May 14 , 2022.
Italy , Stromboli :
PRESS RELEASE ON STROMBOLI’S ACTIVITY. 13 May 2022, 16:44 (14:44 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, reports that monitoring networks recorded a thermal anomaly from surveillance cameras at 4:44 p.m. (2:44 p.m. UTC).
Further updates will be communicated soon.
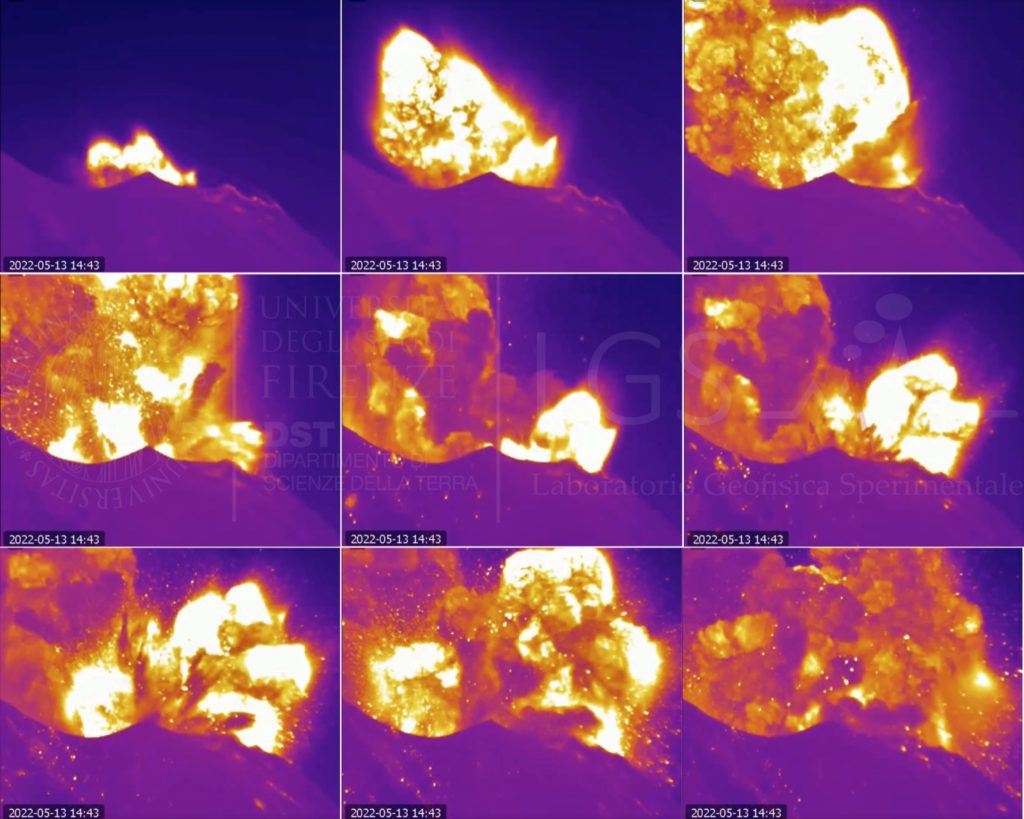
PRESS RELEASE ON STROMBOLI’S ACTIVITY. 13 May 2022, 17:07 (15:07 UTC).
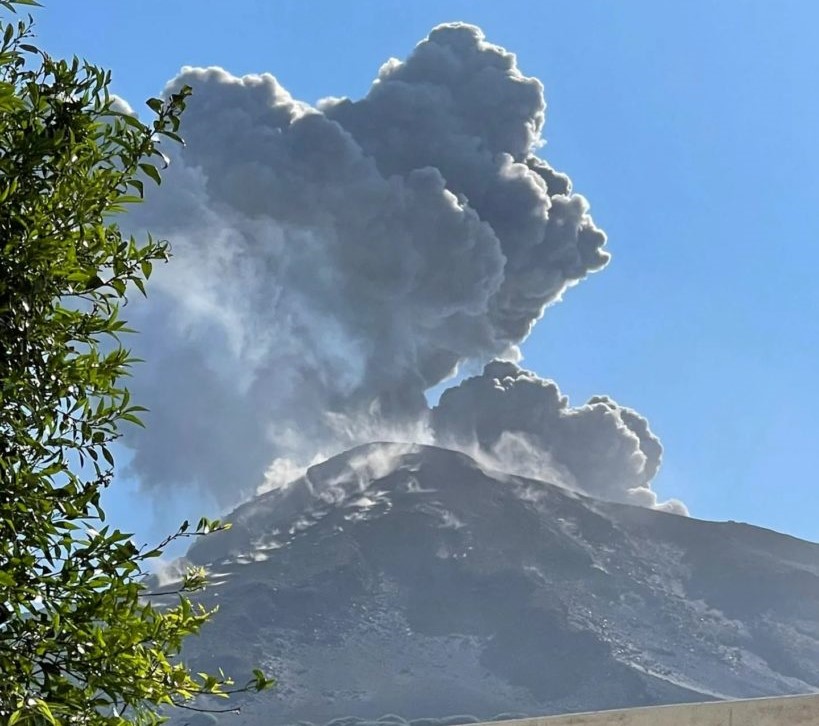
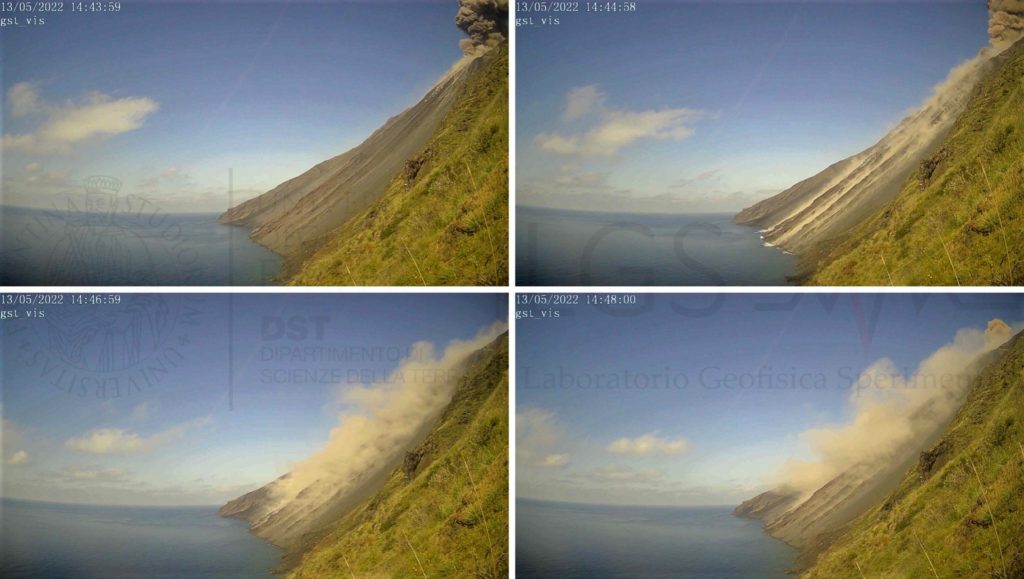
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that the monitoring networks recorded at 14:43 UTC, a sequence of explosions of greater than ordinary intensity coming from various mouths of the Center-South zone of the crater terrace. The activity produced a significant emission of coarse pyroclastic materials which abundantly covered the terrace of the crater and also reached the Pizzo; the ash cloud produced moved towards the southern quadrants. .
Further updates will be communicated promptly and in any case within 3 hours of this press release.
PRESS RELEASE ON STROMBOLI’S ACTIVITY. 13 May 2022, 18:40 (16:40 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that the monitoring networks recorded the return of the parameters to normal activity at 6:35 p.m. (4:35 p.m. UTC).
Images from the CCTV system cameras showed that the previously communicated explosive sequence began from one of the vents of sector CS1 of the Center-South crater area and was followed by at least five other explosions also from the sector CS1, of less intensity due to the height and the dispersion of the coarse products. These covered the crater terrace, they also fell on the Pizzo, and only to a lesser extent on the Sciara del Fuoco. The fine material produced during the sequence was dispersed in the Southeast direction.
From the seismic point of view, the explosive sequence, which was not anticipated by significant variations in the amplitude values of the volcanic tremor and the amplitude and frequency of occurrence of VLP events, was visible at all stations. Stromboli seismic waves with a succession of numerous low-frequency seismic transients. The first event, of moderate magnitude, recorded at 2:42 p.m. UTC, was followed in the following three minutes by a dozen other events, the most energetic of which was at 2:43 p.m. UTC.
After the sequence of events, for about 10 minutes, the amplitude of the volcanic tremor remained higher than the values recorded before the explosive activity.
Currently, the average amplitude of the volcanic tremor, the amplitude and the rate of occurrence of VLP events have normal values.
Analysis of the inclinometric signal from the Timpone del Fuoco station shows a transient of about 0.2 microradians during the explosive sequence, and is preceded by a gradual change in trend of the N-S component of about 0.2 microradians, which tends to enter the explosive phase later. . The GNSS network did not register any significant changes during the explosive activity. However, it should be noted that from 11:30 UTC the stations of Punta Lena and Timpone del Fuoco recorded a shift towards the South-South-West of about 2 cm which returned around 13:30 UTC.
Once the phenomenon is over, the parameters return to ordinary levels.
Source : INGV
Photos : Stromboli Stati d’Animo ,LGS
Indonesia , Merapi :
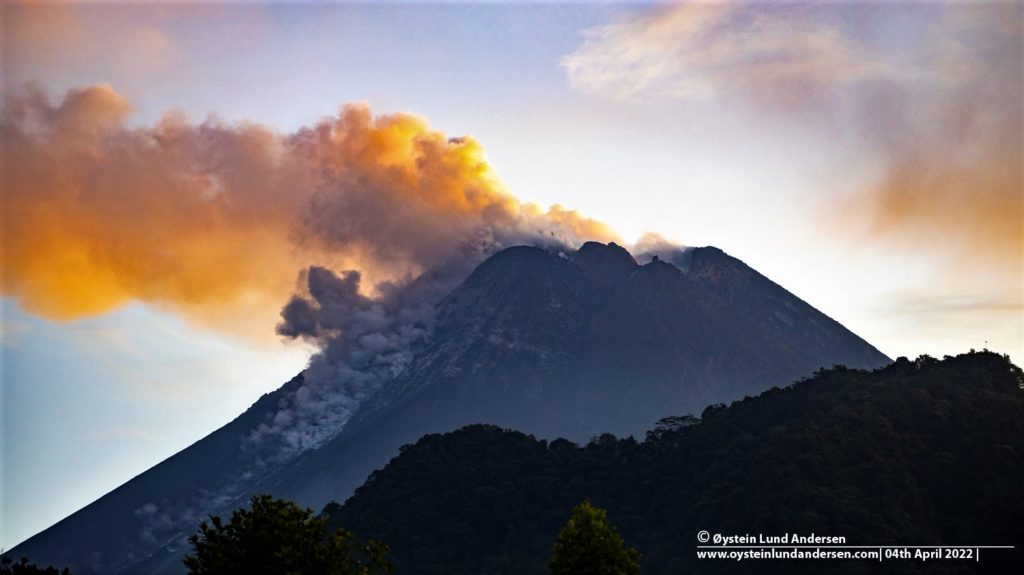
Merapi activity report from May 06 to 12, 2022.
This week, 2 hot cloud avalanches were observed towards the South-West, descending the Bebeng River with a maximum slip distance of 2,000 m.
92 lava avalanches were observed descending the Bebeng River to the southwest with a maximum slip distance of 2,000 m.
– For the South-West dome, we observe that the height of the dome has increased by about ± 2 m. For the middle dome, no significant morphological change was observed. According to the photo analysis, the volume of the Southwest lava dome is 1,551,000 m3 and that of the central dome is 2,582,000 m3.
Seismicity:
This week, the seismicity of Mount Merapi recorded:
2 Avalanches of hot clouds,
90 shallow volcanic earthquakes (VTB),
245 multi-phase earthquakes (MP),
801 avalanche earthquakes (RF),
32 emission earthquakes (DG),
13 tectonic earthquakes (TT).
The intensity of this week’s seismicity is still quite high.
Mount Merapi’s deformation, which was monitored using EDM this week, showed a distance shortening rate of 1.2 cm/day.
– Rainfall intensity was 111 mm/hour for 85 minutes at Kaliurang Post and it was reported that there was an increase in flow in the Boyong River on May 10, 2022.
Conclusion:
1. The volcanic activity of Mount Merapi is still quite high in the form of effusive eruption activity. The state of the activity is defined at the « SIAGA » level.
2. The current potential danger is lava avalanches and hot clouds in the South-South-West sector covering the Boyong River for a maximum of 5 km, the Bedog River, Krasak, Bebeng for a maximum of 7 km. The Southeast sector covers the Woro River for a maximum of 3 km and the Gendol River for a maximum of 5 km. Meanwhile, the ejection of volcanic material in the event of an explosive eruption can reach a radius of 3 km around the summit.
Source : BPPTKG.
Photo : Oystein Lund Andersen.
Alaska , Katmai :
58°16’44 » N 154°57’12 » W,
Summit Elevation 6716 ft (2047 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: NORMAL
Current Aviation Color Code: GREEN
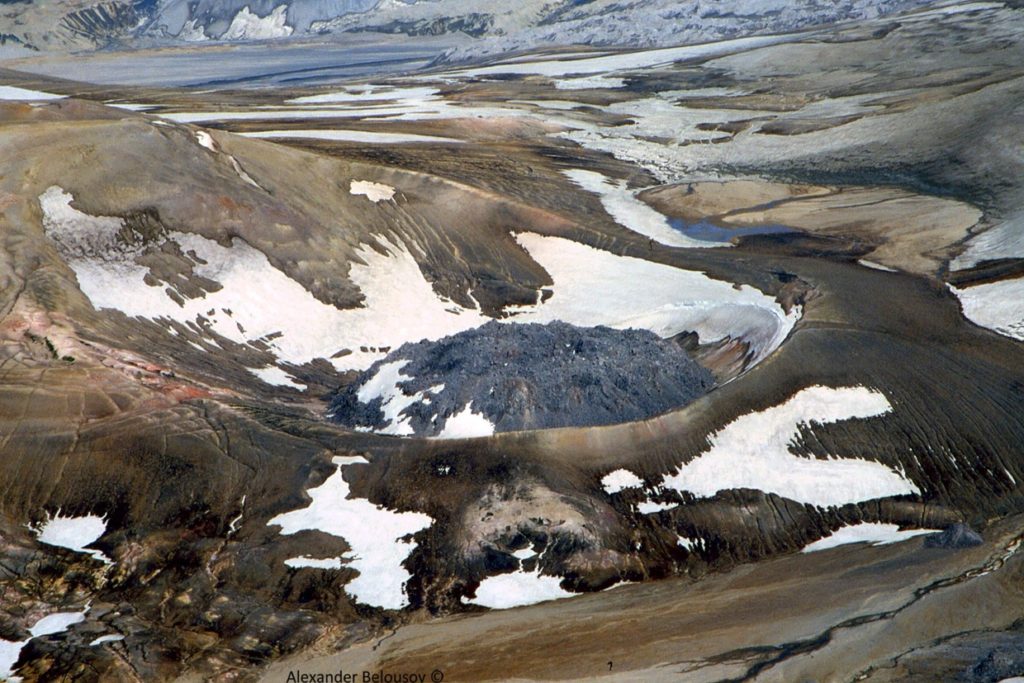
Strong northwesterly winds in the vicinity of Katmai and the Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes have picked up loose volcanic ash erupted during the 1912 Novarupta-Katmai eruption and carried it to the southeast toward Kodiak Island today (May 13). The National Weather Service has issued a SIGMET for this low-level event and suggests that the maximum cloud height is 6,000 ft above sea level.
This phenomenon is not the result of recent volcanic activity and occurs seasonally in the spring and fall during times of high winds and dry snow-free conditions in the Katmai area and other young volcanic areas of Alaska. All of the volcanoes of the Katmai area (Snowy, Griggs, Katmai, Novarupta, Trident, Mageik, Martin) remain at color code GREEN.
Resuspended volcanic ash should be considered hazardous and could be damaging to aircraft and health.
Source : AVO
Photo : Alexander Belousov ( Katmai)
Indonesia , Ili Lewotolok :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : May 14 , 2022
Volcano : Ili Lewotolok (264230)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Ili Lewotolok Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2022LEW15
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 16 min 19 sec E 123 deg 30 min 18 sec
Area : East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 4554 FT (1423 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
The eruption has not yet occurred but an increase in degassing has been observed ad ash emission is continuing.
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 12307 FT (3846 M) above sea level, may be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash-cloud moving to north and northeast
Remarks :
Seismic activity is Dominated by volcanic tremor non harmonik earthquake.
Source : Magma Indonésie.
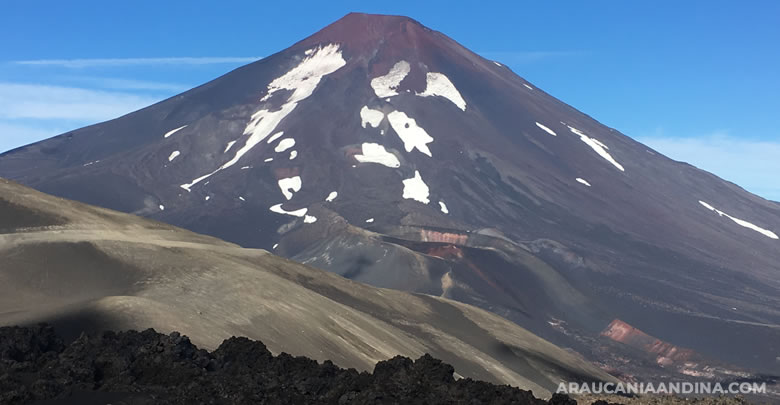
Chile , Lonquimay :
LONQUIMAY VOLCANIC COMPLEX
Seismology
The seismological activity of the period was characterized by the recording of:
10 VT type earthquakes, associated with rock fracturing (Volcano-Tectonics). The most energetic earthquake presented a Local Magnitude (ML) value equal to 1.1, located 4.7 km north-northwest of the volcanic building, at a depth of 11 km in reference to the crater.
1 HB type earthquake, associated with both rock fracturing and fluid dynamics within the volcanic system (Hybrid type). The size of the earthquake estimated from the reduced displacement (RD) parameter was equal to 1 cm2.
Fluid Geochemistry
No anomalies were reported in the emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2) into the atmosphere in the area near the volcanic complex, according to data published by the Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument. (TROPOMI).
Satellite thermal anomalies
During the period, no thermal alert was recorded in the area associated with the volcanic complex, according to data processed by the mid-infrared observation of volcanic activity (MIROVA) and through the analysis by processing Sentinel 2-L2A satellite images, in combination with false color bands.
Geodesy
Based on the data provided by 2 GNSS stations installed on the volcanic edifice, which allow to measure the deformation of the land surface, low displacement rates and no trend in the vertical component were estimated, therefore, no No evidence of deformation was observed on the volcano during the period.
Surveillance cameras
The images provided by the fixed camera installed near the complex do not record any degassing columns or variations linked to surface activity.
Satellite geomorphological analysis
Thanks to the analysis of Planet Scope and Sentinel 2 L2A satellite images, no morphological change associated with volcanic activity has been observed, nor has the luminance in the infrared bands.
Volcanic activity, mainly seismic, continues to be weak and normal, with only records of sporadic sequences of VT and LP earthquakes, possibly the appearance of hybrid earthquakes.
Other volcanic monitoring parameters used for the volcanic complex indicate an absence of anomalies.
As a result, the volcanic technical alert is changed to GREEN TECHNICAL ALERT: Active volcano with stable behavior – There is no immediate risk.
Source : Sernageomin.
Photo : crater-navidad/ Auracaniaandina