January 02 , 2025.
Le Chaudron wishes you all a happy new year 2025.
Hawaii , Kilauea :
Wednesday, January 1, 2025, 8:34 AM HST (Wednesday, January 1, 2025, 18:34 UTC)
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
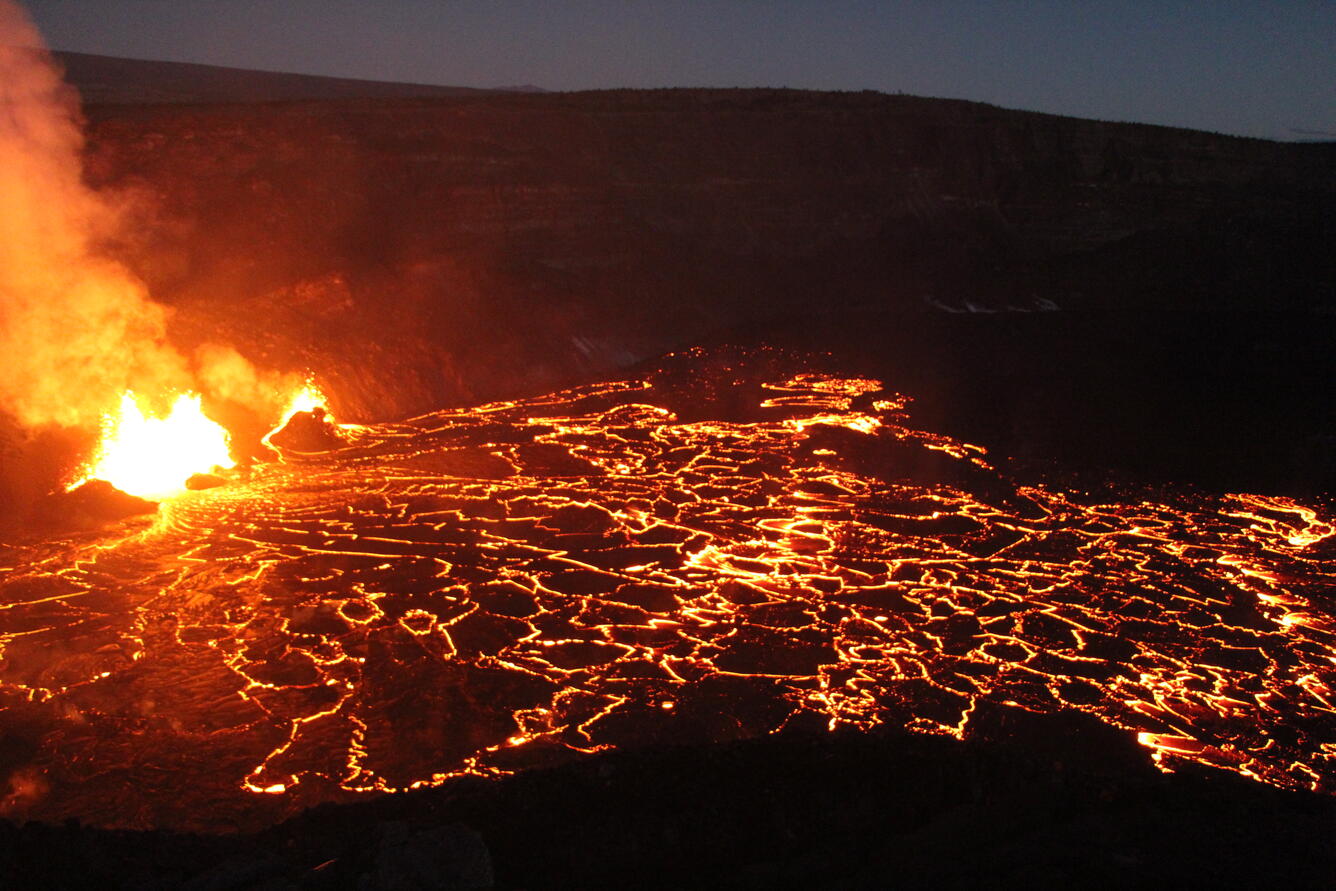
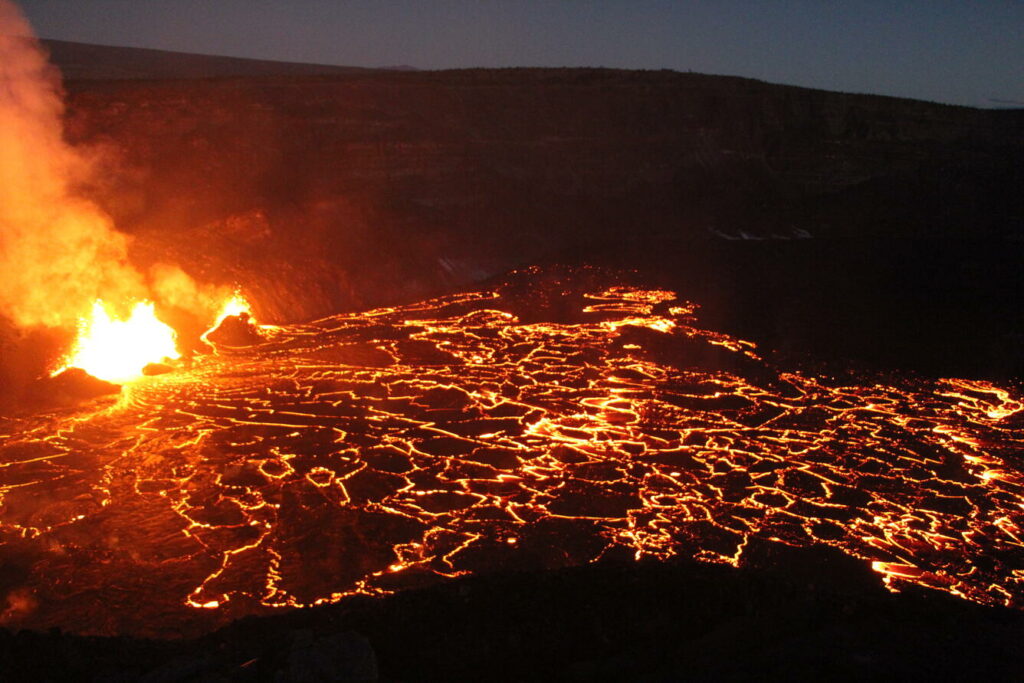
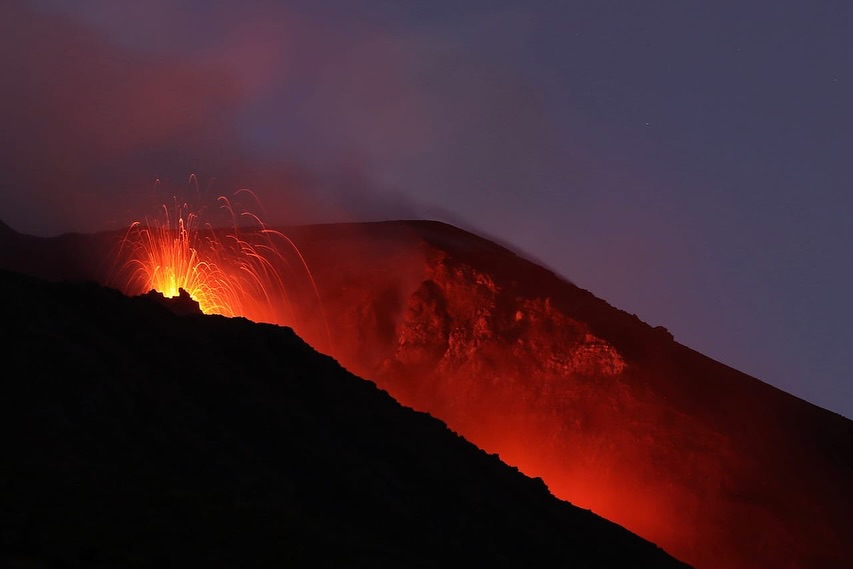
Photo of the lava fountains and flows within the western part of Halema‘uma‘u crater just before dawn on December 30, 2024. The lava fountains have started to build scoria cones around themselves with the fountains consistently reaching to 30 m (100 ft) high. These fountains are feeding lava flows that have covered the western quarter of the crater floor.
Activity Summary:
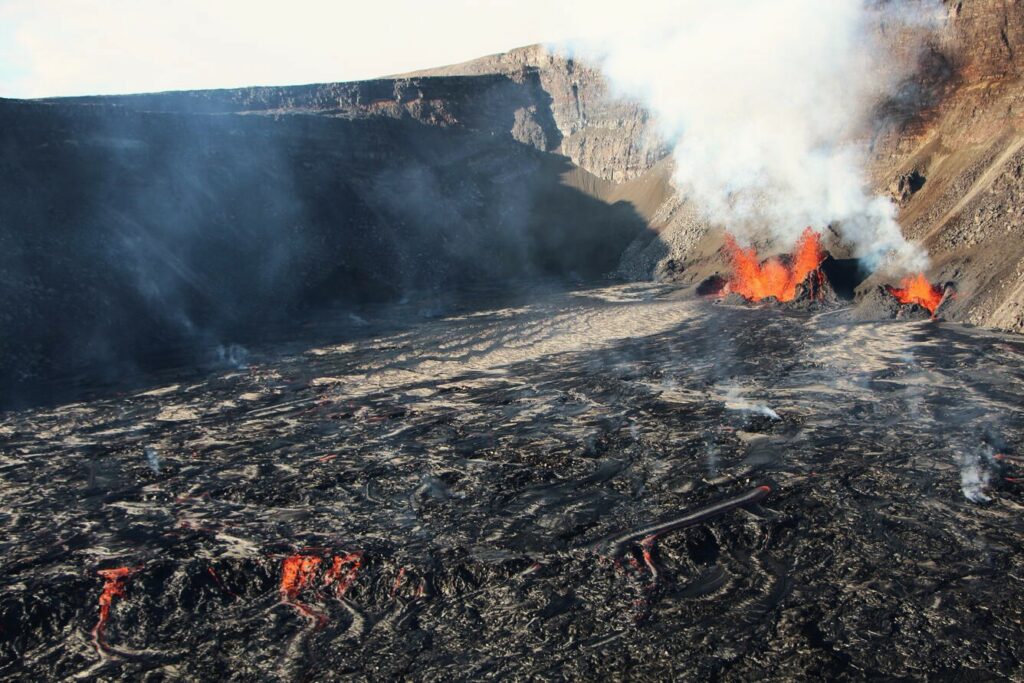
The eruption at Kīlauea volcano that began on Monday, December 23, continues this morning. Over the past day, vents in the southwest portion of the caldera have continued producing a fan of lava flows covering the western portion of the crater floor during sustained lava fountaining. Eruptive activity has been confined to Halemaʻumaʻu and the down-dropped block within the caldera. No unusual activity has been noted along Kīlauea’s East Rift Zone or Southwest Rift Zone.
Summit Instrumental Observations:
Seismicity at the summit over the last 24 hours has been low with 5 small detected earthquakes and none in the upper ERZ or SWRZ. Seismic tremor remains increased during this period of lava fountaining but has remained constant over the past 24 hours. Summit tiltmeters continue to record deflationary tilt that began just after midnight on December 29. SO2 emissions remain elevated, with a gas plume rising above the caldera this morning that is being carried to the southwest.
Aerial view looking to the southwest of the active eruption in Halema‘uma‘u crater on December 30, 2024. The lava fountains are reaching up to 30 m (100 ft) high and feeding the incandescent lava in the foreground. The current activity is concentrated in the western quarter of the crater floor.
Summit Eruption Observations:
Webcam images indicate that the eruption within Kaluapele (the summit caldera) continues this morning from vents on the southwest side of Halemaʻumaʻu crater. Effusion of lava over the past day has produced a broad area of flows that cover the western portion of the crater, with an increase in the area of active flows over the past day. HVO geologists in the field on the morning of December 31, 2024 report fountain reaching about 20-30 m (65-100 ft) high, which is also the case for the lava fountains this morning.
Rift Zone Observations:
Shallow earthquake counts on the East Rift Zone (ERZ) remain at low levels. Over the last 24 hours, there were no earthquakes in the East Rift Zone. The ESC tiltmeter in the upper part of the East Rift Zone shows deformation associated with the ongoing summit eruption. Deformation rates remain low in the middle and lower East Rift Zone and Southwest Rift Zone as recorded by GPS instruments and tiltmeters.
Source : HVO.
Photos : U.S. Geological Survey geologist D. Downs.
Chile , Tatara- San Pedro :
Special Report on Volcanic Activity (REAV), Maule Region, Tatara-San Pedro Volcano, December 29, 2024, 07:00 local time (continental Chile).
The National Geology and Mining Service of Chile (Sernageomin) publishes the following PRELIMINARY information, obtained through the monitoring equipment of the National Volcanic Monitoring Network (RNVV), processed and analyzed at the Volcanological Observatory of the Southern Andes (Ovdas):
Three seismic events occurred on the Tatara-San Pedro Volcano:
1/ On Sunday, December 29, 2024, at 06:28 local time (09:28 UTC), the monitoring stations installed in the vicinity of the Tatara-San Pedro Volcano recorded an earthquake associated with the fracturing of rocks within the volcanic system (volcano-tectonic type).
2/ On Tuesday, December 31, 2024, at 15:52 local time (18:52 UTC), monitoring stations installed in the vicinity of the Tatara-San Pedro volcano recorded an earthquake associated with rock fracturing within the volcanic system (volcano-tectonic type).
3/ On Tuesday, December 31, 2024, at 17:36 local time (20:36 UTC), monitoring stations installed in the vicinity of the Tatara-San Pedro volcano recorded an earthquake associated with rock fracturing within the volcanic system (volcano-tectonic type).
The characteristics of these earthquakes after their analysis are as follows (in order):
TIME OF ORIGIN: 06:28 local time (09:28 UTC), Sunday, December 29, 2024
LATITUDE: 36.035° S
LONGITUDE: 70.886° West
DEPTH: 3.8 km
LOCAL MAGNITUDE: 3 (ML)
TIME OF ORIGIN: 15:52 local time (18:52 UTC), Tuesday, December 31, 2024
LATITUDE: 36.029° S
LONGITUDE: 70.892° West
DEPTH: 4.1 km
LOCAL MAGNITUDE: 3.7 (ML)
TIME OF ORIGIN: 17:36 local time (20:36 UTC), Tuesday December 31, 2024
LATITUDE: 36.029° S
LONGITUDE: 70.893° West
DEPTH: 3.9 km
LOCAL MAGNITUDE: 3.2 (ML)
OBSERVATIONS:
Both before and after this event, other rigid material fracture earthquakes (VT) were recorded, all of low energy.
The volcanic technical alert remains at Green level.
Sources : Sernageomin.
Photo : Oscar González-Ferrán (University of Chile).
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from December 23, 2024 to December 29, 2024. (issue date December 31, 2024)
SUMMARY STATUS OF ACTIVITY
In light of the monitoring data, it appears:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Ordinary explosive activity with a frequency of total explosive activity at a low level, coupled with effusive activity from the lava overflow from the North Crater area. The intensity of the explosions was low to medium in the North Crater area and medium in the Center-South area.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The monitored seismological parameters do not show significant variations, with the exception of the slightly more intense than normal explosion recorded at 05:14 UTC on 12/24, followed by an increase in the tremor amplitude.
3) SOIL DEFORMATIONS: The soil deformation monitoring networks have not shown significant changes over the past week.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux updated for the period from 16 to 22 December at an average level
The soil CO2 flux in the Pizzo area (STR02) shows average values.
The CO2/SO2 ratio in the plume (Stromboli Plume Network) shows high values.
The isotopic ratio of helium (R/Ra) dissolved in the thermal aquifer is increasing compared to the last sampling.
Soil CO2 flux in the San Bartolo area at medium-high values.
Soil CO2 flux in the Scari area at average values.
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally low to moderate with some high-level thermal anomalies corresponding to the intensification of eruptive activity in the North Crater area on 26 December 2024.
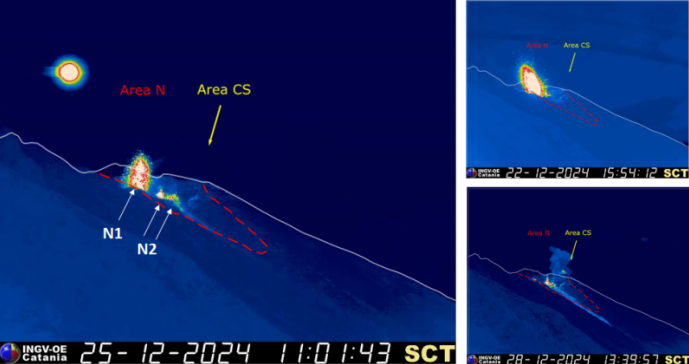
The crater terrace seen from the thermal camera located at an altitude of 190 m with the delimitation of the crater areas South-Central Zone and North Zone (ZONE N, ZONE CS respectively). The arrows indicate the locations of the active vents. On the right, an explosive event produced by the N crater area and the CS filmed by the SCT camera located at 190 meters.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the week, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized thanks to the analysis of the images recorded by the INGV-OE surveillance cameras located at an altitude of 190 m (SCT-SCV) and at Punta dei Corvi (SPCT). The explosive activity was mainly produced by 4 eruptive chimneys located in the North area of the crater and by 3 chimneys located in the South-Central area.
Observations of the explosive activity captured by the surveillance cameras.
In the North Crater area, eruptive activity was produced by four vents with low intensity explosions (less than 80 m in height) and episodically medium (less than 150 m in height), with a mainly coarse component of the erupted material (bombs and lapilli). The vents of the N2 sector continued to present a variable regime spattering activity that, during high intensity transients, produced 4 events of effusive activity from lava overflow. In the Central-South area, explosive activity was produced by at least three chimneys with explosions of intensity varying from medium (less than 150 m in height) to high (more than 250 m in height) emitting fine materials sometimes mixed with coarse materials. The overall average frequency of explosions in both areas remained at a low level.
Effusive activity due to lava overflow (times in GMT)
Between 24 and 26 December, during the phases of intense spattering activity at the N2 mouth of the North Crater area, lava emissions from the crater overflow occurred. The effusive activity was characterized by variable-regime lava flows that propagated along the ravine formed on the Sciara del Fuoco during the eruptive activity of July 2024, remaining confined to the upper part of the Sciara without reaching the coastline. Among the 4 episodes, those of 24 and 26 December stand out for the intensity of the spattering manifested in the early phases of the lava overflow. In detail, the event of 24 December begins at 05:14 with an N2 explosion that distributes the products of the eruption with fallout and expansion of the material in the ravine of the Sciara del Fuoco; Effusive activity ends at 08:00. The activity on December 26 begins as usual at the peak of intense spattering activity that began at 18:37, which rapidly increases in intensity and gradually evolves into a fountaining regime from 18:46 to 19:10. Lava overflow begins at 18:52, characterized by a high effusion rate that sometimes produces landslides from the lava front to the coastline (e.g., 19:36). The event ends at 02:50 on December 27. The activity on December 25 was also triggered by intense spattering that generated two minor overflows that occurred between 02:50 and 05:00 and between 22:09 and 22:40.
Source : INGV
Photos : INGV , Thomas Bretscher via Stromboli stati d’animo.
Indonesia , Lewotobi Laki-laki :
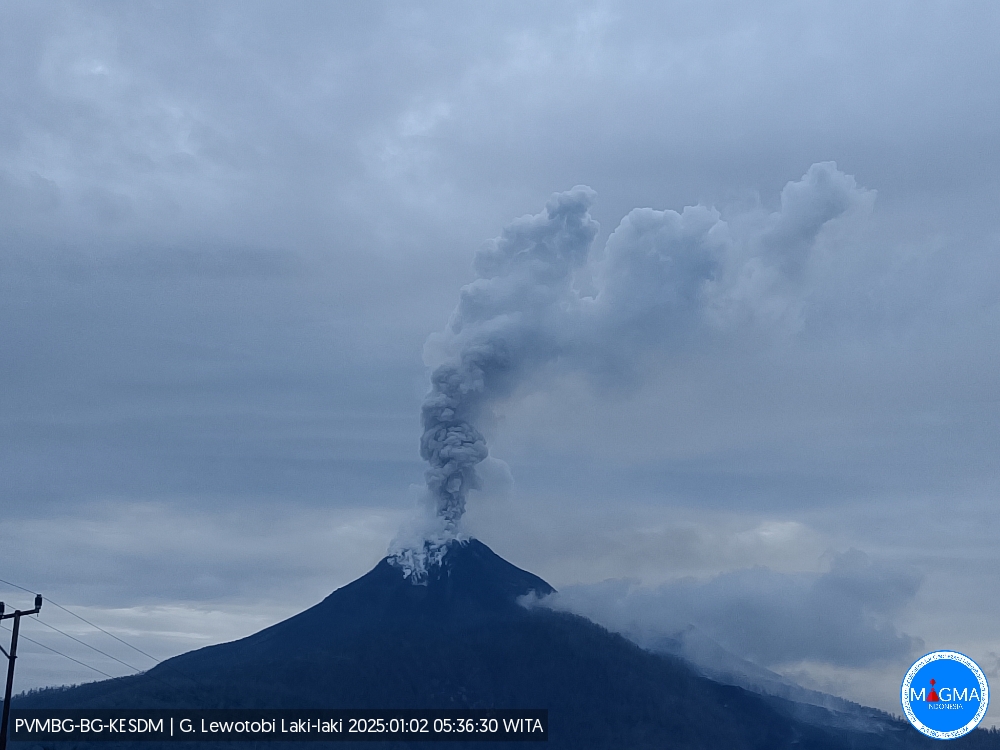
An eruption of Lewotobi Laki-laki occurred on Thursday, January 2, 2025 at 05:34 WITA with the height of the ash column observed at ± 1000 m above the summit (± 2584 m above sea level). The ash column was observed to be gray in color with a thick intensity, oriented towards the Southwest. This eruption was recorded on a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 11 mm and a duration of 67 seconds.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : January 02 , 2025
Volcano : Lewotobi Laki-laki (264180)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Lewotobi Laki-laki Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2025LWK002
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 32 min 20 sec E 122 deg 46 min 06 sec
Area : East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 5069 FT (1584 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 21h34 UTC (05h34 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 8269 FT (2584 M) above sea level or 3200 FT (1000 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to southwest. Volcanic ash is observed to be gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 11 mm and maximum duration 67 second.
Source et photo : Magma Indonésie.
Tonga Islands , Home Reef :
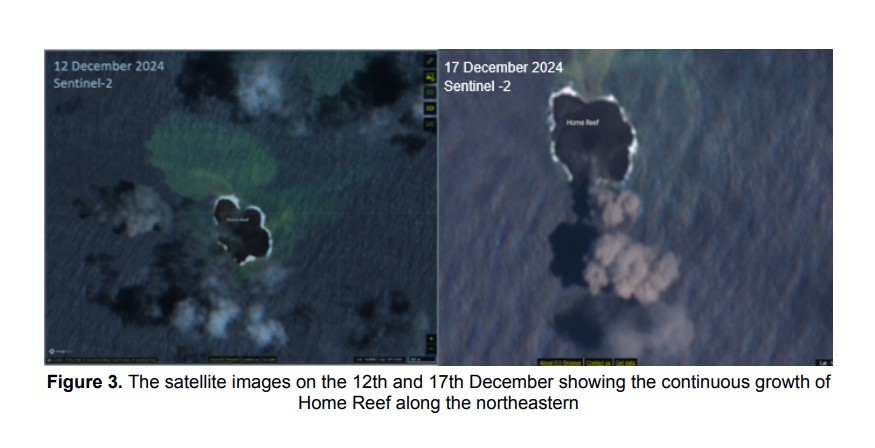
Tonga Geological Services reported that eruptive activity at Home Reef continued as of 24 December. Satellite data processed by the MIROVA monitoring system showed ongoing thermal anomalies. Sentinel-2 images indicated that the NE part of the island grew by at least 1,000 square meters between 7 and 12 December. The new lava had covered approximately 75,000 square meters by 15 December, including the previously existing island and the new NE area.
Satellite imagery on 15 December showed white and gray emissions above the volcano. The Maritime Alert Level remained at Orange (the third level on a four-level scale), and mariners were advised to stay at least 4 km away from the island. The Aviation Color Code was raised to Yellow (the second level on a four-level scale), and the Alert Level for residents of Vava’u and Ha’apai remained at Green (the first level on a four-level scale).
Home Reef, a submarine volcano midway between Metis Shoal and Late Island in the central Tonga islands, was first reported active in the mid-19th century, when an ephemeral island formed. An eruption in 1984 produced a 12-km-high eruption plume, large amounts of floating pumice, and an ephemeral 500 x 1,500 m island, with cliffs 30-50 m high that enclosed a water-filled crater. In 2006 an island-forming eruption produced widespread dacitic pumice rafts that drifted as far as Australia. Another island was built during a September-October 2022 eruption.
Sources: Matangi Tonga Online, Tonga Geological Services, Government of Tonga , GVP.
Photos : Tonga Geological Services, Government of Tonga. GVP / P.J.R. Shepherd (Royal New Zealand Air Force; courtesy of John Latter, DSIR, published in SEAN Bull., 1984).