July 10 , 2025.
Hawaii , Kilauea :
HVO/USGS Volcanic Activity Notice
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Issued: Wednesday, July 9, 2025, 5:11 AM HST
Source: Hawaiian Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2025/H305
Location: N 19 deg 25 min W 155 deg 17 min
Elevation: 4091 ft (1247 m)
Area: Hawaii
Volcanic Activity Summary:
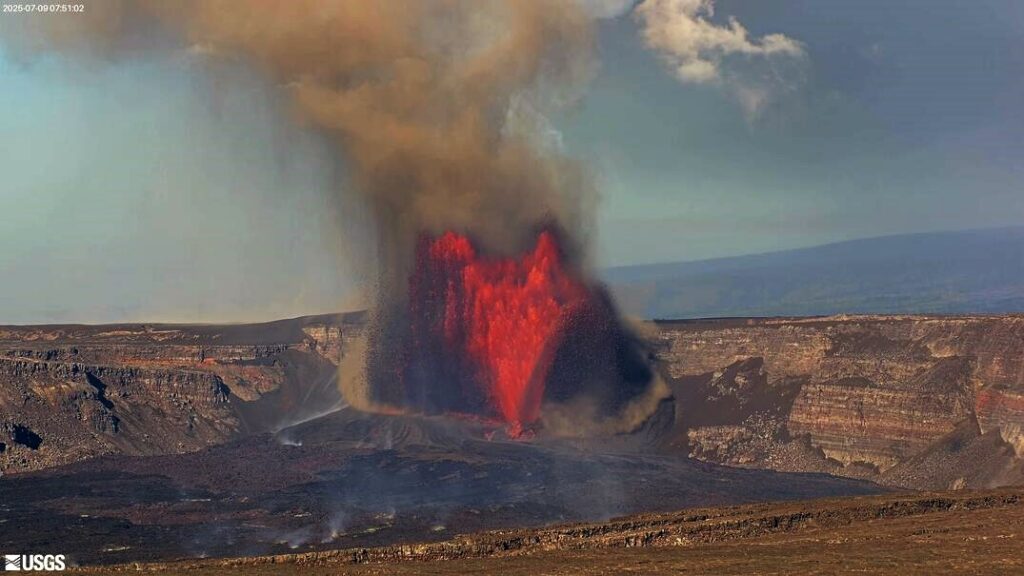
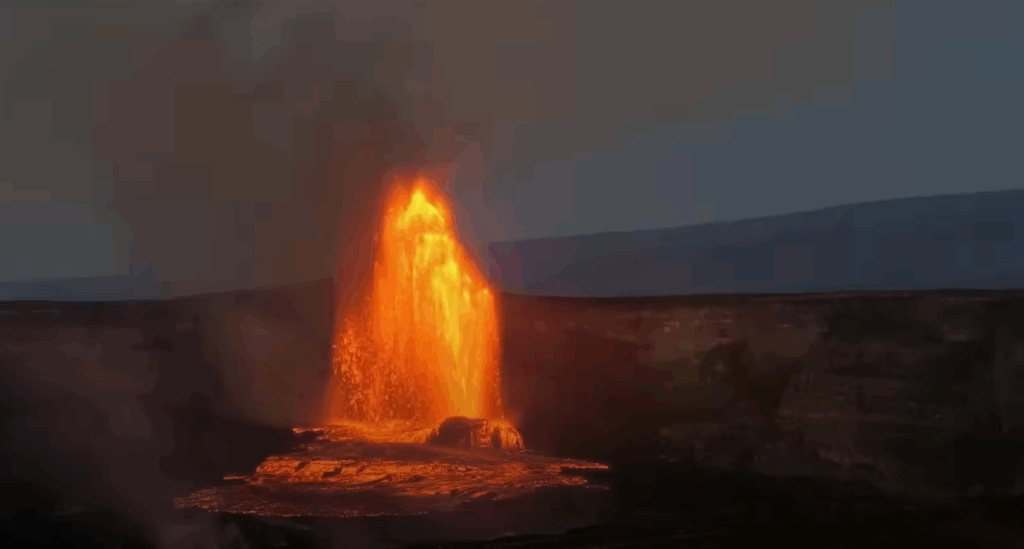
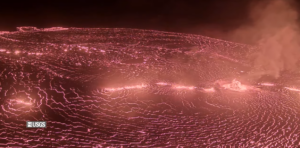
Episode 28 of the ongoing Halemaʻumaʻu eruption began at 4:10 a.m. HST on July 9 and is currently exhibiting a vent overflow and fountains reaching roughly 150 feet (45 meters). Past episodes have produced incandescent lava fountains over 1000 feet (300 meters) high that result in eruptive plumes up to 20,000 feet (6000 meters) above ground level. High fountaining associated with this episode has not yet begun but is expected to start soon, as tremor, deflation, and fountain height are all increasing. According to USGS weather stations just southwest of the summit, winds are blowing from the north-northeast direction at approximately 15 miles per hour, which suggests that volcanic gas emissions and volcanic material will be distributed south-southwest. Such trade winds typically turn more to the northeast during daylight hours.
All eruptive activity is confined to Halemaʻumaʻu crater within Hawaiʻi Volcanoes National Park
Episode 28 was preceded by gas pistoning cycles, some of which produced small lava overflows at the north vent yesterday. Fountains from the north vent are currently 150 feet (45 meters) high and feeding multiple lava streams at 5 a.m. HST.
Inflationary tilt reached approximately 14 microradians since the end of the last episode. Seismic tremor began increasing and tilt at UWD switched from inflationary to slightly deflationary at about 4:15 a.m. HST, a few minutes after lava flows began erupting onto the crater floor.
information
No changes have been detected in the East Rift Zone or Southwest Rift Zone. A VAN/VONA will be issued when sustained lava fountaining ceases and the eruption is paused, or earlier if the situation warrants a further update.
HVO/USGS Volcanic Activity Notice
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Issued: Wednesday, July 9, 2025, 1:49 PM HST
Volcanic Activity Summary:
Episode 28 of the ongoing Halemaʻumaʻu eruption ended abruptly at 1:20 p.m. HST on July 9, 2025, after 9 hours of continuous fountaining, the final 8 of which were high fountaining.
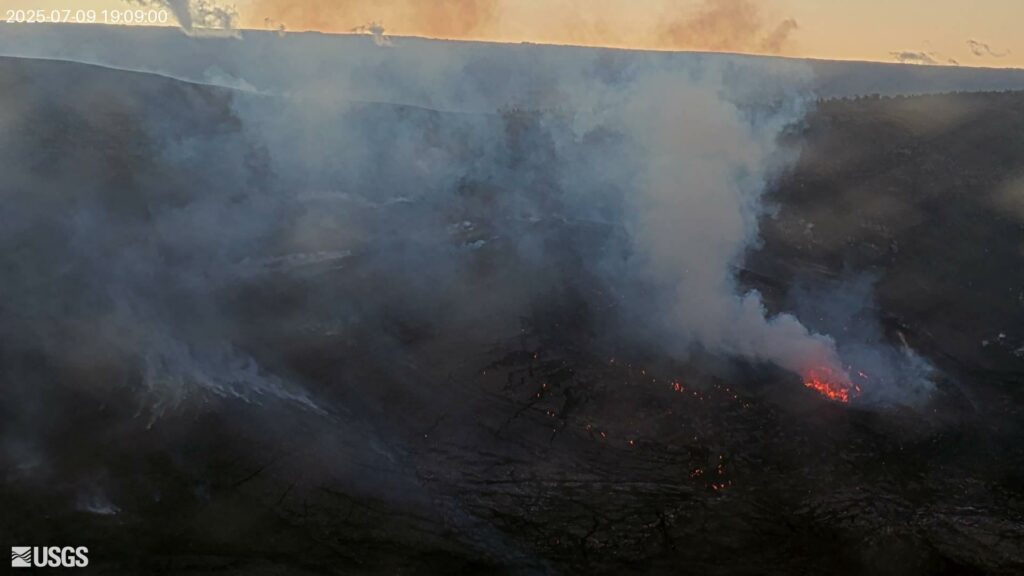
The north vent stopped erupting at approximately 1:20 p.m. HST, marking the end of the episode. The south vent did not appear to activate at all during this episode and has been completely covered by new deposits. The growing cone around the north vent has begun to connect with the top of the surrounding cliff in some places.
Lava fountains reached up to approximately 1200 ft (365 m) during this episode. Volcanic gas emissions have greatly decreased since the end of fountaining. Lava flows from this episode on the floor of Halemaʻumaʻu within the southern part of Kaluapele (Kīlauea caldera) may continue to exhibit slow movement or incandescence as they cool and solidify over the coming days. Slumping of molten cone material around the vent may also continue for the next 24 hours and can produce small, localized lava flows.
The Uēkahuna tiltmeter (UWD) recorded about 15 microradians of deflationary tilt during this episode. The end of the eruption was coincident with a rapid change from deflation to inflation at the summit and a decrease in seismic tremor intensity.
Source : HVO.
Photos : USGS
Indonesia , Lewotobi Laki-Laki :
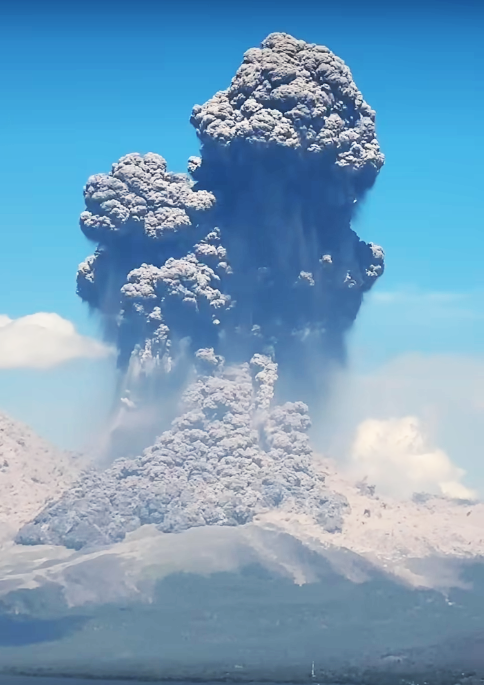
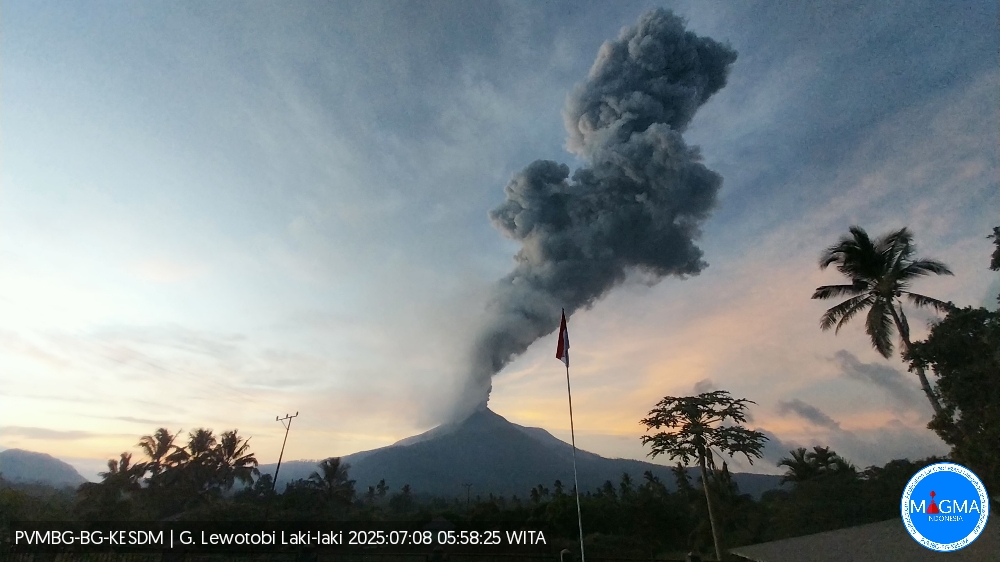
The Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG) reported that an explosive eruption from Lewotobi Laki-laki at 11h05 on 7 July was accompanied by loud booming sounds. A dense gray-to-black ash plume rose to around 18 km above the summit and drifted NE, N. and NW. Photos of the eruption showed pyroclastic flows descending the N and NE flanks as far as 5 km. The eruption lasted about six and a half minutes based on seismic data. According to the Badan Nacional Penanggulangan Bencana (BNPB) ashfall was reported in several villages in the Wulanggitang District including Nawakote, Klatanlo, Hokeng Jaya, Boru, and Pululera. A smaller explosion at 15h19 generated a dense gray ash plume that rose around 1 km above the summit and drifted W. Another significant event at 19h32 produced a dense gray-to-black ash plume that rose about 13 km above the summit and drifted W and NW. Incandescent material descending multiple flanks was visible in a webcam image starting at 19h44.
News outlets reported that some flights from the El Tari Kupang Airport to Frans Seda Maumere Airport, along with a few dozen international flights, were cancelled. The Komodo International Airport, around 300 km W, was closed during 7-8 July. The Alert Level remained at 4 (on a scale of 1-4) and on 25 June the exclusion zone was reduced to 6 km from the center of Laki-laki and 7 km in a semicircle clockwise from the SW to the NE.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : July 9 , 2025
Volcano : Lewotobi Laki-laki (264180)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Lewotobi Laki-laki Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2025LWK356
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 32 min 20 sec E 122 deg 46 min 06 sec
Area : East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 5069 FT (1584 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption at 18h52 UTC (02h52 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Ash-cloud is not observed.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash-cloud is not observed.
Remarks :
Eruption and ash emission is continuing. Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 14.8 mm.
Sources: Pusat Vulkanologi dan Mitigasi Bencana Geologi (PVMBG, also known as CVGHM), Badan Nacional Penanggulangan Bencana (BNPB), Antara News, Antara News, Antara News, Antara News, GVP.
United – States , Mount Rainier :
The Cascades Volcano Observatory (CVO) reported that a small seismic swarm at Rainier began at 01h29 on 8 July. By the 09h26 the seismic network recorded hundreds of earthquakes at rates up to several per minute. The earthquakes were located at depths of 2-6 km below the summit; the largest earthquake, a M 1.7, was detected at 04h52. No earthquakes were felt, no deformation was detected, and no anomalous signals were detected at infrasound monitoring stations. CVO noted that seismicity is typically about 9 earthquakes per month, plus swarms once or twice per year, but with much smaller numbers of events per swarm. The last large swarm at Rainier had over 1,000 earthquakes over three days in 2009 (120 located), had an earthquake with a maximum magnitude of 2.3. Past swarms have been attributed to circulation of fluids interacting with preexisting faults. The Volcano Alert Level remained at Normal (the lowest level on a four-level scale) and the Aviation Color Code remained at Green (the lowest color on a four-color scale).
CASCADES VOLCANO OBSERVATORY STATUS REPORT , U.S. Geological Survey
Wednesday, July 9, 2025, 9:30 AM PDT (Wednesday, July 9, 2025, 16:30 UTC)
46°51’11 » N 121°45’36 » W,
Summit Elevation 14409 ft (4392 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: NORMAL
Current Aviation Color Code: GREEN
This is an update on the ongoing seismic swarm at Mount Rainier that began at 1:29 AM PDT (8:29 UTC) on July 8th.
Seismicity is continuing at low rates. As of 9 AM PDT (16:00 UTC) on July 9th, the Cascades Volcano Observatory (CVO) and the Pacific Northwest Seismic Network (PNSN) have located 229 events since the start of the swarm, although many more have occurred but cannot be located. The largest event of the swarm so far was a magnitude 2.1 on July 8th at 2:56 PM PDT (21:56 UTC). Seismicity has decreased from 26 located events per hour at the swarm’s peak on Tuesday morning to a few per hour as of Wednesday morning. The average earthquake depth is 2.5 miles (4 km) beneath the summit. There have been no changes in ground deformation or other monitoring data.
The cause of the swarm remains consist with the circulation of fluids along preexisting faults beneath the volcano. There is currently no indication that the swarm is associated with magmatic unrest.
PNSN and CVO will continue to monitor activity, locate earthquakes, and provide additional information as needed.
Source: US Geological Survey Cascades Volcano Observatory (CVO), GVP
Sources : Observatoire volcanique des Cascades (CVO) de l’US Geological Survey , GVP .
Photo : Lee Siebert, 1981 (Smithsonian Institution).
Japan , Shinmoedake :
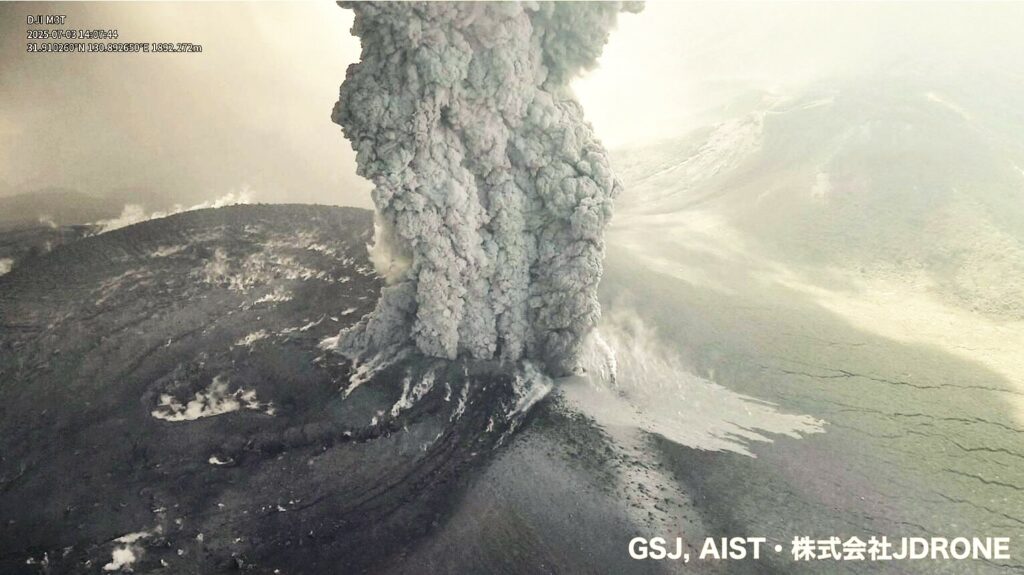
The Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) reported that eruptive activity continued at Shinmoedake (Shinmoe peak, a stratovolcano of the Kirishimayama volcano group) during 2-8 July. The number of volcanic earthquakes with epicenters directly beneath Shinmoedake had been fluctuating since late October 2024, though the rates continue to be high. Beginning at 10h25 on 27 June continuous gas-and-ash plumes with variable densities rose to various heights above the vents on the crater floor, at least through 9 July. The plumes generally rose 300-2,800 m above the crater rim, and occasionally higher, and drifted in various directions, causing periodic ashfall in areas downwind. On 2 July a large amount of ash fell in Makizonocho (14 km SW), Kirishima City, obscuring the white lines on the roads.
At 13h49 on 3 July the plumes rose 5 km above the crater rim and drifted S; the taller plume was associated with rumbling sounds. During a field survey in Kobayashi City that same day observers heard loud rumbling, and a notable amount of ash again fell in Makizonocho. At 16h40 on 4 July plumes rose 3.3 km above the crater rim. Ashfall during 3-4 July was confirmed in Kagoshima City, Kirishima City, Yusui (16 km WNW), Aira City 931 km SW), Minamisatsuma City, and Hioki City (55 km SW) in Kagoshima Prefecture. On 7 July sulfur dioxide emissions averaged 900 tons per day. The Alert Level remained at 3 (on a 5-level scale) and the public was warned to exercise caution within 3 km from Shinmoedake Crater.
Source: Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA), GVP
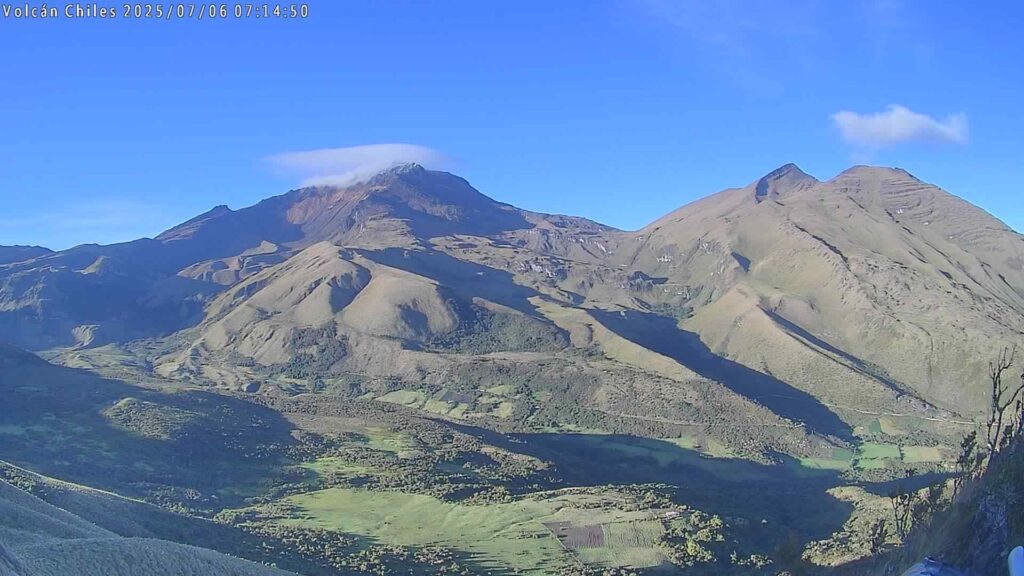
Colombia , Chiles / Cerro Negro :
San Juan de Pasto, July 8, 2025, 4:30 p.m.
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the Chiles-Cerro Negro Volcanic Complex (CVCCN), the Colombian Geological Survey (SGC), an entity affiliated with the Ministry of Mines and Energy, reports that:
From July 1 to 7, 2025, the main variations in the monitored parameters compared to the previous week were:
● Although seismic activity continued to fluctuate, a slight increase was recorded, both in terms of occurrence and seismic energy released. Seismic activity associated with rock fracturing processes continued to predominate in several sectors of the volcanic edifices.
● Seismic activity was mainly located at the summit of Chiles Volcano and near its collapse zone, at depths between 2 and 5 km from the summit (4,700 m above sea level) and with a maximum magnitude of 1.6. Other earthquakes were located southeast of Chiles Volcano, at distances of up to 16 km, with depths between 7 and 16 km from its summit and a maximum magnitude of 1.7.
● Satellite sensors and ground stations measuring crustal deformation continue to show changes related to deformation processes in the volcanic zone.
Based on the assessment and correlation of the monitored parameters, the SGC recommends closely monitoring their development through weekly bulletins and other information published through our official channels, as well as instructions from local and departmental authorities and the National Disaster Risk Management Unit (UNGRD). Volcanic activity remains on yellow alert: active volcano with changes in the basic behavior of the monitored parameters and other manifestations.
Source et photo : SGC.