September 25 , 2024.
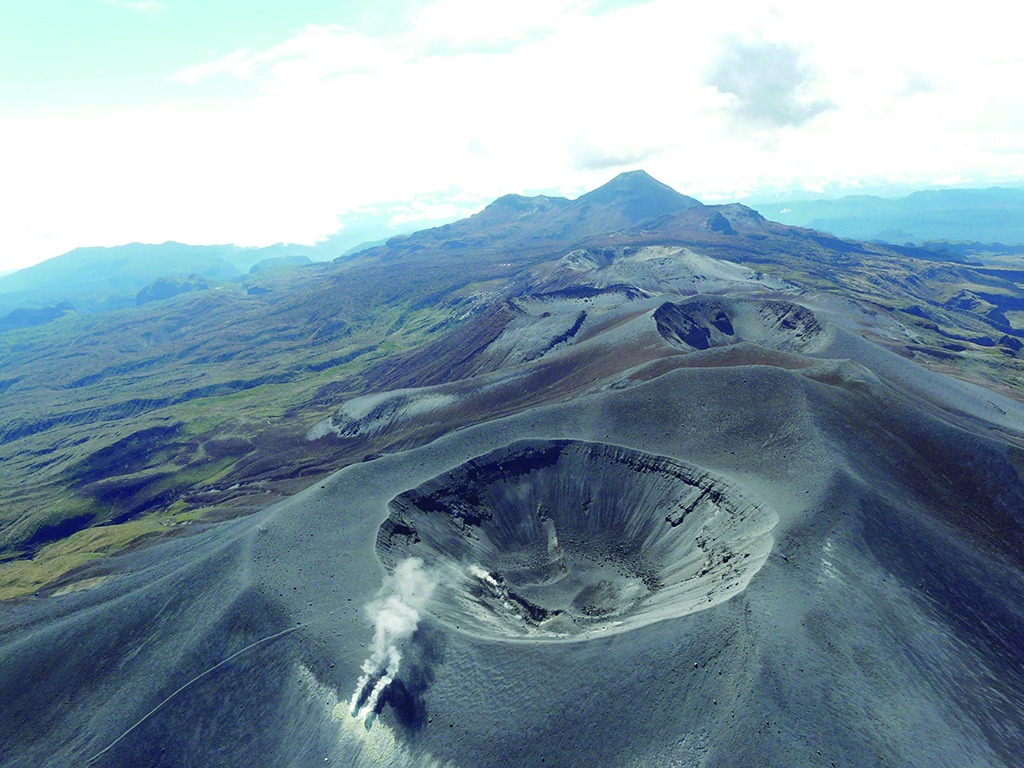
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from September 16, 2024 to September 22, 2024. (issue date September 24, 2024)
SUMMARY STATUS OF ACTIVITY
In light of the monitoring data, it emerges:
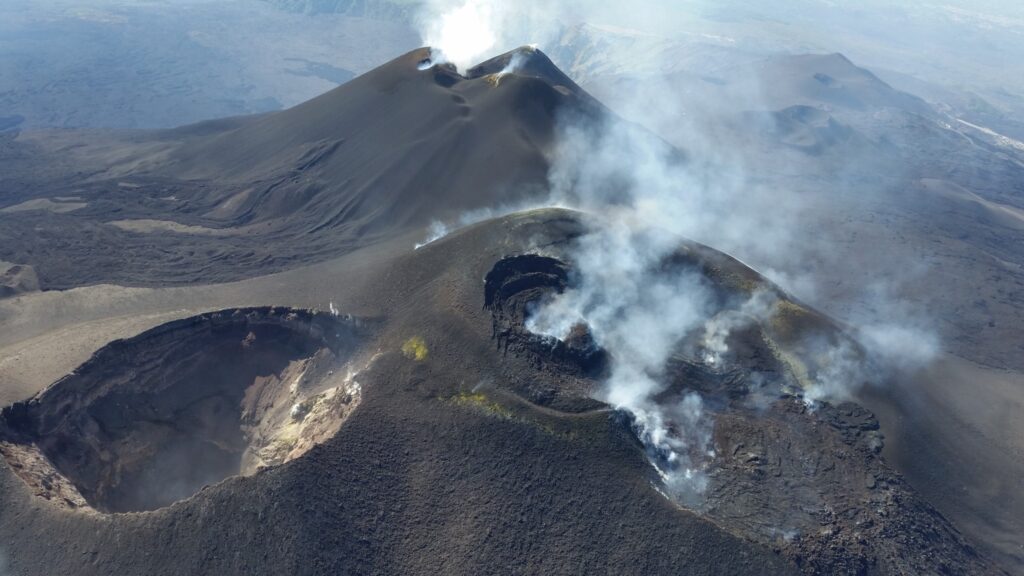
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Degassing activity at the Bocca Nuova crater, the North-East crater and the South-East crater.
2) SEISMOLOGY: No fracturing seismic activity with Ml>=2.0. Volcanic tremors during most of the week in question at average values, sometimes reaching high values.
3) INFRASOUND: Very low infrasound activity over the entire period.
4) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: Over the past week, ground deformation monitoring networks have not recorded significant changes
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux at an average and increasing level.
Soil CO2 flux is at average values.
Partial pressure of dissolved CO2 in groundwater shows values within seasonal variability
Isotope ratio: No update available.
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Satellite observed thermal activity in the summit area was generally low with some moderate thermal anomalies.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
Monitoring of the volcanic activity of Etna was carried out through the analysis of images from the INGV surveillance camera network, Osservatorio Etneo (INGV-OE). During the period studied, Etna’s activity was characterized by continuous degassing of varying intensity at the summit craters. In particular at the Bocca Nuova crater, the degassing was intense and continuous with occasional and slight emission of ash.
SEISMOLOGY
During the week in question, no earthquake located in the Etna area reached or exceeded the threshold of magnitude 2.0.
During the week, the volcanic tremor remained mainly medium. At times, it reached, albeit slightly, the range of high values. In particular, the strongest tremor episode was recorded starting at 01:00 UTC on the 16th, reaching its maximum value at 01:45 UTC. The tremor source locations throughout the week in question were found to correspond to the Bocca Nuova crater, at an altitude between 2,800 and 3,000 meters above sea level.
INFRASOUND
During the week in question, the occurrence rate of localized infrasound events was overall very low, although the presence of strong winds may have led to an underestimation of the count.
The few low-energy events recorded are located in the Southeast crater.
SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS
The thermal activity of Etna was monitored through the processing of a variety of satellite images with different temporal, spatial and spectral resolutions. During the last week, the satellite thermal activity in the summit area was generally low with some moderate thermal anomalies. The maximum value of the heat flux anomalies was 18 MW (SLSTR) on 21 September 2024 at 09:11 UTC.
The last heat flux anomaly was about 9 MW (MODIS) on 23 September 2024 at 09:15 UTC. However, during the last week, poor visibility conditions may have affected the analysis of satellite images.
Source : INGV
Photo : Etnair srl ( 08/2024)
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from September 16, 2024 to September 22, 2024. (issue date September 24, 2024)
SUMMARY STATUS OF ACTIVITY
In light of the monitoring data, it emerges:
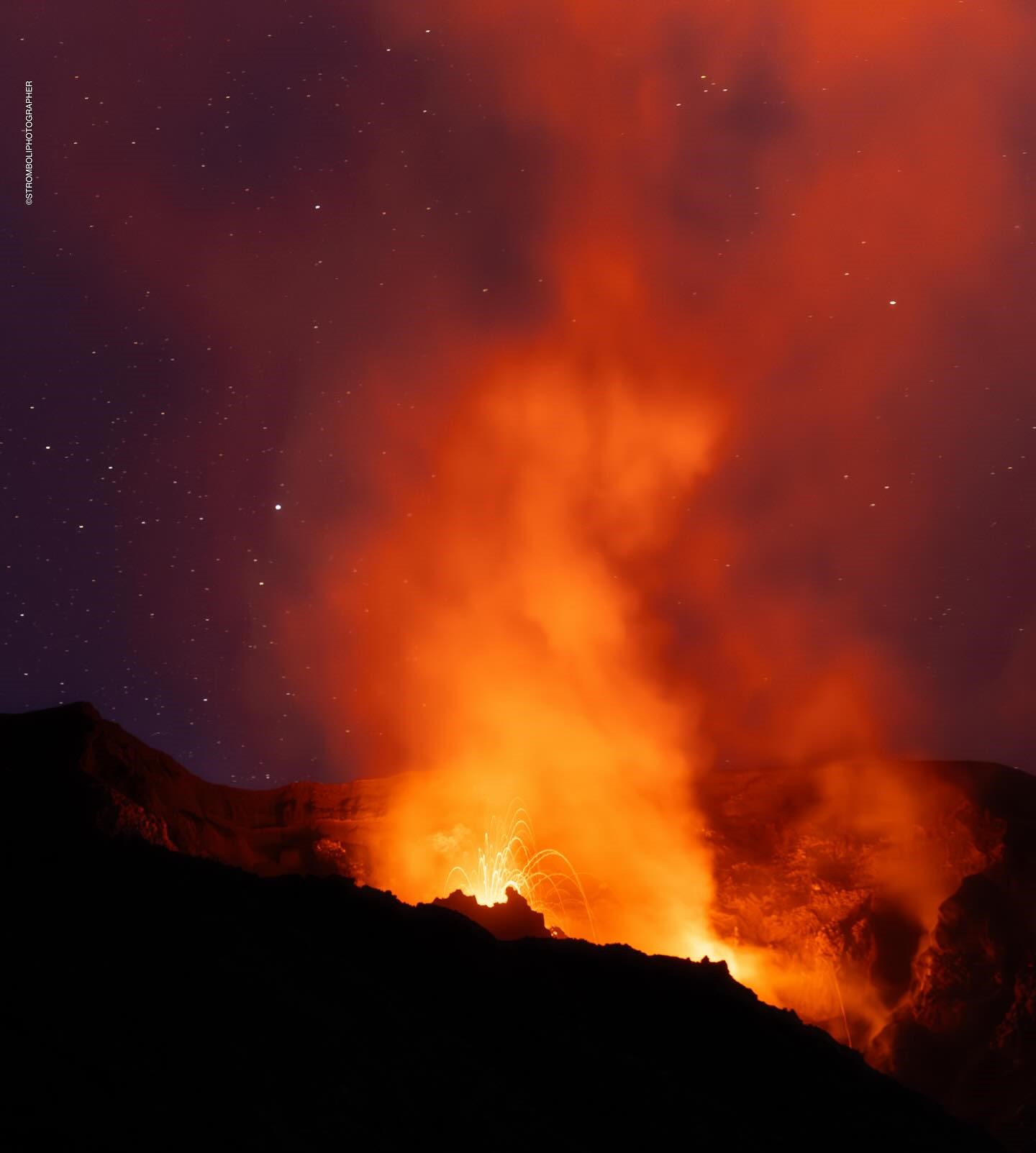
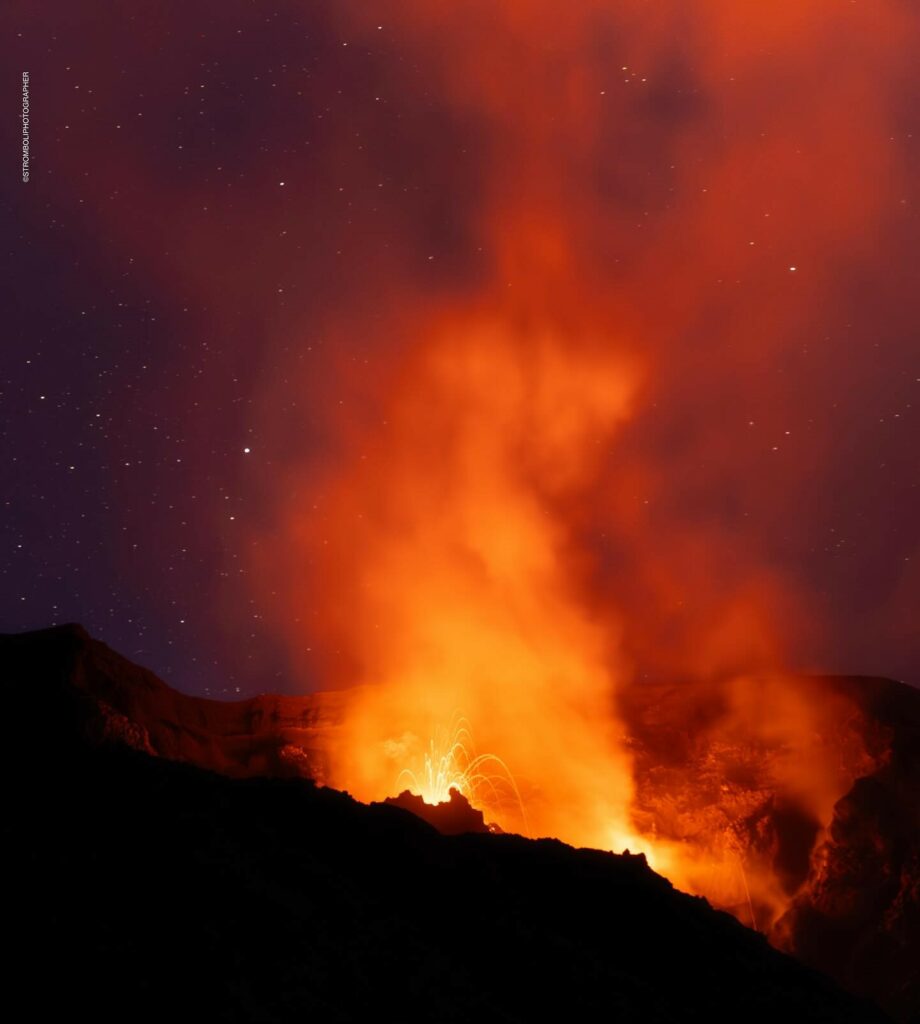
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: During this period, intense eruptive activity with splashes was observed from the North Crater area. The total hourly frequency fluctuated between medium values (8 events/h) and high values (16 events/h). The intensity of the explosions was low in the North Crater area and medium to high in the South Center area.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The monitored seismological parameters do not show significant variations.
3) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: The island’s ground deformation monitoring networks did not show any significant changes to report for the period under review.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux increasing to moderately medium-high level.
The CO2 flux from the ground in the STR02 summit area is at medium values.
The CO2/SO2 ratio in the plume reaches high values.
There is no update of the helium isotope ratio in the thermal aquifer.
CO2 flux at Mofeta in the San Bartolo area: high values.
CO2 flux at Scari: there are no updates due to technical issues.
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally low with some isolated thermal anomalies of moderate level.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the observed period, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized by analyzing the images recorded by the INGV-OE surveillance cameras located at an altitude of 190m (SCT-SCV) and at Punta dei Corvi (SPCT). The explosive activity was mainly produced by 2 (two) eruptive vents located in the North area of the crater and by 1 (one) vent located in the South-Central area.
Observations of the explosive activity captured by the surveillance cameras
In the North (N) crater area, two active vents were observed that produced low-intensity explosive activity (less than 80 m in height). In addition, splashes were observed, sometimes intense, on 16-17 and 19-20 September. The products emitted in eruption were mainly coarse materials (bombs and lapilli). The average explosion frequency ranged from 8 to 13 events/h.
In the Centre-South (CS) area, significant activity was observed on 16 and 18 September; explosions ranged in intensity from medium (less than 150 m high) to high (more than 250 m high) and were composed of fine materials. The average explosion frequency ranged from 2 to 3 events/h.
SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS
The thermal activity of Stromboli was monitored by processing a variety of satellite images with different temporal, spatial and spectral resolutions. During the last week, the thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally low with some isolated thermal anomalies of moderate level. The maximum value of the heat flux anomalies was 15 MW (MODIS) on 20 September 2024 at 12:25 UTC. The last heat flux anomaly was about 6 MW (MODIS) on 23 September 2024 at 09:15 UTC. However, last week, poor visibility conditions may have affected the analysis of satellite images.
Source : INGV
Photo : Stromboli stati d’animo / Sebastiano Cannavo. ( 9/2024)
Iceland , Reykjanes Peninsula:
Magma accumulation continues beneath Svartsengi . Last eruption the largest in the Sundhnúkur area since December 2023
Updated 24. September at 14:00 UTC
Land uplift continues at a similar rate
Total volume of the last eruption is just over 60 million m3
Minor seismic activity at the Sundhnúkur crater row for the last few weeks
Data from GPS instruments suggest that the land uplift in Svartsengi continues at a steady rate. Model calculations based on this data also suggest that magma accumulation beneath Svarstengi has continued at a similar rate for the last weeks. According to measurements of land uplift and estimates of the rate of magma accumulation, the development is similar to previous events in the area.
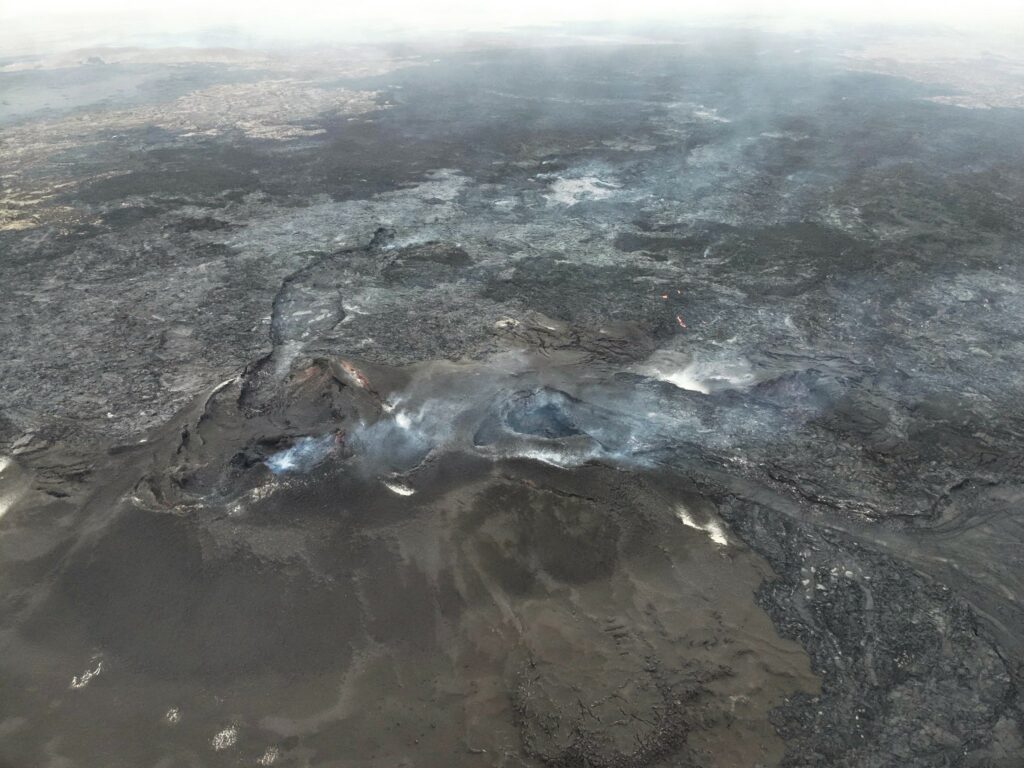
The photogrammetry team of the Icelandic Institute of Natural History (IIHN) and the National Land Survey of Iceland (NLSI) has processed data collected by specialists at Efla Consulting Engineers during a drone survey over the eruption site on 11 September. The data show that the lava flow field formed in the last eruption (22 August – 5 September) was 61.2 million m3 and 15.8 km2. This makes this last eruption the largest in the Sundhnúkur area since December 2023. The thickest part of the lava flow field is located around the crater that was active the longest.
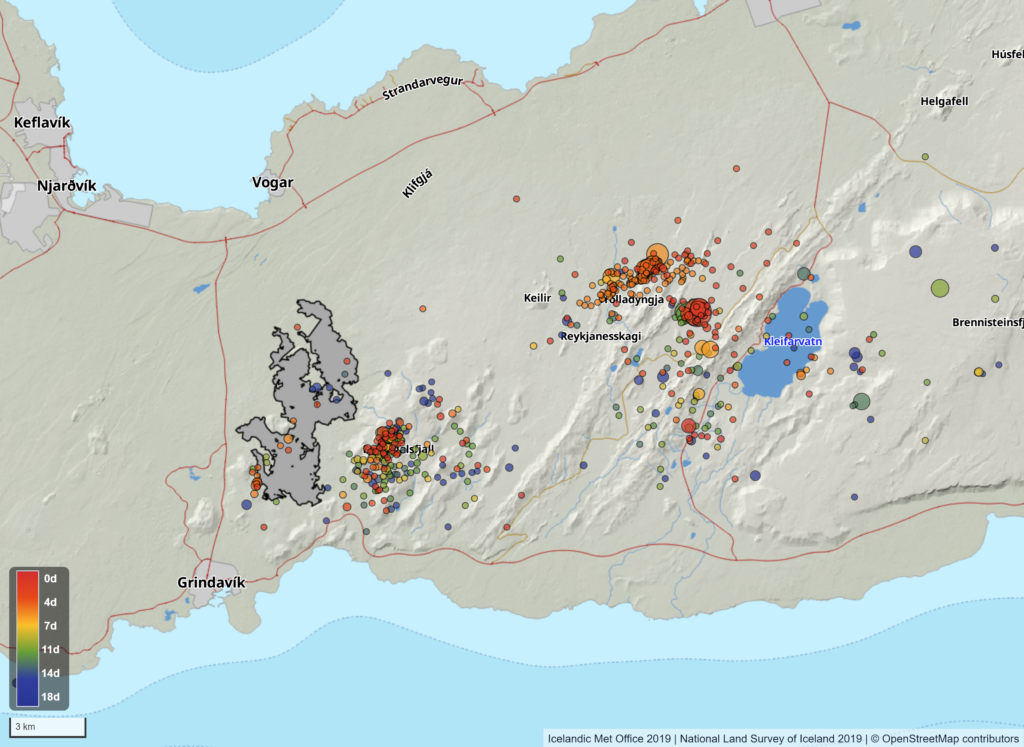
Seismic activity has been minimal for the last two weeks in the Sundhnúkur crater row. However, there has been some activity in the western part of Fagradalsfjall at a depth of about 6-8 km since the eruption ended on 5 September. There has also been considerable activity in Trölladyngja in the last few days. Most of the earthquakes in the area are small, but the largest one was of magnitude 3.0 on 22 September, just east of Trölladyngja. No deformation has been detected in the area around Trölladyngja.
Map showing seismic activity on the Reykjanes peninsula from 6th of 24th of September. The map also shows the contours of the lava flow field that formed in the last eruption. The contours of the lava are based on data collected by specialists at Efla Consulting Engineers which was processed by the photogrammetry team of IIHN and NLSI.
Source : IMO
Photos : Ljósmynd: Almannavarnir/Björn Oddsson , IMO.
Colombia , Puracé – Chaîne volcanique Los Coconucos :
Popayán, September 24, 2024, 4:30 p.m.
From the monitoring of the activity of the Puracé volcano – Los Coconucos volcanic chain, the Colombian Geological Survey (SGC), an entity attached to the Ministry of Mines and Energy, reports that:
During the week of September 17 to 23, seismic activity associated with fluid dynamics inside the volcano continued to record a significant number of events. This seismicity corresponding to Long Period events (LP type) maintained low energy levels and was located under the building of the Puracé volcano at depths of less than 1 km.
Seismicity related to rock fracturing (VT type) also showed low energy contributions and was concentrated near the crater of the Puracé volcano, as well as below the volcano.
Piocollo, with depths that do not exceed 3 km.
In addition, the slow deformation process that began in April 2022 on the Puracé volcano continues to be recorded. On the other hand, the monitoring of volcanic gases, electromagnetic fields and acoustic sensors does not show significant variations. Regarding the images captured through the installed cameras, it is observed that high degassing is maintained in the lateral fumarole.
Based on the above, the SGC recommends carefully monitoring the evolution of volcanic activity through weekly bulletins and other information published in official channels, as well as following the instructions of local, departmental authorities and the National Disaster Risk Management Unit (UNGRD).
The state of alert for volcanic activity remains in yellow alert: active volcano with changes in the behavior of the basic level of the monitored parameters and other manifestations.
Source et photo : SGC.
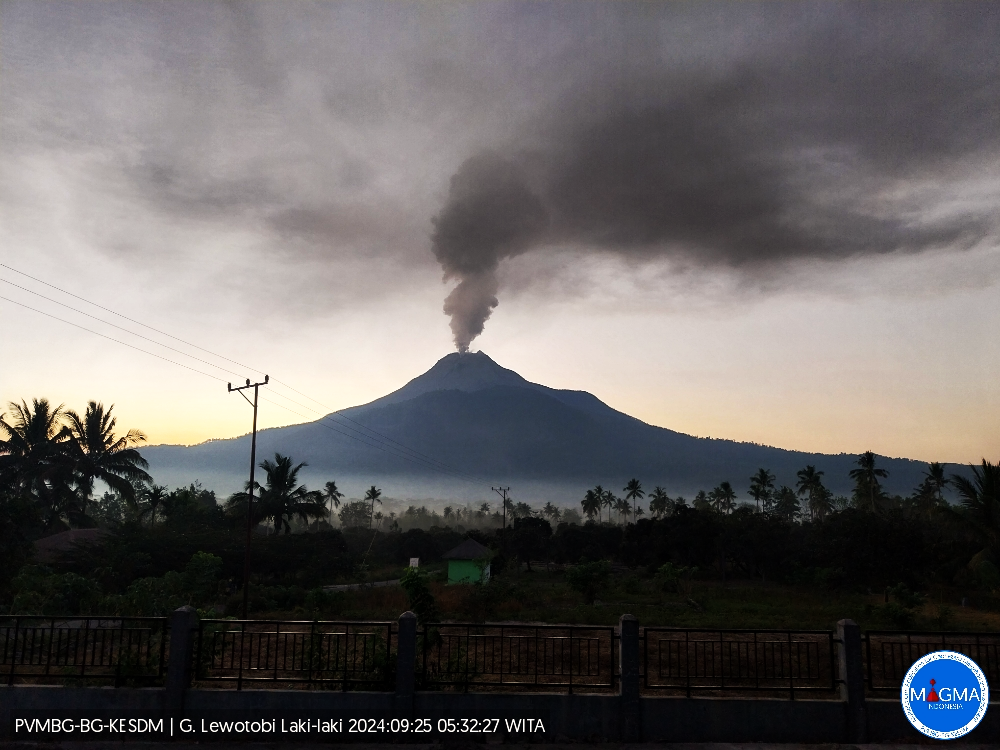
Indonesia , Lewotobi Laki-laki :
An eruption of Lewotobi Laki-laki occurred on Wednesday, 25 September 2024 at 05:26 WITA with the height of the ash column observed at ±700 m above the summit (±2284 m above sea level). The ash column was observed to be grey with moderate intensity, oriented to the southwest. At the time of writing this report, the eruption was still ongoing.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : September 25 , 2024
Volcano : Lewotobi Laki-laki (264180)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Lewotobi Laki-laki Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2024LWK549
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 32 min 20 sec E 122 deg 46 min 06 sec
Area : East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 5069 FT (1584 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 21h26 UTC (05h26 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 7309 FT (2284 M) above sea level or 2240 FT (700 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to southwest. Volcanic ash is observed to be gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be medium.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 4.4 mm and maximum duration 407 second.
Source et photo : Magma Indonésie.