February 8 , 2026.
La Réunion Island , Piton de la Fournaise :
Press release from the Paris Institute of Earth Physics / Piton de la Fournaise Volcanological Observatory. February 7, 2026 – 7:55 a.m. local time – 3:55 a.m. UTC.
Seismicity
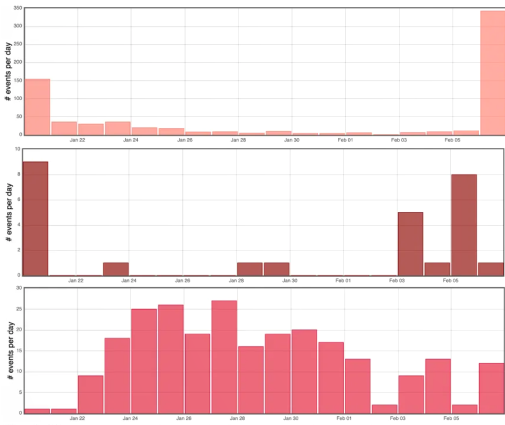
Following the cessation of the eruption on January 20, 2026, seismic activity continues to be recorded beneath the summit of the volcano. This activity fluctuates daily in terms of the type and number of events (Figure 1).
For example, on February 6, 343 summit volcano-tectonic earthquakes were recorded, primarily during a swarm of very low magnitude (<< M1) between 11:08 p.m. and 12:05 a.m. UTC (3:08 a.m. to 4:05 a.m. local time this morning).
Histogram showing the number of shallow volcano-tectonic earthquakes (top), deep volcano-tectonic earthquakes (middle), and long-period earthquakes (bottom) recorded per day since the end of the eruption of January 18-20, 2026 (© OVPF-IPGP).
These earthquakes, of very low magnitude, remain localized between 1 and 2.5 km deep beneath the annular fault, a structure inherited from the collapse of the summit craters and known to concentrate a large part of the seismicity of Piton de la Fournaise. This swarm of earthquakes follows a resumption of deeper seismic activity (8-10 km deep) over the last four days beneath the western rim of the volcano’s summit area.
This seismic swarm was accompanied by very slight ground deformation (a few micro-radians), meaning that a small magma intrusion (magma injection from the shallow reservoir) took place, but whose intensity and propagation distance were much lower than those of December 5, 2025 and January 1, 2026.
In parallel, long-period (LP) earthquakes have been recorded since the end of the eruption. This type of earthquake is generally associated with deep fluid circulation or pressure variations within the magmatic or hydrothermal system.
This seismic activity (VT and LP) indicates that the volcano’s shallow magma supply system continues to pressurize under the influence of magma rising from the depths.
It should be noted that during these pressurization phases, seismic activity beneath Piton de la Fournaise can fluctuate daily, with periods of low seismicity interspersed with periods of higher seismicity.
At this stage, the pressurization process of the shallow reservoir can continue for several days to several weeks, or even several months, before a new injection of magma occurs towards the surface; it can also cease without leading to an eruption in the short term.
Current alert level: Vigilance.
Source : OVPF.
Photos : OVPF , Clicanoo.
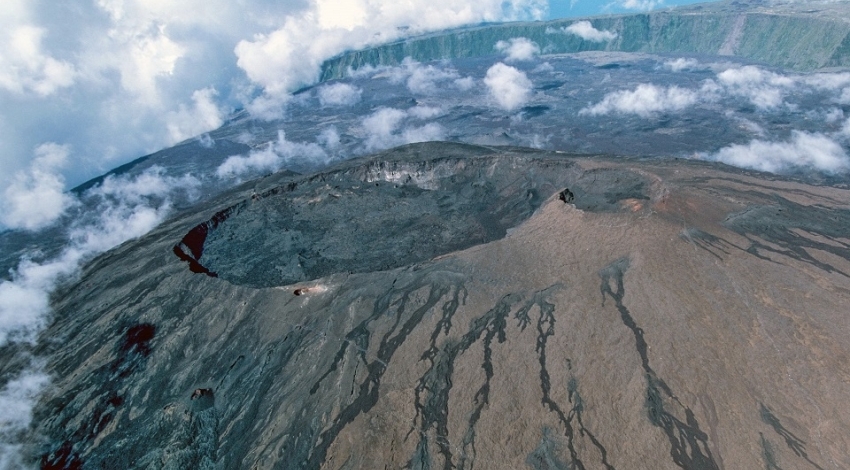
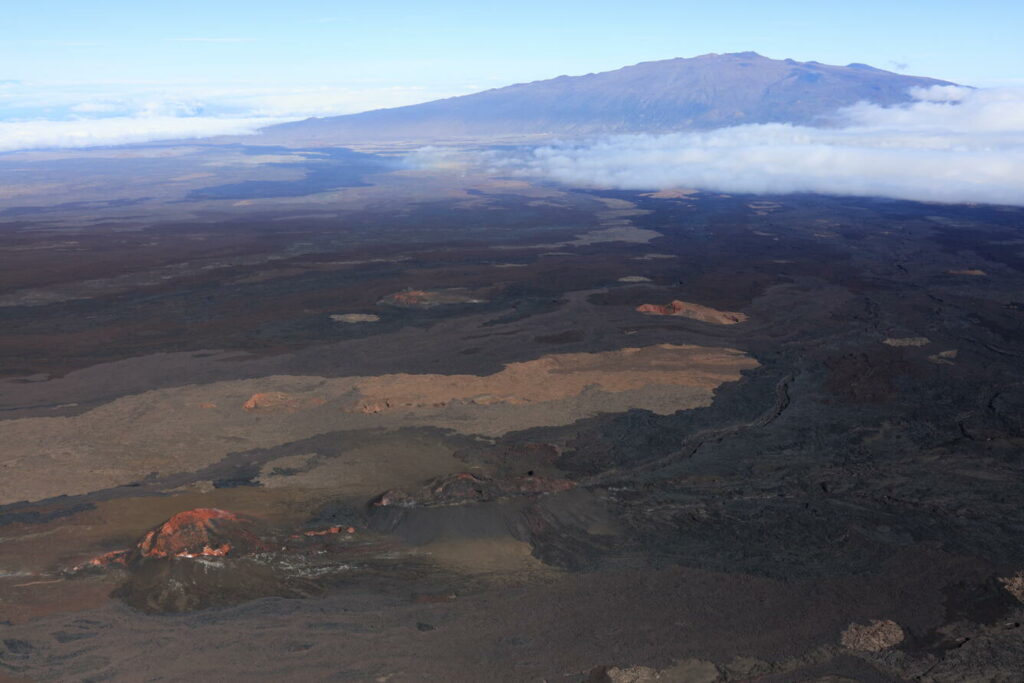
Hawaii , Mauna Loa :
HAWAIIAN VOLCANO OBSERVATORY MONTHLY UPDATE , U.S. Geological Survey
Thursday, February 5, 2026, 4:17 PM HST (Friday, February 6, 2026, 02:17 UTC)
19°28’30 » N 155°36’29 » W,
Summit Elevation 13681 ft (4170 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: NORMAL
Current Aviation Color Code: GREEN
Mauna Loa seismic activity increased slightly over the past month, with a tight clustering of events under Mokuʻāweoweo and upper Southwest Rift Zone early in the month (a continuation of elevated earthquake production from the end of the previous month). A total of 123 earthquakes were detected beneath Mauna Loa’s summit region in the January reporting period, while the prior month had 94 earthquakes. Data from Global Positioning System (GPS) instruments on Mauna Loa show variable rates of inflation at the summit over the past six months .
At the end of their flyover of Mauna Loa summit on December 23, geologists from the Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (USGS) flew over the 2022 eruption site in the Northeast Rift Zone. In this photo, an old vent, called the Steaming Cone, is visible in the lower left (in red and white), with the 2022 Fissure 3 cone just to its right (in black and brown). Lava flows from 2022 descending toward Humu‘ula Pass are also visible to the right, along with Mauna Kea in the distance.
This is associated with refilling of the summit reservoir system following the 2022 eruption, as well as recent refilling of a magma chamber under the southern caldera region.
Gas and temperature data from a station on Mauna Loa’s Southwest Rift Zone indicate these values are at background levels, with little change relative to previous months.
HVO continues to closely monitor Mauna Loa and will issue another update in one month, or earlier, should conditions change significantly.
Source : USGS.
Photo : USGS/M. Zoeller.
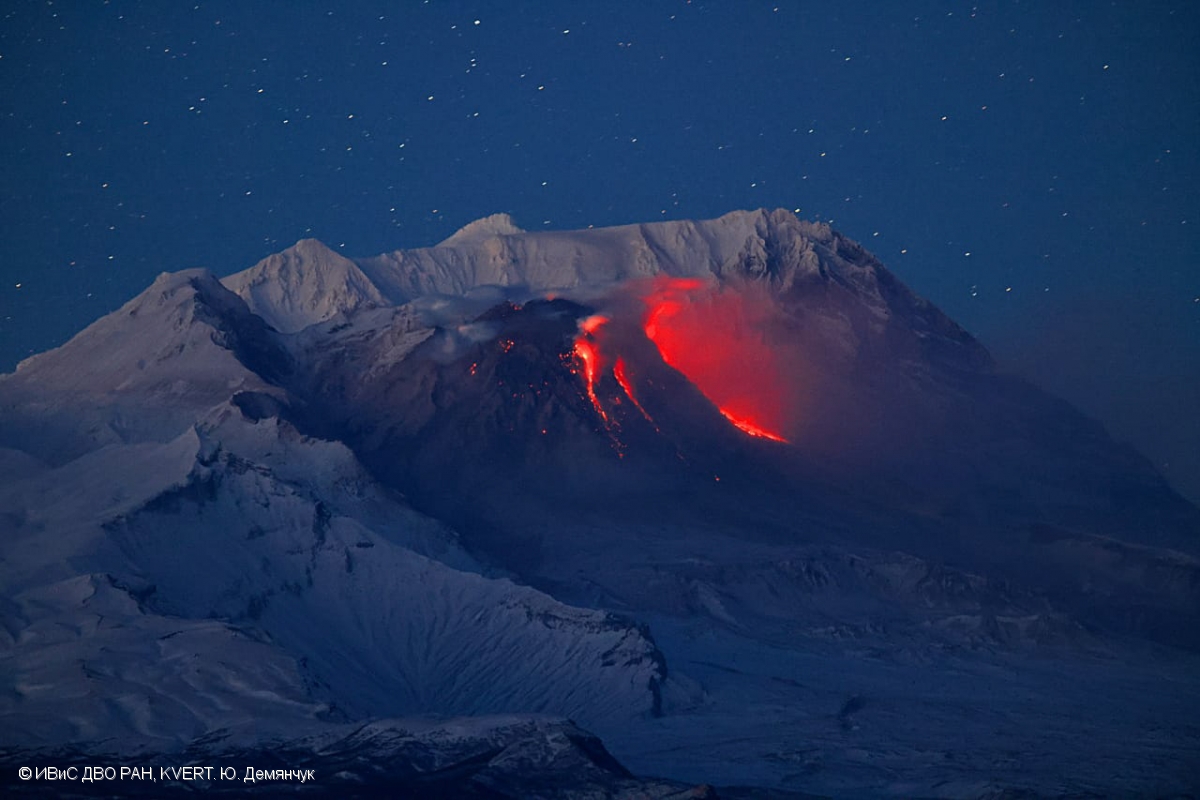
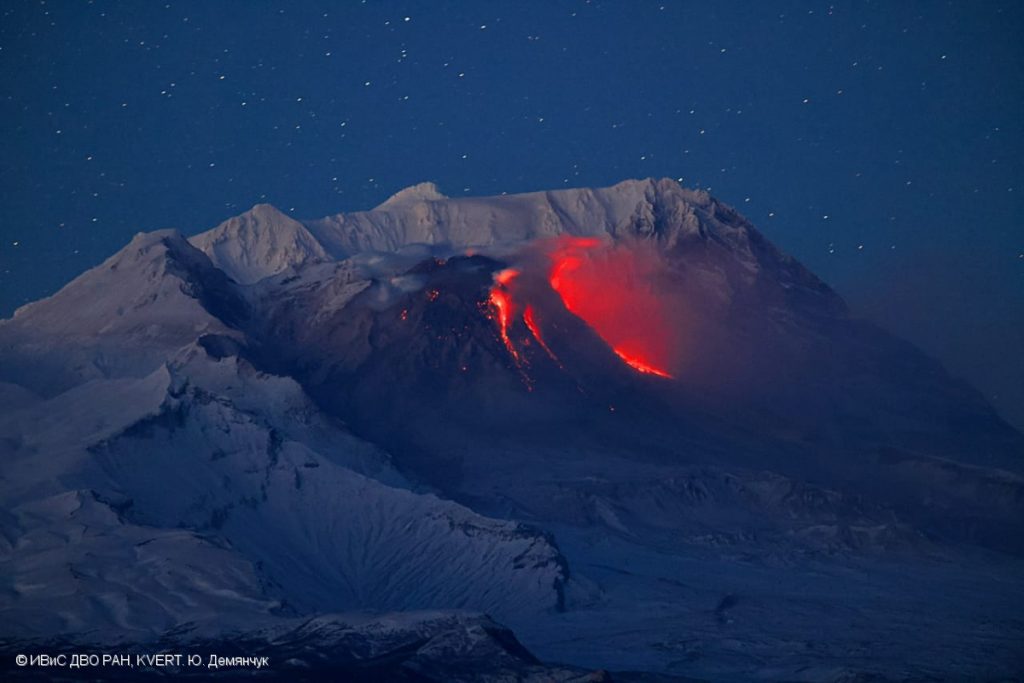
Kamchatka , Sheveluch :
KVERT VOLCANIC ACTIVITY NOTICE (VAN)
Issued: Fébruary 8 , 2026
Volcano: Sheveluch (CAVW #300270)
Current aviation colour code: RED
Previous aviation colour code: orange
Source: KVERT
Notice Number: 2026-23
Volcano Location: N 56 deg 38 min E 161 deg 19 min
Area: Kamchatka, Russia
Summit Elevation: 3283 m (10768.24 ft), the dome elevation ~2500 m (8200 ft)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
An explosive-extrusive eruption of the volcano continues, accompanied by powerful gas-steam activity. Explosions sent ash up to 11.6 km a.s.l., and ash cloud move for 40 km to the north-west of the volcano.
Ongoing activity could affect international and low-flying aircraft.
Volcanic cloud height:
11600 m (38048 ft) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20260208/0208Z – JPSS-1 15m16
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 40 km (25 mi)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: WNW / azimuth 285 deg
Time and method of ash plume/cloud determination: 20260208/0208Z – JPSS-1 15m16
Remarks:
EXPLOSION SENT ASH UP TO 11.6 KM ASL, ASH CLOUD MOVE FOR 40 KM TO 285 AZIMUTH AT 02:08 UTC ON FEBRUARY 08.
Source : Kvert.
Photo : Yu. Demyanchuk, IVS FEB RAS, KVERT ( Archive 2022)
Indonesia , Ibu :
Mount Ibu experienced an eruption on Sunday, February 8, 2026 at 9:05 a.m. (local time). An ash column was observed approximately 800 meters above the summit (at an altitude of about 2,125 meters). This gray ash column was of moderate intensity and directed northwest. The eruption was recorded by a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 28 mm and a duration of 51 seconds.
Seismicity Observations
104 eruption earthquakes with amplitudes between 10 and 28 mm and durations of 38 to 66 seconds.
11 harmonic tremors with amplitudes between 2 and 28 mm and durations of 55 to 138 seconds.
84 low-frequency earthquakes with amplitudes between 2 and 8 mm and durations of 17 to 29 seconds.
128 shallow volcanic earthquakes with amplitudes between 2 and 6 mm and durations of 7 to 21 seconds.
A deep volcanic earthquake with an amplitude of 8 mm, a time interval of 1.7 seconds, and a duration of 19.5 seconds.
A local tectonic earthquake with an amplitude of 9 mm and a duration of 26 seconds.
Eight distant tectonic earthquakes, ranging in magnitude from 3 to 28 mm and lasting from 31 to 82 seconds, were recorded.
Recommendations
Mount Ibu is currently under a Level II alert. The following recommendations apply:
1. Residents living near Mount Ibu and visitors/tourists are advised to refrain from all activities within a 2 km radius and up to 3.5 km from the crater opening in the northern part of Mount Ibu’s active crater.
2. In the event of ashfall, people engaging in outdoor activities are advised to wear a mask covering their nose, mouth, and eyes, as well as protective eyewear.
Source et photo : Magma Indonésie .
Ecuador , Sangay :
DAILY REPORT ON THE STATE OF SANGAY VOLCANO, Saturday, February 7, 2026.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface Activity Level: High, Surface Trend: No Change
Internal Activity Level: Moderate, Internal Trend: No Change
Seismicity: From February 6, 2026, 11:00 AM to February 7, 2026, 11:00 AM:
Seismicity:
The table below shows the number of seismic events recorded at the reference station:
Explosion (EXP): 419
Rainfall/Lahars:
Rainfall has been recorded in the volcano area, but it has not generated any mudflows or debris. **In the event of heavy rainfall, accumulated material could be remobilized, causing mudflows and debris flows that would cascade down the volcano’s flanks and into nearby rivers.**
Emission Column/Ash:
Yesterday, satellite imagery showed a gas and ash plume reaching an altitude of 1,600 meters above the crater, drifting northwest. This plume was associated with a report of light ashfall from the Alao Community Risk Management Secretariat in Pungalá Parish, Chimborazo Province. Simultaneously, the VAAC agency in Washington reported an ash plume reaching an altitude of 2,100 meters above the crater, drifting north.
Other monitoring parameters:
The MIROVA-MODIS satellite system recorded a thermal anomaly, and the MIROVA-AVIIRS 375 satellite system recorded another within the last 24 hours.
Observation:
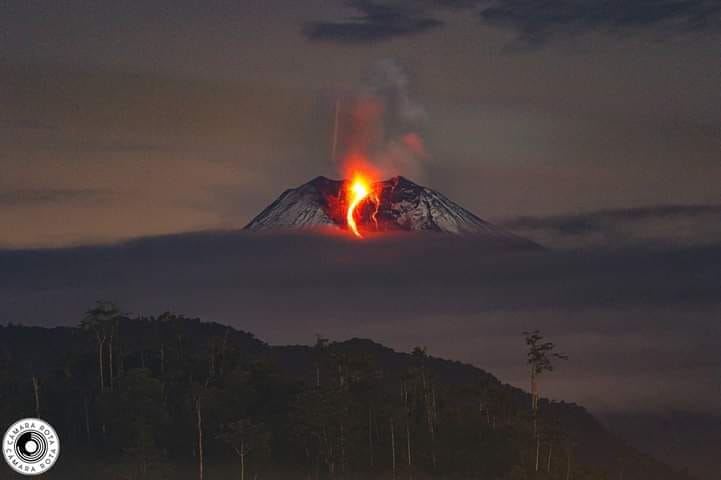
Incandescence was observed at the crater last night. At the time of writing, the volcano remained shrouded in clouds.
Alert level: Yellow
Source : IGEPN
Photo : Cámara Rota