February 15 , 2026.
La Réunion Island , Piton de la Fournaise :
Press release from the Paris Institute of Earth Physics / Piton de la Fournaise Volcanological Observatory, February 15, 2026 – 7:15 a.m. local time – 3:15 a.m. UTC
Eruption in progress
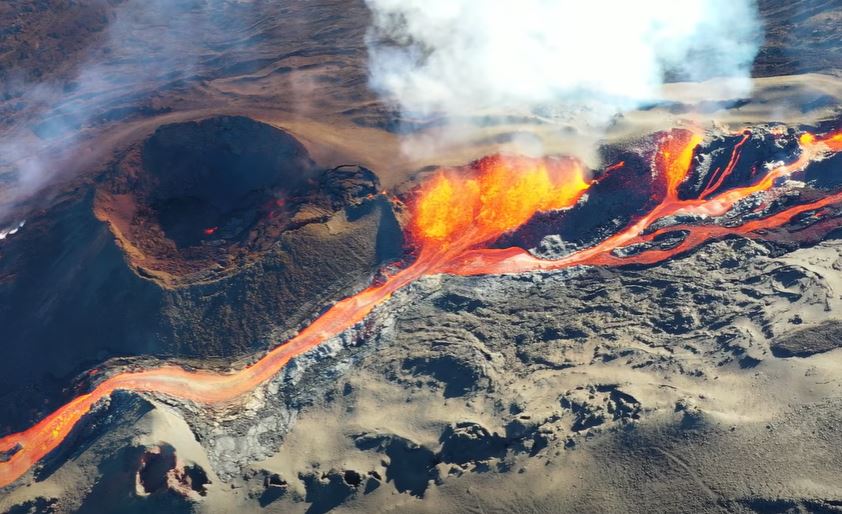
The eruption that began on February 13, 2026, shortly after 10:00 a.m. local time, at Piton de la Fournaise continues.
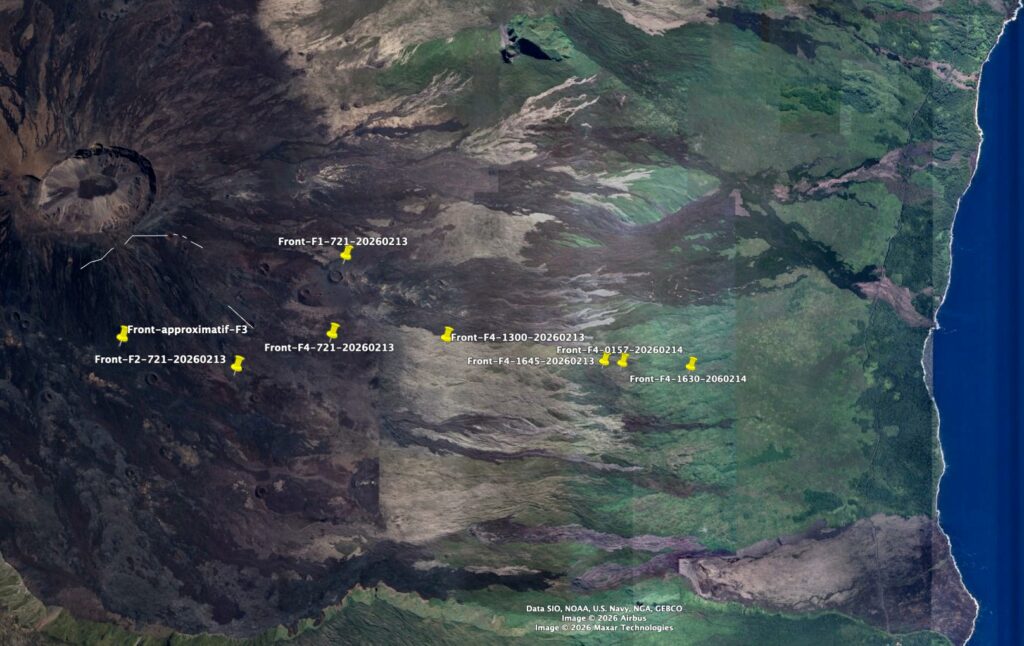
Only one site remains active, located near Piton Morgabim on the south-southeast flank, where lava fountains are gradually building an eruptive cone and several levees. Yesterday evening, the lava flows were located in the lower part of the Grandes Pentes, approximately 2.2 km from the RN2 highway.
Tonight, the active parts of the flow were concentrated at the top of the Grandes Pentes.
Evolution of the flow front of the various fissures since the start of the eruption. The lowest point corresponds to the position of the flow front on February 14 at 8:30 PM local time. Front name: Fissure number – UTC time – date (©OVPF-IPGP)
The intensity of the eruptive tremor (an indicator of lava and gas emissions at the surface) has decreased by a factor of 2 over the last 24 hours.
Surface flow rates, estimated from satellite data via the HOTVOLC platform (OPGC – Clermont Auvergne University), have shown values between 2 and 22 m³/sec over the last 24 hours. Note that these estimates can vary rapidly depending on cloud cover and be zero in the event of total cloud cover.
Due to continued seismic activity beneath the summit, indicating that the magma supply system remains under pressure, further fissure openings are possible in the coming hours, particularly further downstream. The OVPF-IPGP remains on continuous alert to monitor the situation.
Alert level: Alert 2-1
Source : OVPF/IPGP.
Photos : OVPF , Réunion la 1ère.
Indonesia , Ibu :
Mount Ibu experienced an eruption on Saturday, February 14, 2026, at 9:12 AM WIT. An ash column was observed approximately 600 meters above the summit (at an altitude of about 1,925 meters). This column was white to gray in color, of moderate to strong intensity, and drifted southwest to west. At the time of writing, the eruption was still ongoing.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : February 14 , 2026
Volcano : Ibu (268030)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Ibu Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2026IBU069
Volcano Location : N 01 deg 29 min 17 sec E 127 deg 37 min 48 sec
Area : North Maluku, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 4240 FT (1325 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 00h12 UTC (09h12 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 6160 FT (1925 M) above sea level or 1920 FT (600 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving from southwest to west. Volcanic ash is observed to be white to gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed from medium to thick.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 28 mm and maximum duration 49 second.
Source et photo : Magma Indonésie.
Hawaii , Kilauea :
HAWAIIAN VOLCANO OBSERVATORY DAILY UPDATE , U.S. Geological Survey
Saturday, February 14, 2026, 8:27 AM HST (Saturday, February 14, 2026, 18:27 UTC)
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Activity Summary:
The Halemaʻumaʻu eruption of Kīlauea is paused. There has been no gain in tilt recorded at the summit in the past day. Glow at both the south and north vents was visible in the webcams overnight. The forecast for the onset of episode 42 lava fountaining has been adjusted to February 15 through 17, though continued deflation events may delay the episode onset further.
The 3rd precursory north vent flow lasted from 5:56 to 6:05 pm HST. Inflation slowed since the 2nd overflow at 4:41 pm HST. Lava has been spattering in the south vent. The onset of episode 42 fountains is expected Sunday or Monday.
No significant activity has been noted along Kīlauea’s East Rift Zone or Southwest Rift Zone.
Summit Observations:
Moderate to strong glow was visible at the south and north vents overnight in the webcams.
Seismic tremor continued over the past 24 hours and has been relatively steady over the past day. Only 2 earthquakes were located in the summit region during the past day.
The Uēkahuna tiltmeter (UWD) has been recording inflation and deflation over the last three days. There was no net gain in inflation during the past 24 hours. The net inflation since the end of episode 41 remains at 28.6 microradians of inflationary tilt.
In recent days, the sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission rate from the summit has varied within the typical range of 1,000 to 5,000 tonnes of SO2 per day, as has been observed during previous eruptive pauses. This is considerably lower than rates observed during lava fountaining episodes. This morning, webcams show that the plume from the summit vents is being carried to the southwest. The National Weather Service forecast for the Kīlauea summit region for today and tonight indicates northeast winds at 14-17 mph, with some higher gusts up to 24 mph.
Rift Zone Observations:
Rates of seismicity and ground deformation remain very low in the East Rift Zone and Southwest Rift Zone. SO2 emissions from the East Rift Zone remain below the detection limit.
Source et photo : HVO.
Colombia , Cumbal :
San Juan de Pasto, February 10, 2026, 3:30 PM
Regarding the monitoring of activity at the Cumbal Volcanic Complex (CVC), the Colombian Geological Survey (SGC), an agency under the Ministry of Mines and Energy, reports the following:
During the week of February 3-9, 2026, the main variations in monitored parameters compared to the previous week were as follows:
● An increase in the frequency of earthquakes and their energy release was recorded.
The most significant contribution comes from seismicity associated with rock fracturing.
● The events exhibited low energy levels, allowing for the localization of only one earthquake, west of the volcanic complex, with a magnitude of 1.6 and a depth of 5 km, using the La Plazuela crater (4,700 m altitude) as a reference point.
Gas emissions were recorded at the El Verde fumarole field, located to the northeast, and at the Rastrojos field, located to the southwest of the CVC, with variable dispersal directions due to wind.
Other volcanic monitoring parameters remained stable.
Given the above, the SGC recommends closely monitoring the evolving situation by consulting the weekly bulletins and other information disseminated through its official channels, as well as following the instructions of local and departmental authorities and the National Unit for Disaster Risk Management (UNGRD).
Volcanic activity remains at the yellow alert level: active volcano with changes in the reference behavior of monitored parameters and other manifestations.
Source et photo : SGC.
Ecuador , Sangay :
DAILY REPORT ON THE STATE OF SANGAY VOLCANO, Saturday, February 14, 2026.
Geophysical Information Institute – EPN.
Surface Activity Level: High, Surface Trend: No Change
Internal Activity Level: Moderate, Internal Trend: No Change
Seismicity: From February 13, 2026, 11:00 AM to February 14, 2026, 11:00 AM:
Seismicity:
The table below shows the number of seismic events recorded at the reference station:
Explosion (EXP): 160
Rainfall/Lahars:
No rainfall has been recorded in the volcano area. **Heavy rainfall could remobilize accumulated material, generating mudflows and debris flows that would cascade down the volcano’s flanks and into nearby rivers.**
Emissions/Ash:
Due to cloud cover in the area, emissions could not be observed by surveillance cameras. However, the GOES-19 satellite system detected several gas and ash plumes drifting northwest and southwest, reaching altitudes below 1,200 meters above the crater. Regarding this activity, the Washington VAAC issued three reports concerning ash plumes drifting west, northwest, and southwest, reaching altitudes of 900 and 1,200 meters above the crater.
Gas:
The MOUNTS satellite system detected 99.2 tonnes of sulfur dioxide (SO₂), measured yesterday at 1:39 p.m. local time.
Observation:
From yesterday afternoon until the time of writing this report, the volcano remains completely obscured by clouds.
Alert level: Yellow
Source : IGEPN
Photo : Cristopher Cárdenas
.