April 23 , 2025.
Hawaii , Kilauea :
Tuesday, April 22, 2025, 4:36 AM HST (Tuesday, April 22, 2025, 14:36 UTC)
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Activity Summary:
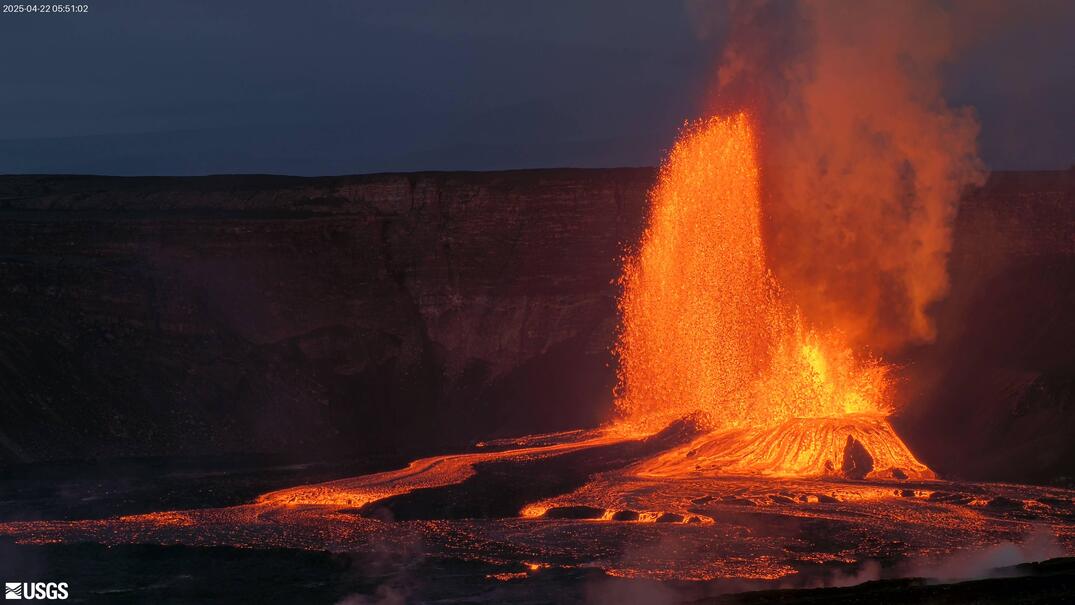
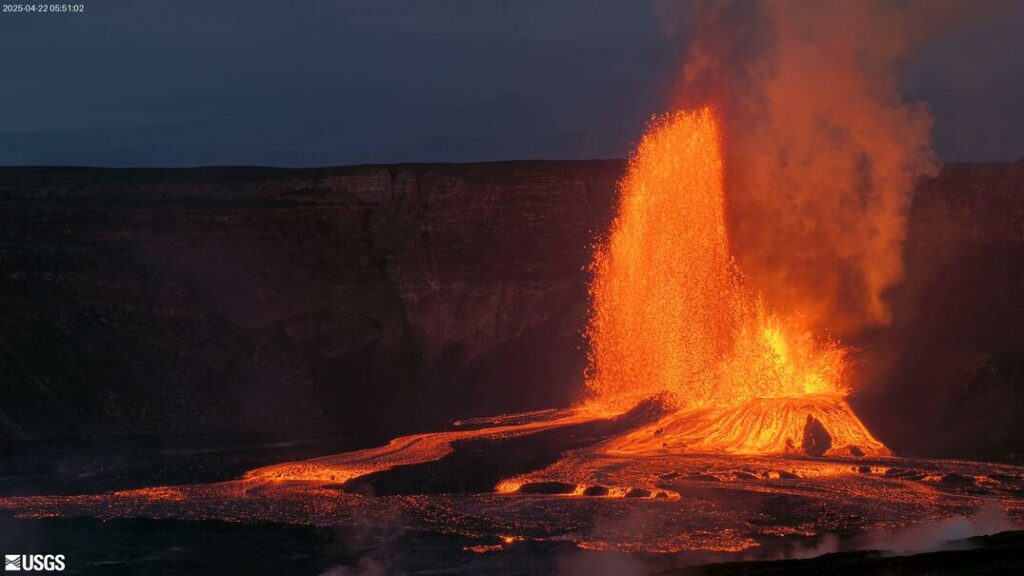
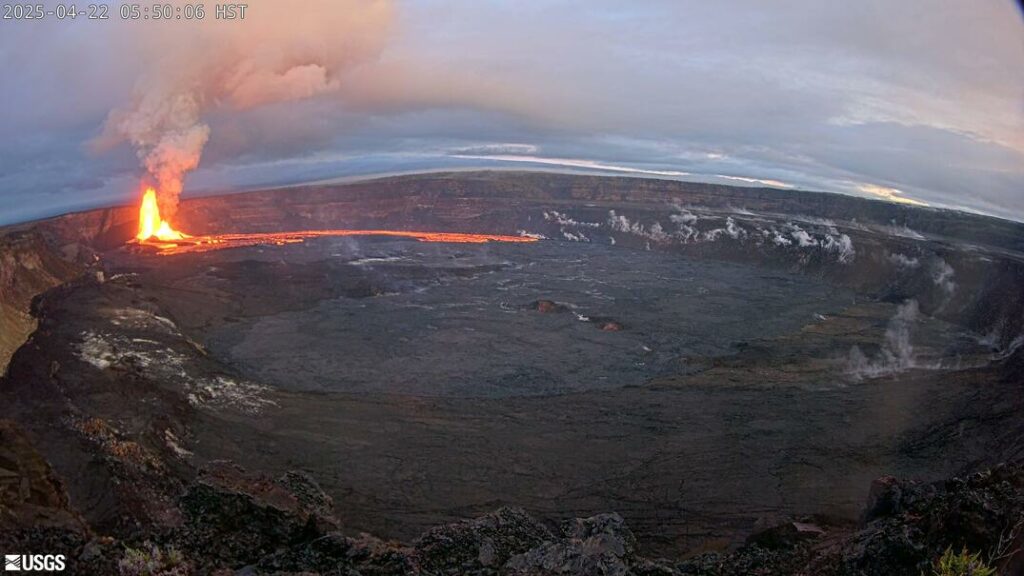
Episode 18 of the ongoing Halemaʻumaʻu eruption resumed with lava overflowing the south vent at 3:20 a.m. HST on April 22 followed by the onset of fountaining from both vents at 3:30 a.m. HST. Lava began overflowing the north vent at 3:47 a.m. HST. Fountains are currently over 650 feet (200 meters) high at the south vent and over 160 feet (50 meters) at the north vent. Both fountains are feeding a vigorous flow on the floor of Halemaʻumaʻu crater. Lava has currently covered about over 20% of the floor of Halemaʻumaʻu crater. Strong deflation accompanied the onset of lava flows at 3:20 a.m. and tremor increased with the onset of fountaining from both vents.
Prior to the onset of high fountaining, intermittent spattering began at the north vent around 1:30 a.m. HST and increased in frequency until 3:20 a.m. HST when lava began erupting. Additional information on the resumption of episode 18 can be found in the April 20 Kīlauea update and the April 21 Kīlauea update.
Kīlauea’s current eruption in Halemaʻumaʻu crater within Kaluapele (the summit caldera) began on December 23, 2024. There have now been 18 episodes separated by pauses in activity. All eruptive activity remains within Hawaiʻi Volcanoes National Park. No significant activity has been noted along Kīlauea’s East Rift Zone or Southwest Rift Zone. Current hazards include volcanic gas emissions and windblown volcanic glass (Pele’s hair) and tephra that have impacted Hawaiʻi Volcanoes National Park and nearby communities.
Volcanic gas emissions remain elevated and at heightened levels due to lava fountaining. The last sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission rate measured on April 10 was approximately 1,200 tonnes per day. Typical levels of Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission have been about 1,000 tonnes per day during previous pauses. Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission rates during earlier high fountaining episodes have reached 50,000 tonnes per day.
Tuesday, April 22, 2025, 2:20 PM HST (Wednesday, April 23, 2025, 00:20 UTC)
Activity Summary:
Episode 18 of the ongoing Halemaʻumaʻu eruption ended abruptly at 1:28 p.m. HST on April 22.
The north and south vents stopped erupting at approximately the same time. The fountaining phase of episode 18 began at 3:20 a.m. this morning and lasted for 10 hours and 8 minutes. Lava erupted from both vents with maximum fountains from the south vent reaching over 600 feet (200 meters) high while those from the north vent remained below 200 feet (60 meters high). Approximately 5 million cubic meters were erupted at about 140 cubic meters per second. Lava flows from both vents covered over 60% of the floor of Halemaʻumaʻu within the southern part of Kaluapele (Kīlauea caldera).
Deflationary tilt at the summit recorded 13 microradians during this episode. The end of the eruption was coincident with a rapid change from deflation to inflation at the summit and a rapid drop in seismic tremor intensity.
Each episode of Halemaʻumaʻu lava fountaining since December 23, 2024, has continued for 13 hours to 8 days and episodes have been separated by pauses in eruptive activity lasting less than 24 hours to 12 days.
Source : HVO
Photos : USGS
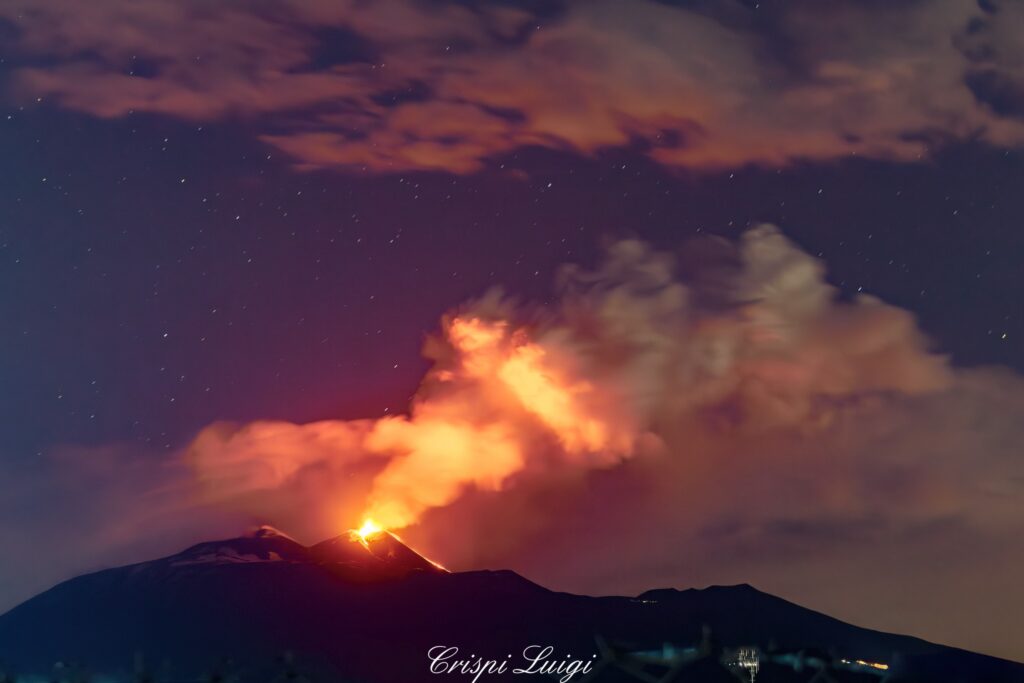
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from April 14, 2025 to April 20, 2025 (publication date: April 22, 2025)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
Based on monitoring data, the following points are highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Strombolian and effusive activity at the Southeast Crater (April 15 and 18). Degassing activity at the summit craters.
2) SEISMOLOGICAL: Low seismic activity due to fracturing. Low tremor amplitude, except for two episodes of increased strombolian activity at the Southeast Crater.
3) INFRASOUND: Moderately low infrasound activity. High values were reached during the two episodes of Strombolian activity at the Southeast Crater. 4) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: Over the past week, ground deformation monitoring networks have not recorded any significant variations. Two small deflations and decompressions were recorded by the DRUV borehole dilatometer and the ECP inclinometer during the Strombolian phases of April 15 and 18.
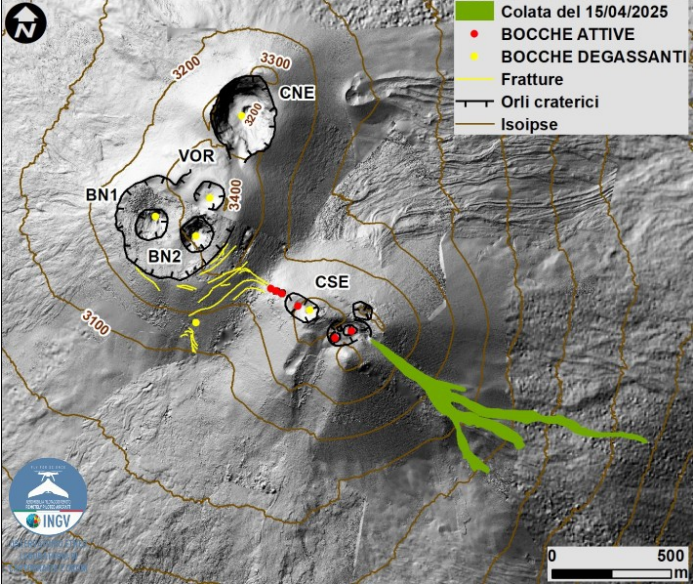
Map of the summit area of Mount Etna and the April 15th lava flow, superimposed on the shaded terrain relief, obtained by processing drone images acquired between February, March, and April 2025 for BN and CSE, and on September 12, 2024 for VOR and CNE. Geoid contours are plotted every 100 m. CSE = Southeast Crater, CNE = Northeast Crater, VOR = Voragine, BN = Bocca Nuova.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 Flux: Average Level
The CO2 flux from the ground is at average values.
The partial pressure of dissolved CO2 in groundwater does not show significant variations.
The helium isotope ratio at peripheral sites is at average to high values (last updated on April 3, 2025). 6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally low, with high to very high values corresponding to eruptive activity in the Southeast Crater on April 15 and 18, 2025.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the observation period, Etna’s volcanic activity was monitored through image analysis from the surveillance camera network of the Osservatorio Etneo of the National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology (INGV-OE).
Specifically, two eruptive events were observed in the Southeast Crater, on April 15 and 18, respectively. The eruptive activity of these episodes was manifested by Strombolian activity producing modest clouds containing a small amount of very dilute ash, accompanied by effusive overflow activity whose flows progressed slowly and exhausted themselves within a few hours.
The April 15 episode began at 7:00 GMT with Strombolian activity at the southeast crater, which gradually increased until 9:30 GMT. Simultaneously, a lava flow began on the southeast side of the crater, stopping concurrently with the end of the explosive activity around 9:50 GMT.
The lava flow of April 15, 2025, was delineated by analyzing two Skysat images from April 17 and 18. It measures 0.82 x 105 m², is approximately 1.2 km long, and the most advanced front reached a minimum altitude of 2,620 m.
The April 18 episode began at 5:05 p.m. GMT and, like the previous one, initially manifested itself through Strombolian activity that gradually increased in intensity until approximately 9:30 p.m. During the explosive activity, two lava flows were observed: one in a southeasterly direction, following the same path as the previous one, and the other on the southwest slope. In this case, both flows dried up when the Strombolian activity ceased around 10:55 p.m. GMT.
Etna Activity Report, April 22, 2025, 8:40 PM (6:40 PM UTC)
The Etna Observatory of the National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology (INSV) reports that, starting around 6:00 PM GMT, Strombolian activity has been observed by INGV-OE surveillance cameras in the southeast crater. The forecast model indicates that any eruptive clouds produced by the ongoing activity would disperse eastward. A lava flow is also observed on the southeast slope of the crater.
From a seismic perspective, starting around 1:00 PM UTC, the average amplitude of volcanic tremor increased rapidly, reaching peak values around 5:20 PM UTC. Currently, the values are high and tend to increase. The centroid of the tremor sources is located in the southeast crater area, at an altitude of approximately 2,800 m above sea level. Infrasound activity has shown a gradual and moderate increase since 17:50 UTC, and the events are located in the southeast crater area with medium amplitudes.
Signals from the inclinometer and GNSS ground deformation monitoring networks show no significant variations.
Updates will be provided shortly.
Source : INGV
Photos : INGV , Luigi Crispi
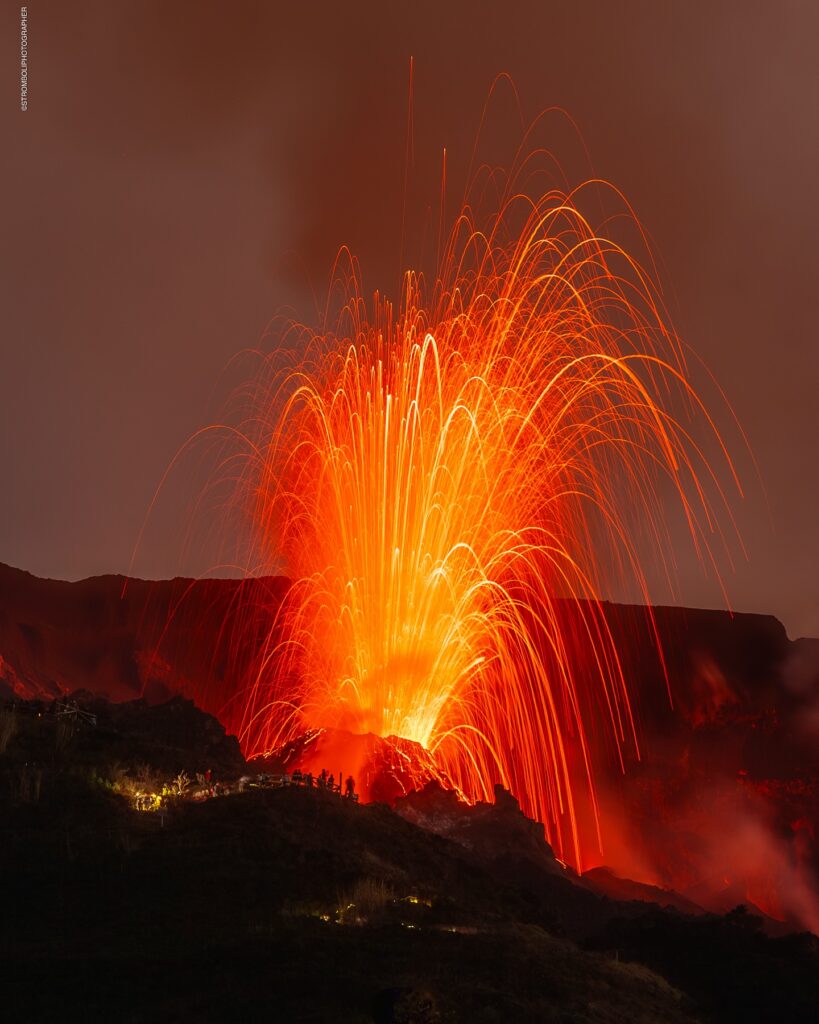
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from April 14, 2025 to April 20, 2025 (publication date: April 22, 2025)
SUMMARY OF ACTIVITY STATUS
Based on monitoring data, the following points are highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: During this period, ordinary Strombolian eruptive activity was observed. The total hourly frequency ranged between average (11 events/h) and high (17 events/h) values. The intensity of the explosions was low and medium in the North and South-Central crater areas.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The monitored seismological parameters do not show any significant variations.
3) GROUND DEFORMATION: The island’s ground deformation monitoring networks did not show any significant variations for the period studied. 4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux: medium level.
Soil CO2 flux from the Pizzo region (STR02): very high values (data up to April 16).
C/S ratio in the plume: high values.
Helium isotope ratio (R/Ra): no update.
CO2 flux at Mofeta in the San Bartolo region: medium to low values.
Soil CO2 flux in the Scari region: medium to low values.
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally low.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the observation period, Stromboli’s eruptive activity was characterized by analyzing images recorded by INGV-OE surveillance cameras located at an altitude of 190 m (SCT-SCV) and at Punta dei Corvi (SPCT). Explosive activity was mainly produced by four eruptive vents located in the North Crater area and by at least two vents located in the Central-South area.
Observations of Explosive Activity Recorded by Surveillance Cameras
In the North Crater (N) area, four active vents were observed, producing explosive activity of low intensity (less than 80 m in height) and sometimes of medium intensity (less than 150 m in height). The eruptive products consisted mainly of coarse materials (bombs and lapilli). The average explosion frequency was between 8 and 13 events per hour. In the South-Central (SC) area, explosive activity was produced by at least two vents. The explosions were mainly of low and medium intensity, composed of fine materials (ash) mixed with coarse materials (lapilli and bombs). The average explosion frequency ranged from 2 to 6 events per hour.
Source : INGV
Photo : Stromboli stati d’animo / Sebastiano Cannavo
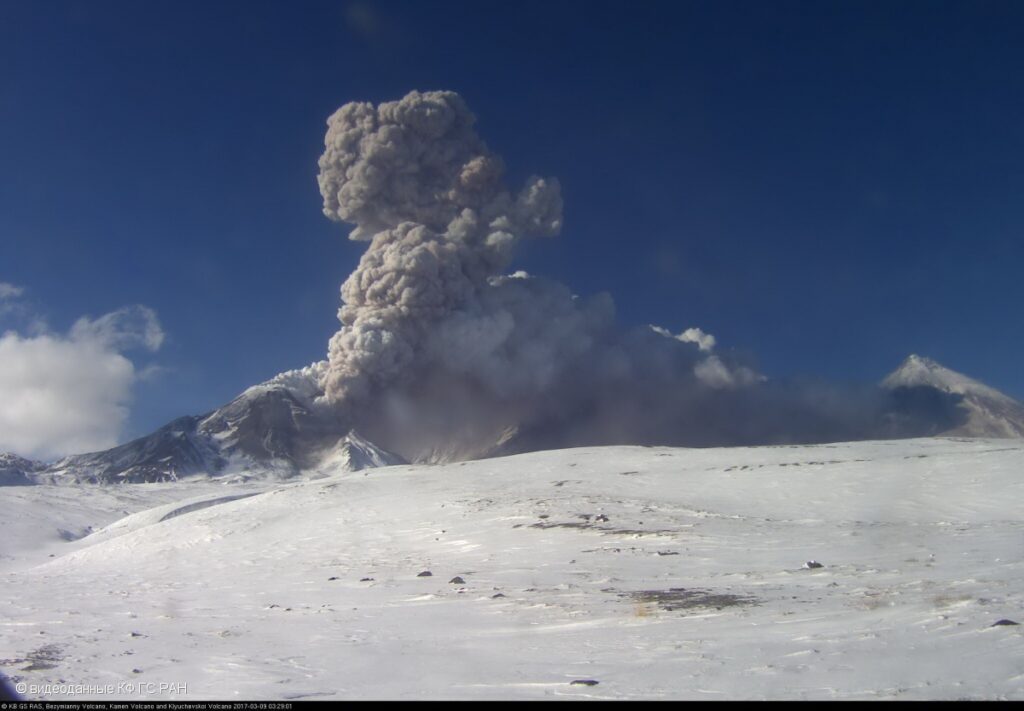
Kamchatka , Bezymianny :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Issued: April 23 , 2025
Volcano: Bezymianny (CAVW #300250)
Current aviation colour code: RED
Previous aviation colour code: orange
Source: KVERT
Notice Number: 2025-22
Volcano Location: N 55 deg 58 min E 160 deg 35 min
Area: Kamchatka, Russia
Summit Elevation: 2882 m (9452.96 ft)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
Probably an explosive eruption of the Bezymianny volcano began at 01:45 UTC on 23 April. Dense clouds obscures the volcano, but an ash cloud 10×10 km in size was noted in 45 km to the north-northwest of the volcano. KVERT continues to monitor the Bezymianny volcano.
An explosive eruption of the volcano continues. The danger of ash explosions up to 10-15 km (32,800-49,200 ft) a.s.l. remains. Ongoing activity could affect international and low-flying aircraft.
Volcanic cloud height:
8000-9000 m (26240-29520 ft) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20250423/0200Z – Himawari-9 14m15
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 45 km (28 mi)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: NNW / azimuth 328 deg
Time and method of ash plume/cloud determination: 20250423/0230Z – Himawari-9 14m15
Source : Kvert.
Photo : videodata KB GS RAS 2017
Indonesia , Lewotobi Laki-laki :
An eruption of Mount Lewotobi Laki-laki occurred on Tuesday, April 22, 2025, at 3:54 PM WITA. The observed ash column was ± 1,300 m above the summit (± 2,884 m above sea level). The ash column was gray and intense, oriented toward the west and northwest. At the time of this report, the eruption was still ongoing.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : April 22 , 2025
Volcano : Lewotobi Laki-laki (264180)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Lewotobi Laki-laki Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2025LWK294
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 32 min 20 sec E 122 deg 46 min 06 sec
Area : East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 5069 FT (1584 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 07h54 UTC (15h54 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 9229 FT (2884 M) above sea level or 4160 FT (1300 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving from west to northwest. Volcanic ash is observed to be gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption and ash emission is continuing. Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 8.8 mm. Tremor recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 8.8 mm.
Source et photo : Magma Indonésie .