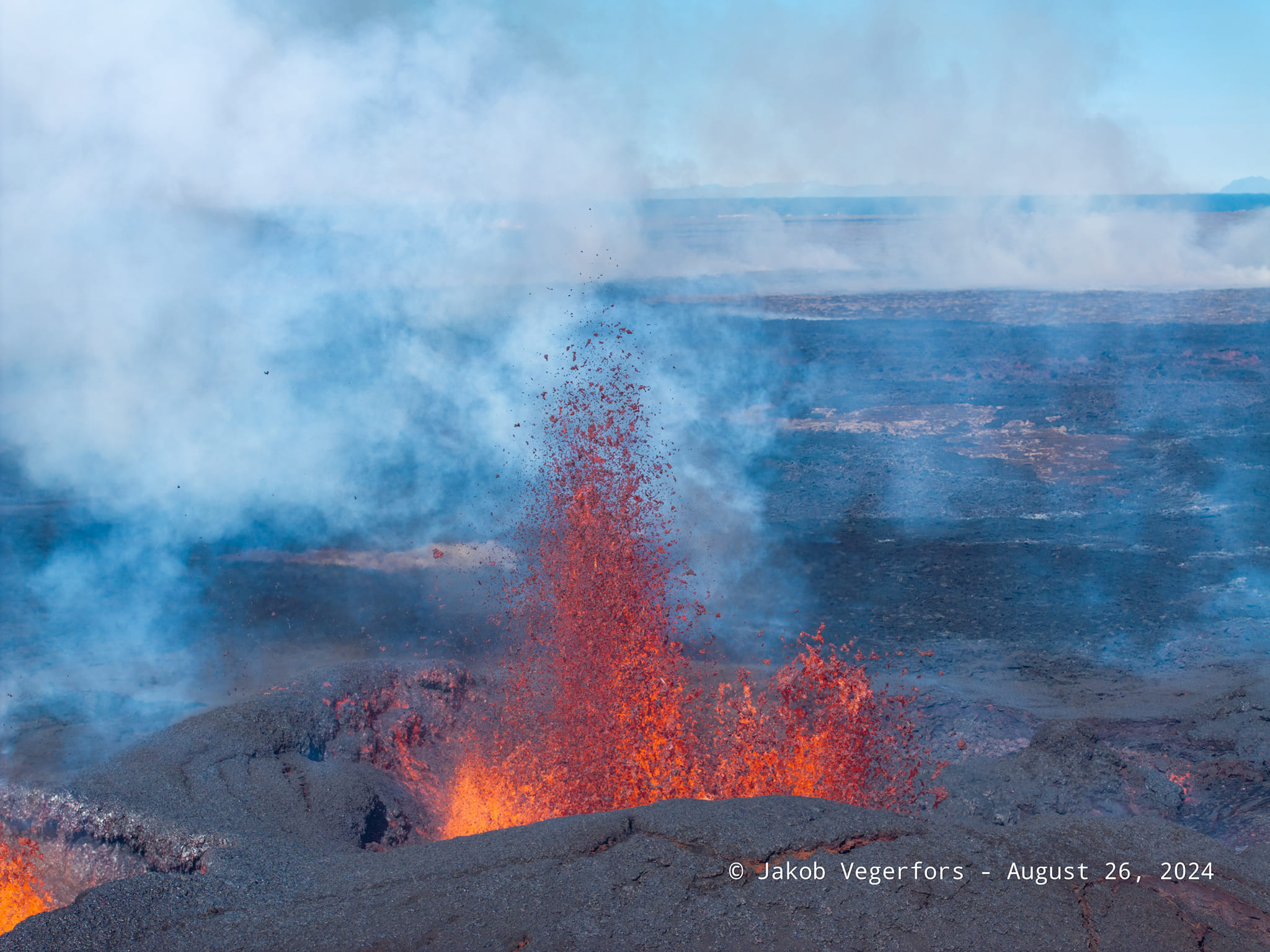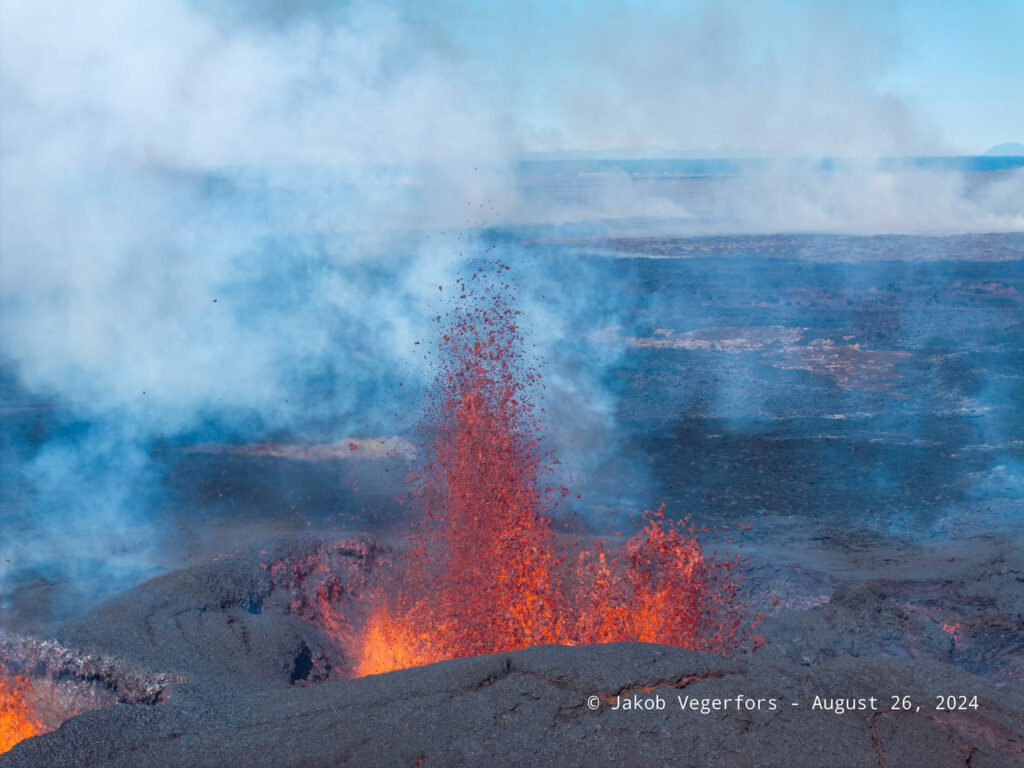September 04 , 2024.
Italy , Stromboli :
BULLETIN HEBDOMADAIRE , du 26 Aout 2024 au 01 Septembre 2024 (date de parution 03 Septembre 2024).
SUMMARY STATUS OF ACTIVITY
In light of the monitoring data, it emerges:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: During this period, an intense eruptive activity was observed with spattering activity in the northern area of the crater and consequently an emission of lava flows along the Sciara del Fuoco. The total hourly frequency of explosions fluctuated between medium (10 events/hour) and high (18 events/hour) values. The intensity of the explosions varied from low to medium in the area of the Northern Crater and medium to high in the area of the Central-Southern Crater.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The monitored seismological parameters do not show significant variations.
3) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: No significant changes were reported in the time series of the ground deformation monitoring stations during the last week.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: Medium-level SO2 flux.
The CO2 flux from the soils in the STR02 summit area is at medium values.
The CO2/SO2 ratio in the plume is at medium values.
There is no update of the helium isotope ratio in the thermal aquifer.
CO2 flux at Mofeta in the San Bartolo area: high values.
CO2 flux at Scari: there are no updates due to technical problems in data transmission.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the observed period, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized through the analysis of images recorded by the INGV-OE surveillance cameras located at 190 m altitude (SCT-SCV) and at Punta dei Corvi (SPCT). Explosive activity was mainly produced by three eruptive vents located in the North Crater area and one vent located in the South-Central Crater area.
On 30 and 31 August, three lava flows were produced from the North Crater Terrace area.
Observations of explosive activity captured by surveillance cameras.
In correspondence with the North Crater (N) area, three active vents were observed that produced explosive activity ranging in intensity from low (the erupted products reached a height of less than 80 m) to medium (height of less than 150 m). In addition, projection activity was observed, the most intense and continuous at the southernmost of the three vents. The products emitted in eruption were mainly coarse materials (bombs and lapilli). The average frequency of explosions ranged from 8 to 14 events/hour.
In the Centre-South (CS) area, the explosions ranged in intensity from medium (height of less than 150 m) to high (height of more than 250 m) with the emission of fine materials sometimes mixed with coarse materials. The average frequency of explosions ranged from 1 to 4 events/hour.
Lava flows of 30 and 31 August 2024.
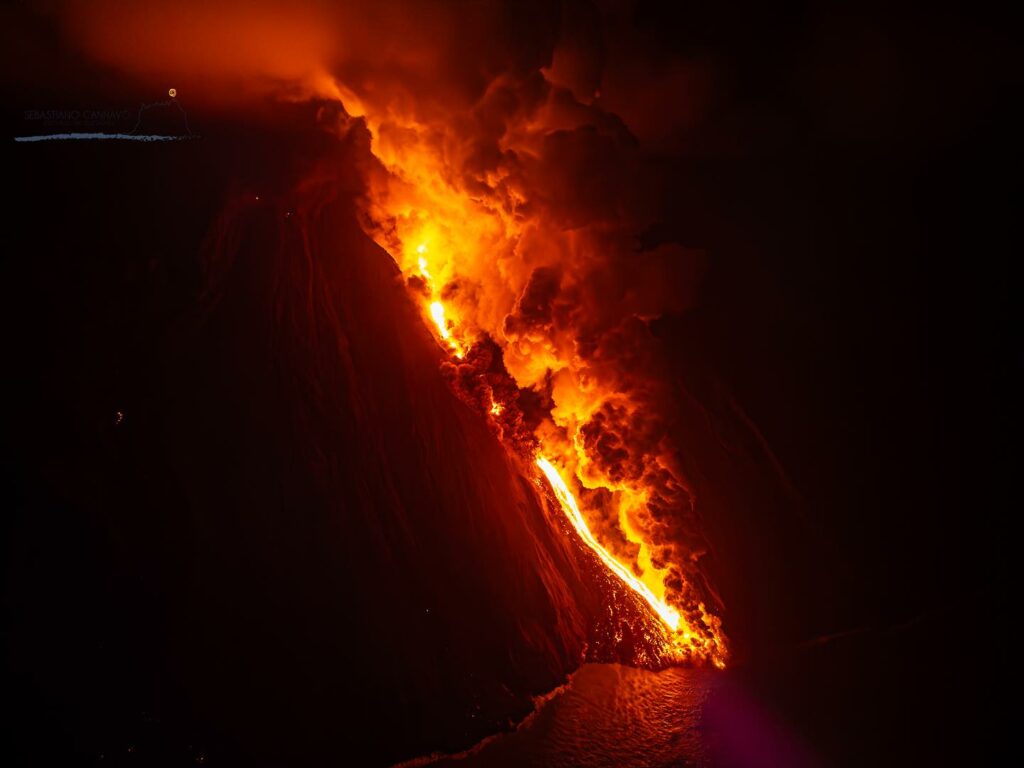
From the early hours of 30 August until the morning of 31 August 2024, three lava flows were emitted from the northern area of the crater along the Sciara del Fuoco. Below is the detailed description.
On 30 August from 00:44 UTC, following an intense spattering activity that affected the mouth of the northern area located near the incision originating in July, a lava flow was observed that was channeled inside the aforementioned incision. After a first phase characterized by a high emission rate, around 05:00 UTC the flow appears poorly fed.
From 10:32 UTC, intense spattering activity began at the North vent of the northern area, which preceded the emplacement of a second lava flow that started flowing after a few minutes to reach the highest emission rate in the early afternoon. At 21:00 UTC, this flow appeared poorly fed.
From 02:30 UTC on 31 August, the third lava flow started flowing in the aforementioned incision, overlapping the previous flows. The flow rate reached the maximum emission level after a few hours. From 08:00 UTC, it appeared poorly fed and cooled.
It should be emphasized that most of the material was deposited along the Sciara del Fuoco and only modest volumes of lava material reached the coast.
Source : INGV
Photo : Stromboli stati d’animo / Sebastiano Cannavo. ( archive 07/2024).
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from August 26, 2024 to September 01, 2024 (publication date September 03, 2024).
SUMMARY STATUS OF ACTIVITY
In light of the monitoring data, it emerges:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Degassing of the summit craters, in particular of the eastern mouth of the Southeast Crater.
2) SEISMOLOGY: Low seismic activity due to fracturing; the amplitude of the volcanic tremor remained mainly at average levels.
3) INFRASOUND: Absence of infrasound activity.
4) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: The ground deformation monitoring networks did not show any significant variations during the week.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: Low to medium level SO2 flux.
Soil CO2 flux shows high values.
Partial pressure of dissolved CO2 in groundwater shows values in seasonal variability
There is no update on the helium isotope ratio.
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally low with some isolated thermal anomalies of moderate level.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
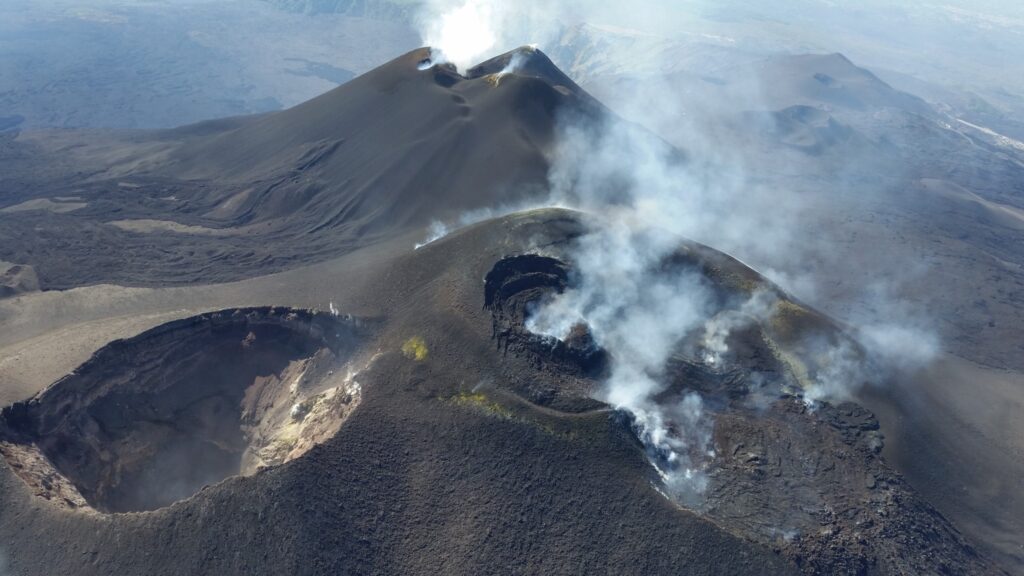
During the week in question, the monitoring of the volcanic activity of Etna was carried out through the analysis of the images from the surveillance cameras of the INGV – Osservatorio Etneo (INGV-OE). Every day, during the day, the volcano was shrouded in clouds, making visual observations impossible at that time; in addition, the images from some cameras disappeared for 1-2 days.
In general, during the observation period, the activity of Etna was characterized by a continuous degassing of variable intensity at the eastern mouth of the South-East crater and emissions of vapors from the other summit craters, especially in conditions of high humidity, being particularly visible at the Voragine crater. On August 27, 28 and 29, during a series of intense thunderstorms, the summit area and the upper slopes of the mountain were covered with a layer of hail and snow up to 2600 m above sea level.
Source : INGV
Photo : Etnair srl (27/08/2024)
Iceland , Reykjanes Peninsula :
Updated hazard assessment. Regions 3, 5 and 6 expanded to the northeast
Updated 3 September at 11:50
Influx into the magma accumulation zone beneath Svartsengi is likely equal to outflow from the eruption.
Two active vents north of the fissure
Seismic activity has decreased in recent days
The hazard assessment will be updated later today
In recent days, there has been no uplift or subsidence at Svartsengi. This indicates that influx into the magma accumulation zone beneath Svartsengi is comparable to outflow from the volcanic eruption.
To say that the uplift has started again, one must observe the evolution of the measurements over several days. Indeed, changes between days can occur due to various effects, e.g. atmospheric moisture content or solar storms.
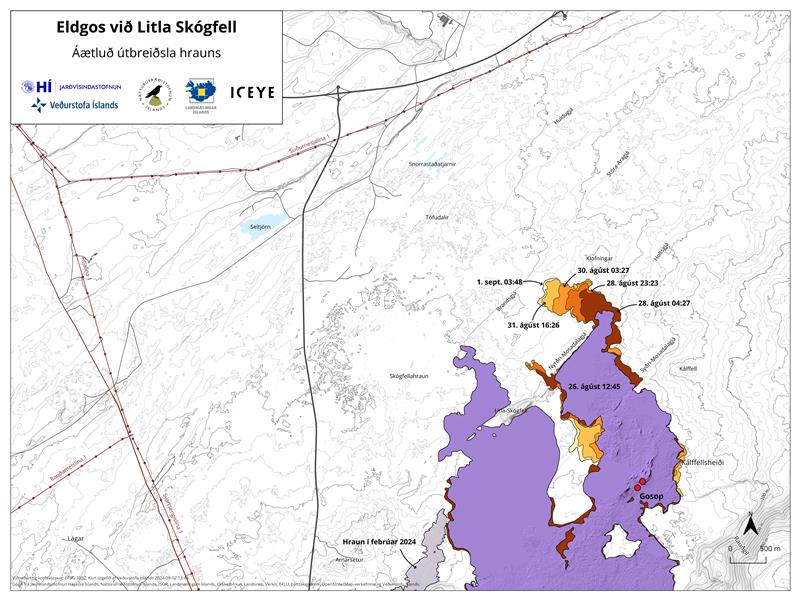
Two vents are now active since the eruption that began on August 22. Although the power of the eruption has decreased somewhat in recent days. The lava spread north of the crater continues to expand, but the rate of propagation has slowed considerably. At present, the lava flows do not threaten infrastructure near the eruption centers. The attached map based on Iceye satellite data shows the evolution of the lava bed from August 26 to September 1.
Map showing the active part of the lava bed that formed during this eruption. The map is based on data from the Iceye satellite
Seismic activity around the Sundhnúks crater series has decreased significantly in recent days. Most of the small earthquakes measured are occurring north of the active fissure at the beginning of this eruption.
Updated September 3 at 15:15 .
Today’s weather forecast is northwesterly and air pollution will reach southeast
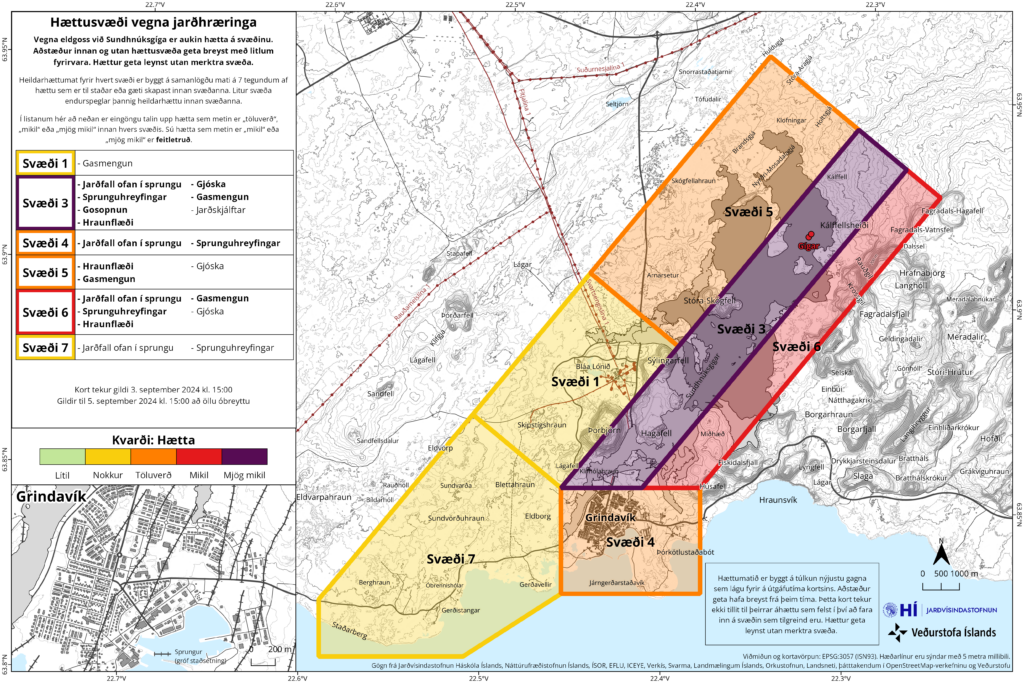
Risk assessment updated. Map expanded 2 km northeast in zones 3, 5 and 6
Risk assessment in zone 5 is upgraded from high to considerable
The Norwegian Meteorological Agency has updated its risk assessment based on the development of the eruption, and it remains valid until September 5. The main changes are that zone 5 is being changed from high risk (red) to considerable risk (orange). This is because pyroclastic material is not considered as dangerous. The risk of gas pollution is assessed based on the weather forecast for the next few days for each zone.
Another change to the map is that zones 3, 5 and 6 have been expanded by 2 km to the northeast. This change is being made for two reasons. First, because the lava bed that formed during this eruption has extended beyond the previous zone boundaries. Secondly, to take into account that the magma tunnel that formed on August 22 has reached further northeast of zone 3 than it did previously.
Source : IMO
Photo : Jakob Vegerfors 26/08/2024
Kamchatka , Sheveluch :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Issued: Septmber 02 , 2024
Volcano: Sheveluch (CAVW #300270)
Current aviation colour code: ORANGE
Previous aviation colour code: orange
Source: KVERT
Notice Number: 2024-68
Volcano Location: N 56 deg 38 min E 161 deg 18 min
Area: Kamchatka, Russia
Summit Elevation: 3283 m (10768.24 ft), the dome elevation ~2500 m (8200 ft)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
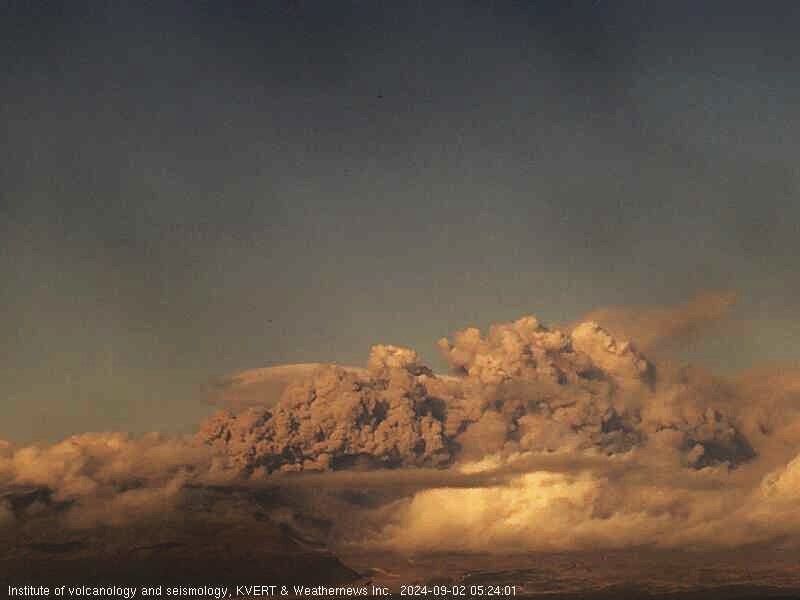
A moderate explosive eruption of the 300 years of RAS lava dome continues. The explosions sent ash up to 3.5 km a.s.l., and ash plume extended for 65 km to the east of the volcano.
An explosive-extrusive eruption of Sheveluch volcano continues. The danger of ash explosions up to 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l. remains. Ongoing activity could affect international and low-flying aircraft.
Volcanic cloud height: 3500 m
(11480 ft) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20240902/1920Z – Video data
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 65 km (40 mi)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: E / azimuth 90 deg
Time and method of ash plume/cloud determination: 20240902/2100Z – Himawari-9 14m15
Source : Kvert
Photo : IVS FEB RAS, KVERT ( 2/9/2024 )
Indonesia , Ibu :
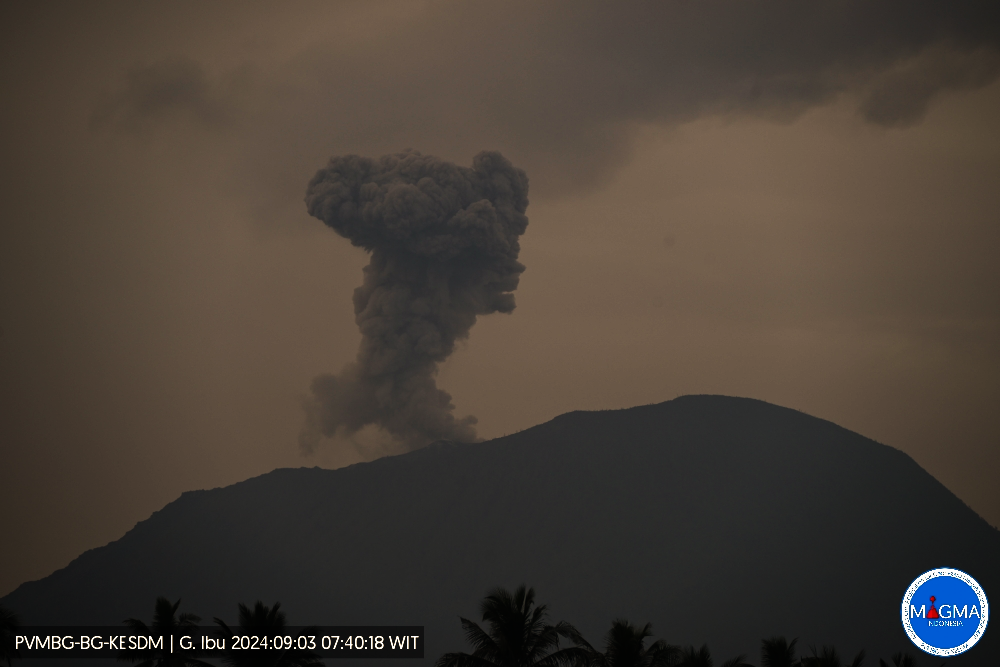
Mount Ibu exhibited an eruption on Tuesday September 3, 2024 at 07:39 WIT with the height of the ash column observed at ± 600 m above the summit (± 1925 m above sea level). The ash column was observed to be gray with thick intensity, oriented towards the West. This eruption was recorded on a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 28 mm and a duration of 58 seconds.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : September 03 , 2024
Volcano : Ibu (268030)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Ibu Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2024IBU653
Volcano Location : N 01 deg 29 min 17 sec E 127 deg 37 min 48 sec
Area : North Maluku, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 4240 FT (1325 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 22h39 UTC (07h39 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 6160 FT (1925 M) above sea level or 1920 FT (600 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to west. Volcanic ash is observed to be gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 28 mm and maximum duration 58 second.
Source : Magma Indonésie .