March 24 , 2022.
Azores , São Jorge :
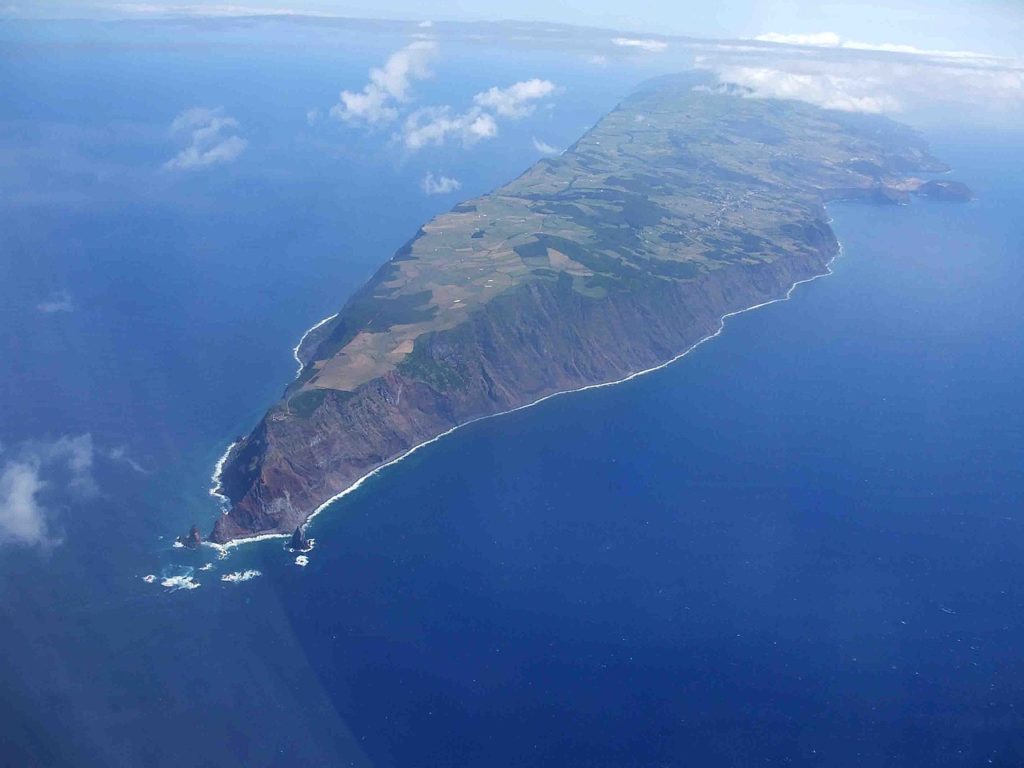
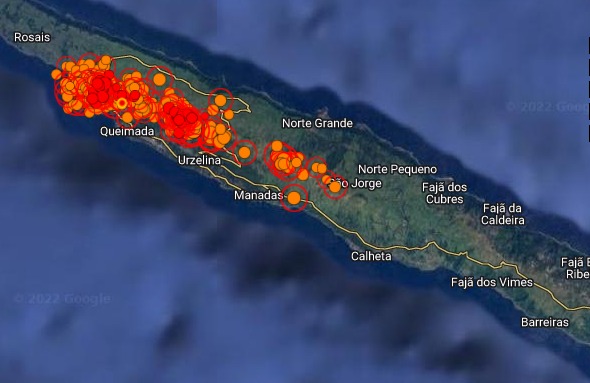
On March 19, an earthquake measuring 2.9 on the Richter scale was felt on the island of São Jorge in the Azores. Since then, seismic activity on the island has increased significantly and remains above baseline values, and on Tuesday alone more than 1,800 earthquakes were recorded.
On Sunday, the local CIVISA reported that in 24 hours it had recorded about seven hundred earthquakes, all of low magnitude, following the seismic crisis that originated on Saturday in the fissured volcanic system of Manadas, on the São Jorge Island. However, only 48 had been felt by the population.
This fissure system, which coincides with the major volcanic cones on the island, is still active and has now recorded an unusual release of energy in recent years.
In order to closely follow the evolution of the seismic crisis – which is occurring in an area located between the village of Velas, in the southern part of the island of São Jorge, and Fajã do Ouvidor, on the northern coast – four technicians from CIVISA were sent to the island. Two seismic stations were also transported, joining the two that already existed in São Jorge. The seismic activity is at a depth of between six and 12 kilometers, which « does not indicate any imminent risk of volcanic activity ».
The Chief Executive, who is expected to travel to São Jorge Island on Thursday due to the seismic crisis, noted that the earthquakes « are very deep ». “What is worrying is that these earthquakes are in the tectonic mass of the island itself,” he said.
Bolieiro also reiterated that the recorded swarm « has been tectonic », but said that if « cracks are created in the rock », it « may evolve into a volcanic situation ».
“Opening cracks can allow magma to find an opportunity to climb up the cracks,” he said, saying he had a meeting with CIVISA at the University of the Azores.
According to the IPMA, « the origin of this earthquake can be linked to the rise of magma in a magmatic dyke, a phenomenon that causes the fragmentation of rocks at depth which results in the release of elastic energy in the form of earthquake « .
The Azores Seismo-Volcanic Information and Monitoring Center (CIVISA) on Wednesday raised the volcanic alert level on the island of São Jorge to V4 (out of a total of five), which means « real possibility of eruption,” the regional government said.
“Today at 3:30 p.m. [4:30 p.m. in Lisbon] the volcanic alert has been reported to rise to level V4, which means a real possibility of an eruption,” said Azores regional health secretary Clélio. Meneses, who oversees civil protection, during a press conference in Angra do Heroísmo, on the island of Terceira.
Sources : 24.sapo.pt , Observador.pt
Photos : Civisa , José Luís Ávila Silveira/Pedro Noronha e Costa (wikipedia).
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from March 14, 2022 to March 20, 2022. (issue date March 22, 2022)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
In the light of the surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Degassing activity of the summit craters.
2) SEISMOLOGY: Seismic activity of fracturing characterized by an event of M = 3.3. Average amplitude of the tremor at the average level.
3) INFRASOUND: Moderate infrasound activity.
4) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: Ground deformation monitoring networks have not recorded any significant changes over the past week.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux at a low level.
Soil CO2 flux shows average values.
The partial pressure of dissolved CO2 in groundwater shows values in seasonal variability.
There are no updates on the isotope ratio of helium. The latest available data showed high values (data from March 08, 2022).
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity in the summit area was at a low level after the lava fountain on Feb 21, 2022.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the week in question, the monitoring of Etna’s volcanic activity was carried out through the analysis of images from the network of surveillance cameras of the INGV, Osservatorio Etneo (INGV-OE) and through an inspection in the summit area.
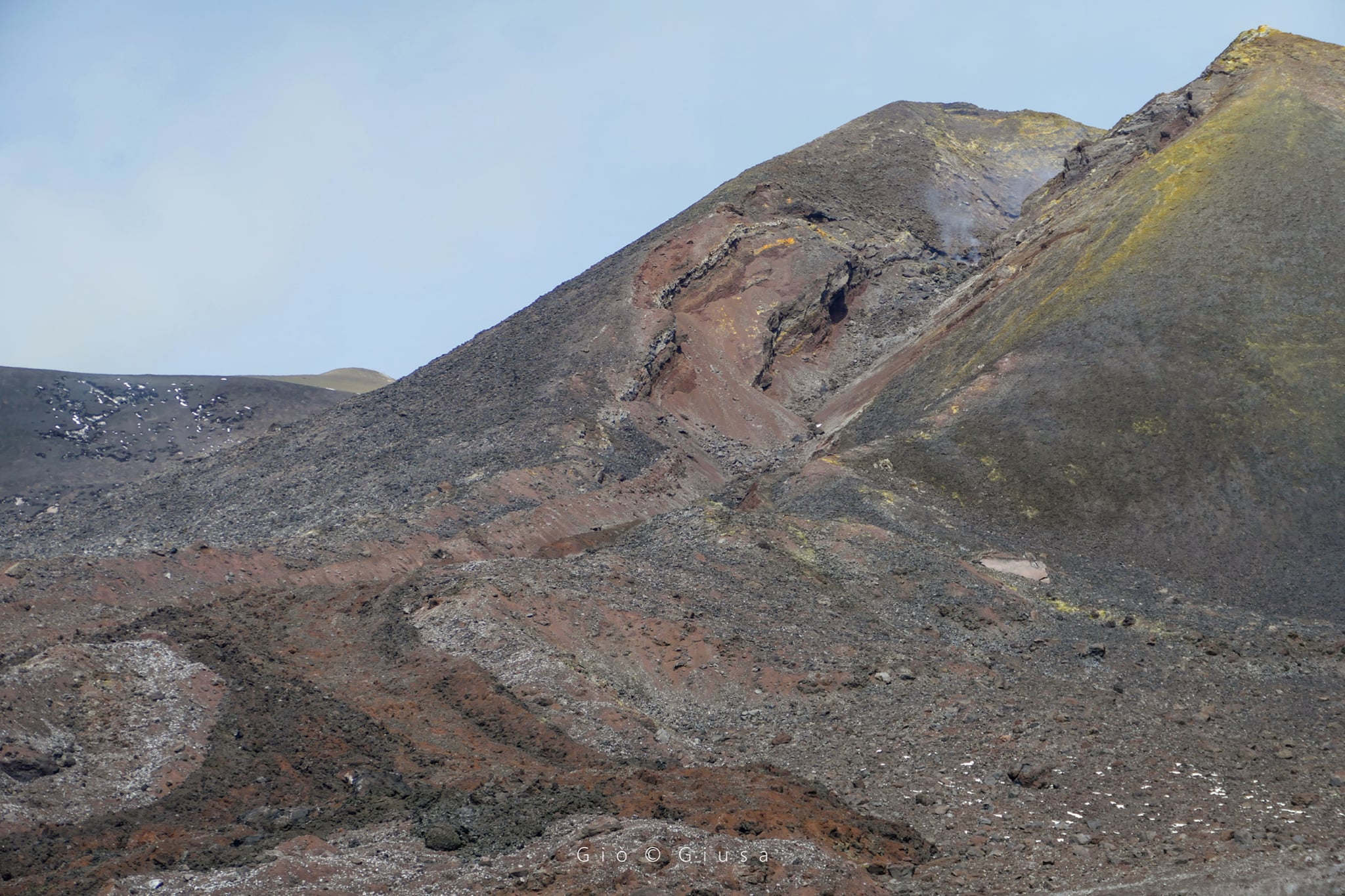
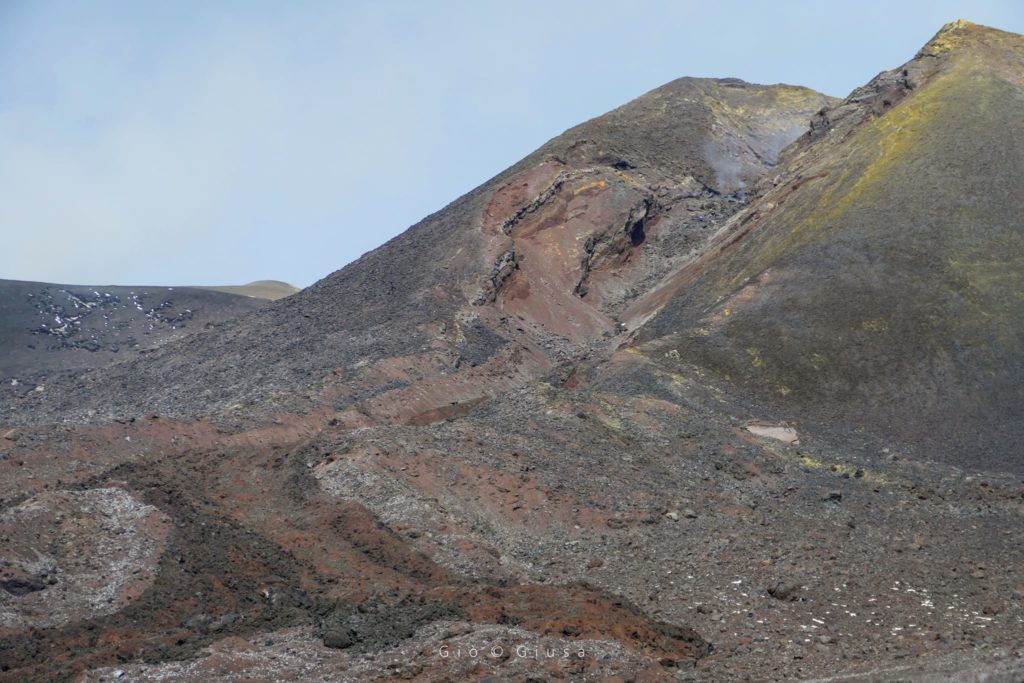
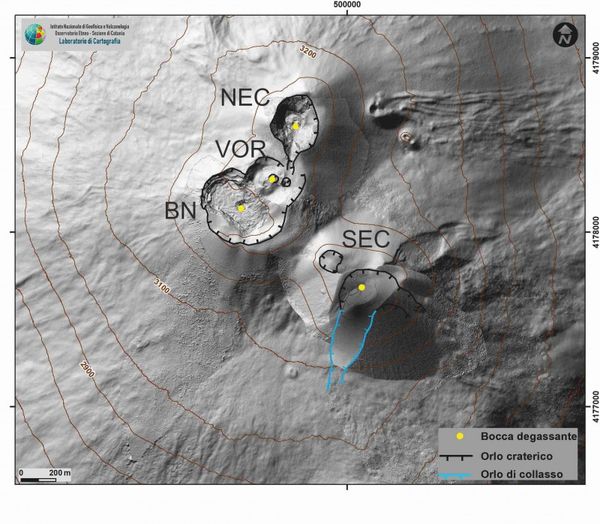
Overall, the state of activity of the summit craters showed no change from what was observed the previous week (see Rep. N. 11/2022). In particular, the degassing activity of the summit craters was mainly carried out by the collapse crater located in the North-West sector of Bocca Nuova (BN in the Fig.), characterized by an intense sometimes impulsive degassing.
The Voragine craters and the Northeast crater, on the other hand, showed a predominant degassing linked to the fumarole systems present along the edges of the crater.
Finally, the Southeast crater was affected by a small ash emission on the morning of March 18, which occurred at the base of the breached part of the southern slope of the cone.
Source : INGV.
Photos : INGV , Gio Giusa .
Indonesia , Anak Krakatau :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : March 24 , 2022
Volcano : Anak Krakatau (262000)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : yellow
Source : Anak Krakatau Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2022KRA14
Volcano Location : S 06 deg 06 min 07 sec E 105 deg 25 min 23 sec
Area : Lampung, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 502 FT (157 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud observed at 04h10 UTC (11h10 local). Eruption and ash emission is still continuing.
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 4205 FT (1314 M) above sea level, may be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Volcanic ash cloud is moving south, as observed from a CCTV at Sertung Island.
Remarks :
Volcanic activity is dominated by tremor. The volcanic tremor is still ongoing.
The volcano is clearly visible. The observable smoke from the crater is white with low intensity about 50 meters above the summit. The weather is sunny, the wind is weak to moderate from the North-East. The air temperature is around 16-25°C. Humidity 63-69%.
Seismicity is linked to magma and tectonic activity. It was recorded:
– 68 emission earthquakes.
Mount Anak Krakatau experienced two eruptions this afternoon. During the second eruption, the height of volcanic ash reached 1,000 meters.
The first eruption occurred at 09:12 WIB. The ash column during the first eruption reached 500 meters above the summit or 657 meters above sea level.
the second eruption occurred at 11:10 a.m. WIB. This second eruption was recorded as larger than the first. Its plumes of volcanic ash reached a height of 1,000 meters.
Sources : Magma Indonésie , PVMBG. Detik.com.
Photo : Archive PVMBG.
Japan , Suwanosejima :
JMA reported that eruptive activity continued to be recorded at Suwanosejima’s Ontake Crater during 14-21 March. As many as 27 explosions were recorded, and crater incandescence was visible nightly. Eruption plumes rose as high as 1.9 km above the crater rim and ejected blocks 300-500 m away from the crater. Ashfall was reported as far as 5 km away, including in Toshima village (3.5 km SSW) during 18-21 March. The Alert Level remained at 3 and the public was warned to stay 2 km away from the crater.
The 8-km-long, spindle-shaped island of Suwanosejima in the northern Ryukyu Islands consists of an andesitic stratovolcano with two historically active summit craters. The summit is truncated by a large breached crater extending to the sea on the east flank that was formed by edifice collapse. Suwanosejima, one of Japan’s most frequently active volcanoes, was in a state of intermittent strombolian activity from Otake, the NE summit crater, that began in 1949 and lasted until 1996, after which periods of inactivity lengthened. The largest historical eruption took place in 1813-14, when thick scoria deposits blanketed residential areas, and the SW crater produced two lava flows that reached the western coast. At the end of the eruption the summit of Otake collapsed forming a large debris avalanche and creating the horseshoe-shaped Sakuchi caldera, which extends to the eastern coast. The island remained uninhabited for about 70 years after the 1813-1814 eruption. Lava flows reached the eastern coast of the island in 1884. Only about 50 people live on the island.
Source : GVP.
Photo : N. Geshi. Geological Survey of Japan, H.Seo.
Hawaii , Kilauea :
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Activity Summary:
The summit eruption of Kīlauea Volcano, within Halemaʻumaʻu crater, continued over the past 24 hours. All recent activity has been confined to the crater, and there are no indications of activity migrating elsewhere on Kīlauea.
Halemaʻumaʻu Lava Lake Observations:
Eruption of lava from the western vent into the active lava lake (approximately 2.5% of Halemaʻumaʻu crater floor surface) continued over the past 24 hours. There were also oozeouts along the northern margin of the crater floor. Since the beginning of this eruption on September 29, 2021, the crater floor has seen a total rise of about 89 meters (292 feet). The volume of lava effused since the beginning of this eruption was approximately 58 million cubic meters (76 million cubic yards) as measured on March 17, 2022.
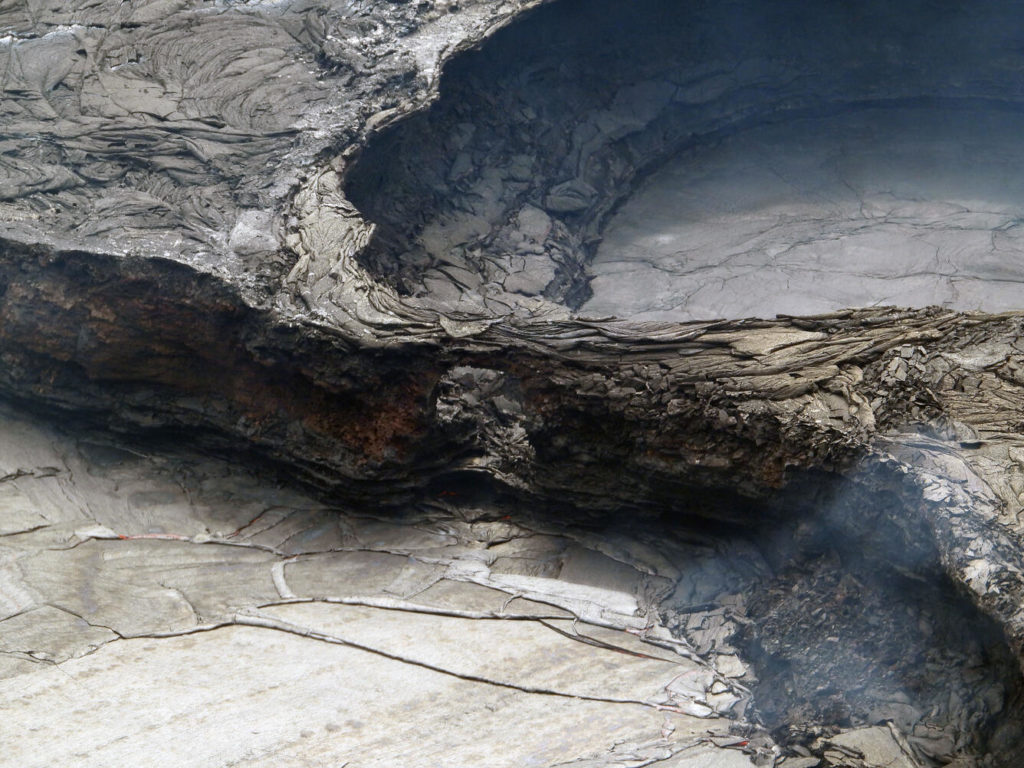
A small bridge of lava 3 meters (10 feet) in height is left behind during a lull in activity within Halema‘uma‘u crater at Kīlauea’s summit. The repeated ebb and flow of lava into the active lake surface has caused the pond behind this feature to start pinching off from the main part of the active lake that fills with lava when activity is more vigorous. This telephoto picture was taken from the western rim of Halema‘uma‘u.
Summit Observations:
Summit tiltmeters have been recording minor inflation since about 5:00 a.m. this morning, following a period of deflation that began on the evening of March 21, 2022. Seismic data show that volcanic tremor remains above background levels. A sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission rate of approximately 1900 tonnes per day (t/d) was measured on March 10.
Source : HVO.
Photo : USGS / L. Gallant.