November 03 , 2023.
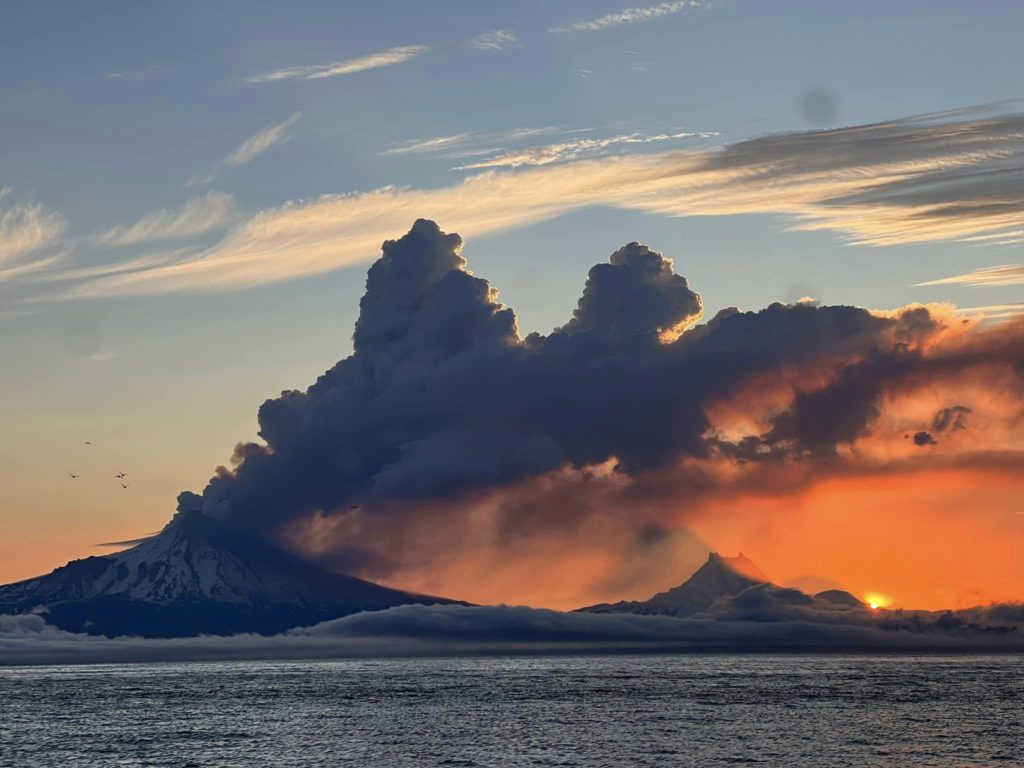
Iceland , Reykjanes Peninsula :
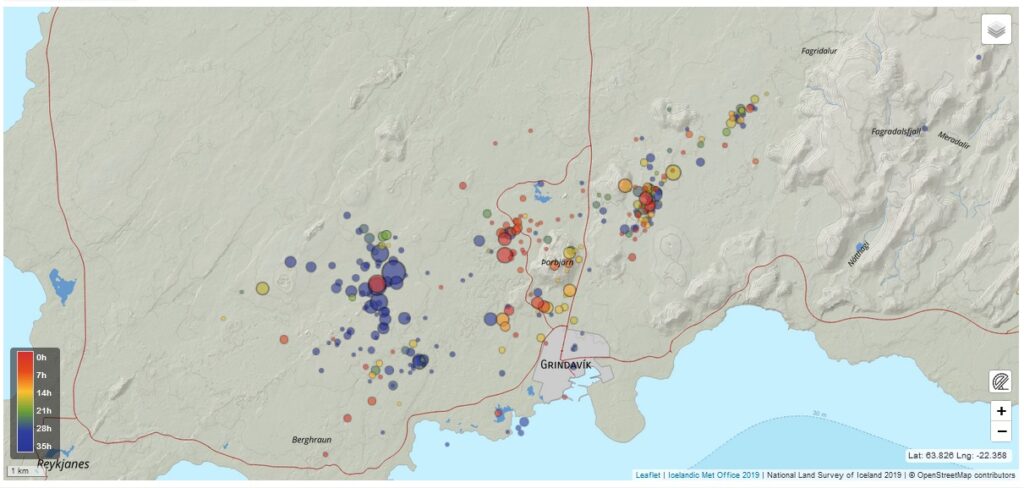
Volcanic unrest continues on the Reykjanes Peninsula . Around 800 earthquakes in the area yesterday . Updated 2. November at 3pm
GPS data from the last 24 hours indicate that uplift continues at a similar rate in the area northwest of Mt. Þorbjörn. Earthquake activity has been quite stable, but yesterday around 800 earthquakes were recorded in the area around Þorbjörn, and the largest was M3.7 at 12:56 am. Since midnight today, around 400 earthquakes have been recorded in the area, the largest measuring M2.8 at 9:51 am. More detailed analysis of recent GPS data confirms that a magma intrusion is forming at a depth of 4-5 km under the area northwest of Þorbjörn.
It is important to note that seismic activity is will likely continue northwest of Þorbjörn, and earthquakes over M4.0 could be found in populated areas. Triggered seismic activity can also be expected in the coming days because the magma intrusion causes increased tension in the area. Rockfall can occur following strong earthquakes, so it is important to be cautious on steep slopes.
At 03:51 a earthquake of M4.2 was measured about 1.2km west of the Blue Lagoon. A M3.7 was located just SW of Þorbjorn at 4:25 and another M3.3 at 1:18 at a similar location. Earlier tonight a M3.3 quake was measured about 1km NW of Mt. Thorbjorn at 01:18. The earthquakes are felt over SW Iceland and the seismic swarm in Reykjanes is ongoing.
Over 10.000 earthquakes have been measured in a seismic swarm that started on October 25th, just north of Grindavík. The swarm is still ongoing, but activity has decreased slightly. A total of 20 earthquakes above M3 have been detected, there of three over M4, the largest earthquake was a M4.5 on the 25th at 8:18 UTC.
Source et photo : IMO
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Weekly bulletin on the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano
From the monitoring of the activity of the NEVADO DEL RUIZ VOLCANO, the MINISTRY OF MINES AND ENERGY through the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE (SGC) reports that:
In the week of October 24 to 30, 2023, the volcano maintained unstable behavior, characterized by low to moderate activity levels and fluctuations, particularly in terms of seismicity and degassing. Compared to the previous week, the main variations in the parameters monitored were:
– Seismicity linked to fluid dynamics inside volcanic conduits increased in the seismic energy released. Signal energy levels were variable with low to slightly moderate values. Throughout the week, seismic signals associated with pulsatile emissions of gas or ash into the atmosphere were recorded, but these decreased compared to the previous week. Between October 27 and 29, the recording of signals associated with the continued emission of gas and ash increased. This phenomenon was confirmed by cameras used to monitor the volcano and by SGC personnel during field work in the region. Additionally, it was also possible to confirm several changes in the relative temperature of the emitted material associated with this type of signals.
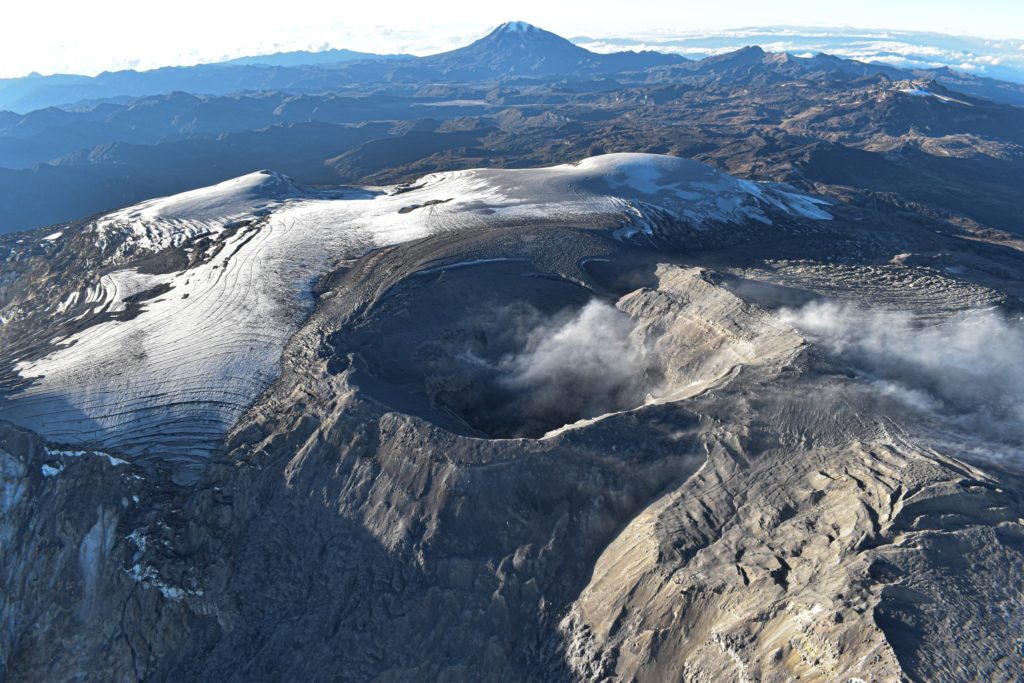

– Seismic activity associated with the fracturing of rocks inside the volcanic edifice has decreased in the number of earthquakes recorded and in seismic energy released. Most of the earthquakes were of magnitude less than 1 and were located mainly in the Arenas crater and on the distal East-Southeast and North-East flanks of the volcano, and scatteredly on the South-West flank, at distances of up to approximately 12 km from the volcano. The depths of the earthquakes varied between 1 and 7 km from the summit of the volcano. In addition, low-energy seismicity was recorded on October 24, 25, 26 and 30, linked to the activity of the lava dome (protrusion or mound) located at the bottom of the crater.
– The emission of water vapor and gas into the atmosphere continued at the volcano. Although for most of the week the preferential wind direction did not favor the sulfur dioxide (SO2) measuring stations, the degassing rates of this gas were variable and showed a maximum value on October 30 , which corresponds to the highest daily SO2 degassing rate recorded this year. The maximum height of the gas and ash column was 1,600 m and 1,800 m vertically and dispersed, respectively. These values were measured at the summit of the volcano on October 27. Concerning the direction of dispersion of the column, it was variable with a preference towards the North-North-East of the volcano.
– When monitoring thermal anomalies from satellite monitoring platforms, several were detected at the bottom of the crater, with low to moderate energy levels.
Source et photo : SGC
Alaska , Shishaldin :
AVO/USGS Volcanic Activity Notice
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Previous Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Previous Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Issued: Thursday, November 2, 2023, 8:31 PM AKDT
Source: Alaska Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2023/A1575
Location: N 54 deg 45 min W 163 deg 58 min
Elevation: 9373 ft (2857 m)
Area: Aleutians
Volcanic Activity Summary:
The level of unrest has increased at Shishaldin Volcano. An increase in tremor has been observed in seismic and infrasound data beginning at around 7:00 pm AKDT (3:00 UTC 11/3). These signals indicate that the volcano is likely erupting. No ash cloud has been observed in satellite data. Due to the increase in activity, the Aviation Color Code and Volcano Alert Level for Shishaldin Volcano are being raised to ORANGE/WATCH.
Shishaldin Volcano is monitored by local seismic and infrasound sensors, web cameras, and a telemetered geodetic network. In addition to the local monitoring network, AVO uses nearby geophysical networks, regional infrasound and lighting data, and satellite images to detect eruptions.
Recent Observations:
[Volcanic cloud height] NA
[Other volcanic cloud information] Unknown
Remarks:
Shishaldin Volcano, located near the center of Unimak Island in the eastern Aleutian Islands, is a spectacular symmetric cone with a base diameter of approximately 10 miles (16 km). A 660 ft. (200 m) wide funnel-shaped summit crater typically emits a steam plume and occasional small amounts of ash. Shishaldin is one of the most active volcanoes in the Aleutian volcanic arc, with at least 54 episodes of unrest including over 26 confirmed eruptions since 1824. Most eruptions are relatively small, although the April-May 1999 event generated an ash column that reached 45,000 ft. (14 km) above sea level.
Issued: Thursday, November 2, 2023, 9:45 PM AKDT
Volcanic Activity Summary:
An explosive eruption of Shishaldin Volcano began around 03:40 UTC on November 3 (19:40 AKDT on November 2). Ash was first observed in satellite data at 04:00 UTC (20:00 AKDT) at an altitude of 20,000 ft above sea level. This is a decrease in the cloud height from the initial estimate and the National Weather Service has modified their SIGMET because of the refined analysis of the cloud altitude. Seismic, infrasound and satellite data show the eruption continues at a constant level. The Aviation Color Code and Alert Level remain at ORANGE/WATCH. AVO is monitoring the volcano closely and will issue additional Volcanic Activity Notices about significant changes in activity as they occur.
Recent Observations:
[Volcanic cloud height] 20,000 ft
[Other volcanic cloud information] moving towards the west
Source : AVO
Photo : Nick Enloe
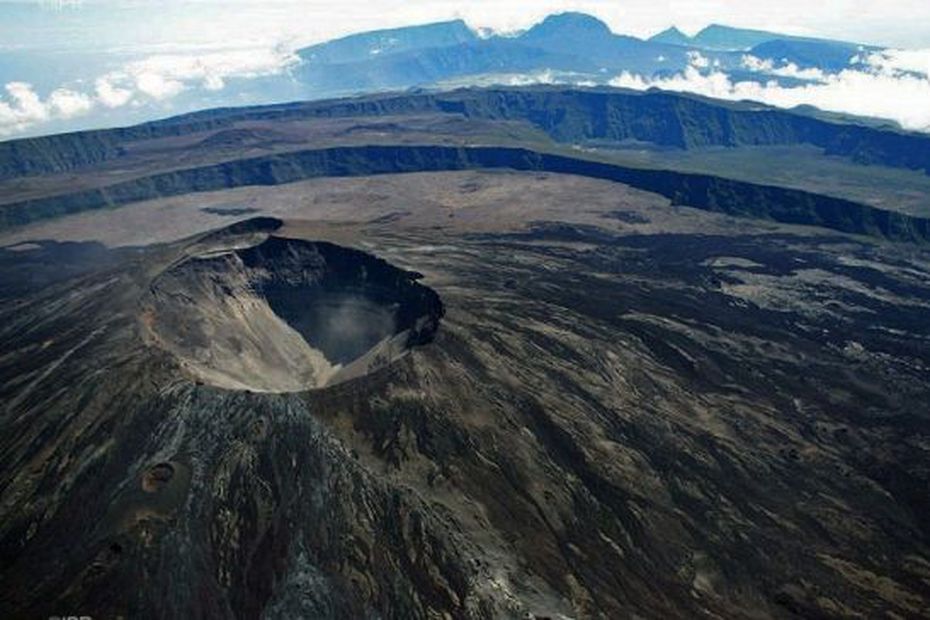
La Réunion , Piton de la Fournaise :
Monthly newsletter, October 2023.
Seismicity
In October 2023, the OVPF-IPGP recorded in total at the Piton de la Fournaise massif:
• 12 superficial volcano-tectonic earthquakes (0 to 2.5 km above sea level) under the summit craters;
• 12 deep earthquakes (below sea level);
• 1 long-period earthquake;
• 299 landslides.
The month of October 2023 was marked by low seismicity under the Piton de la Fournaise with an average of 0.4 superficial volcano-tectonic earthquakes per day.
Most of these events were located beneath the eastern rim of Dolomieu crater.
Twelve deep earthquakes were also recorded, under the Bory crater and under the eastern flank of the volcano.
Numerous landslides in the Dolomieu Crater, at the Cassé de la Rivière de l’Est and at the level of recent lava flows have also been recorded.
Balance sheet
Following the end of the last eruption on August 10, 2023, seismic activity remained relatively low under the Piton de La Fournaise with an average of 0.4 superficial volcano-tectonic earthquakes per day in October 2023. From from mid-August the inflation of the building stopped indicating the end of the pressurization of the superficial magma reservoir.
Source : OVPF
Photo : Imaz Press
Indonesia , Dukono :
An eruption of Mount Dukono occurred on Friday, November 3, 2023 at 08:30 WIT with the height of the ash column observed at ±700 m above the summit (±1787 m above sea level). The ash column was observed to be white, gray to black, with medium to thick intensity, oriented towards the South. At the time of writing, the eruption was still ongoing.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : November 02 , 2023
Volcano : Dukono (268010)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Dukono Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2023DUK006
Volcano Location : N 01 deg 41 min 35 sec E 127 deg 53 min 38 sec
Area : North Maluku, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 3933 FT (1229 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 23h30 UTC (08h30 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 6173 FT (1929 M) above sea level or 2240 FT (700 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to west. Volcanic ash is observed to be white to dark. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Source : Magma Indonésie
Photo : Sylvain Chermette / 80 Jours voyages.