November 21 , 2023.
Iceland , Reykjanes Peninsula :
Clear evidence of uplift in Svartsengi
Around 700 earthquakes have been detected near the magma intrusion since midnight, largest M2.7. Updated 20. November at 13:20 UTC
Since midnight today, over 700 earthquakes have been detected in the region of the magma intrusion, the largest of which was magnitude 2.7 near to Hagafell.
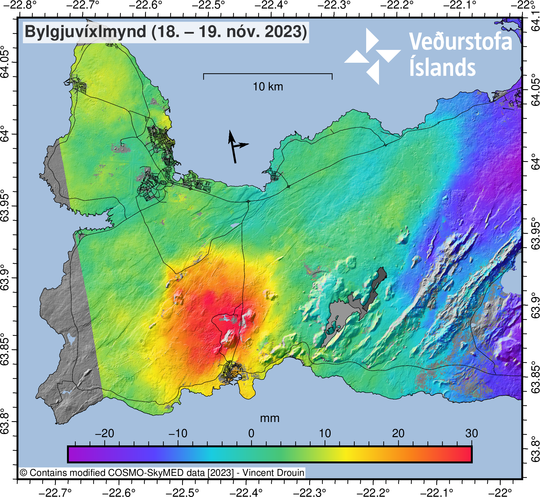
In recent days, between 1,500 and 1,800 daily earthquakes have been measured in the region, with the largest event registering magnitude 3.0 last Friday (17 November). Based on radar imagery from 18 and 19 November 2023, the latest interferogram of the magma intrusion and the surrounding area shows significant crustal uplift in the vicinity of Svartsengi. The newly processed interferogram was reviewed by experts during the weekend (18 – 19 November) from the Icelandic Meteorological Office, the University of Iceland, and the Department of Civil Protection and Emergency Management. The results were also discussed in today’s status meeting, held at IMO. The rapid, ongoing uplift close to Svartsengi is occurring in the same area where uplift was measured before the magma intrusion formed on November 10. Geodetic models derived from satellite images show that the uplift in Svartsengi area is considerably faster than before. Generally, when a magma intrusion forms, subsidence occurs above the centreline of the intrusion, as seen in Grindavík, with signs of land uplift discernible adjacent to the intrusion. Crustal uplift in the Svartsengi region due to magma accumulating at depth has been measurable since the intrusion began to form on 10 November. Initially, the uplift sign was influenced by the formation of the intrusion, but now the dominance of deep magma recharge is apparent.
The clear sign of crustal uplift in Svartsengi region does not change the likelihood of an eruption from the magma intrusion. This is assessed, amongst other things, on the fact that the Earth’s crust over the magma intrusion is much weaker than the crust over the uplift region close to Svartsengi. As long as there is not significant seismicity in the Svartsengi region, there is not a high likelihood of an eruption at that location. Moreover, an eruption is still deemed more likely from the intrusion, particularly if there is a sudden, large inflow of magma into the intrusion.
Our monitoring and hazard assessment preparations are still based on the assumption that the situation could change suddenly with little warning. The Icelandic Meteorological Office, in close cooperation with experts from the University of Iceland, will continue to monitor the area closely, with the goal of continually interpreting and evaluating all available monitoring observations.
Source : IMO
Papua New Guinea , Ulawun :
Eruption in Papua New Guinea: danger of tsunami
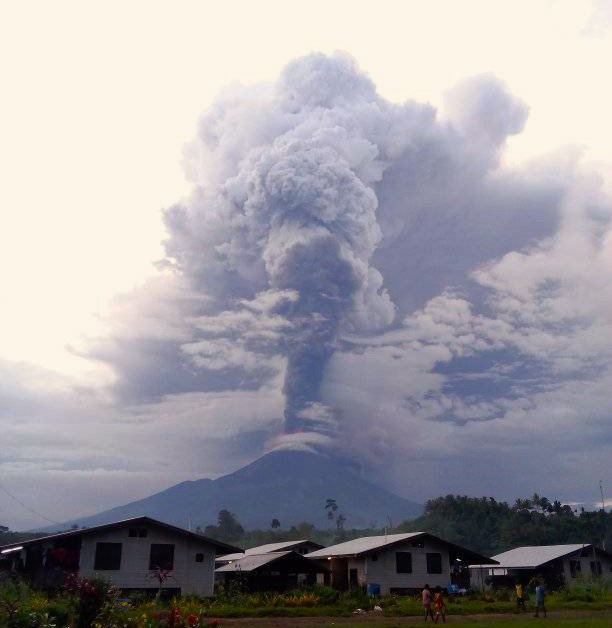
The Ulawun volcano erupted in Papua New Guinea. The Volcanic Ash Advisory Center (VAAC) in Darwin, Australia, reported today that the ash cloud had reached a height of more than 15,000 meters.
Japan’s Kyodo news agency, citing the state meteorological agency, wrote that the eruption could potentially trigger a tsunami that could reach Japan. However, there were no tsunami warnings. The volcano entered crisis in the afternoon (local time).
Ulawun is a stratovolcano approximately 2,300 meters high on the island of New Britain. It belongs to a whole group of volcanoes in the region. Starting in 1970, several major eruptions caused violent lava flows and hot avalanches. More than 1,000 people were killed. Ulawun was also extremely active in 2019, at which time volcanic ash reached approximately 16,700 meters. The ashes also contaminated drinking water.
Source : https://orf.at/
Photo : Robin Warilai Jim
Philippines , Mayon :
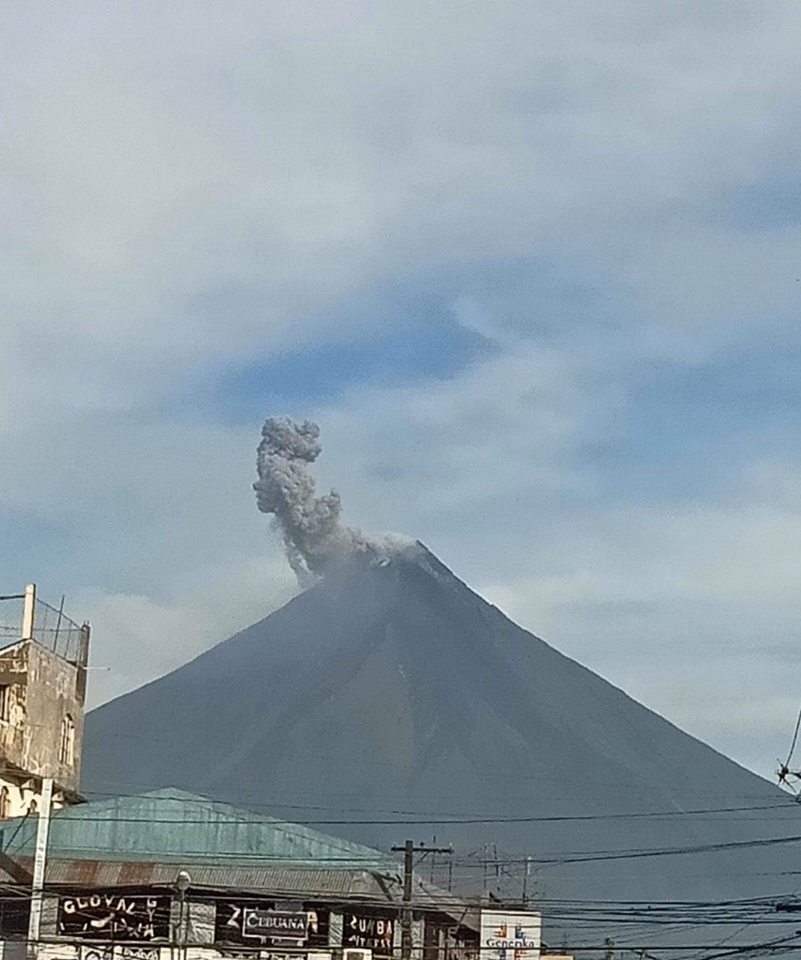
MAYON VOLCANO BULLETIN 21 November 2023 8:00 AM
In the past 24-hour period, the Mayon Volcano Network recorded nine (9) volcanic earthquakes, including two (2) volcanic tremors having durations of one (1) to two (2) minutes, one (1) ashing event, ninety-five (95) rockfall events, and two (2) pyroclastic density current (PDC) events. The lava flows have maintained their advances to approximately 3.4 kilometers in Bonga (southeastern), 2.8 kilometers in Mi-isi (south), and 1.1 kilometers in Basud (eastern) Gullies. Rockfalls and PDCs generated by the collapse of the summit dome deposited debris still within four (4) kilometers of the crater. Volcanic sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission averaged 1,709 tonnes/day on 16 November 2023.
Short-term observations from electronic tilt and GPS monitoring indicate inflation of the northwestern upper and middle slopes since late July 2023 and October 2023, respectively. Longer-term ground deformation parameters from EDM, precise leveling, continuous GPS, and electronic tilt monitoring indicate that Mayon is still generally inflated relative to baseline levels.
Alert Level 3 is maintained over Mayon Volcano, which means that it is currently in a relatively high level of unrest, and hazardous eruption within weeks or even days could still be possible.
Source : Phivolcs
Photo : CNN Philippines
Peru , Sabancaya :
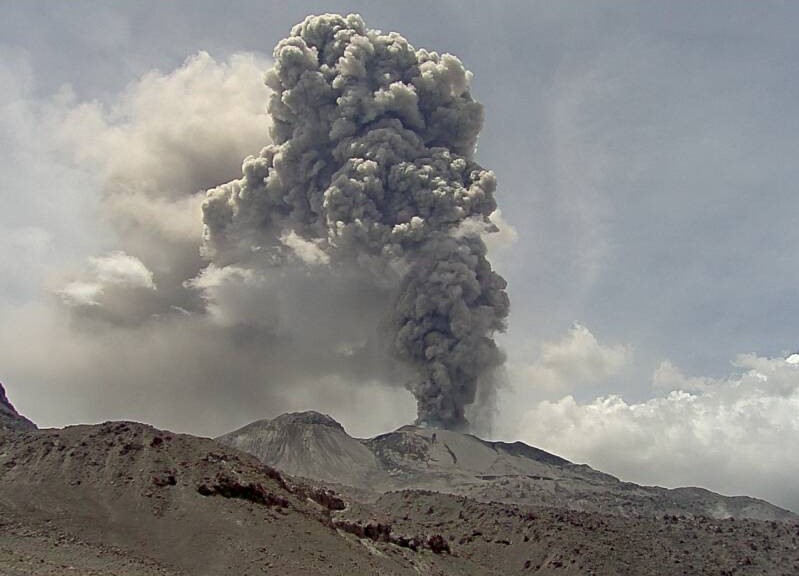
Analysis period: from November 13, 2023 to November 19, 2023, Arequipa, November 20, 2023.
Alert level: ORANGE
The Geophysical Institute of Peru (IGP) reports that the eruptive activity of the Sabancaya volcano remains at moderate levels, that is, with the recording of an average of 22 daily explosions, with columns of ash and of gas up to 3.1 km altitude above the summit of the volcano and their subsequent dispersion. Therefore, for the following days, no significant changes are expected regarding eruptive activity.
The IGP recorded and analyzed the occurrence of 179 earthquakes of volcanic origin, associated with the circulation of magmatic fluids inside the Sabancaya volcano. An average of 22 explosions were recorded daily, in addition to recording of Volcano-Tectonic (VT) type events associated with rock fracturing inside the Sabancaya volcano.
Monitoring the deformation of the volcanic structure using GNSS techniques (processed with fast orbits) does not present significant anomalies. However, in general, a slight inflation process was observed in the northern sector (around the Hualca Hualca volcano). Visual monitoring identified columns of gas and ash up to 3.1 km above the volcano summit, which were dispersed towards the northeast and southeast sectors of Sabancaya. Satellite recordings identified the presence of 13 thermal anomalies, with a maximum value of 13 MW, associated with the presence of a lava body on the surface of the volcano crater.
RECOMMENDATIONS
• Keep the volcano alert level in orange.
• Do not approach within a radius of less than 12 km from the crater.
Source : Cenvul.
Photo : Ingemmet.
Indonesia , Ibu :
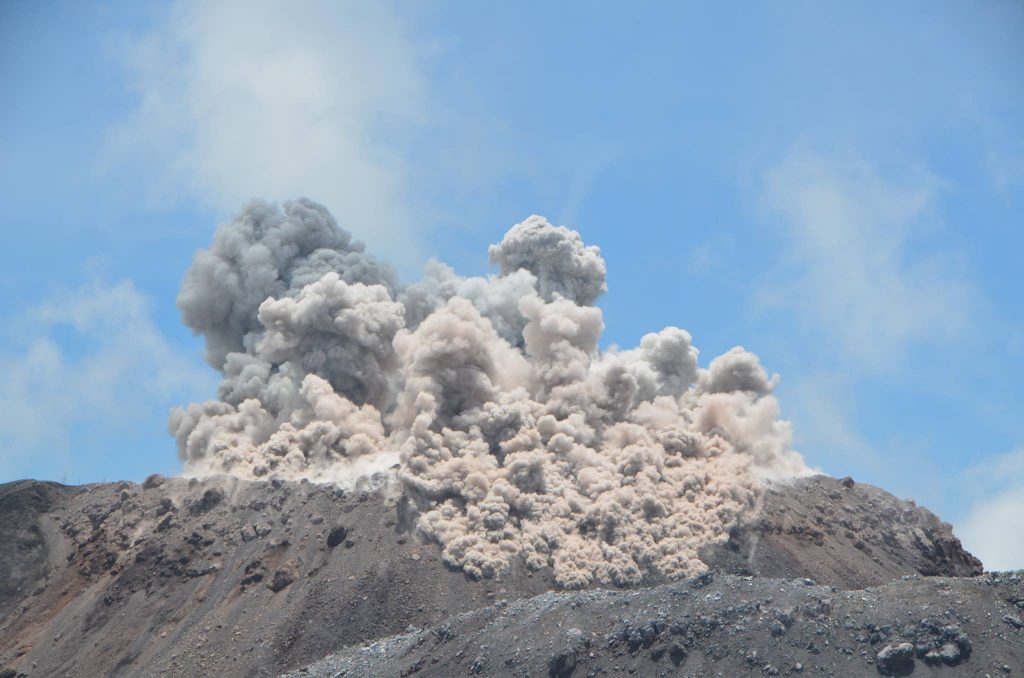
Mount Ibu erupted on Tuesday, November 21, 2023, at 09:58 WIT. The height of the eruptive column was observed to be ±1,000 m above the peak (±2,325 m above sea level). The ash column was observed to be gray with thick intensity, oriented towards the West. The eruption was recorded on a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 28 mm and a duration of 91 seconds.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : November 21 , 2023 .
Volcano : Ibu (268030)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Ibu Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2023IBU057
Volcano Location : N 01 deg 29 min 17 sec E 127 deg 37 min 48 sec
Area : North Maluku, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 4240 FT (1325 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 00h58 UTC (09h58 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 7440 FT (2325 M) above sea level or 3200 FT (1000 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to west. Volcanic ash is observed to be dark. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 28 mm and maximum duration 91 second.
Source : Magma Indonésie.
Photo : 80 Jours voyages / S Chermette ( archives) .