March 09 , 2019.
La Réunion , Piton de la Fournaise :
Activity bulletin of Friday, March 8, 2019 at 17:00 (local time).
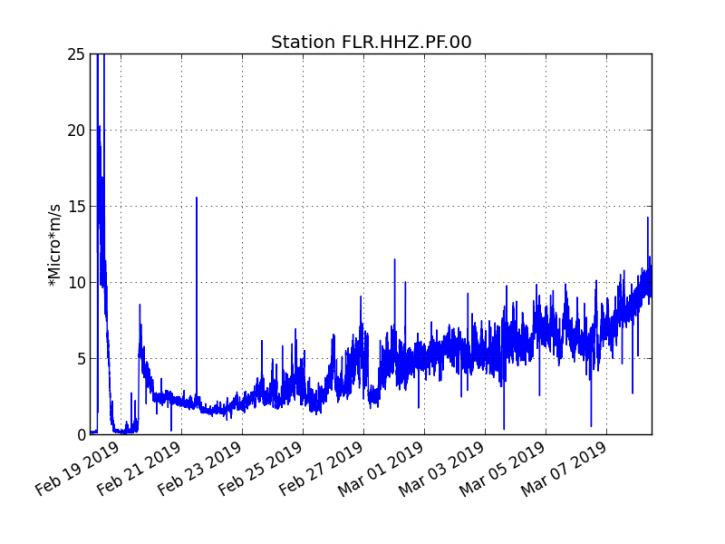
The eruptive activity that resumed on February 19, 2019 at Piton de la Fournaise around 7:10 pm local time continues. The intensity of the eruptive tremor continues the rise started 48 hours ago.
Figure 1: Evolution of the RSAM (indicator of the volcanic tremor and the intensity of the eruption) between 09h48 (05h48 UTC) on February 18th and March 8th at 15h30 (11h30 UTC) on the seismic station of FLR. (© OVPF / IPGP)
– Over the last 36 hours, 49 superficial superficial volcano-tectonic earthquakes (above sea level) have been recorded.
– The CO2 concentrations in the near-field soil (cottage volcano area) remain high.
– Over the last 36 hours, surface flows estimated from satellite data, via the HOTVOLC platform (OPGC – University of Auvergne), fluctuated between <1 and 50 m3 / s (these measures may be affected / reduced by the cloud cover). It should be noted that most of the measurements remain however less than 30 m3 / s and that following the cloud cover these measures are no longer possible since 9:30 this morning.
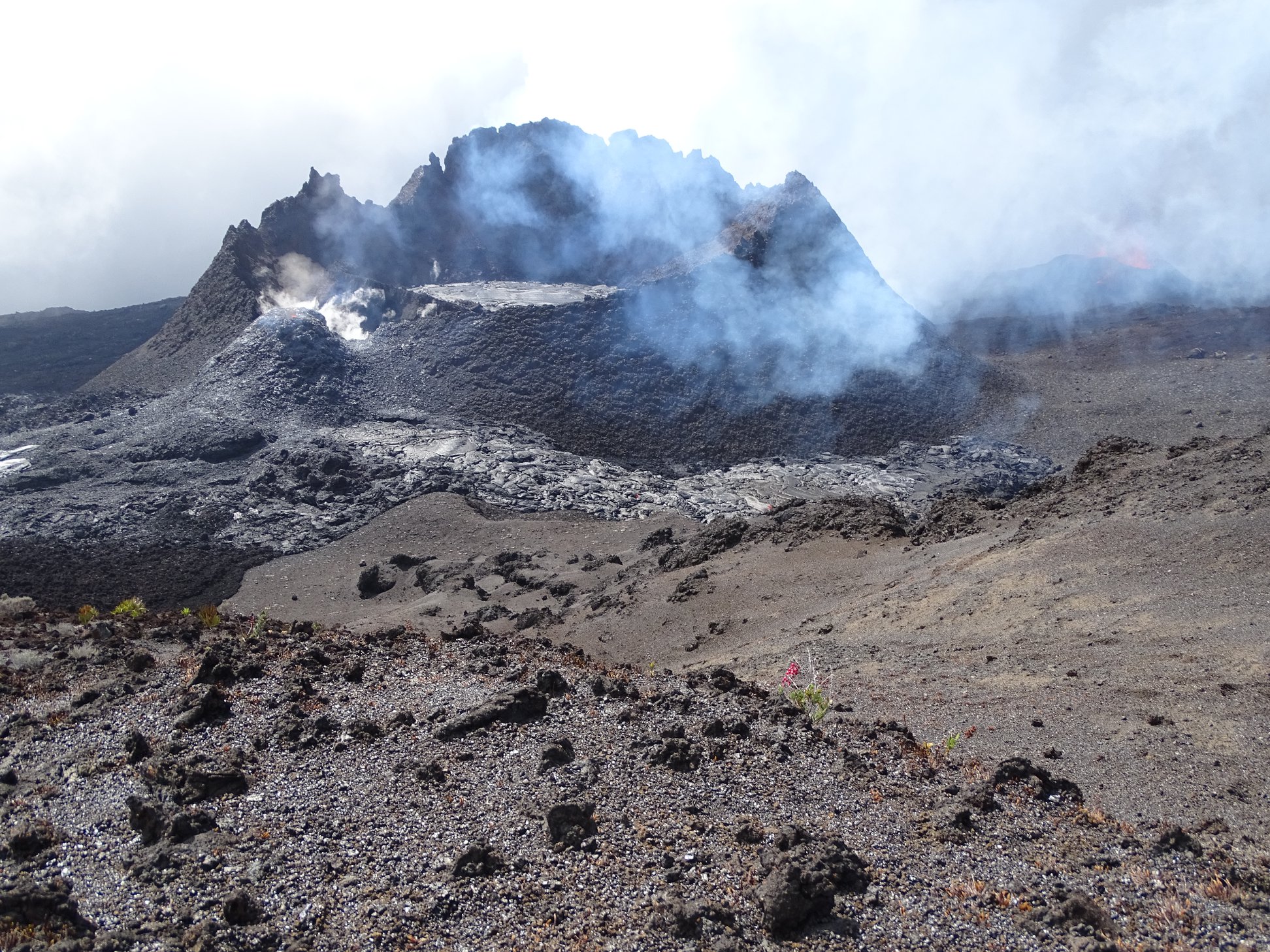
An intervention led by SAG and PGHM allowed a team of the volcanological observatory to go to the scene of the eruption today in order to locate the cracks that opened during the last days. perform lava sampling, make a survey of the extension of the flows
This mission made it possible to establish that the crack which opened on March 5th on the north-west flank of the Madoré peak (upstream of the active mouth since March 19th) remains active.
A small cone of projections up to ten meters has been built and two low flow flows remain active west side (extension of a few tens of meters) and north side. The main flow is that which flows north side and progresses east (direction of the slope). The crack that opened yesterday morning, March 7, is located 300 m south of the active vent since March 19 and is oriented in a west-easterly direction. It was very active this morning with 2 fountains of lava of about fifty meters high.
The lava samples taken show that the eruptive vents of March 5 and March 7 produce lava of different compositions.
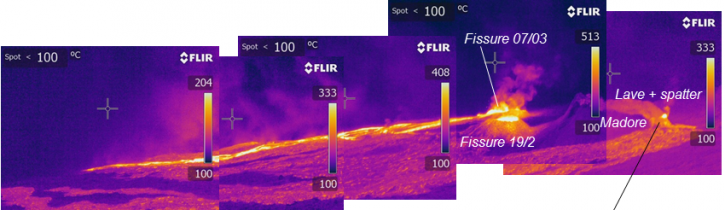
Figure 2: Infra-red view of the eruptive site and the upper parts of the flows from the north of the eruptive site. (© OVPF / IPGP)
Cloud cover did not locate the end of the sinks. However, a simple geometric computation done on the images acquired last night by our webcam, makes it possible to estimate that the front of flows was last night slightly above 1000 m of altitude.
Niveau d’alerte : Alerte 2-2
Source : OVPF
Photo : OVPFIPGP.
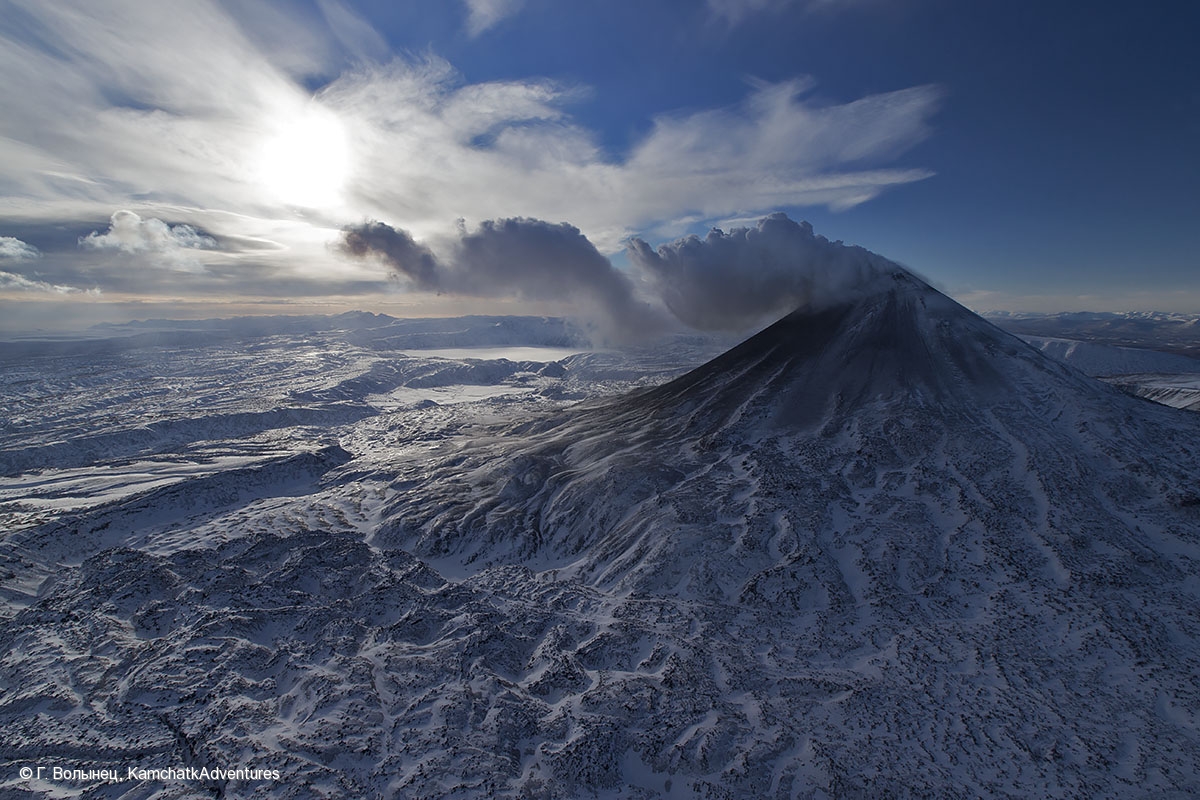
Kamchatka , Karymsky :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA).
Issued: March 09 , 2019
Volcano:Karymsky (CAVW #300130)
Current aviation colour code:ORANGE
Previous aviation colour code:orange
Source:KVERT
Notice Number:2019-53
Volcano Location:N 54 deg 2 min E 159 deg 26 min
Area:Kamchatka, Russia
Summit Elevation:4874.08 ft (1486 m)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
Satellite data shows an ash plume is extending about 31 km to the north-east from volcano.
A moderate eruptive activity of the volcano continues. Ash explosions up to 13,100-19,700 ft (4-6 km) a.s.l. could occur at any time. Ongoing activity could affect low-flying aircrafts.
Volcanic cloud height:
9840-11480 ft (3000-3500 m) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20190309/0040Z – Himawari-8
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 19 mi (31 km)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: NNE / azimuth 30 deg
Time and method of ash plume/cloud determination: 20190309/0040Z – Himawari-8.
Karymsky, the most active volcano of Kamchatka’s eastern volcanic zone, is a symmetrical stratovolcano constructed within a 5-km-wide caldera that formed during the early Holocene. The caldera cuts the south side of the Pleistocene Dvor volcano and is located outside the north margin of the large mid-Pleistocene Polovinka caldera, which contains the smaller Akademia Nauk and Odnoboky calderas. Most seismicity preceding Karymsky eruptions originated beneath Akademia Nauk caldera, located immediately south. The caldera enclosing Karymsky formed about 7600-7700 radiocarbon years ago; construction of the stratovolcano began about 2000 years later. The latest eruptive period began about 500 years ago, following a 2300-year quiescence. Much of the cone is mantled by lava flows less than 200 years old. Historical eruptions have been vulcanian or vulcanian-strombolian with moderate explosive activity and occasional lava flows from the summit crater.
Source : Kvert. GVP.
Photo : G. Volynets, KamchatkAdventures , 9/12/2015 .
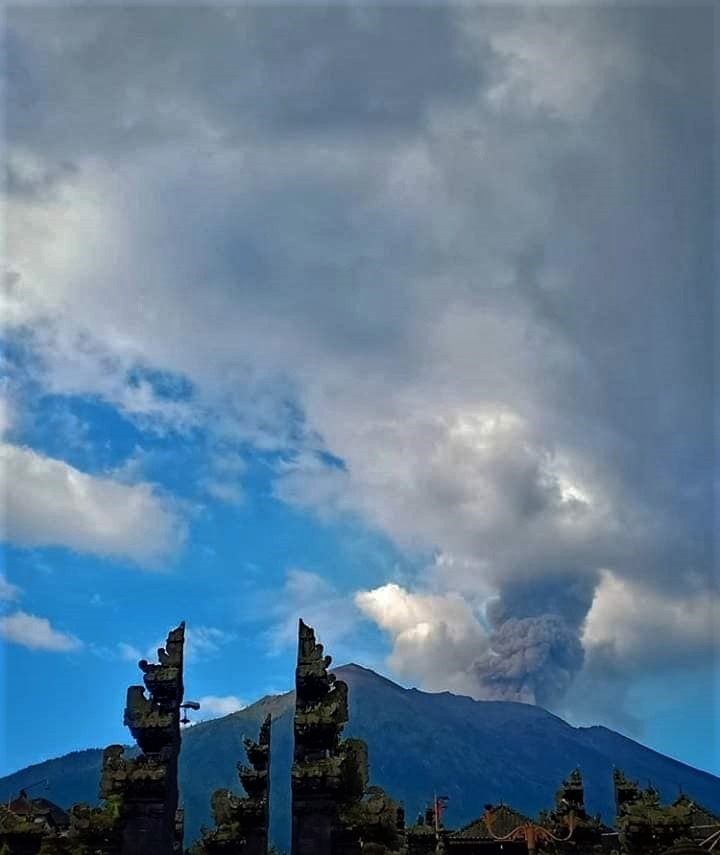
Indonesia , Agung :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA.
Issued: March 08 , 2019
Volcano: Agung (264020)
Current Aviation Colour Code: ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code: orange
Source: Agung Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2019AGU09
Volcano Location: S 08 deg 20 min 31 sec E 115 deg 30 min 29 sec
Area: Bali, Indonesia
Summit Elevation: 10054 FT (3142 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 16h47 UTC (00h47 local). Eruption and ash emission is not continuing
Volcanic Cloud Height:
No Ash Cloud Produced.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information:
Ash-cloud moving to east
Remarks:
Seismic activity recorded with maximum amplitude 21 mm and maximum duration 230 second
Level of activity at Level III (SIAGA). G. Agung (3142 m altitude) resumed its activity since November 21, 2017. The last eruption occurred on February 24, 2019 with a column of emission from a height of 300 to 700 meters with a smoke gray.
Since yesterday and until this morning, it was clearly visible then covered with fog, it was observed smoke from the crater, white, a maximum height of 400 meters above the summit, an intensity low to moderate. The wind was weak in the west.
Seismograph records dated March 7, 2019 noted:
1 shallow volcanic earthquake
3 distant tectonic earthquakes
On March 8, 2019 (00: 00-06: 00 WITA) it was recorded:
1 earthquake emission
1 distant tectonic earthquake
Recommendations:
The communities around G. Agung and mountaineers / visitors / tourists should not be present, operating in the estimated risk zone, ie in all areas within 4 km of Mount Agung Crater. .
The estimated risk area is dynamic and continues to be evaluated. It can be modified at any time to follow the most recent observation data from G. Agung.
Communities living and traveling around streams from Gunung Agung are sensitized to the potential secondary danger in the form of lahars that can occur especially during the rainy season and if the eruption material is still exposed in the area. Summit.
Level III (SIAGA) status applies only within a 4 km radius, as indicated above. Outside the risk zone, the activity can run normally while remaining safe, but must remain vigilant.
Source : Magma Indonésie , PVMBG.
Photo : Peter Rendez Vous , 22 Février 2019.
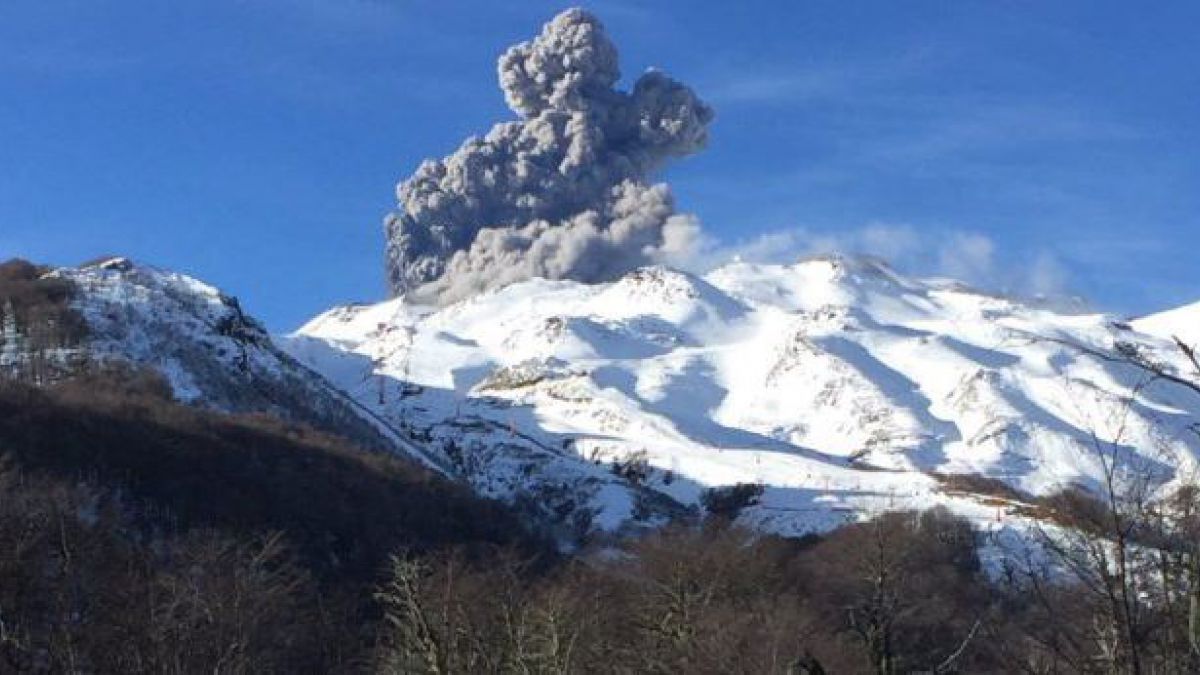
Chile , Nevados de Chillan :
Nuble Region, Nevados Volcano of Chillan, 08 March 2019, 09:45 local time (mainland Chile).
The National Geological and Mining Service of Chile (Sernageomin) publishes the following PRELIMINARY information, obtained from monitoring equipment of the National Volcanic Monitoring Network (RNVV), processed and analyzed at the Volcanological Observatory of the Southern Andes (OVDAS) :
Yesterday, Friday 08 March 2019 at 08:45 local time (11:45 UTC), the monitoring stations installed near the Nevados volcano of Chillan recorded a long period type earthquake, associated with the dynamics of the fluids inside the volcano (Type LP).
The location of the earthquake after its analysis is:
TIME OF ORIGIN: 08h45 Local time (11h45 UTC)
LATITUDE: 36,868 ° S
LONGITUDE: 71.380 ° W
DEPTH: 0.9 KM
REDUCED MOVEMENT: 51 cm2
ACOUSTIC SIGNAL: 0.6 Pa (reduced to 1 km as a reference)
OBSERVATIONS:
The LP earthquake mentioned was associated with the occurrence of an explosion with a column of gas at an altitude of approximately 2700 m above the level of the crater. In addition, particulate materials around the active crater have been detected which, as usual, have been deposited mainly in the northern sector.
The level of volcanic technical alert remains at the level: ORANGE.
Sernageomin continues online monitoring and will inform in a timely manner about any changes observed.
Source : Sernageomin.
Photo : Auteur Inconnu .
Costa Rica , Poas :
Since March 7, 2019, there has been a continuous eruption on the Poás volcano, with a column rising 200 meters above the crater height and 2908 m.s.m. (meters above sea level, or 9538.24 ft).
The seismic activity is similar to that of yesterday.
At the time of writing, winds are blowing from the southwest.
An almost continuous emission of ashes is observed. The CO2 / SO2 ratio decreases, the H2S / SO2 ratio has returned to low values after a slight increase.
https://www.facebook.com/RSN.CR/videos/363201464409829/
March 7, 2019: During today’s day, the Poás volcano has maintained vigorous emanations of water vapor, gas and ashes in small quantities. The inhabitants of San Miguel Naranjo and Sarchí report an odor of sulfur, in agreement with the direction of the wind, towards the South-West.
March 8, 2019: the eruption continues with a constant emission of gas as well as the presence of sulfur and water vapor, and a sporadic presence of ashes. As the wind continues to blow in the southwest, it is likely that the inhabitants of Naranjo, Grecia, among others, smell of sulfur and note falls of ashes.
Source : Ovsicori
Video : RSN ( 11 Février )