November 12 , 2021.
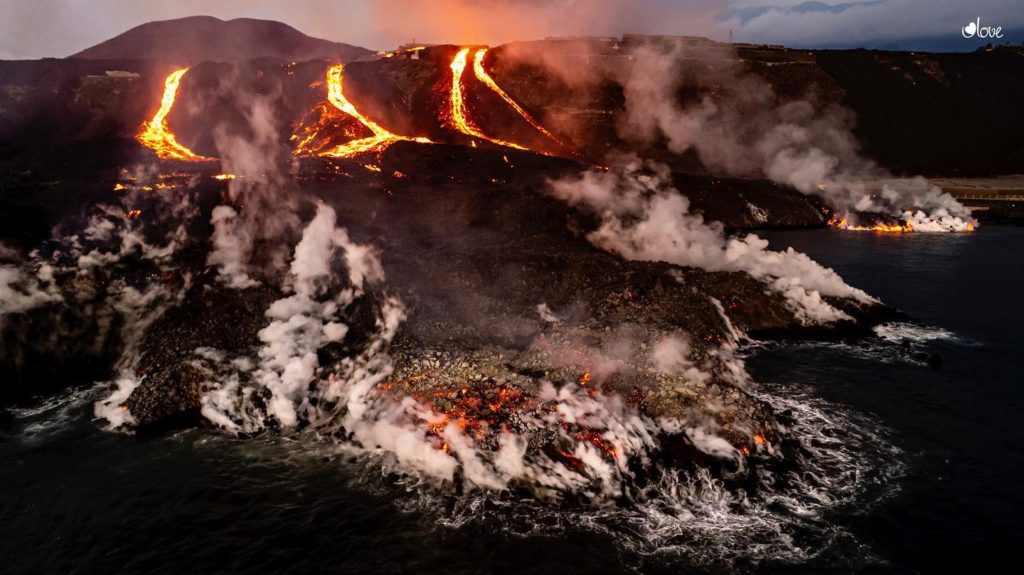
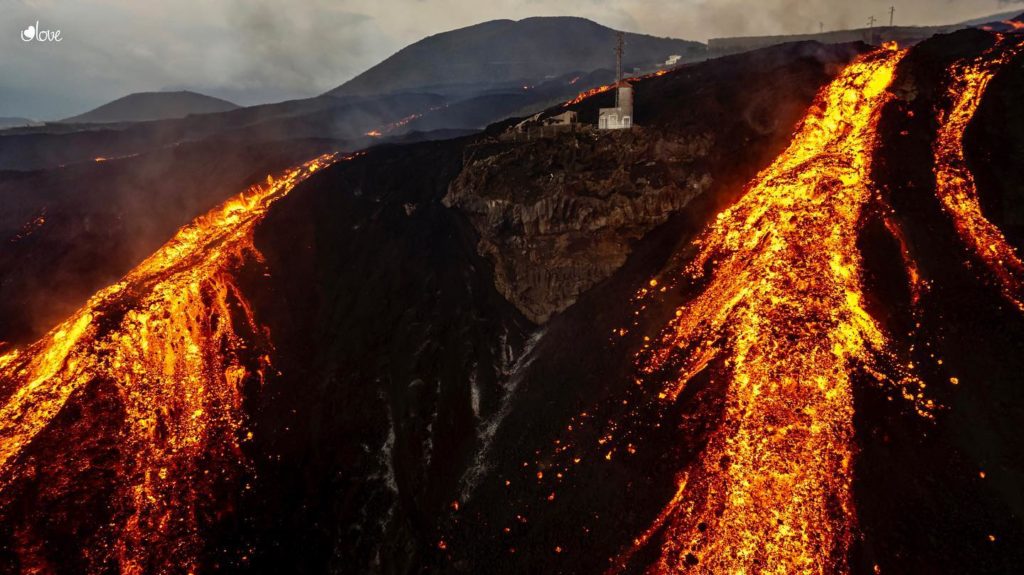
Spain / La Palma , Cumbre Vieja :
November 11, 2021, 09:00 UTC. Eruptive activity continues on La Palma.
Since the last declaration, 72 earthquakes have been located in the area affected by the reactivation and the volcanic eruption of Cumbre Vieja, of which seven were felt by the population of the epicentral area.
It should be noted that most of the activity recorded in the last 24 hours is at depths greater than 30 km below the central area of Cumbre Vieja. It is in this area that the largest earthquake was recorded at 03:37 (UTC) today and corresponds to an earthquake of magnitude 5.0 (mbLg) which was felt with a maximum intensity of IV-V (EMS) . This earthquake was followed by a dense swarm of earthquakes at the same depth.
The tremor signal continues to remain at low values, with an episode of significant intensification between 03:00 and 04:00 UTC, coinciding with the swarm of deep earthquakes.
The island’s network of permanent GNSS stations shows that after reversing the inflation on days 4 and 5 at station LP03, which is closest to the eruptive centers, it remains at a lower level than previously established. On the other hand, the southwest deformation recorded in the station still continues
In the rest of the stations, the slight deflation possibly linked to the deep seismicity has moderated.
Based on the calibrated image, a column height of 2,500 m is estimated at 08:45 UTC.
Air quality is good throughout the island except in Puntagorda where regular levels of air quality change have been recorded.
The weather conditions are favorable for the dispersion of gas and ash as well as for the operation of La Palma airport.
The lava flows cross ancient flows and branch off south of Todoque Mountain, flowing into Los Guirres Beach.
The affected area amounts to more than 1,005 hectares, 7.46 more than yesterday.
Seismicity at depths greater than 20 km has increased in number and magnitude. The number of locations at these depths over the past 24 hours was the highest since the eruption began.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions, associated with the volcanic plume of the ongoing eruptive process (visible volcanic gas fumes), recorded on Wednesday continue to be high.
Scientists observed this Thursday an overflow in the area of the cone of the volcano of La Palma in which there was a lava lake, as reported by the director of the National Geographic Institute (IGN) of the Canary Islands and spokesperson from the Scientific Committee of Pevolca, María José Blanco.
This lava overflow occurred at a time when the island of La Palma recorded an increase in seismicity at depths greater than 20 kilometers, both in number and in magnitude, and a strong emission of sulfur dioxide. (SO2). Today, although lower levels have been recorded than yesterday, they are still high.
Sources : IGN es , El Pais .
Photos : I love the world ,
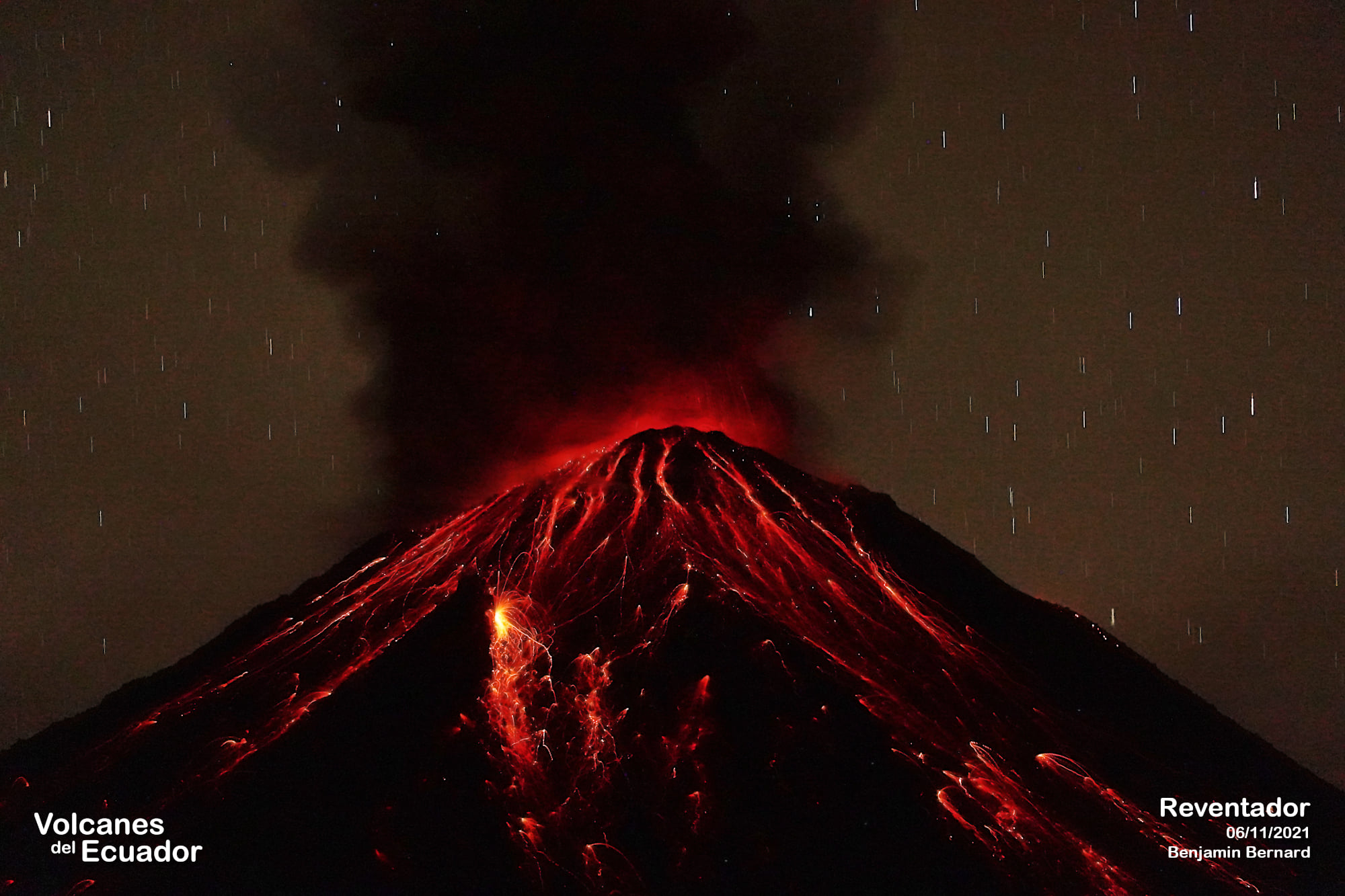
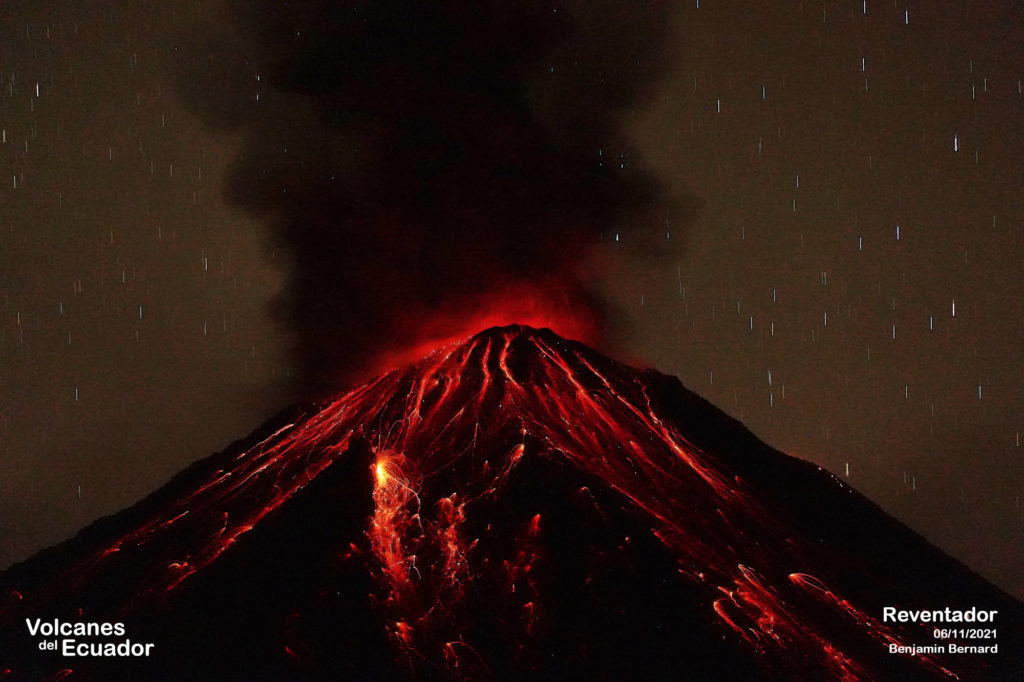
Ecuador , Reventador :
DAILY REPORT OF THE STATE OF THE REVENTADOR VOLCANO, Wednesday 28 November 2021.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface activity level: High, Surface trend: No change.
Internal activity level: Moderate, Internal trend: No change.
Seismicity: From November 09, 2021, 11:00 a.m. to November 10, 2021, 11:00 a.m.
The LAV4 seismic station has remained uninterrupted in the transmission of data and the seismic statistics are complete.
Explosion (EXP) 72
Long Periods (LP) 66
Emission tremor (TREMI) 14
Harmonic Tremor (TRARM) 2.
Rains / Lahars:
There was no rain in the area.
Emission column / ash:
No transmissions were observed via the cameras, however, the Washington VAAC issued 4 alerts for transmissions observed via satellites, the directions of these transmissions were North, Southwest and South. The heights of the emissions did not exceed 1000 meters above the level of the crater.
Other monitoring parameters:
No thermal alert was recorded in the FIRMS and MIROVA satellite systems.
Observation:
Over the past 24 hours, the volcano has cleared over short periods of time, allowing glow in the crater to be observed at night and the rolling of boulders along the volcano’s flanks up to 500 meters below crater level. .
Alert level: Orange.
Source : IG-EPN.
Photo : Benjamin Bernard. http://www.facebook.com/groups/75524169527/user/1058688191/
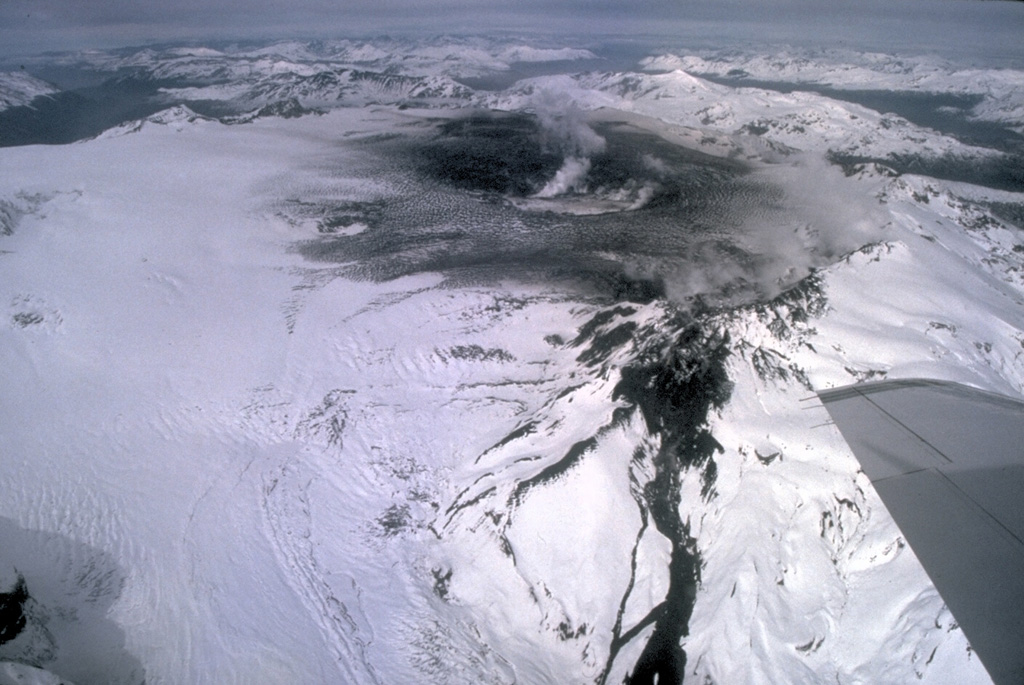
Alaska , Pavlof :
55°25’2″ N 161°53’37 » W,
Summit Elevation 8261 ft (2518 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Seismicity has remained elevated at Pavlof over the last day, and satellite images show strongly elevated surface temperatures near the active vent reflecting lava effusion. Steam emissions from the vent area obscured observation of the lava flow itself, but a 2 km-long narrow lahar was evident down the SE flank, which was probably generated by lava interaction with snow on the upper flank of the volcano.
Small explosions accompanied by low-level ash emissions could happen at any time, and are typically a hazard in the immediate vicinity of the summit. The level of unrest at Pavlof can change quickly and the progression to more significant eruptive activity can occur with little or no warning.
Pavlof is monitored by local seismic and infrasound sensors, satellite data, web cameras, and remote infrasound and lightning networks.
Source : AVO.
Photo : Musselwhite, Levi .
Italy , Vulcano :
An automatic « Multigas » station has been installed on Vulcano, November 11, 2021.
On October 12, an automatic “Multigas” type station was installed on the edge of the crater of the Fossa di Vulcano, near the fumaroles. After a first test phase, from November 4, the station began to carry out continuous measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2) and hydrogen sulphide (H2S) as well as environmental parameters such as atmospheric pressure, temperature and humidity. The data is transmitted in real time to the acquisition room of the Palermo section by radio link via the Lipari observatory.
Multigas stations have been developed in the technological laboratories of Section Palermo. They are equipped with special sensors which allow the simultaneous determination of different gas species. More precisely, this station is equipped with an infrared spectrometer to determine the concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) up to 10% by volume and two electrochemical sensors to determine the concentrations of SO2 and H2S with an acquisition range of 0-200 ppm and 0 -50 ppm, respectively. The electrochemical sensors are both manufactured by Citycell. The gas taken from the outside passes through the sensors by means of a constant flow pump. The electrical signals produced during the acquisition are transformed into concentrations and recorded in a data logger.
The station also acquires certain environmental parameters such as atmospheric pressure, temperature and humidity. The measurements acquired by this automatic station will contribute to a better evaluation of the level of activity of the volcano.
Multigas stations have been used for 15 years in the monitoring of active volcanoes in Italy and also in many foreign countries. The first installations in Italy took place in 2006 on the Etna and Stromboli volcanoes, where they constitute two monitoring networks included in the volcanic monitoring plan of the National Directorate of Civil Protection. More recently, another Multigas station was installed inside the fumarolic field of Pisciarelli (Agnano), near Naples, as part of the volcanic monitoring and surveillance of the Phlegraean Fields.
The installation on Vulcano is part of the activities of the extension of the monitoring network of the volcano, following the change of the alert level from green to yellow ordered by the Department of Civil Protection of the island of Vulcano.
Source : INGV / Giovanni Giuffrida et Giancarlo Tamburello .
Read the article : https://ingvvulcani.com/2021/11/11/installata-una-stazione-automatica-multigas-a-vulcano/?fbclid=IwAR0eXMjZLW-UsuGsYjNWmK93hzgojSZYsBogjQwx8GyXxnZaHZey9iDk7-Q
Photo : INGV.
Chile , Hudson :
263 earthquakes classified as volcano-tectonic (VT) have been recorded, associated with the fracturing of rigid materials, the locations of which are located around the volcanic caldera. The highest energy earthquake had a local magnitude (ML) of 2.8 and was located 3.2 km west-southwest of the caldera center with a depth of 8.4 km.
– Likewise, 15 earthquakes of the long period (LP) were classified, linked to the dynamics of the fluids inside the volcanic building and / or produced by the action of the glacial dynamics; the largest earthquake had a size evaluated from the reduced displacement parameter (DR) equal to 11.2 cm2.
– 4 earthquakes classified as hybrid types (HB) were recorded, generally linked to a mechanism composed of fracturing of rigid materials and subsequent disturbances due to the circulation of fluids inside the volcanic conduits. The most energetic earthquake (REAV Region of Aysén del General Carlos Ibáñez del Campo, October 22, 2021, 02:50 (local time) had a Local Magnitude equal to 2.9 and a DR equal to 673 cm2; it was located at 3.2 km east-south-east of the center of the caldera with a depth of 4.0 km.
– From the processing of Sentinel 2 – L2 A, Sentinel 1 and Planet Scope satellite images, it is concluded that there are no morphological changes or thermal radiation anomalies associated with volcanic processes. Surface variations observed by surveillance cameras during the period evaluated are also not recorded.
– According to the data provided by 2 GNSS stations, slight variations are observed compared to the period previously reported. The trend of the horizontal displacement of the HMLS station varies towards the South-East, behavior that responds to a cyclic pattern recorded from 2017 to date, which does not show in particular a signal caused by variations inside the volcano.
– No anomalies were reported in sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions into the atmosphere in the area near the volcano, according to data published by the Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) and the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) Sulfur Dioxide Group.
– During the period, no thermal alert was recorded in the area associated with the volcanic building, according to data processed by the Medium Infrared Observation of Volcanic Activity (MIROVA.
Previous monitoring parameters remained below the baseline activity threshold. They remained at levels considered low, suggesting a stability of the volcanic system.
The alert is maintained at the level:
GREEN TECHNICAL ALERT: Active volcano with stable behavior – No immediate risk.
Source : Sernageomin.
Photo : Norm Banks, 1991 (U.S. Geological Survey).
Iceland , Hekla :
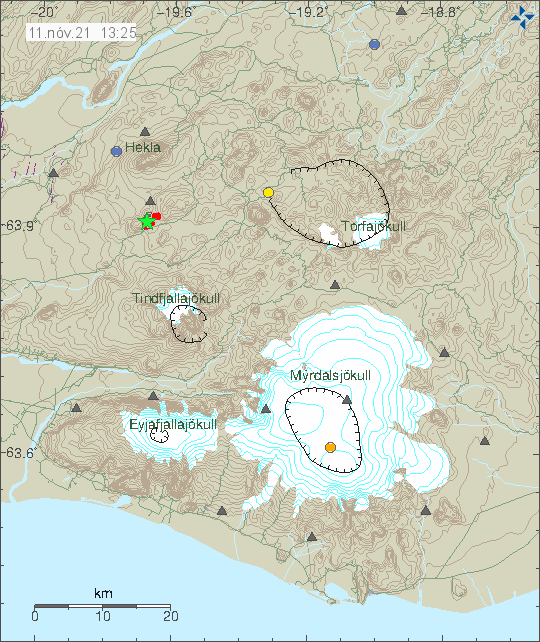
Early information: Magnitude Mw5,2 earthquake in Hekla volcano system. November 11 , 2021.
This is early information but it seems that a magnitude Mw5,2 or larger earthquake took place in Hekla volcano system at 13:21 UTC. This might be a start of an eruption in Hekla volcano, but currently it is too early to know for sure. This is inside Hekla volcano system in a area called Vatnafjöll that have regularly erupted.
Earthquake activity in Hekla volcanos system in a area that is called Vatnafjöll. Copyright of this image belongs to Icelandic Met Office.
It is not possible to know what is going to happen next in this area. But there is a risk of a magnitude Mw7,0 earthquake. If that is going to happens is impossible to know.
Yesterday at 13:21 an M5.2 earthquake occurred in Vatnafjöll in S-Iceland, around 7,5 km S of Hekla volcano. The earthquake was felt widely in S-Iceland and the capital area. Earthquake activity started in the area around noon yesterday and there is considerable aftershock activity. The largest aftershocks are around M3.
Sources : icelandgeology.net , Vedur is .