March 01 , 2019.
La Réunion , Piton de la Fournaise :
Activity Bulletin from Thursday, February 28, 2019 at 16:30 (local time).
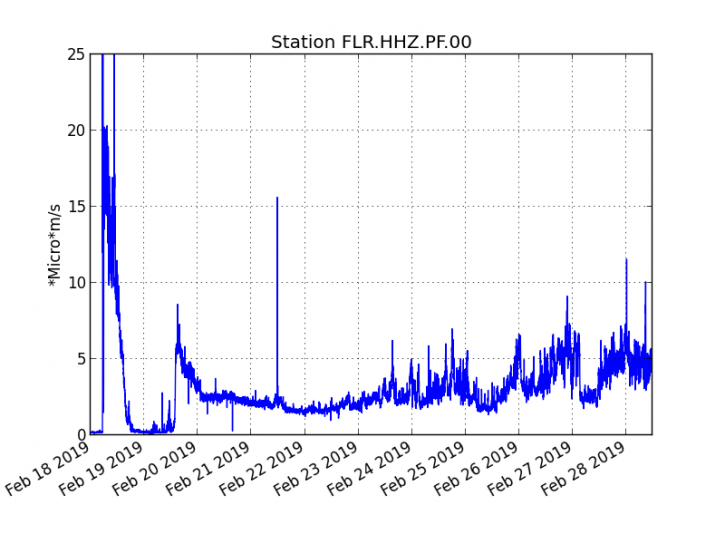
The eruptive activity that resumed on February 19, 2019 at Piton de la Fournaise around 7:10 pm local time continues. Despite slight fluctuations in intensity since February 25, the eruptive tremor remained relatively constant for several days (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Evolution of the RSAM (indicator of the volcanic tremor and the intensity of the eruption) between 09:48 (05:48 UTC) February 18 and 16:00 (12:00 UTC) February 28 on the seismic station of FLR. (© OVPF / IPGP)
– Over the last 36 hours, 3 superficial volcano-tectonic earthquakes (above sea level) have been recorded.
– After a deflation of the building related to the transfer of magma that occurred on 18/02/2019, the deformations of the summit zone do not show any particular signals.
– The CO2 concentrations in the near-field soil (cottage volcano area) remain high.
– Over the last 36 hours, surface flows estimated from satellite data, via the HOTVOLC platform (OPGC – University of Auvergne), fluctuated between <1 and 16 m3 / s. Note that low values (or zero values) are recorded when cloud cover does not allow acquisition.
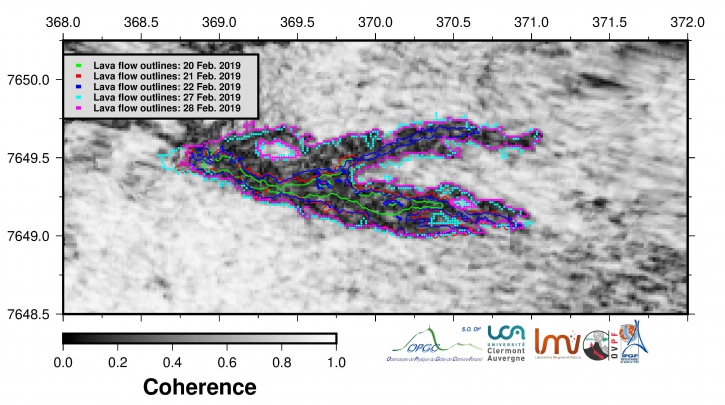
– A cartography of the lava flow dated 28/02/2018 carried out by the OI2 platform (OPGC – Clermont Auvergne University) from satellite data has confirmed the slow progression of the lava flow (300 m in 5 days). The casting front is located at 1200m above sea level and only the north arm is currently active (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Contours of the lava flows associated with the eruptive episode of 19/02/2019 determined from satellite data by the OI2 platform (Université Clermont Auvergne), dated 20 (green), 21 (red), 22 (blue), 27 (turquoise) and 28/02/2019 (pink).
Alert level: Alert 2-2.
Source : OVPF
Photo : RB et mon ami , imazpress.
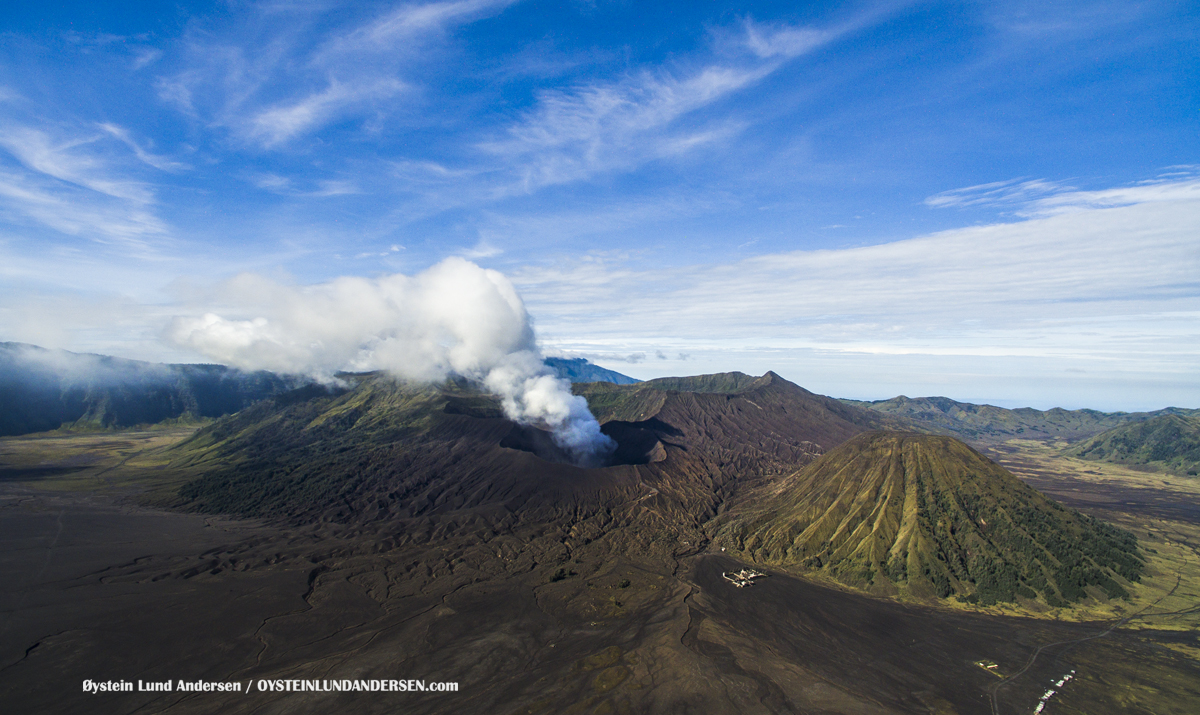
Indonesia , Bromo :
Bromo Tengger Semeru National Park (TNBTS) is closing all public access to Mount Bromo for 24 hours from 5 a.m. Western Indonesia Time (WIB) on March 7 to 5 a.m. on March 8 to respect the local Hindu observance of Nyepi (Day of Silence).
Mount Bromo is home to the Tengger indigenous tribe, which follows a unique form of Hinduism that shares some similarities with Balinese Hinduism.
« The closure of all tourism at Mount Bromo is to respect all Hindus who are observing Nyepi, » TNBTS agency head John Kenedie said in a statement on Thursday, as quoted by Antara.
The closure affects all access to the mountain, including the entrance gates of the National Park Management Resort (RPTN) Cemorolawang in Tengger Laut Pasir (Tengger Sand Sea), the RPTN Mount Pananjakan and the RPTN Coban Trisula.
Access routes will be closed to Mount Bromo from Ngadas village in Sukapura district, Probolinggo, and Wonokitri village in Tosari district, Pasuruan. Access routes from Malang and Lumajang to Blok Jemplang will also be closed.
The closure applies to public access points within an 8-kilometer radius of Bromo, from the entrance gates in Ngadas village, Wonokitri village and Blok Jemplang to the Sand Sea.
Source : The Jakartapost
Photo : Oystein Lund Andersen
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Weekly activity bulletin of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano
The level of activity continues at the level: Yellow activity level or (III): Modifications of the behavior of the volcanic activity.
With regard to monitoring the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE announces that:
The Nevado del Ruiz volcano over the past week continued to show instability in its behavior. The seismicity caused by rock fracturing resulted in a slight decrease in the number of earthquakes but similar levels of seismic energy released compared to the previous week. The earthquakes were located mainly in the Arenas crater and in the South-West and East-North-East areas of the volcano, at depths between 0.9 and 6.0 km. The higher energy earthquake was recorded on February 23 at 18:22 local time and had a magnitude of 1.0 ML (local magnitude). It was located 6.5 km northeast of the crater Arenas, 4.1 km deep.
Seismicity related to fluid dynamics within the volcanic structure ducts showed similar levels in the number of earthquakes and a slight decrease in released seismic energy compared to the previous week. This seismic activity was characterized by the appearance of slight pulses of volcanic tremor and earthquakes of very long type. The earthquakes occurred mainly in the crater Arenas and its surroundings.
The volcano continues to emit water vapor and gases into the atmosphere, among which is the sulfur dioxide (SO2), as evidenced by the values obtained by the SCANDOAS stations installed in the region of the volcano. satellite image analysis. During the week, the NASA FIRMS and MIROVA portals reported several low-energy thermal anomalies.
The column of gas and vapor reached a maximum height of 2,000 m, measured at the top of the volcano on February 21. The direction of dispersion of the column was governed by the direction of the wind in the region, which prevailed towards the northwest of the volcano.
The Nevado del Ruiz volcano continues at the level of yellow activity.
Source : SGC.
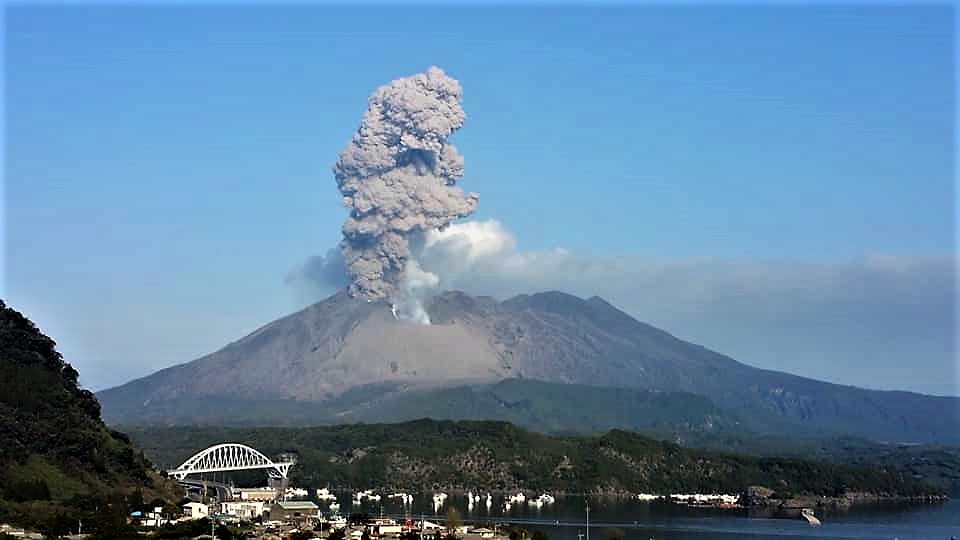
Japan , Aira Caldeira ( Sakurajima ) :
31.593°N, 130.657°E
Elevation 1117 m
JMA reported that incandescence from Minamidake crater (at Aira Caldera’s Sakurajima volcano) was occasionally visible during 18-25 February. At 00h59 on 22 February an event generated a plume that rose 1 km above the crater rim and ejected material 600-900 m from the crater. During 22-25 February there were two events, one of which was explosive. Plumes rose as high as 1.2 km, and material as ejected as far as 900 m from the crater. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a 5-level scale).
The Aira caldera in the northern half of Kagoshima Bay contains the post-caldera Sakurajima volcano, one of Japan’s most active. Eruption of the voluminous Ito pyroclastic flow accompanied formation of the 17 x 23 km caldera about 22,000 years ago. The smaller Wakamiko caldera was formed during the early Holocene in the NE corner of the Aira caldera, along with several post-caldera cones. The construction of Sakurajima began about 13,000 years ago on the southern rim of Aira caldera and built an island that was finally joined to the Osumi Peninsula during the major explosive and effusive eruption of 1914. Activity at the Kitadake summit cone ended about 4850 years ago, after which eruptions took place at Minamidake. Frequent historical eruptions, recorded since the 8th century, have deposited ash on Kagoshima, one of Kyushu’s largest cities, located across Kagoshima Bay only 8 km from the summit. The largest historical eruption took place during 1471-76.
Source: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) , GVP
Photo : Auteur Inconnu .