March 24 , 2024.
Russia / Kuril Islands , Ebeko :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Issued: March 24 , 2024
Volcano: Ebeko (CAVW #290380)
Current aviation colour code: ORANGE
Previous aviation colour code: orange
Source: KVERT
Notice Number: 2024-14
Volcano Location: N 50 deg 41 min E 156 deg 0 min
Area: Northern Kuriles, Russia
Summit Elevation: 1156 m (3791.68 ft)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
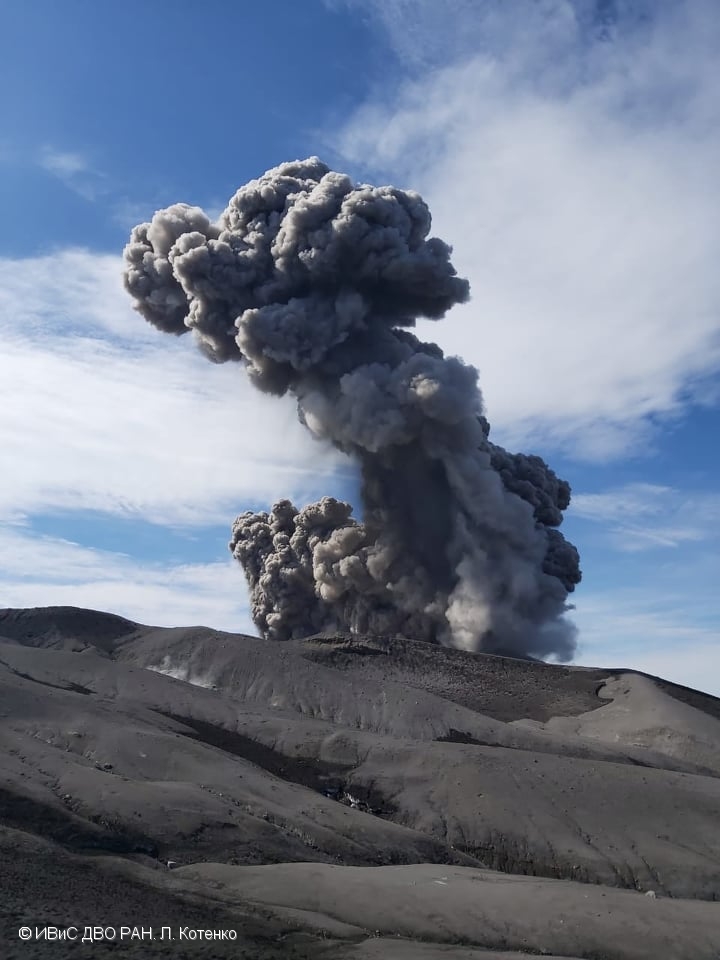
A moderate explosive eruption of the volcano continues. According to visual data from Severo-Kurilsk, explosions sent ash up to 2.8 km a.s.l., and ash cloud drifted to the east of the volcano.
A moderate explosive eruption of the volcano continues. Ash explosions up to 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. could occur at any time. Ongoing activity could affect low-flying aircraft and airport of Severo-Kurilsk.
Volcanic cloud height:
2800 m (9184 ft) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20240323/2354Z – Visual data
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 5 km (3 mi)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: E / azimuth 80 deg
Time and method of ash plume/cloud determination: 20240323/2354Z – Visual data
Source : Kvert
Photo : L. Kotenko. IVS FEB RAS ( Archive).
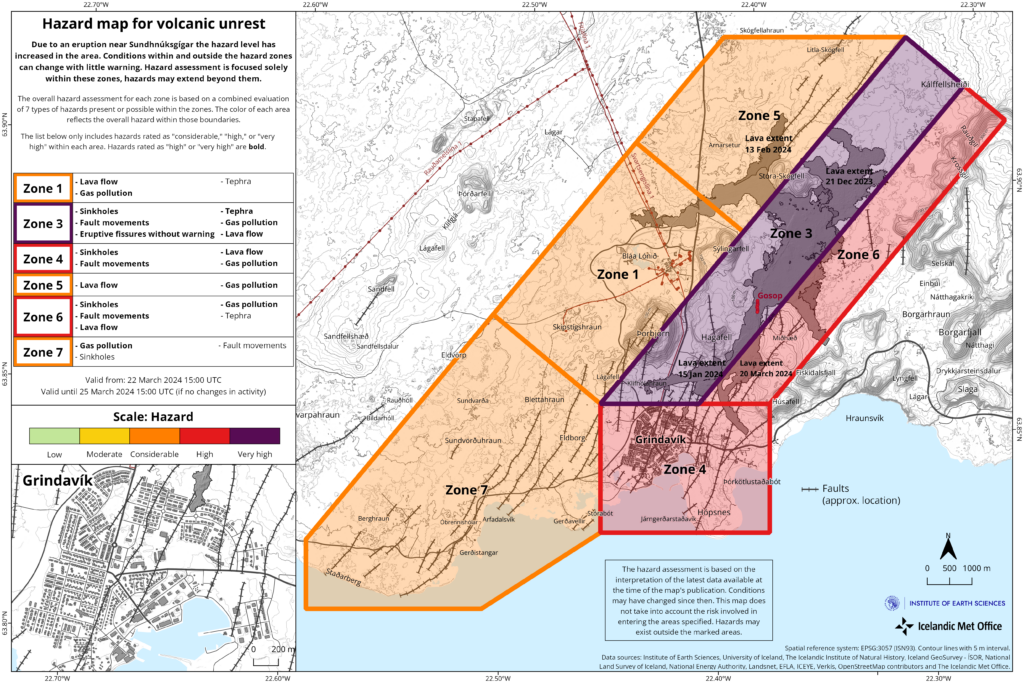
Iceland , Reykjanes Peninsula :
Increased hazards due to gas emissions
The hazard assessment has been updated and is valid from 15:00 today, Friday, March 22, until 15:00 on Monday, March 25. The risk due to gas emissions is assessed to be higher within all regions compared to the previous days. This is due to the unfavorable weather forecast for the next few days and higher measured values of sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions from the eruption sites and the lava field than before.
In areas 1 and 5 (northwest of the eruption sites), the risk of lava flows is lower than it was in the past three days. This risk has decreased because the lava flow north of the eruption sites has stabilized, and lava is now preferentially flowing to the south. However, the lava field remains hazardous because it formed very recently.
Source et photo : IMO.
Indonesia , Semeru :
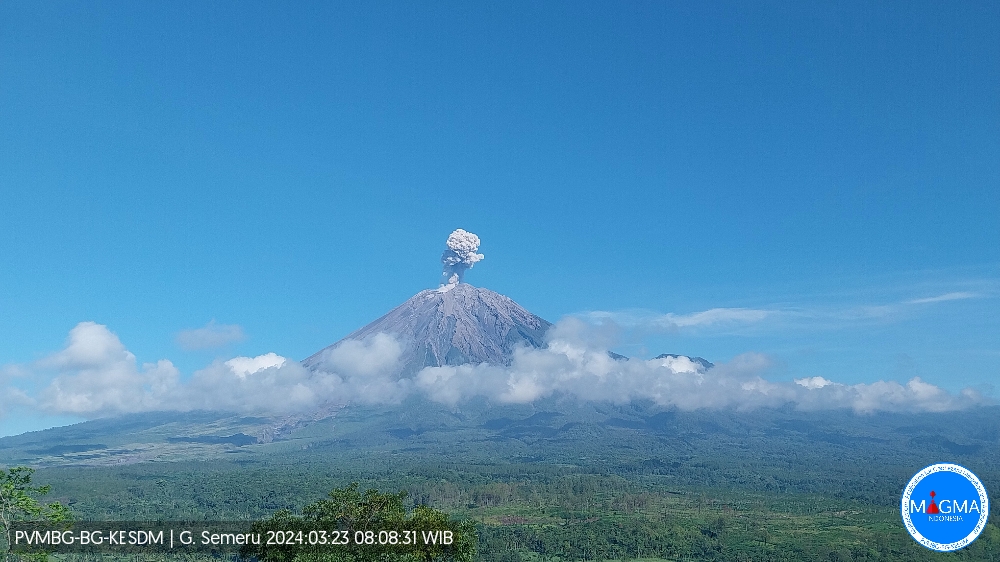
Mount Semeru exhibited an eruption on Saturday, March 23, 2024 at 08:07 WIB with the height of the ash column observed at ± 1000 m above the summit (± 4676 m above sea level). The ash column was observed to be white to gray in color with thick intensity, oriented towards the North-West. This eruption was recorded on a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 21 mm and a duration of 73 seconds.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : March 23 , 2024
Volcano : Semeru (263300)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Semeru Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2024SMR207
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 06 min 29 sec E 112 deg 55 min 12 sec
Area : East java, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 11763 FT (3676 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 01h07 UTC (08h07 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 14963 FT (4676 M) above sea level or 3200 FT (1000 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to northwest. Volcanic ash is observed to be white to gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 21 mm and maximum duration 73 second.
Source et photo : Magma Indonésie.
Chile , Villarica :
Seismology
The seismological activity of the period was characterized by the recording of:
182 seismic events of type VT, associated with the fracturing of rocks (Volcano-Tectonics). The most energetic earthquake had a Local Magnitude (ML) value equal to 3.3, located 8.6 km east-southeast of the volcanic edifice, at a depth of 6.8 km compared to to the crater.
8852 LP type seismic events, associated with fluid dynamics inside the volcanic system (Long Period). The size of the largest earthquake evaluated from the Reduced Displacement (RD) parameter was equal to 50 cm2.
2782 TR type seismic events, associated with the sustained dynamics over time of fluids inside the volcanic system (TRemor). The size of the largest earthquake evaluated from the Reduced Displacement (DR) parameter was equal to 39 cm2
Fluid geochemistry
The sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions data obtained by the differential optical absorption spectroscopy (DOAS) equipment, corresponding to the Los Nevados and Tralco stations, installed respectively at 10 km in an East-North-East direction and 6 km East-South-East of the active crater, presented an average value of 2,045 ± 438 t/d, considered atypical values for this volcanic system. The maximum daily value was 6,880 t/d on March 1, considered an abnormal value for this system. 2 satellite anomalies were reported in atmospheric SO2 emissions in the area near the volcano on March 4 and 5, according to data published by Tropopheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) and Mounts.
Thermal anomalies by satellites
During the period, 19 thermal alerts were recorded in the area associated with the volcano, with a maximum volcanic radiative power (VRP) of 106 MW on March 11, a value considered high according to data processed by the Observation of the volcanic activity in the mid-infrared. (MIROVA).
Thanks to the analysis of Sentinel 2-L2A satellite images, 6 radiance anomalies were detected in the area associated with the crater during the evaluated period. The NHI tools platform detected a maximum area of anomalous radiation in the crater area of 42,300 m2 on March 1.
Geodesy
The geodetic activity, monitored through 5 GNSS and radar interferometry (InSAR) stations, was characterized by:
– Rate of variation of horizontal and vertical components of GNSS monitoring stations of medium/low magnitude and with slight changes compared to the previous period.
– The online extension of the SE-NW monitoring reaches 0.7 cm/month, included in an obvious annual/seasonal cyclical variation identified since 2013.
– Thanks to InSAR, no signs of deformation have been observed over the last 3 months.
In conclusion, a period of stability is evident in the deformation monitoring, with small magnitude changes that do not show the appearance of surface morphological changes.
Surveillance cameras
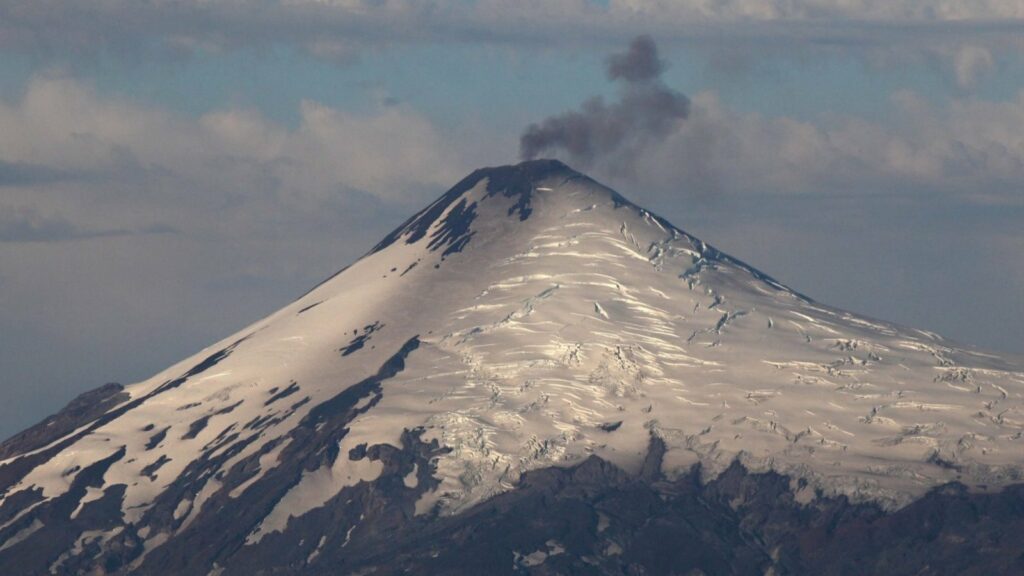
From surveillance cameras installed on the volcano, degassing was observed recurrently, with columns whose heights did not exceed 500 meters, lower than those observed in February. These are mainly columns with a predominance of water vapor. However, on March 1, 3, 5, 7, 10, 14 and 15, passive emissions were observed with a higher content of pyroclasts, highlighting that of March 3, whose height reached 400 m above the crater level. Concerning the explosive activity, Strombolian episodes were observed with proximal impact, inside and at the edge of the crater.
Satellite geomorphological analysis
Thanks to the photo-interpretation of Planet Scope, Sentinel 2 L2A, SkySat collect and Pléiades images, the crater was observed with inside an emerging cone built from the accumulation of pyroclasts resulting from the explosions, the dimensions of which are maintained compared to what was observed in February:
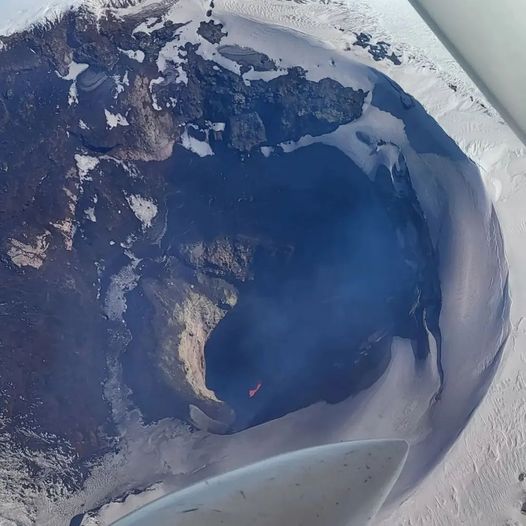
E-W diameter of 67 m (Pléiades image of March 11). Inside, the melt can be observed through a circular section with a maximum diameter of 27 m in the NNW-SSE direction and an area of 421 m2.
. The downward trend observed since the second half of February continues, showing a decrease in the surface exposure of the lava lake.
The activity of the volcanic system remains with a tendency towards stabilization of the energy values of the continuous seismic signal at values close to 1.4 µm/s and the recurrent recording of
seismicity linked to fluid dynamics. In addition, at the beginning of the fortnight, energetic VT earthquakes were recorded located in the eastern sector of the volcanic building, which justified the issuance of a special report. On the other hand, moderate Strombolian explosions which lead to ballistic projections in the area close to the crater, incandescences and thermal anomalies continue to be observed, highlighting the appearance of an ash emission recorded on March 3 which generated a column of 400 m and dispersed in a northeast direction. SO2 values were repeatedly detected above values considered abnormal (1,800 tonnes/day). The monitoring parameters indicate the constant activity of a near-surface lava lake, which results in geometric variations of the outlet conduit and the exposed lava lake area, linked to an unstable volcanic process and the potential for generation of explosive activity.
In this way, the volcanic technical alert is maintained by:
YELLOW TECHNICAL ALERT: Changes in the behavior of volcanic activity.
Source : Sernageomin
Photos : TVN , Richard L. ( archives).
Ecuador , Sangay :
DAILY REPORT ON THE STATE OF THE SANGAY VOLCANO, Saturday March 23, 2024.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface activity level: High, Surface trend: No change
Internal activity level: High, Internal trend: No change
Seismicity: From March 22, 2024, 11:00 a.m. to March 23, 2024, 11:00 a.m.:
The number of seismic events recorded at the reference station over the past 24 hours is shown below. The level of seismic activity of the volcano remains high.
Explosion Event (EXP): 268
Precipitation/Lahars:
Light rains were recorded in the volcano area, without generating mud or debris flows. **Heavy rains could remobilize accumulated material and generate flows of mud and debris that would flow down the volcano’s flanks and flow into adjacent rivers.
Emissions/ash column:
Since yesterday afternoon until the closing of this report, thanks to the surveillance camera system, several gas and ash emissions have been recorded with heights between 500 and 1000 meters above the level of the crater with North and North-East directions. In connection with these emissions, the Washington VAAC published two emission reports with heights of 600 meters above the level of the crater in a North and West direction.
Observation:
Despite the cloudiness in the volcano area, last night an episode of light incandescence was observed in the volcano’s crater. Until the closing of this report, the volcano remained completely cloudy.
Alert level: yellow
Source : IGEPN.
Photo : Eqphos_fotografía