May 21 , 2025.
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from May 12, 2025 to May 18, 2025 (issue date May 20, 2025)
SUMMARY OF ACTIVITY STATUS
Based on monitoring data, the following is highlighted:
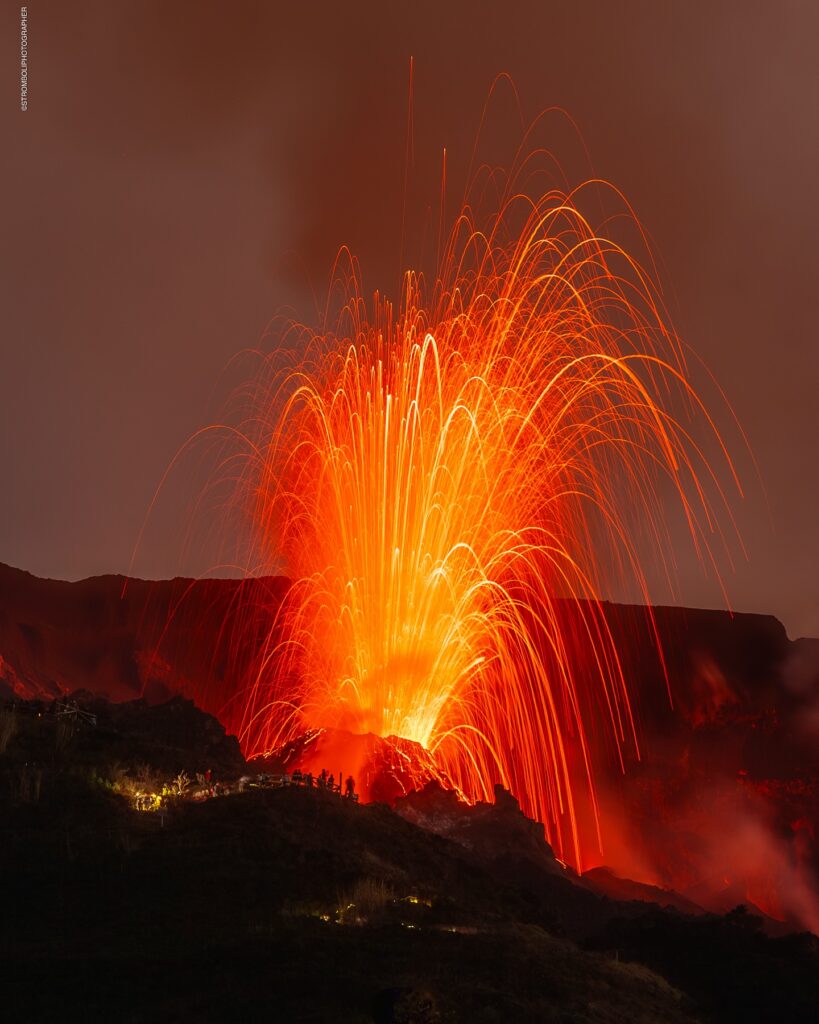
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: During this period, ordinary Strombolian eruptive activity was observed. The total hourly frequency ranged between average values (7-13 events/h). The intensity of the explosions was low and medium in the North and South-Central crater areas.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The monitored seismic parameters show no significant variations.
3) GROUND DEFORMATION: Ground deformation monitoring networks showed no significant variations.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 fluxes at an average level and moderately increasing. Soil CO2 fluxes in the Pizzo area (STR02): no updates.
C/S ratio in the plume: high to very high values.
Dissolved helium isotope ratio (R/Ra) in the thermal aquifer: high values (updated May 6).
Soil CO2 fluxes in the San Bartolo area: medium values.
Soil CO2 fluxes in the Scari area: medium-high values.
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally low, with some moderate thermal anomalies.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the observation period, Stromboli’s eruptive activity was characterized by analyzing images recorded by INGV-OE surveillance cameras located at an altitude of 190 m (SCT-SCV) and at Punta dei Corvi (SPCT). The explosive activity was produced mainly by four eruptive vents located in the northern area of the crater and at least two vents located in the central-southern area.
Due to adverse weather conditions, visibility of the crater terrace on May 12 and 16 was insufficient to accurately describe the eruptive activity.
Observations of explosive activity captured by surveillance cameras
In the North (N) crater area, four active vents were observed, producing low-intensity explosive activity (less than 80 m in height) and sometimes medium-intensity explosive activity (less than 150 m in height). The ejected products consisted mainly of coarse materials (bombs and lapilli). The average explosion frequency ranged from 6 to 12 events/h.
In the South-Central (SC) area, explosive activity was produced by at least two vents. The explosions were mainly of low and medium intensity, emitting fine materials (ash) sometimes mixed with coarse materials (lapilli and bombs). The average explosion frequency ranged from less than 1 to 2 events/h.
Source : INGV
Photo : Stromboli stati d’animo / Sebastiano Cannavo
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from May 12, 2025 to May 18, 2025. (Issue date May 20, 2025)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
Based on monitoring data, the following is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Eruptive episode of Strombolian activity and lava flows at the Southeast Crater on May 12. Variable degassing activity from the summit craters.
2) SEISMOLOGICAL: Low seismic activity due to fracturing. Tremor amplitude at a low level, except for the Strombolian activity episode.
3) INFRASOUND: Infrasound activity is mainly low or medium; high during the Strombolian activity episode. 4) GROUND DEFORMATION: Ground deformation monitoring networks did not record any significant changes except for small tilt/deformation variations during the May 12 activity.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux at an average level.
Soil CO2 flux: medium-low values.
Partial pressure of dissolved CO2 in groundwater: no significant changes.
Helium isotope ratio at peripheral sites: last updated on April 22, 2025, with medium-high values.
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally low-level, with high to very high values corresponding to the eruptive activity of the Southeast Crater on May 12, 2025.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the week, monitoring of Mount Etna’s volcanic activity was carried out through the analysis of images from the INGV-Osservatorio Etneo (INGV-OE) surveillance camera network.
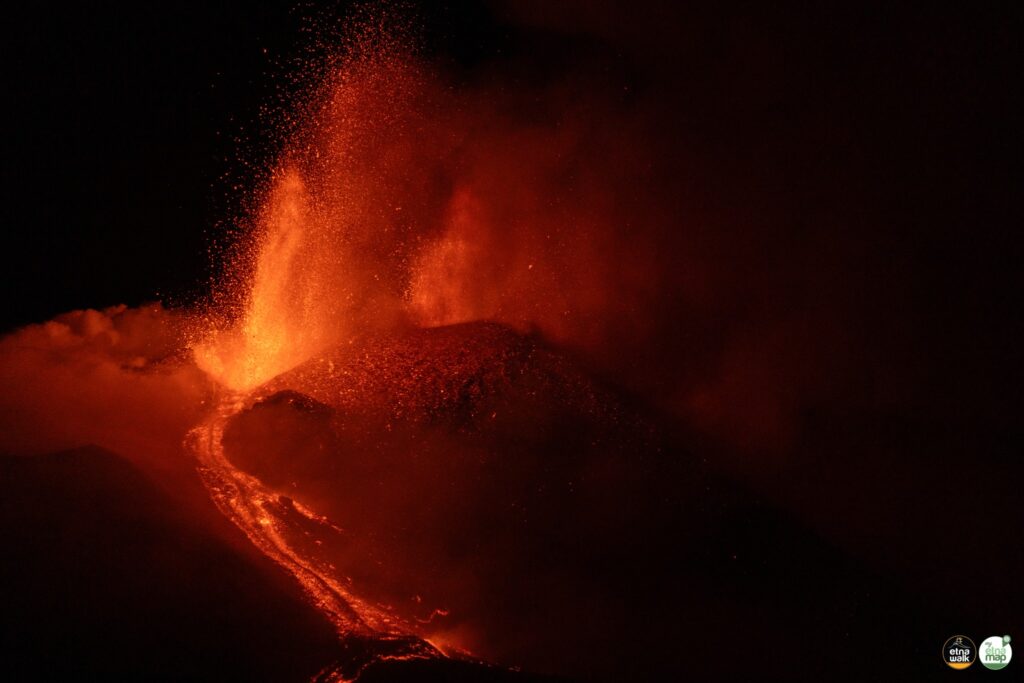
During the observation period in question, Etna’s activity was characterized by an eruptive episode with Strombolian activity and lava overflows from the Southeast Crater (CSE) on May 12.
As for the other summit craters, degassing activity of varying intensity was observed from the Bocca Nuova Crater (BN), the Northeast Crater (CNE), and the Voragine Crater (VOR). In particular, the Northeast Crater (CNE) is characterized by intense impulsive degassing from a vent located on the crater floor.
The brief eruptive event that affected the Southeast Crater on May 12 followed a similar pattern to the episodes that characterized the previous months.
The episode began in the late afternoon of May 12, but due to the cloud cover that persisted over the volcanic edifice, it was not possible to observe the initial phases of Strombolian activity.
It was only from 18:30 UTC, following the thinning of this cloud cover, which in any case severely limited the observation of the details of the ongoing activity, that it was possible to observe Strombolian activity at the Southeast Crater. The activity produced a modest eruptive cloud that caused a small fall of pyroclastic material onto the southeast quadrant of the volcano, which affected the towns of Petrulli and Zafferana Etnea. The eruptive episode also generated two modest lava flows, which spread respectively towards the South and the East.
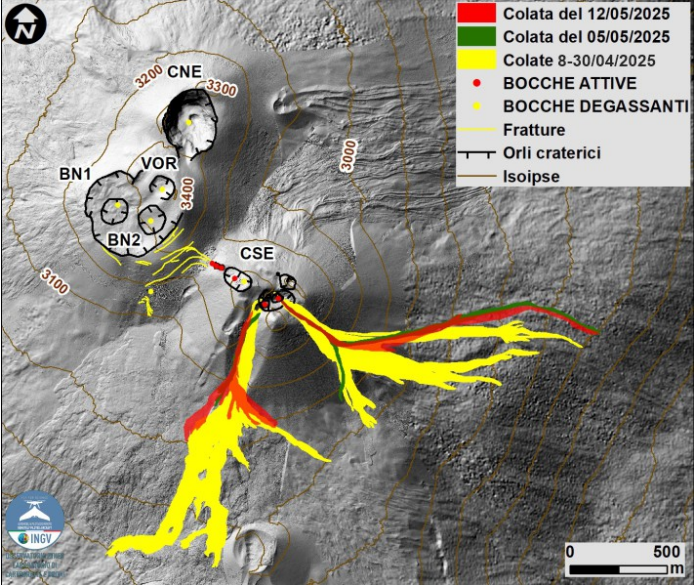
Map of the summit area of Mount Etna and the lava flows of May 5 and 12, 2025, superimposed on the shaded terrain relief obtained by processing drone images acquired between February, March, and April 2025 for BN and CSE, and on September 12, 2024 for VOR and CNE. Geoid contours are plotted every 100 m. CSE = Southeast Crater, CNE = Northeast Crater, VOR = Voragine, BN = Bocca Nuova.
The lava flows of May 5, 2025, were delineated by analyzing two Skysat images from May 10 and 14, 2025. The southward flow has an area of 0.13 x 10^5 m^2 and a volume of 0.13 x 10^5 m^3 with an error of 40%, its length is approximately 0.5 km, and the front reached a minimum height of 3040 m above sea level. The eastward flow has an area of 0.49 x 10^5 m^2 and a volume of 0.49 x 10^5 m^3 with an error of 40%, its length is approximately 1.8 km, and the front reached a minimum height of 2490 m above sea level.
The lava flows of May 12, 2025, were delineated by analyzing two images Skysat from May 13 and 14 and a Sentinel-2 image from May 13, 2025. The southward flow has an area of 0.54 x 10^5 m^2, and a volume of 0.54 x 10^5 m^3 with an error of 40%, its length is about 0.8 km and the front reached a minimum height of 3000 m above sea level. The eastward flow has an area of 0.60 x 10^5 m^2 and a volume of 0.60 x 10^5 m^3 with an error of 40%, its length is about 1.8 km and the front reached a minimum height of 2490 m above sea level.
Source : INGV
Photos : Etna Walk /Giuseppe Distefano / Marco Restivo , INGV.
Hawaii , Kilauea :
Tuesday, May 20, 2025, 10:14 AM HST (Tuesday, May 20, 2025, 20:14 UTC)
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
On Monday, May 20 at 9:37 a.m. HST, a magnitude-4.2 earthquake occurred 11 mi (18 km) southeast of Pāhala on the Island of Hawaiʻi at a depth of 20 mi (32 km) below sea level. The earthquake had no apparent impact on either Mauna Loa or Kīlauea volcanoes.
This earthquake is part of the seismic swarm under the Pāhala area, which has been going on since 2019. Earthquakes in this region have been observed at least as far back as the 1960s.
The USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory continues to monitor Hawaiian volcanoes for any changes.
EARTHQUAKE DESCRIPTION
Magnitude: 4.2
Date and Time: May 20, 2025, at 9:37 a.m. HST
Location: 11 mi (18 km) southeast of Pāhala, Island of Hawaiʻi
Depth: 20 mi (32 km) below sea level
Aftershocks are possible in the coming days to weeks
The ongoing eruption at the summit of Kīlauea remains paused, although there is a persistent glow from vents indicating magma is not far from the surface.
Episode 22 ended on Friday afternoon after more than 10 hours of sustained lava fountaining. The USGS Hawaiian Volcano Observatory was able to share a new view of the eruption (before it stopped abruptly) with a third webcam .
Scientists say the next episode is likely to occur between Wednesday and Friday, although that estimate could be refined as more data become available.
Sources : HVO , BIVN.
Photo : USGS
Indonesia , Ibu :
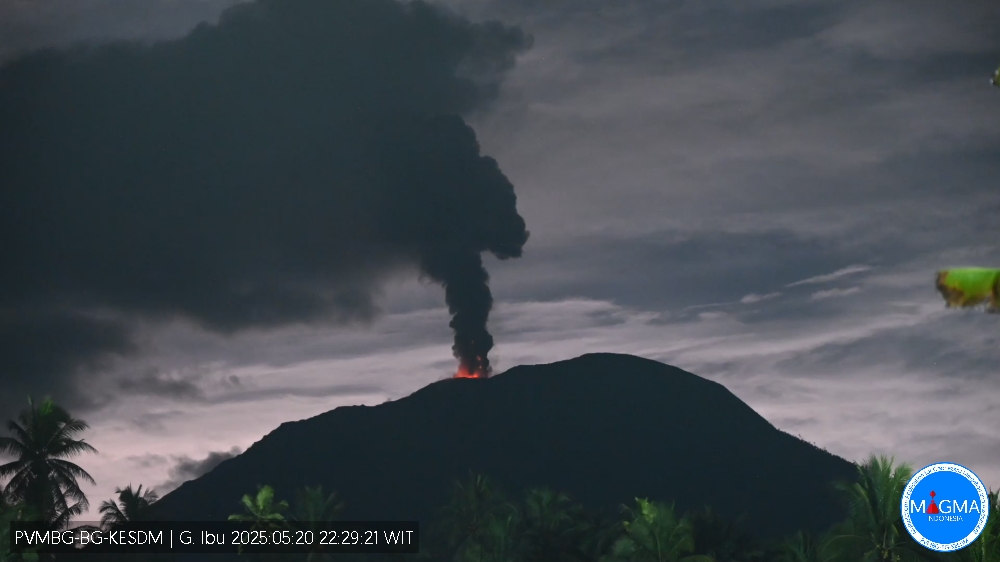
An eruption of Mount Ibu occurred on Tuesday, May 20, 2025, at 10:27 PM WIT with an observed ash column height of ± 600 m above the peak (± 1925 m above sea level). The ash column was observed to be gray in color with a thick intensity, oriented toward the northwest. This eruption was recorded on a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 28 mm and a duration of 66 seconds.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : May 20 , 2025
Volcano : Ibu (268030)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Ibu Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2025IBU781
Volcano Location : N 01 deg 29 min 17 sec E 127 deg 37 min 48 sec
Area : North Maluku, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 4240 FT (1325 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 13h27 UTC (22h27 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 6160 FT (1925 M) above sea level or 1920 FT (600 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to northwest. Volcanic ash is observed to be gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 28 mm and maximum duration 66 second.
Source et photo : Magma Indonésie .
Colombia , Chiles / Cerro Negro :
San Juan de Pasto, May 20, 2025, 5:00 p.m.
According to monitoring of the activity of the Chiles-Cerro Negro Volcanic Complex (CVCCN), the Colombian Geological Survey (SGC), an entity affiliated with the Ministry of Mines and Energy, reports that:
During the period from May 13 to 19, 2025, the main variations in the monitored parameters compared to the previous week were:
• Although the total number of earthquakes decreased (from 11,000 to 2,800 events), a significant increase in seismicity associated with fluid dynamics within the volcanic system was observed, recording approximately 1,300 earthquakes. This increase represents the largest recorded on the CVCCN so far in 2025. Most of these events had a dominant frequency range between 1.0 and 1.5 Hz. On May 17, more than 400 such earthquakes were recorded, with a minimum interval between them of about 14 seconds.
• Most of the earthquakes were concentrated in the Chiles Volcano collapse zone, within a 2.2 km radius of its summit (reference level above 4,700 m), with depths ranging from 1.1 to 5.3 km. Within this group, the highest-energy event, with a magnitude of 2.4, was recorded 1.0 km east-southeast of the Chiles Volcano summit, with a depth of 3.1 km. The remaining seismic activity was located scattered throughout the CVCCN’s area of influence, with distances of up to 9.2 km and depths of up to 8.9 km.
• Analysis of information obtained from satellite sensors and ground stations continues to indicate variations related to deformation processes in the volcanic zone.
Based on the assessment and correlation of monitored parameters, the SGC recommends closely monitoring developments through weekly bulletins and other information published through our official channels, as well as instructions from local and departmental authorities and the National Disaster Risk Management Unit (UNGRD).
Volcanic activity remains on Yellow alert: Active volcano with changes in the baseline behavior of monitored parameters and other manifestations.
Source et photo : SGC .