March 23 , 2025 .
Alaska , Spurr :
Unrest continues at Mount Spurr volcano. Seismicity remains elevated with numerous small, shallow volcanic earthquakes detected beneath the volcano over the past day. An AVO overflight conducted yesterday observed continued steaming from the summit fumaroles and gas emissions. Steaming from the summit was readily apparent in webcam and by eye from Anchorage last night and this morning.
Looking south toward Mount Spurr summit (foreground), taken during an overflight on March 17, 2025. A steam and gas cloud is rising from the fumaroles on the lakeshore within the depression at the summit. Crater Peak is the point just behind and to the left of the summit. Cook Inlet is on the horizon (left) and Mount Redoubt is partially cloud-obscured on the horizon directly behind Spurr summit.
AVO continues monitoring activity at Mount Spurr for signals indicating that the volcano is moving closer to an eruption. Based on previous eruptions, changes from current activity in the earthquakes, ground deformation, summit lake conditions, and fumarolic activity would be expected if magma began to move closer to the surface. Therefore, if an eruption occurred, it would be preceded by additional signals allowing warning.
The volcano is monitored using local seismic, infrasound, web camera, and GNSS stations along with regional infrasound, lightning networks and satellite data.
Source : AVO.
Photo : Ketner, Dane.
Indonesia , Dukono :
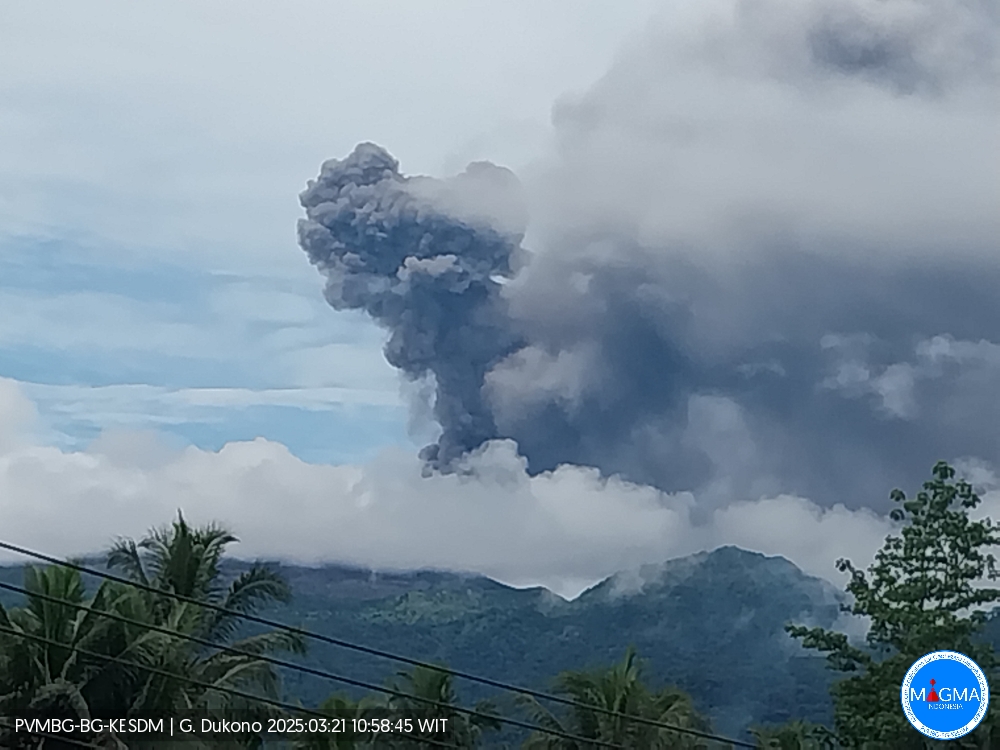
An eruption of Mount Dukono occurred on Friday, March 21, 2025, at 10:57 WIT with an observed ash column height of ± 1100 m above the peak (± 2187 m above sea level). The ash column was observed to be gray in color with a thick intensity, oriented northwest. At the time of writing, the eruption was still ongoing.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : March 21 , 2025
Volcano : Dukono (268010)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Dukono Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2025DUK038
Volcano Location : N 01 deg 41 min 35 sec E 127 deg 53 min 38 sec
Area : North Maluku, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 3478 FT (1087 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 01h57 UTC (10h57 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 6998 FT (2187 M) above sea level or 3520 FT (1100 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to northwest. Volcanic ash is observed to be gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 34 mm and maximum duration 52.93 second.
Source et photo : Magma Indonésie .
Chile , Lascar :
Special Volcanic Activity Report (REAV), Antofagasta region, March 22, 2025, 8:05 a.m. local time (Continental Chile)
The National Geology and Mining Service of Chile (Sernageomin) is publishing the following information, obtained using the monitoring equipment of the National Volcanic Monitoring Network (RNVV), processed and analyzed at the Southern Andean Volcanological Observatory (OVDAS).
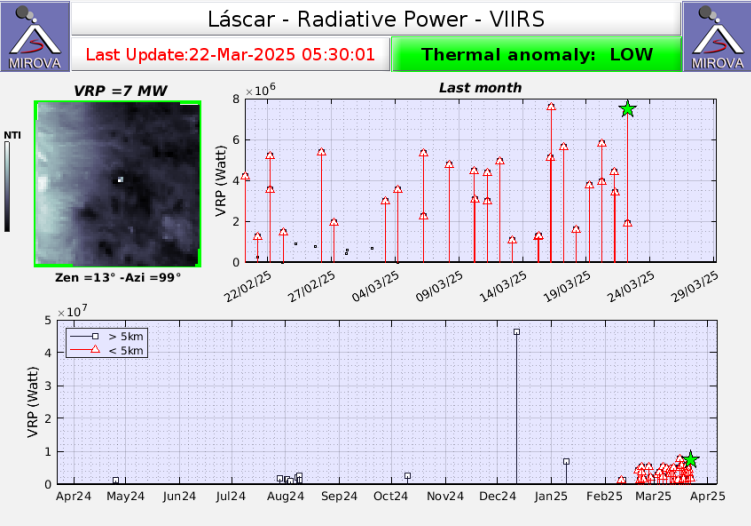
Yesterday, Saturday, March 22, the MIROVA platform ( www.mirovaweb.it) reported a 7.5 MW satellite thermal anomaly, detected by the VIIRS sensor, originating from the active crater. Meanwhile, Sentinel 2L2A satellite images updated through March 20, 2025, continue to record three areas of thermal radiation within the active crater, a pattern that has been occurring since February 6 of this year. Surveillance cameras installed around the volcano recorded whitish degassing, without pyroclastic emissions, and visible incandescence at night.
However, the seismological network installed near the volcano continues to record a decline in Long Period (LP) activity since early February. The volcano is in a state of surface activity instability that could potentially lead to the occurrence of minor explosions with an impact limited to the proximal zone of the active crater, and to the emission of pyroclastic material from low-energy eruptive columns.
The technical alert for this volcanic system remains at yellow alert.
Sernageomin continues its online monitoring and multiparameter tracking of the Lascar volcano, and promptly reports any significant changes in volcanic activity via official communication channels.
Source : Sernageomin
Photo : Mirova
Ecuador , Sangay :
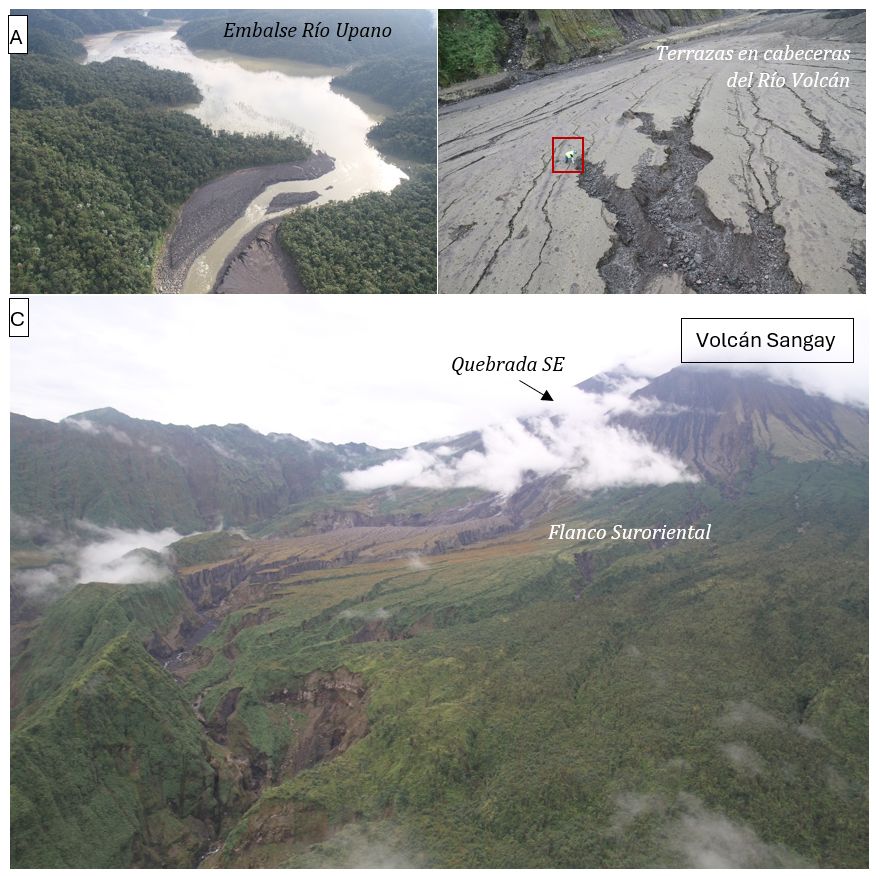
The Sangay volcano is one of the most active volcanoes in the Ecuadorian volcanic front. With an approximate height of 5,230 m, it is also one of the highest volcanoes in the Andes. From May 2019 to the present day, this volcano is experiencing one of its most significant eruptive periods, causing different types of damage at the local and regional level, due to the fall of ash and the generation of secondary lahars following the remobilization of the material deposited during the different eruptions, under the effect of rains.
Thanks to the availability of a helicopter, an inspection was carried out on the drainages of the Upano River and the Volcán River, with the reservoir (dam) formed in recent years. The photographs in Figure 2 show the Upano River dam, which has accumulated sediment, decreasing its depth (Figure 2.A); The second table shows in the Volcán River watershed, different deposits associated with the presence of lahars (Figure 2.B). The flanks of the Sangay Volcano (Figure 2.C) show the lower areas of the volcano, eroded by the impacts of phenomena (burning clouds, rock projectiles) associated with the explosive activity recorded during the eruptive process from 2019 to the present day.
Emission/Ash Column:
Since yesterday, no gas or ash emissions have been observed using surveillance cameras or satellite images. In light of this low activity, the Washington VAAC agency has also not issued any activity reports in the past 24 hours.
Observation:
No incandescent incidents have been observed in the past 24 hours using surveillance cameras. Furthermore, the volcano remained partially or completely cloudy most of the time.
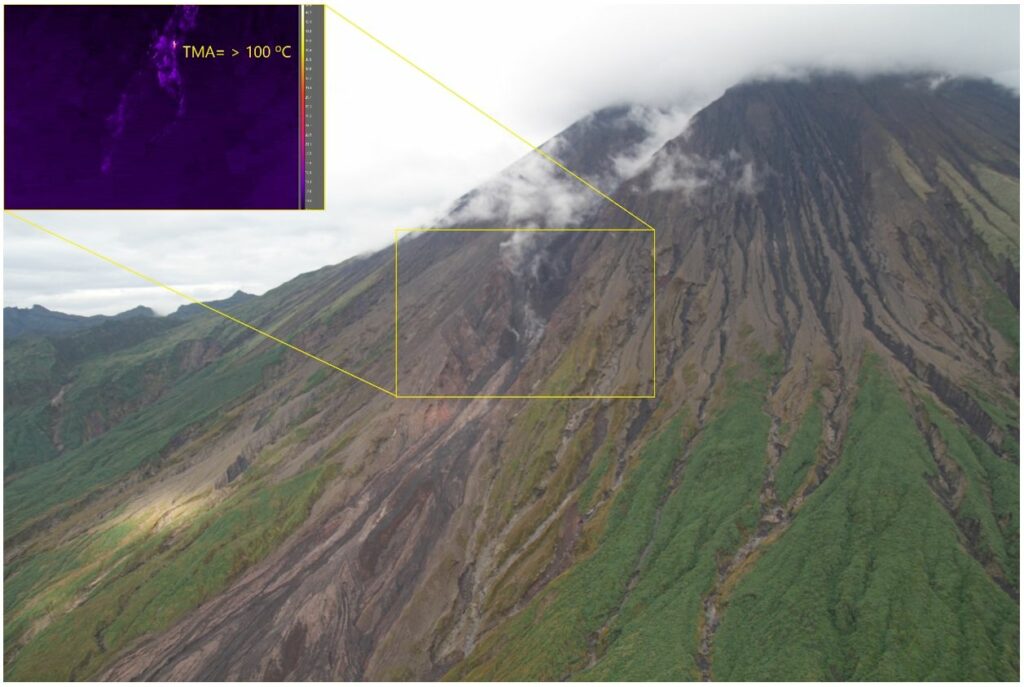
The use of infrared cameras allows for visualization of hot products emitted by the volcano, such as lava flows, incandescent rocks, burning clouds, or hot lahars. In this case, the figure shows in the yellow box the identification of hot rocks released by an active lava flow. All these products descend through the southeast ravine of the volcano.
Source : IGEPN
Photos : E. Gaunt/UCL , a) F. Naranjo, b) y c). M. Almeida.
Guatemala , Santiaguito :
Weather Conditions: Clear
Wind: Southeast.
Precipitation: 0.0 mm.
Activity:
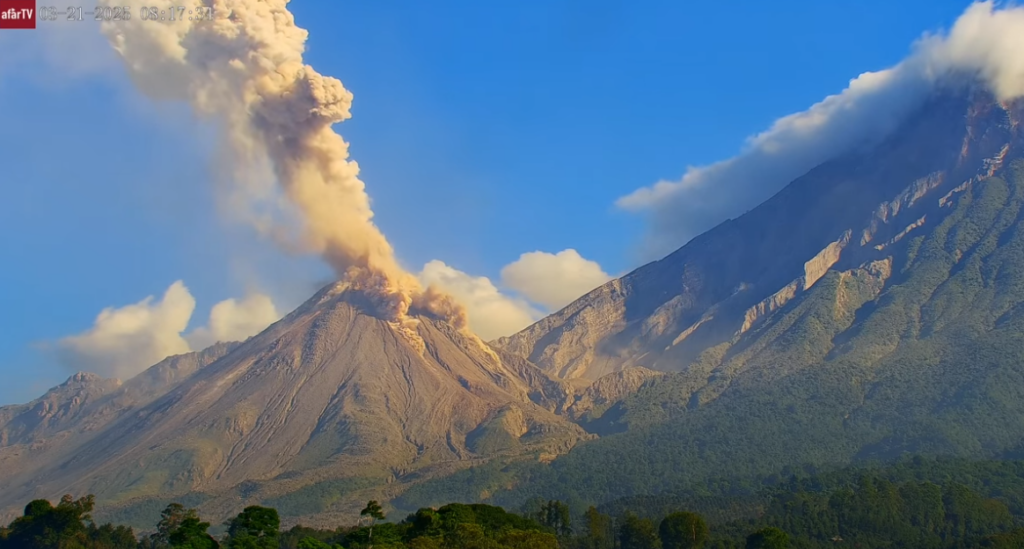
Outgassing is observed recurrently above the Caliente Dome, with increasing pulses forming gas columns up to 400 meters high. Weak to moderate explosions are recorded, which can cause incandescence and columns of gas and ash up to 3,500 meters above sea level (10,498 feet), as well as avalanches in south, southwest, and west directions.
The ash could spread 15 to 40 km to the west and northwest, potentially causing fine ashfall on farms and communities near the volcano, such as San Martín Sacatepéquez and central Quetzaltenango. The Santiaguito volcano continues to be very active. Therefore, the presence of moderate to strong block and ash flows, as well as possible long-distance pyroclastic flows in different directions, cannot be ruled out. It is therefore advisable to follow the recommendations of special bulletin BESAN-002-2025.
Source : Insivumeh
Photo : Capture écran Afar tv.