July 17 , 2024.
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from July 8, 2024 to July 14, 2024. (issue date July 16, 2024)
SUMMARY STATEMENT OF ACTIVITY
In light of the monitoring data, it appears:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Effusive activity with lava flows coming from eruptive fractures along the Sciara del Fuoco and paroxysmal explosive event; cessation of effusive activity since July 11 and absence of ordinary explosive activity.
2) SISMOLOGY: The monitored seismological parameters do not show significant variations, with the exception of the paroxysmal event of 07/11 which was followed by an increase in tremors to VERY HIGH values.
3) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: The networks monitoring ground deformations on the island, in particular the inclinometer network, showed variations linked to the eruptive activity occurring during the period considered.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux at a medium-high level
The CO2 flux values show stable values, at high values (10,000 g/m2/day).
There is no new data on the isotope ratio of Helium
The C/S ratio is at low values.
CO2 flow in Mofeta in the San Bartolo area: slightly increasing, at high values.
CO2 flux in Scari: values slightly increasing at medium-high levels.
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite was generally at a moderate to high level corresponding to effusive activity and paroxysm.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
During the week, the activity of Stromboli was observed through INGV surveillance cameras and through different inspections and data acquisitions on the ground by INGV staff as part of the activities of the Annex A and UNO and Dynamo projects.
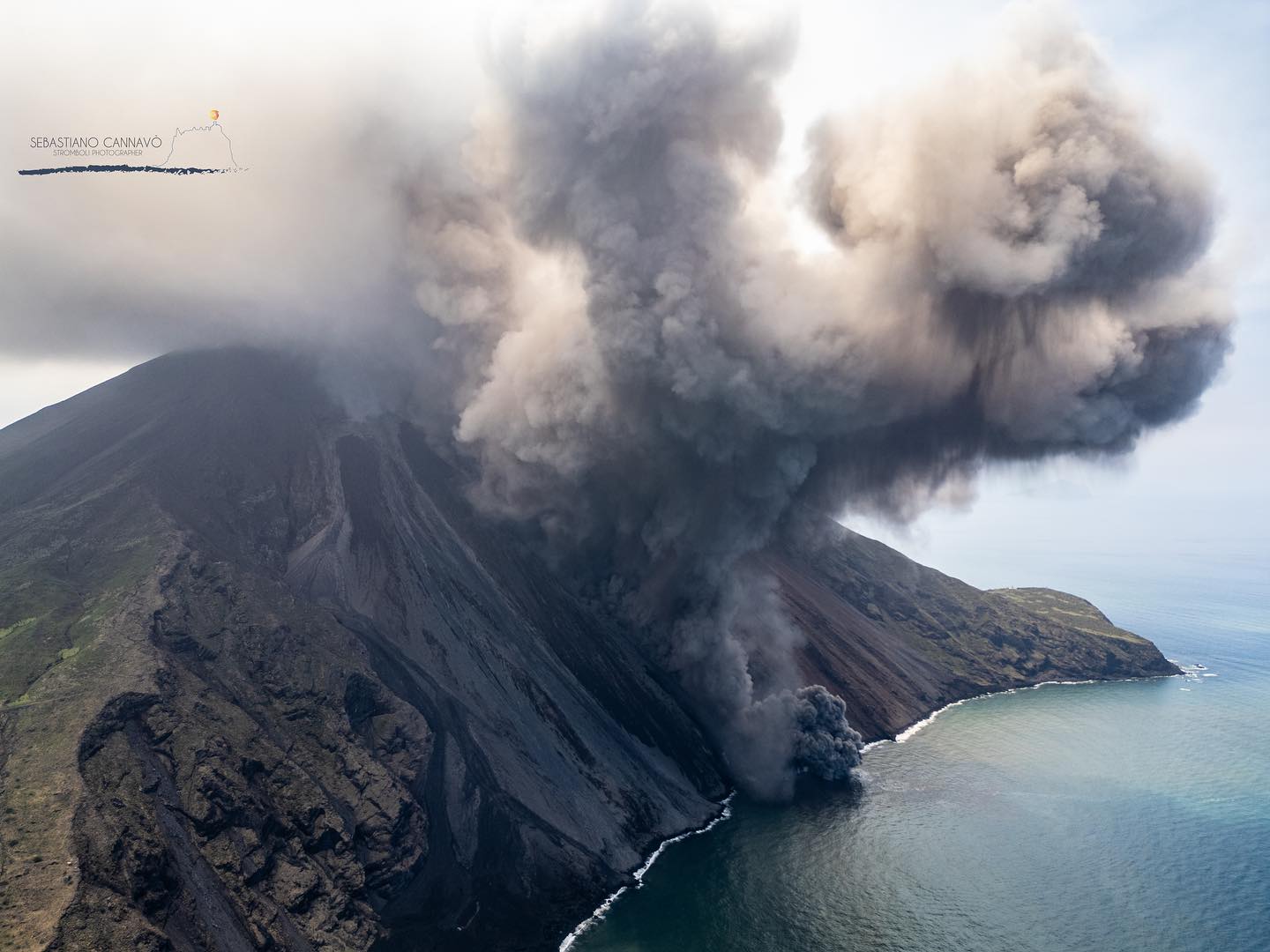
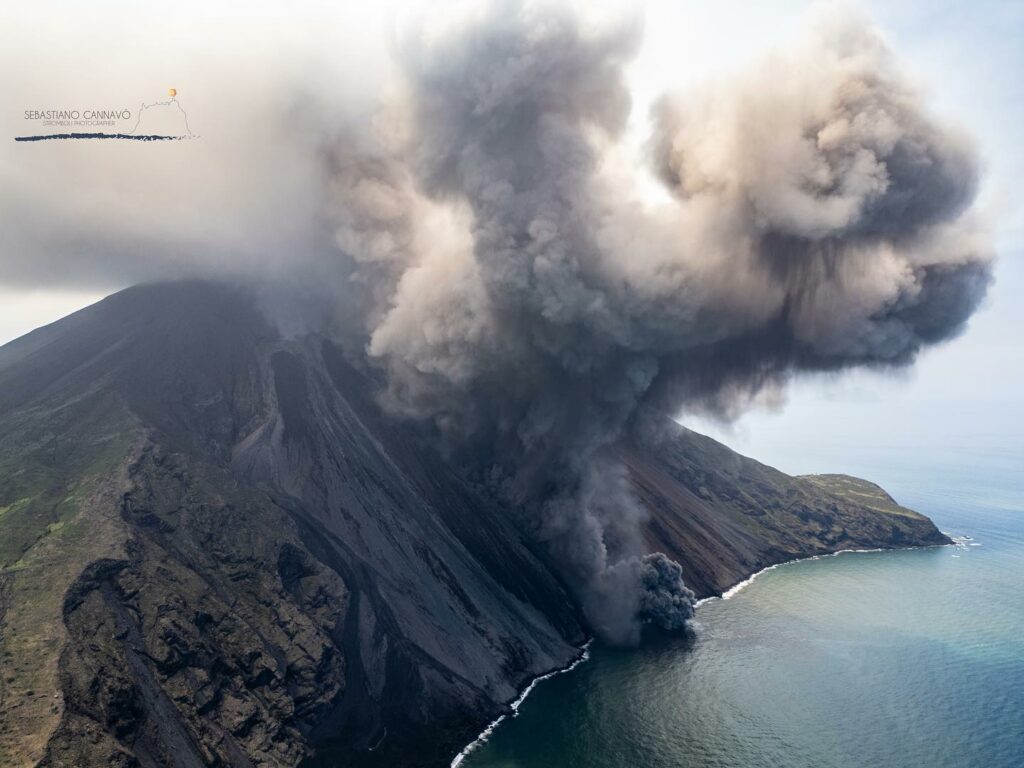
In particular, the effusive activity begun on July 4 continued during this period, produced by the two eruptive chimneys that opened along the Sciara del Fuoco at an altitude of approximately 500 m above sea level. the sea ; at the same time, with the onset of effusive activity, the ordinary explosive activity produced by the North and South-Central crater zones ceased. As noted in the previous weekly bulletin, the effusive regime in the days following the start of eruptive activity showed overall stability with the confluence of the two lava flows produced by the two vents into a single flow which progressed the along the Sciara del Fuoco and reached the coastline, forming a lava delta.
On July 11, around 12:08 UTC, a higher than usual explosion occurred and can be classified as a paroxysmal explosive event produced by the northern area of the crater terrace, with the development of rapidly expanding and extensive pyroclastic flows. in the sea (fig 3.2 E). Phenomenology develops as a sequence of events (Fig. 3.2 a-d):
• ~12:08:52: first modest explosion coming from the central-south zone of the crater with a predominant component of moderately hot ash (fig 3.2a),
• ~12:08:54: paroxysmal explosion from the northern zone with rose-shaped development, production of an eruptive column of approximately 5 km altitude and dispersion towards the southwest quadrants of the island (fig. 3.2 c, b, e)
• ~12:09:08: rapidly expanding pyroclastic flow along the Sciara and reaching the coast in ~23 seconds at a speed of ~58 m/s (fig 3.2 d)
• ~between 12:10 p.m. and 12:15 p.m.: the paroxysm ends with a series of secondary pyroclastic flows of significantly lower energy than the first.
In the hours following the event, the interruption of effusive activity and the continued absence of ordinary explosive activation was observed, with the exception of a single modest explosive event in the northern area of the crater that occurred July 12 at 08:28 UTC (fig 3.1e, f). The event was followed by a slight landslide of the basal and outer part of the northern area of the crater.
Source : INGV
Photo : Stromboli stati d’animo / Sebastiano Cannavo. ( 6 juillet 2024)
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
WEEKLY BULLETIN, from July 8, 2024 to July 14, 2024. (issue date July 16, 2024)
SUMMARY STATEMENT OF ACTIVITY
In light of the monitoring data, it appears:
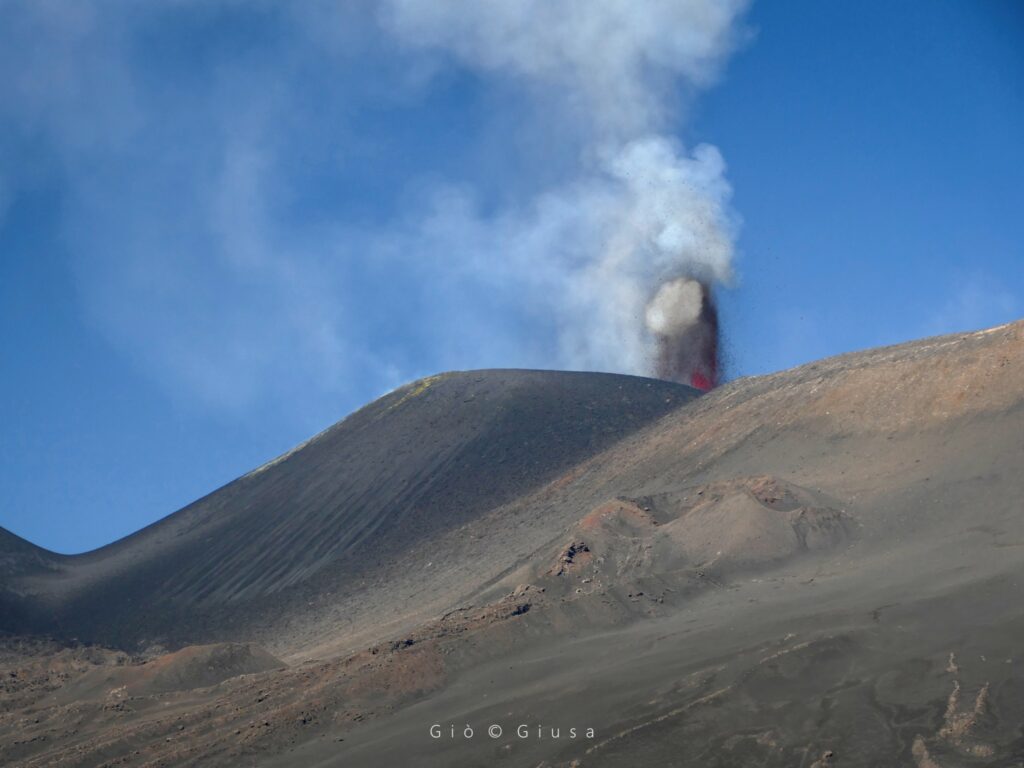
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Degassing activity at the Bocca Nuova Crater and the South-East Crater. Strombolian activity and lava flows produced by the Voragine crater in the summit zone.
Explosive activity with emission of ash at Voragine and the North-East Crater.
2) SISMOLOGY: Absence of seismic fracturing activity with Ml>=2.0. Average amplitude of the volcanic tremor at low level until the afternoon of July 10; sudden increase to high values until the early hours of July 12; average level the rest of the week.
3) INFRASOUND: Very strong infrasound activity on July 11. Moderate infrasound activity for the rest of the week.
4) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: During the last week of observation, the ground deformation monitoring networks did not record any significant changes. An inflation/compression phase is indicated by the summit inclination of the CPN and the dilatometric station of the DRUV.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: The SO2 flow remains at an average level
The soil CO2 flux remains at low values. The helium isotope ratio confirms a slight upward trend.
CO2 dissolved in groundwater does not show significant variations.
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity observed by satellite in the summit area was generally at a moderate to high level with very high values corresponding to the activity of the lava fountains on July 15, 2024.
7) OTHER OBSERVATIONS: The magma which fueled both the Strombolian activity of Voragine at the end of June 2024 and the two paroxysms of July 4 and 7, 2024 has an overall more primitive composition than that of the products that erupted on June 17, 2024 It is therefore probable that, in the second half of June 2024, the superficial magma reservoir of the volcano was affected by the arrival of deeper and more primitive magma.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
The monitoring of the volcanic activity of Etna, during the period in question, was carried out through various inspections in the summit area and through the analysis of images from the surveillance cameras of the INGV, Observatory of Etna (INGV-OE).
During the observation period, the activity of the summit craters was characterized in the afternoon of July 10 by a progressive increase in Strombolian activity in the Voragine crater with emission of ash in the summit area. This activity decreased in the following days, with a regression of the lava flow produced during the Lava Fountain of July 7. On the 14th, a gradual increase in explosive activity in the Northeast craters and Voragine caused an emission of ash which quickly dispersed above the craters. After this activity, the Northeast Crater and Voragine will continue to emit light emissions of ash in the following days.
Source : INGV
Photo : Gio Giusa , 11/07/2024.
Iceland , Reykjanes Peninsula :
Magma recharge continues to Svartsengi reservoir at steady rate
Another diking event and/or eruption is likely to occur in the coming three to four weeks
Updated 16 July at 15:25
As of today, the estimated magma recharge to the Svartsengi reservoir has reached the lower limit of what was lost during the 29 May diking event and first week of the eruption
The lower limit is around 13 million cubic meters and the upper limit 19 million cubic meters of magma.
A photo taken on June 22 in the only crater that remained active until the end of the eruption which began on May 29. (Photo: Civil Defense)
Assuming a similar volume of magma needs to be recharged to build up enough pressure in the system to trigger the next event (dike and/or eruption), geodetic modelling indicates that there is a very high probability that this will occur within the next three weeks
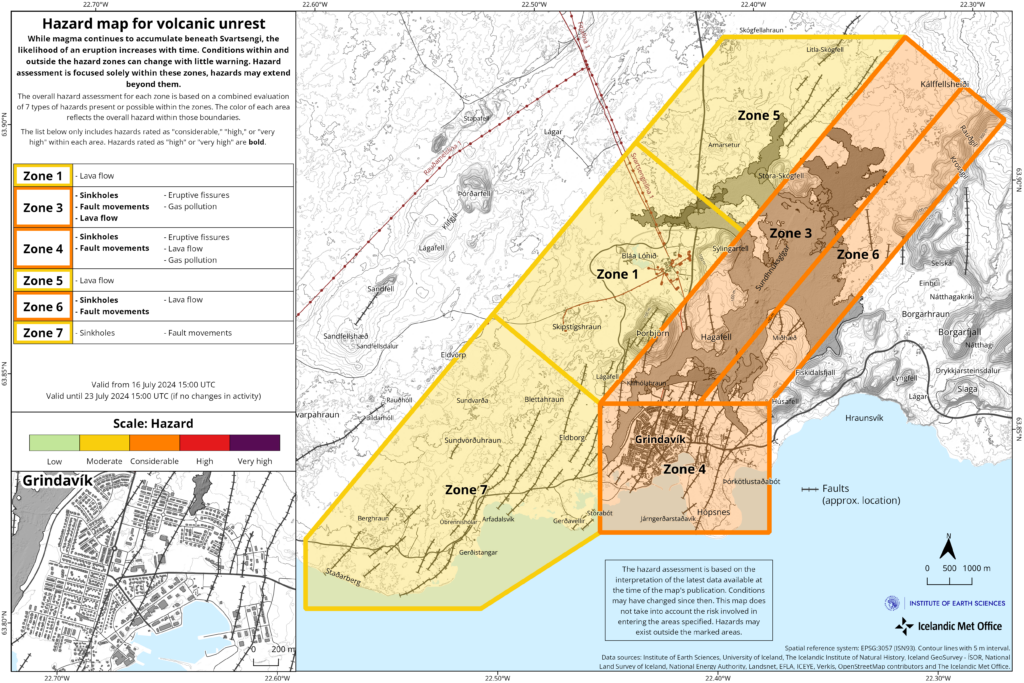
The hazard map has been updated and is valid until 26 July
If, however, a higher volume change is required (similar to that reached prior to the 29 May event, ~ 20 million m3) then this will be achieved within the next three to four weeks. This is based on the assumption that the inflow rate of magma from depth remains constant as of today.
Recent data analysis of the temporal evolution of fissure openings for previous Sundhnúks eruptions indicates a systematic southwest migration. Considering this data and the considerable amount of fault movement within Grindavík since November 2023, the likelihood of lava extrusion in Zone 4 is now considered higher for future eruptions.
Therefore, the likelihood of occurrence for fissure openings, lava flows and gas pollution has been raised to medium in Zone 4, in line with the assessment of these hazards in Zone 3.
This change does not currently affect the overall hazard level in Zone 4, which remains considerable (orange).
The hazard map is valid until 23 July (unless there is change in activity)
Source : IMO
Photos : Défense civile , IMO.
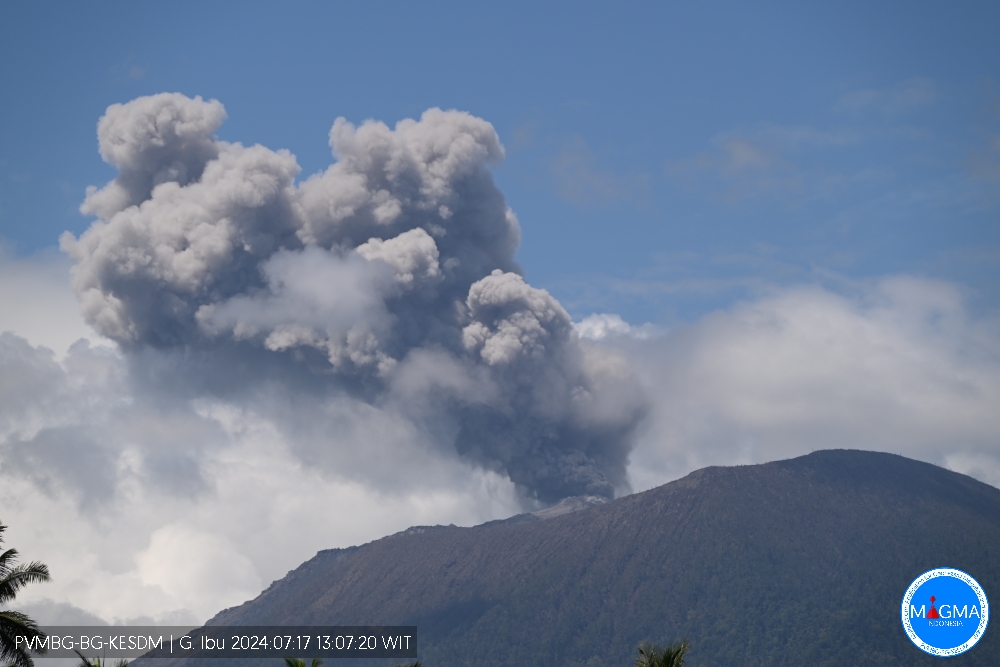
Indonesia , Ibu :
An eruption of Mount Ibu occurred on Wednesday July 17, 2024 at 1:05 p.m. WIT with the height of the ash column observed at ±1000 m above the summit (±2325 m above sea level). The ash column was gray in color with thick intensity, oriented towards the Northeast. This eruption was recorded on a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 22 mm and a duration of 178 seconds.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : July 17 , 2024
Volcano : Ibu (268030)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Ibu Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2024IBU094
Volcano Location : N 01 deg 29 min 17 sec E 127 deg 37 min 48 sec
Area : North Maluku, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 4240 FT (1325 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 04h05 UTC (13h05 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 7440 FT (2325 M) above sea level or 3200 FT (1000 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving to northeast. Volcanic ash is observed to be gray. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 22 mm and maximum duration 178 second.
Source et photo : Magma Indonésie .
Colombia , Chiles / Cerro Negro :
San Juan de Pasto, July 16, 2024, 3:45 p.m.
Weekly Activity Bulletin: Chiles Volcanic Complex and Cerro Negro (CVCCN)
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the CHILES AND CERRO NEGRO VOLCANOES, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE (SGC), an entity attached to the MINISTRY OF MINES AND ENERGY, reports that:
Between July 9 and 15, 2024 and compared to the previous week, there was a significant decrease in earthquake occurrence levels; however, the seismic energy released increased. The predominance of seismicity linked to rock fracture remains, followed by earthquakes associated with the movement of fluids, some of which have very low dominant frequencies.
The fracture earthquakes were preferentially located in two regions. The first source is located in the collapse zone located north of the summit of the Chiles volcano, with depths between 2 and 4 km compared to the reference height (4,700 m above sea level) and with a maximum magnitude of 2.2. The second source was located south-southeast of the summit of Chiles Volcano, with distances less than 9.4 km, depths less than 12 km, and a maximum magnitude of 1.4. Other earthquakes were located scattered in other sectors of these volcanoes. No felt earthquakes were reported. Deformation processes detected by both field stations and satellite information are maintained.
The evolution of activity in the CVCCN is the result of internal processes derived from the complex interaction between the magmatic system, the hydrothermal system and the geological faults of the area. Therefore, the probability of the occurrence of energetic earthquakes that can be felt by residents in the region of influence of the CVCCN persists.
Volcanic activity remains in a YELLOW ALERT state: active volcano with changes in the behavior of the base level of monitored parameters and other manifestations.
Source : Ingeominas
Photo : SGC ,( date ?)