April 24 , 2021.
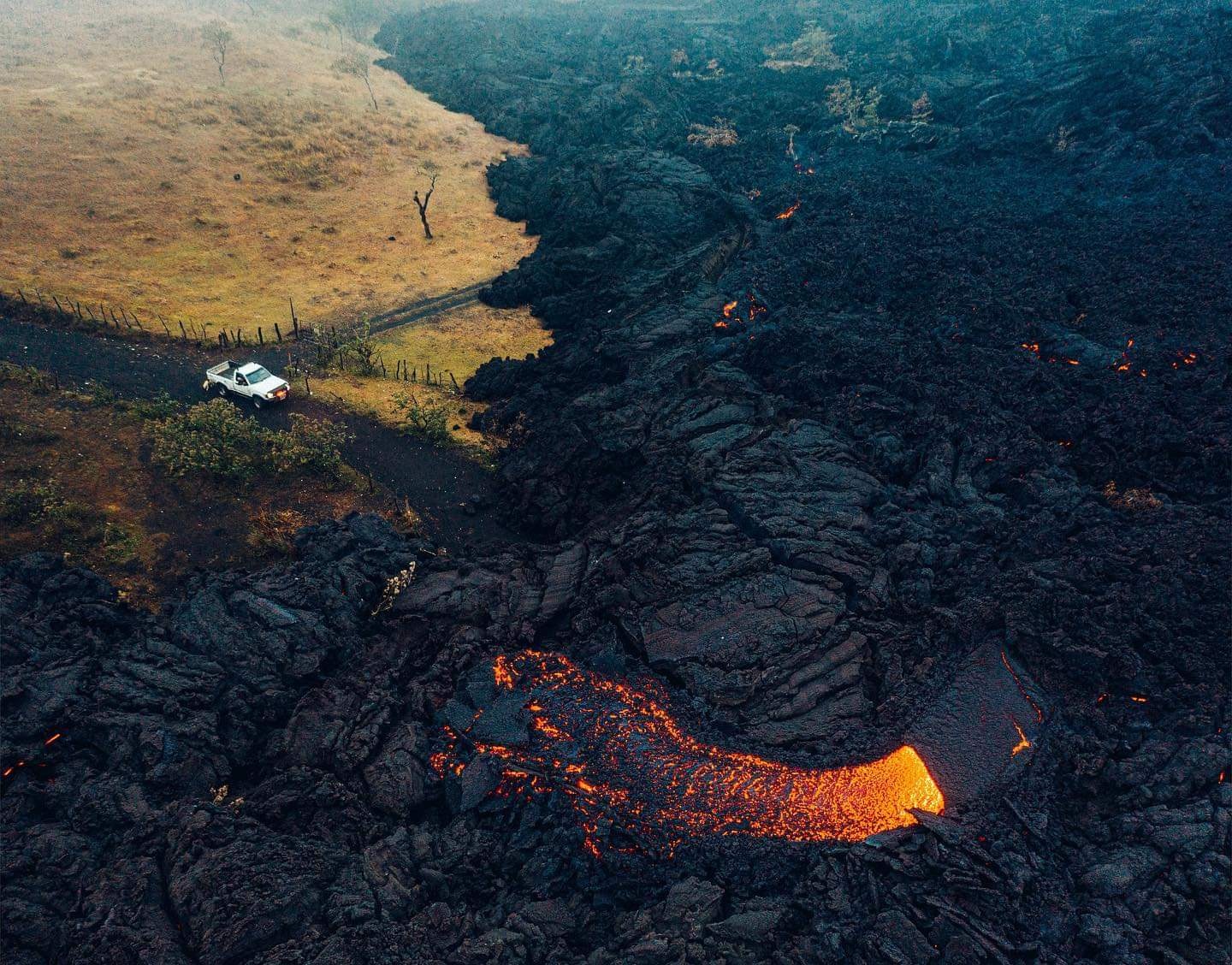
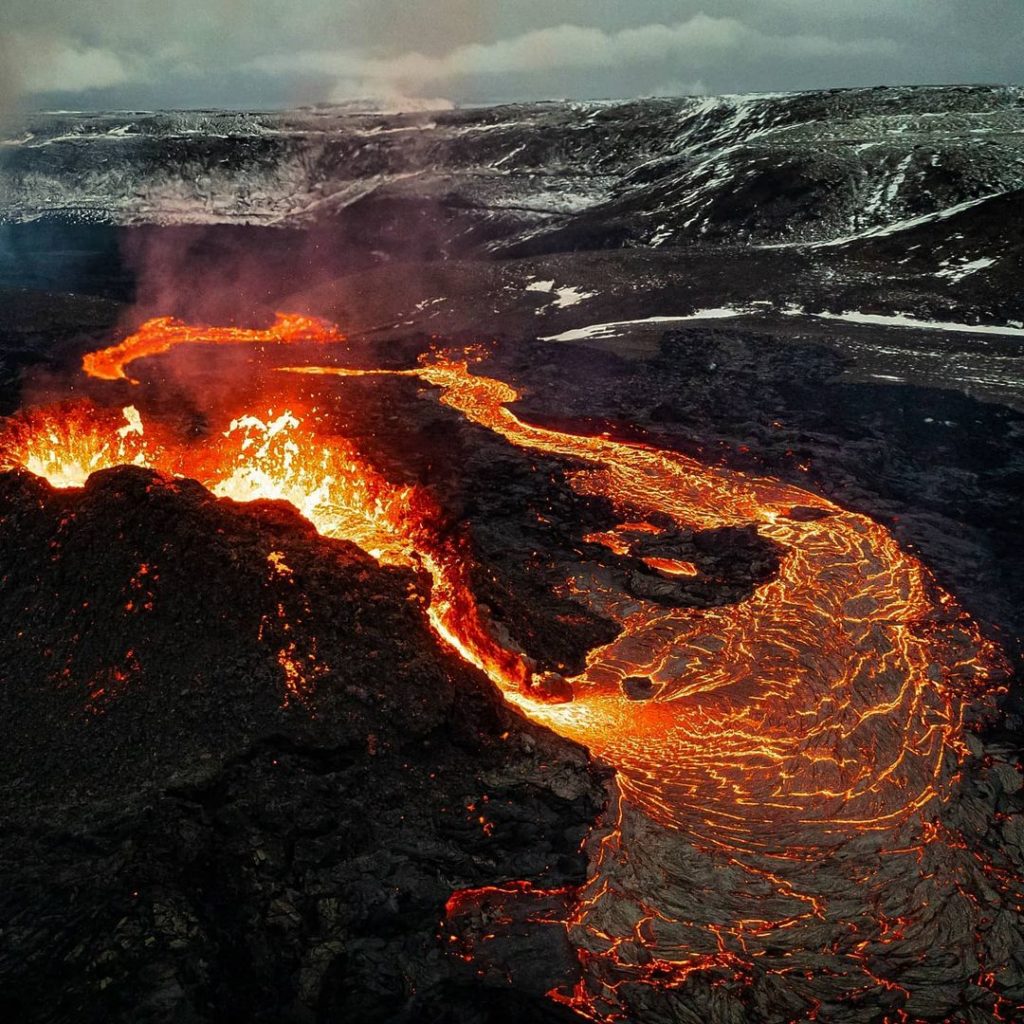
Iceland , Geldingadalur :
Progress of the eruption Updated 21.04. at 16:00
With the Fagradalsfjall eruption continuing for over a month, it is natural to ask how long the eruption will last. New fissure openings have formed several times since the eruption began and, in recent days, volcanic activity at the northernmost crater has ceased.
„It is not clear what this means for the progress of the eruption.“ says Sara Barsotti, volcanic hazards coordinator at IMO. „Since the eruption began about thirty days ago, it has been changing constantly. Presently, there is no magma flowing from the first crater that opened outside Geldingadalir. This, for example, reflects the constant changes, although it is uncertain if the crater is completely asleep”, says Sara. « Therefore, it is not possible to claim that these are the first signs that the eruption is subsiding. On the contrary, the latest summary of our colleagues at the University of Iceland shows that lava flow has not decreased. If anything, it has increased slightly in recent days « , Sara concludes.
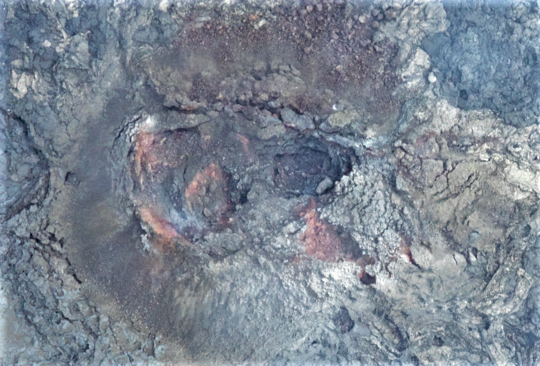
Aerial photo of the northernmost crater at the eruption site, taken on Sunday 18 April. Judging from the picture, there seems to be no activity in the crater. (Photo: Icelandic Institute of Natural History).
A summary from the Institute of Earth Sciences states that the average lava flow for the first 30 days of the eruption was 5.6 m3/s. Compared to most other Icelandic eruptions, the flow is remarkably low and relatively stable. The measurements on the lava now show that there has been some increase in the last 1-2 weeks. The average flow for the first 17 days was 4.5-5 m3 / s, but for the last 13 days it is close to 7 m3 / s.
A comparison with other eruptions shows that despite the increase, the flow is now only about half of what occurred on average during the first 10 days at Fimmvörðuháls in the spring of 2010, which was a small eruption. A comparison with Holuhraun shows that the current flow is 6-7% of the average lava flow during the six months that the eruption lasted. In terms of lava flow, the closest historical example would be the effusive phase of the Surtsey eruption, which began in April 1964 and continued until the end of the eruption in June 1967.
The power of the eruption has increased in parallel with the opening of more craters
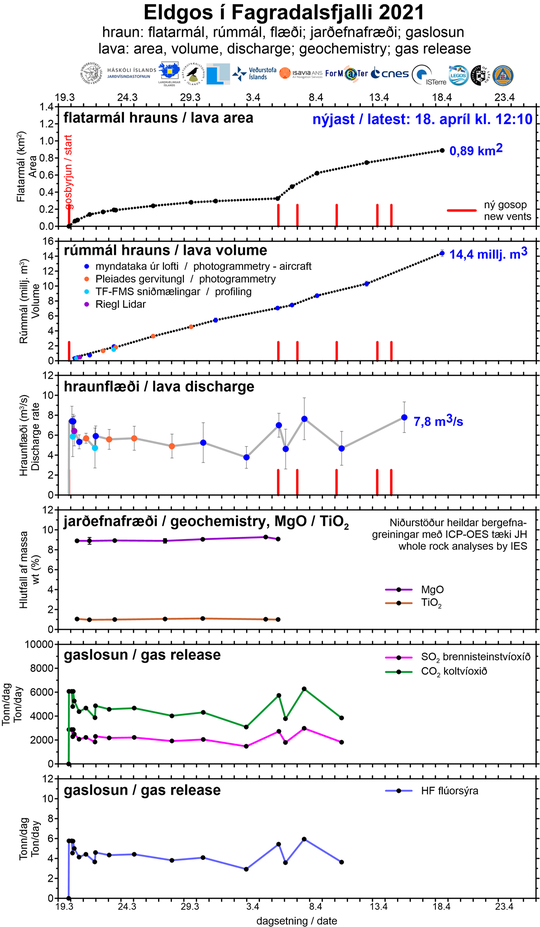
Below you can see an overview published on 19 April by the Institute of Earth Sciences of lava discharge from the Fagradalsfjall eruption. The results represent the total flow from all craters over a six-day period, 12-18 April. This is a slight increase from the average flow in the eruption and confirmation that in parallel with the opening of more craters last week, the power of the eruption has increased somewhat, the area of the lava has reached 0.9 km2 and the total volume is now over 14 million cubic meters.
The graphs above show, among other things, the development of the area and volume of lava and lava flow. Development of the area of the lava is not as « linear » as the development of the volume, but that is because to begin with, the lava field grew in thickness within Geldingadalur rather than spreading out. Ongoing work on processing geochemical and gas data is being done, and the graphs will be updated as soon as it is completed.
Source : Vedur
Photos : Vedur , Visit Reykjavik .
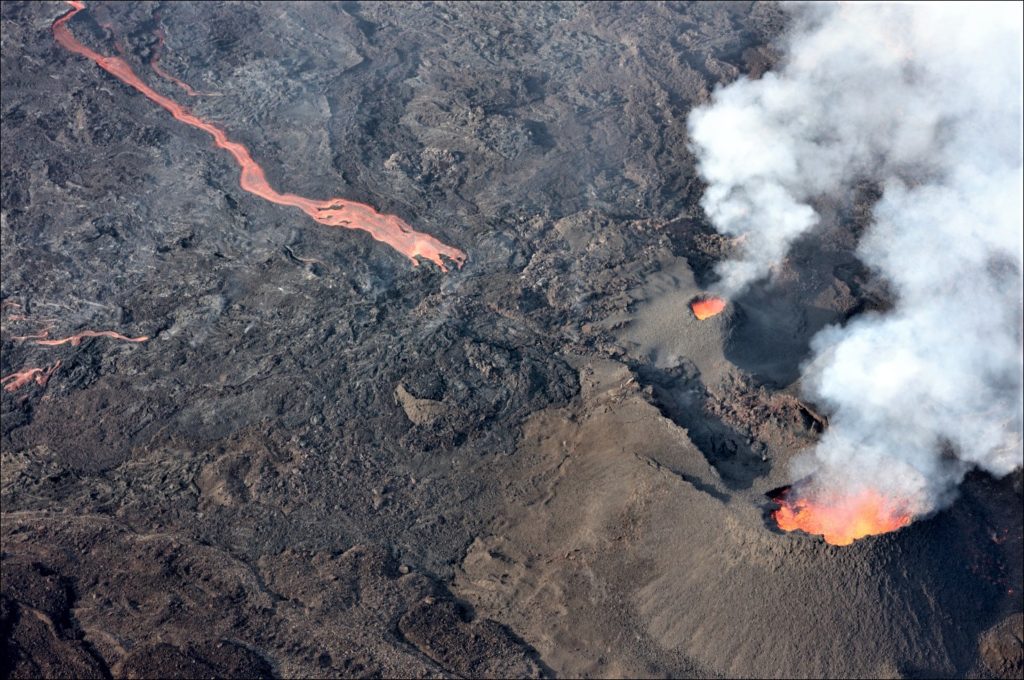
La Réunion Island , Piton de la Fournaise :
Press release of April 23, 2021 – 1:00 p.m.
The eruption that started on 04/09/2021 at 7 p.m. (appearance of the tremor) continues. The intensity of the volcanic tremor (indicator of a surface lava emission) over the last 24 hours has remained relatively stable and comparable to that observed the previous days.
– Over the last 24 hours, 10 superficial volcano-tectonic earthquakes (between sea level and the surface) have been recorded under the summit craters.
– CO2 fluxes in the soil are still increasing both in the far field (Plaine des Cafres and Plaine des Palmistes) and in the near field (Gîte du volcan).
– Averaged over the past few days, no significant trend can be seen in the deformations of the building (neither in deflation nor in inflation). It could suggest a flow of magma
deep entering the superficial magmatic reservoir equivalent to the outlet flow of the reservoir which feeds the eruptive site.
– The SO2 fluxes measured by the DOAS « NOVAC » network make it possible to estimate lava flows.
Considering a partially degassed magma during the first days of the eruption, the maximum lava flow probably did not exceed 20 m3 / sec on April 9 and 10; the proportions of less degassed magma then probably increased over time, thus making it possible to estimate an average flow rate of the order of 24 m3 / sec for the day of 03/13 (with peaks up to 59 m3
/dry). Since a lower average flow, between 1.2 and 8.3 m3 / sec, is estimated for the period from 16 to 22/04. It should be noted that bad weather conditions can affect the accuracy of the measurements.
– The surface flows estimated from satellite data via the HOTVOLC platform (OPGC – Clermont Auvergne University) could not be estimated with precision in recent days given the bad weather conditions on the eruptive site.
Source et photo : OVPF.
Read the article: https://www.ipgp.fr/sites/default/files/ovpf_20210423_13h00_communique_eruption_0.pdf
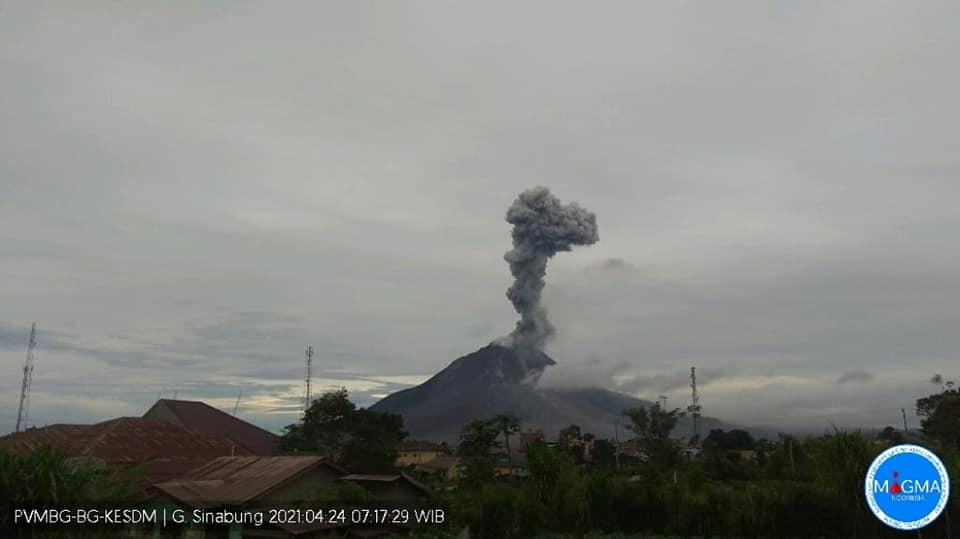
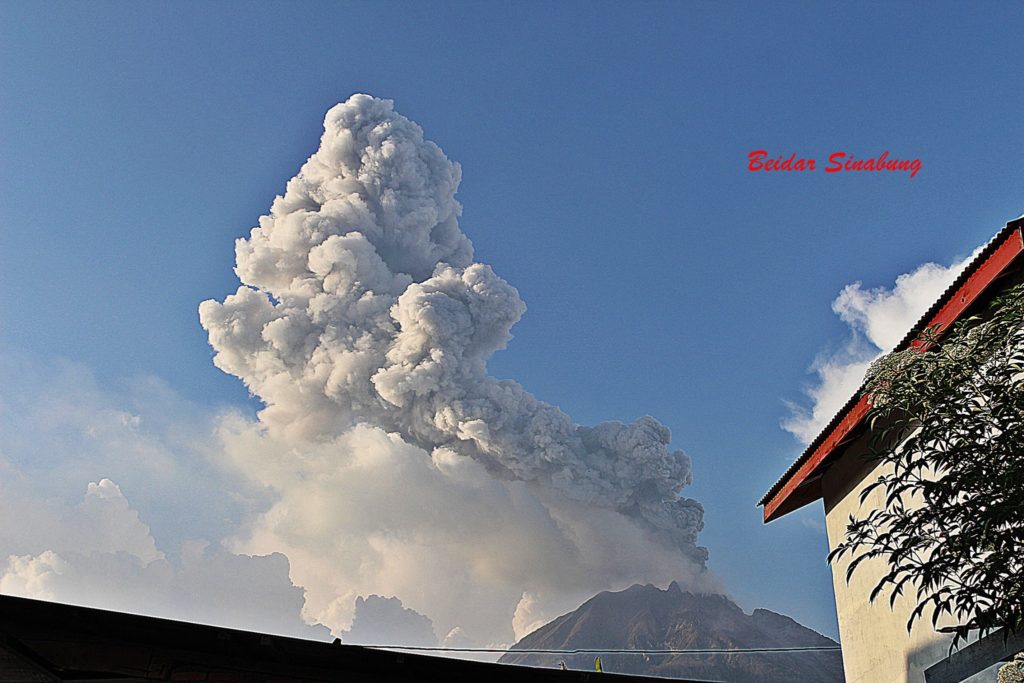
Indonesia , Sinabung :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA .
Issued : April 24 , 2021
Volcano : Sinabung (261080)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Sinabung Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2021SIN54
Volcano Location : N 03 deg 10 min 12 sec E 98 deg 23 min 31 sec
Area : North Sumatra, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 7872 FT (2460 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 00h15 UTC (07h15 local)
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 14272 FT (4460 M) above sea level, may be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash-cloud moving to E-SE.
Remarks :
Seismic activity is characterized by eruption
The activity level has been at level III (SIAGA) since May 20, 2019 at 10:00 a.m. WIB. Mount Api Sinabung (2460m above sea level) has been erupting since 2013. The last eruption occurred on April 13, 2021 with a maximum column height of 500-1600 meters above the summit.
The volcano was clearly visible until it was covered in fog. The crater emits white smoke with a great thickness, rising about 50 to 300 meters above the summit. The weather is sunny to rainy, with weak to moderate winds to the east and south-east. An avalanche was observed with a sliding distance of 1000 meters from the summit and in an east-south-east direction.
According to the seismographs of April 23, 2021, it was recorded:
1 eruption / explosion earthquake
106 avalanche earthquakes
4 emission earthquakes
8 low frequency earthquakes
12 hybrid / multi-phase earthquakes
1 deep volcanic earthquake
1 distant tectonic earthquake
Source : Magma Indonésie , PVMBG.
Photos : Magma , Beidar Sinabung.
Guatemala , Pacaya :
ACTIVITY:
The Pacaya Volcano Observatory reports that an incandescence was observed in the Mackenney crater overnight and early in the morning. This shows only degassing activity, rising with white columns composed mainly of water vapor to heights of 300 meters above the crater and dispersing up to 5 kilometers to the south. The lava flow on the western flank near El Patrocinio and El Rodeo has shown no progress, however, it preserves areas of high temperature and several outgassing vents with sulfur gases. The seismic stations around the volcano record internal tremors, associated with the movement of magma inside the volcanic building and the emission of gas.
The eruptive phase of the Pacaya volcano in Guatemala, which since February 5 has alarmed neighboring villages with powerful explosions and lava flows, « is over, » said the National Institute of Volcanology on Friday.
The 2,552-meter-high volcano, located about 25 km south of Guatemala City, exhibits only “a few weak explosions (…), little ash, water vapor and sulphurous gases. abundance, ”said Emilio Barillas, spokesperson for the National Institute of Volcanology (Insivumeh).
He explained that the lava rivers on the slopes of the massif, the longest of which is 3.8 km, « have not shown any progression in any direction » in recent days.
The civil protection spokesman added that the tip of the main lava flow solidified about 450 meters from the first houses of the villages on the side of the volcano, where residents and authorities had prepared plans to evacuation.
Source : Insivumeh , TVAnouvelles.
Photo : Villa nueva news.
Saint Vincent , Soufrière Saint Vincent :
La Soufrière, St. Vincent SCIENTIFIC UPDATE – 23/04/21 6:00PM
– Seismic activity at La Soufrière, St Vincent has been low after the tremor associated with the explosion and ash venting around noon on 22 April.
– Only a few long-period, hybrid and volcano-tectonic earthquakes were recorded and there was no further tremor.
– The seismic network recorded signals from multiple lahars (mudflows) at about 9 pm on 22 April. The locations of these lahars have not been determined.
– Measurements of sulphur dioxide flux (mass) at La Soufriere volcano was again undertaken along the west coast today with the assistance of the coastguard. An average SO2 flux of 992 tons per day was recorded.
– Since the initial depressurization (deflation) seen immediately after the April 9 explosive phase, the continuous GPS network has recorded a decrease in the overall rates of horizontal and vertical movement.
-The volcano continues to erupt. Its pattern of seismic activity over the last few days is typical of the growth and destruction of lava domes. Explosions with accompanying ashfall, of similar or larger magnitude, can occur with little or no warning.
– The volcano is at alert level Red.
Source : UWI.
Photo : Saint Vincent & the Grenadines