September 23 , 2018.
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Subject: Activity bulletin of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano.
The level of activity continues at the level: Yellow or (III): changes in the behavior of volcanic activity.
With regard to monitoring the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE informs that:
During the past week, the seismicity caused by the fracturing of the rocks that make up the volcano has shown a decrease in the number of earthquakes and a slight increase in seismic energy released, compared to the previous week. The earthquakes are located mainly in the proximal north, southwest, southeast and Arenas crater at depths between 0.9 and 6.3 km. The maximum magnitude recorded during the week was 1.8 ML (local magnitude) for the earthquake that occurred on September 11 at 10:32 am (local time), located southeast, 3.1 km from the crater Arenas at a depth of 3.4 km.
The seismicity related to fluid dynamics in the channels of the volcanic structure showed a slight increase in the number of earthquakes and released seismic energy, compared to the previous week. This type of seismic activity has been characterized by the appearance of earthquakes with variable energy levels, long period type (LP), very long period (VLP) of tremors impulses and episodes of tremor continuous volcanic. The earthquakes were mainly in the crater Arenas and its surroundings. Some of these seismic signals have been associated with emissions of gas and ash into the atmosphere, as confirmed by the images captured by the cameras installed in the volcano area, by officials of the Los Nevados National Natural Park (PNNN) and Residents near the volcano, Civil Aviation and the Washington Ash Advisory Center (W-VAAC). These ash emissions have been duly reported to civil aviation through Vona notifications (Aviation Volcano Observatory Notification).
Volcanic deformation measured from electronic inclinometers, GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) stations and radar images have so far shown stability behavior without recording significant deformation processes of the volcanic structure.
The volcano continues to emit in the atmosphere water vapor and gases, including sulfur dioxide (SO2) which is highlighted, as shown by the values obtained by the SCANDOAS stations installed in the volcano area. and satellite image analysis. During the week, the MIROVA portal reported a thermal anomaly with a very low energy level.
The column of gas and steam reached a maximum height of 1650 m measured at the summit of the volcano on 13 September. The direction of dispersal of the column was governed by the direction of the wind in the area, which prevailed during the week northwest of the Arenas crater.
The Nevado del Ruiz volcano continues its activity at the level of yellow activity.
Source : SGC
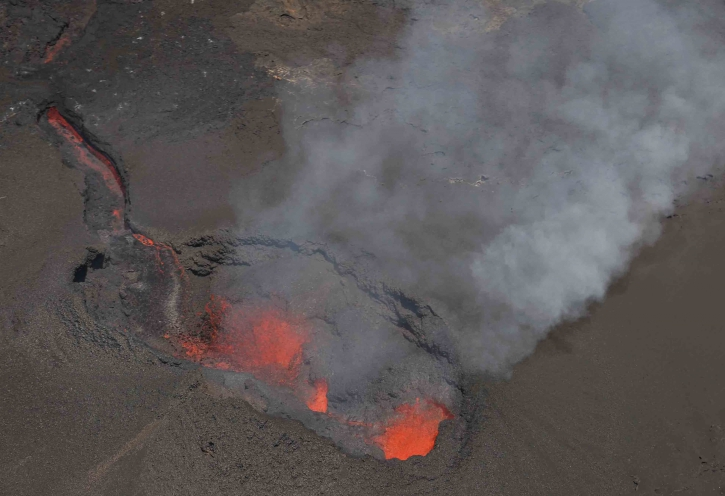
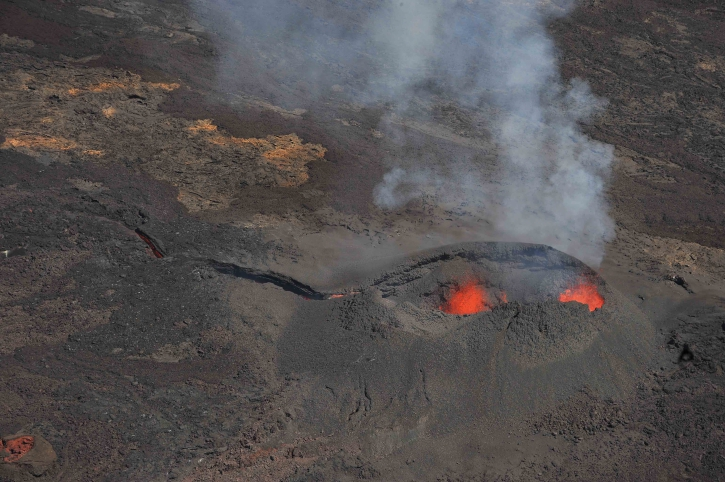
Hawai , Kilauea :
9 ° 25’16 « N 155 ° 17’13 » W,
Summit: 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current alert level of the volcano: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Kīlauea Summit and Lower East Rift Zone
On Kīlauea Volcano’s lower East Rift Zone (LERZ), no incandescence was visible overnight in the collapse pit within the fissure 8 cone. Minor fuming is visible during the day. Seismicity and ground deformation remain low at the summit of Kīlauea. Small aftershocks from the magnitude-6.9 earthquake in early May are still being generated on faults located on Kīlauea’s South Flank.
No collapses within Puʻu ʻŌʻō crater have been observed over the past week. Rates of tilting throughout the East Rift Zone are much lower than those observed during the period of major eruptive activity. There has been no change in seismicity during the past week.
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission rates at the summit, Puʻu ʻŌʻō, and LERZ are drastically reduced; the combined rate is less than 1,000 tonnes/day, which is lower than at any time since late 2007. SO2 emission rates from LERZ vents were below the detection threshold of the measurement technique when last measured on Sept. 11. Minor amounts of H2S are being emitted at the summit and at Puʻu ʻŌʻō.
The Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) continues to closely monitor Kīlauea’s seismicity, deformation, and gas emissions for any sign of reactivation, and maintains visual surveillance of the summit and LERZ. HVO will continue to issue daily updates and additional messages as needed.
Source : HVO .
Photo : Bruce Omori
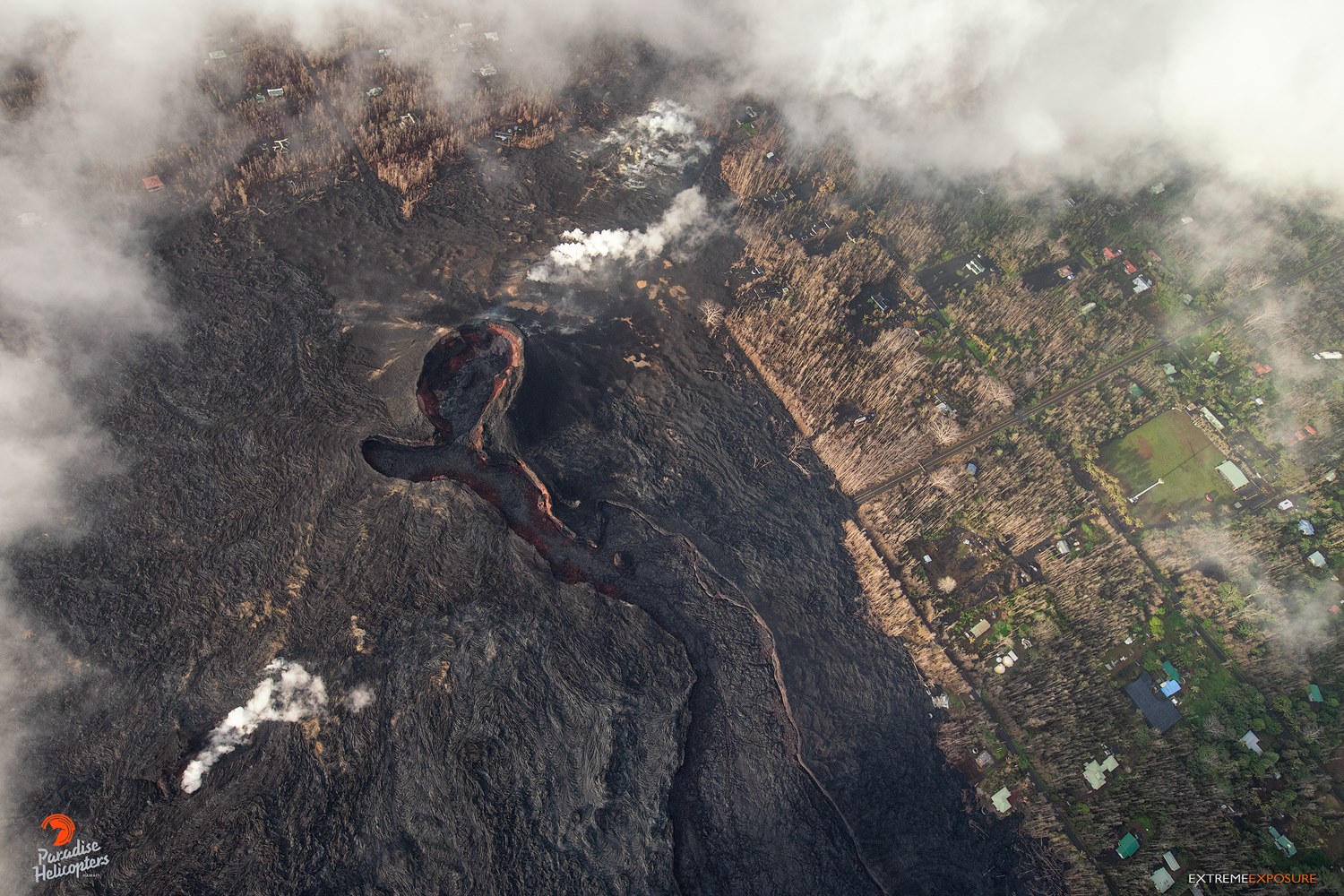
La Réunion , Piton de la Fournaise :
Activity Bulletin of Saturday, September 22, 2018 at 17:15 (local time)
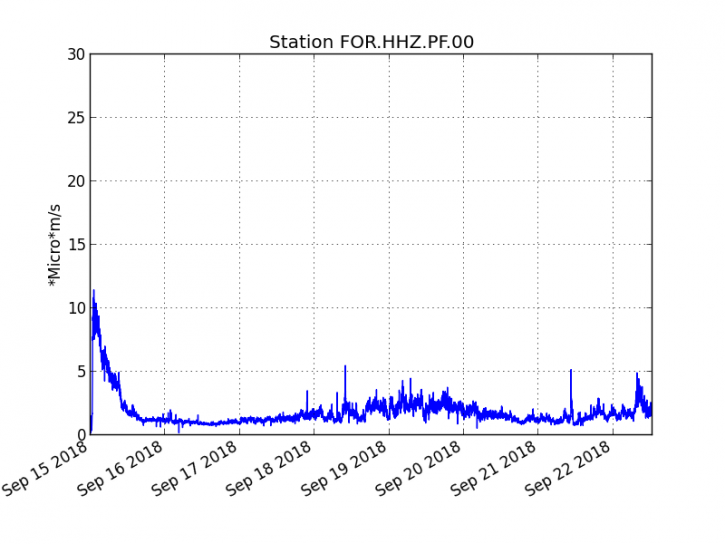
The eruption started on September 15th at 4:25 am local time continues. The volcanic tremor (indicator of eruptive intensity on the surface) has undergone many fluctuations in the last 24 hours, certainly related to fluctuations in the geometry of the volcanic cone being formed (successions of obstructions and partial dismantling, Figure 1) .
Figure 1: Evolution of the RSAM (indicator of the volcanic tremor and the intensity of the eruption) between 04h00 (00h UTC) on September 15th and 16h30 (12h30 UTC) on September 22nd on the seismic station FOR, located near the crater Chateau Fort (2000 m altitude on the southeast flank of the terminal cone). (© OVPF / IPGP)
– A deep volcano-tectonic earthquake (about 2.6 km below sea level) was recorded under the east flank of the volcano during the day of 21 September. No volcano-tectonic earthquakes have been recorded during the current day.
– No significant deformity is noticeable since the beginning of the eruption.
– The surface flows estimated from the satellite data, via the HOTVOLC platform (OPGC – Clermont Auvergne University) are between 1 m3 / s and 3 m3 / s over the last 24 hours.
– Fallout from Pele’s hair has been reported in the Grand Coude area this morning. Pele’s hair is formed from very fluid lava ejecta (at the level of the eruptive vent) which stretch into fine filaments under the action of the wind, which can disperse over long distances under the action of the wind.
– A helicopter mission of the OVPF was organized this morning to recover the elements of a seismological station threatened by the various arms of lava flows which continue slowly their progress towards the east.
During the flyover at 11am this morning, the cone continued its construction and the hanging wall East, observed yesterday was gradually covered with fallout slag.
The cone, still south-facing, lets out a main stream in a deep channel (Figure 2). Lava tunnels were observed during formation in the most upstream part of this main channel (Figure 3).
Three regimes of lava fountains were still visible inside the cone.
Figure 2: Shooting of the eruptive site on September 22 at 11am (local time). (© OVPF / IPGP)
Figure 3: Shooting of the eruptive site on September 22 at 11am (local time). (© OVPF / IPGP)
Alert level: Alert 2-2 – Eruption in the Enclos .
Source : OVPF
Alaska , Semisopochnoi :
51°55’44 » N 179°35’52 » E,
Summit Elevation 2625 ft (800 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Unrest continues at Semisopochnoi volcano. Seismicity remains elevated, alternating between periods of continuous and intermittent bursts of tremor. Tremor bursts yesterday at 21:19 UCT (13:19 local) and today at 18:34 UTC (10:34 local) produced airwaves detected on a regional infrasound array on Adak Island. No volcanic activity was observed in cloudy satellite data around these times or in other imagery over the past day. A low cloud ceiling during this morning’s event suggest that ash emissions, if they occurred, remained below 7000 ft asl. The infrasound detections likely reflect a recent change in atmospheric conditions facilitating airwave propagation between Semisopochnoi and Adak, rather than a change in volcanic activity.
Semisopochnoi is monitored with an on-island seismic network, and remotely by satellite and lightning sensors. An infrasound array on Adak Island may detect explosive emissions from Semisopochnoi with a 13 minute delay if atmospheric conditions permit.
Source : AVO
Photo : Clifford, Roger
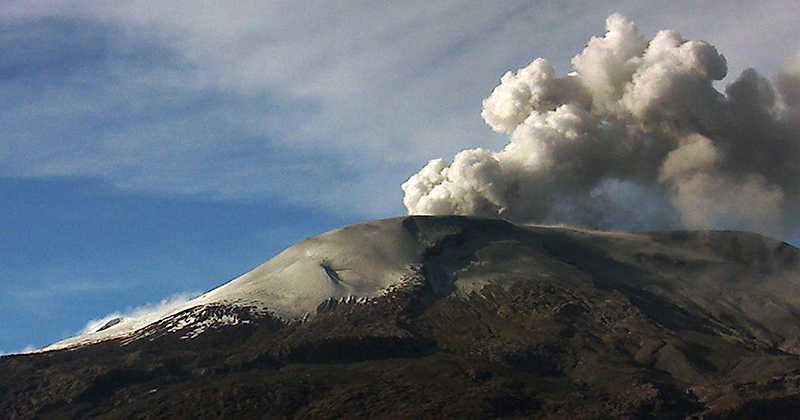
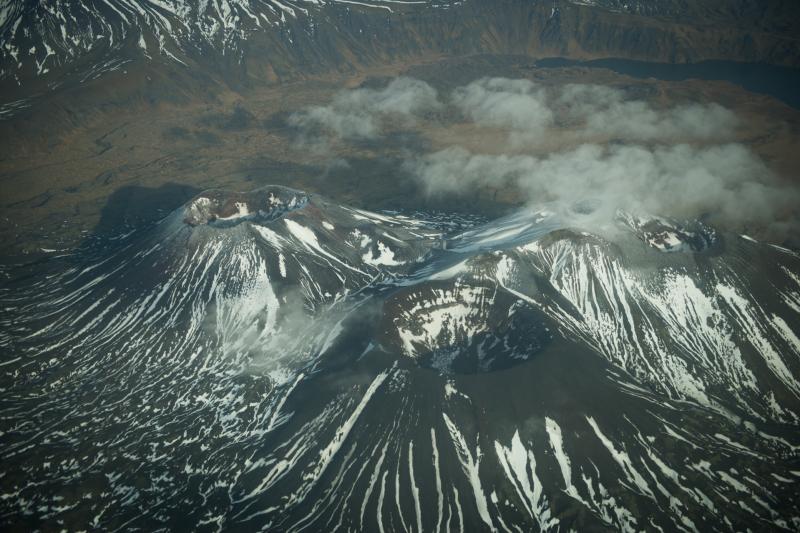
Kamchatka , Ebeko :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA).
Issued: September 23 , 2018 .
Volcano:Ebeko (CAVW #290380)
Current aviation colour code:ORANGE
Previous aviation colour code:orange
Source:KVERT
Notice Number:2018-92
Volcano Location:N 50 deg 41 min E 156 deg 0 min
Area:Northern Kuriles, Russia
Summit Elevation:3791.68 ft (1156 m)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
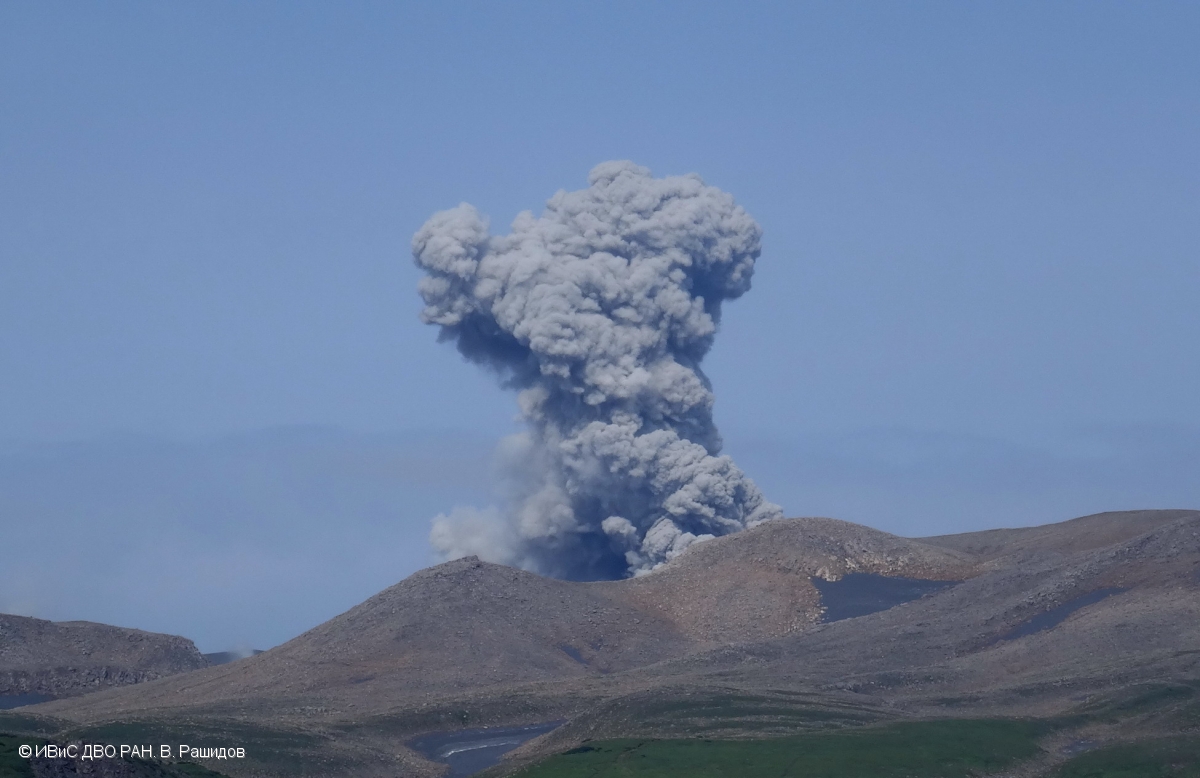
A moderate explosive activity of the volcano continues. Visual data from Severo-Kurilsk showed an explosion sent ash up to 3.5 km a.s.l., an ash plume is extending to the south-east from the volcano.
A moderate eruptive activity of the volcano continues. Ash explosions up to 19,700 ft (6 km) a.s.l. could occur at any time. Ongoing activity could affect low-flying aircraft and airport of Severo-Kurilsk.
Volcanic cloud height:
11480 ft (3500 m) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20180923/0215Z – Visual data
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 3 mi (5 km)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: SE
Source : Kvert
Photo : V. Rashidov, IVS FEB RAS , 2017 .