
Occurrence of tremors of varying amplitude
Light to moderate ash rains in the surrounding towns and in some more distant towns
Ejection of incandescent fragments within the 12-kilometer exclusion radius
The occurrence of lahars can be expected to descend into the ravines, due to the accumulation of ash on the slopes and its interaction with the rains expected in the coming weeks.
Possibility of pyroclastic flows not reaching the populations
Source : Cenapred