September 19 , 2020.
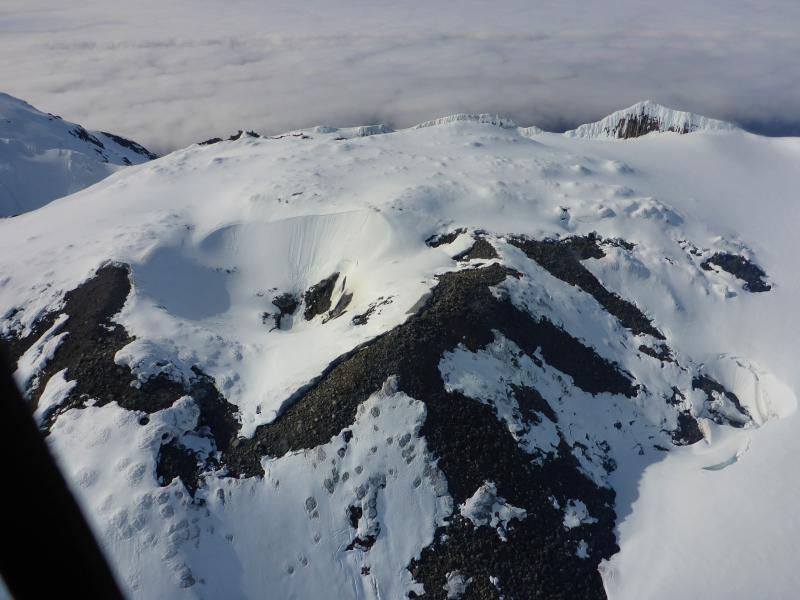
Alaska , Great Sitkin :
52°4’35 » N 176°6’39 » W,
Summit Elevation 5709 ft (1740 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Small local earthquakes continued over the past week. The overall rate of earthquakes continues to slowly decline to near background levels. No signs of unrest were observed in most cloudy satellite or web camera images during the past week.
Great Sitkin Volcano is monitored by local seismic and infrasound sensors, satellite data, web cameras, and remote infrasound and lightning networks.
Great Sitkin Volcano is a basaltic andesite volcano that occupies most of the northern half of Great Sitkin Island, a member of the Andreanof Islands group in the central Aleutian Islands. It is located 43 km (26 miles) east of the community of Adak. The volcano is a composite structure consisting of an older dissected volcano and a younger parasitic cone with a 3-km-diameter summit crater. A steep-sided lava dome, emplaced during the most recent significant eruption in 1974, occupies the center of the crater. That eruption produced at least one ash cloud that likely exceeded an altitude of 25,000 ft above sea level. A poorly documented eruption occurred in 1945, also producing a lava dome that was partially destroyed in the 1974 eruption. Within the past 280 years a large explosive eruption produced pyroclastic flows that partially filled the Glacier Creek valley on the southwest flank.
Source : AVO.
Photo : Clor, Laura
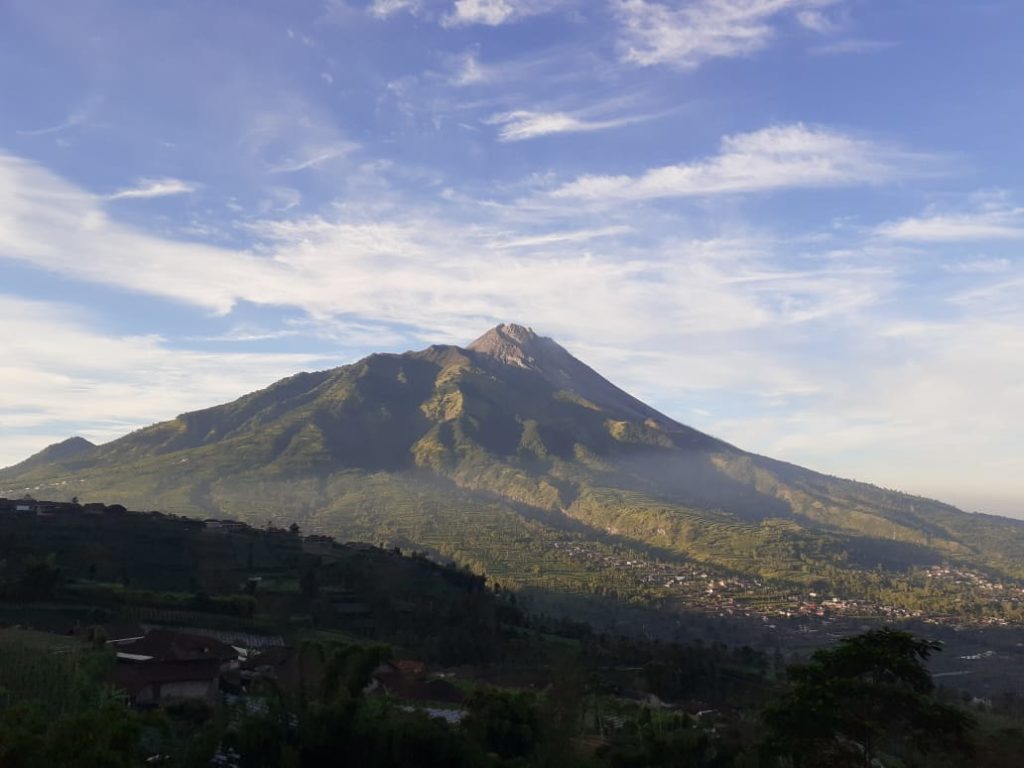
Indonesia , Mérapi :
Mount Merapi Activity Report September 11-17, 2020
I. OBSERVATION RESULTS
Visual
The weather around Mount Merapi is generally clear in the morning and at night, while the afternoon until evening is foggy. The smoke from the crater is white, thin to thick with low pressure. A maximum smoke height of 200 m was observed from the Mount Merapi observation post in Babadan on September 13, 2020 at 5:40 a.m.
The analysis of the morphology of the crater area from photos of the Southeast sector did not show any change in the morphology of the dome. The volume of the lava dome based on measurements using aerial photos with drones from July 26, 2020 was 200,000 m3.
Seismicity
This week, the seismicity of Mount Merapi recorded:
18 earthquakes of emissions (DG),
2 deep volcanic earthquakes (VTA),
15 shallow volcanic earthquakes (VTB),
130 multiphase earthquakes (MP),
18 low frequency earthquakes (LF),
40 avalanche earthquakes (RF),
12 tectonic earthquakes (TT).
The seismic intensity this week is higher than last week.
Deformation
The deformation of Mount Merapi which was monitored by EDM this week showed a shortening of the distance of the reflectors of about 2 cm.
Rain and lahars:
This week there have been no reports of rain, lahars or additional flow in the rivers flowing down from Mount Merapi.
Conclusion
Based on the results of visual and instrumental observations, it is concluded that:
1. The lava dome is currently in stable condition.
2. The volcanic activity of Mount Merapi is still quite high and is at the “WASPADA” activity level.
Source : BPPTKG.
Photos : Magma Indonésie , Archive Frekom .
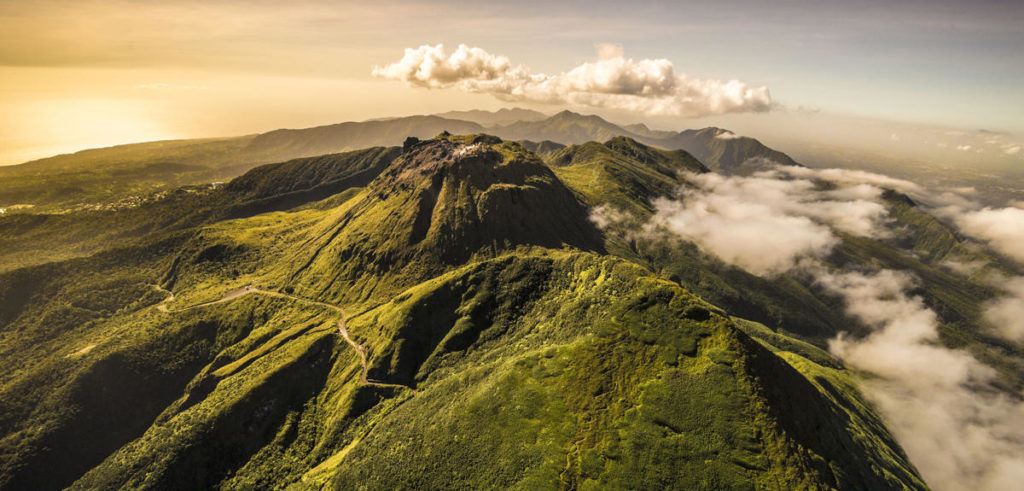
Guadeloupe , La Soufrière :
Tuesday September 15 at 1:00 p.m. (local time)
End of seismic sequence in the La Soufrière area of Guadeloupe – Basse Terre.
The sequence of volcanic earthquakes that began on Saturday September 12, 2020 at 07:20 a.m. local time (Saturday September 12, 2020 at 11:20 a.m. UT *) ended on Tuesday 15 september 2020 at 1:00 p.m. local time (Tuesday, September 15, 2020 at 5:00 p.m. UT *).
During this sequence, 180 earthquakes were recorded.
The earthquakes were of very low magnitude (M <1). The events are located at a depth of <2.5 km below the top of the dome of La Soufrière. No earthquakes were reported
as having been felt.
The alert level remains: yellow, vigilance.
Source : Direction de l’OVSG-IPGP.
Photo : A.-Brusini-hemis-fr.
Guatemala , Fuego :
DESCENT OF LAHARES IN THE RAVINES LAS LAJAS, HONDA AND JUTE.
The abundant rains of the last days and of this moment in the area of the volcanic complex, generate at the moment, lahars of low to moderate category in the ravines Las Lajas,, Honda and El Jute. The first and second canyons are tributaries of the Guacalate River, the third is a tributary of the Achíguate River. The lahars, descend with fine volcanic material, branches and tree trunks as well as blocks of 30 cm up to 1.5 meters in diameter.
The rains of the last few days keep the volcanic deposits saturated with moisture, so lahars will continue to be generated in the afternoon and at night around the volcano, so proper precautions should be taken.
Weak, moderate and strong explosions are recorded, in a range of 12 to 16 per hour, expelling columns of ash, at a height of 4700 meters above sea level (15,419 feet), dispersing over 20 kilometers to the west, to the southwest. Moderate to strong explosions generate rumblings, with shock waves that vibrate the roofs and windows of villages at a distance of 7 kilometers. Certain explosions generate avalanches of blocks in the direction of the canyons, Seca, Ceniza, Trinidad, Las Lajas and Honda. Ash falls are reported in the villages of Panimache, Morelia, Santa Sofía, Yucales, El Porvenir.
Source : INSIVUMEH.
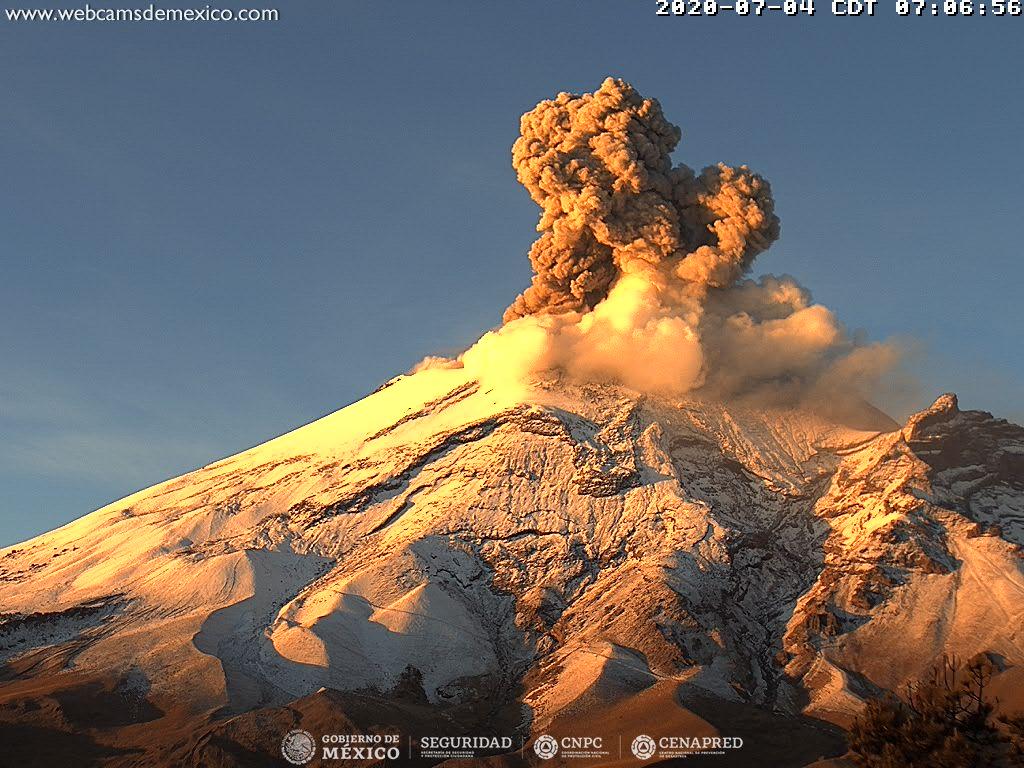
Mexico , Popocatepetl :
September 18, 11:00 a.m. (September 18, 4:00 p.m. GMT).
During the last 24 hours, 89 exhalations and 237 minutes of tremor have been identified according to the monitoring system of the Popocatépetl volcano. The events were accompanied by gas and ash emissions. Due to cloudy conditions, not all emissions could be observed. In addition, today at 01:26, a volcano-tectonic earthquake with a calculated magnitude of 2.3 was recorded.
At the time of this report, there is no visibility towards the volcano, however, in the early hours of the morning it was possible to observe emissions of ash and volcanic gases which were dispersing towards the West-South- Where is .
CENAPRED urges not to go near the volcano and in particular the crater, because of the danger posed by the fall of ballistic fragments and, in the event of heavy rains, to stay away from the bottom of the ravines because of the danger of mudslides and debris.
The Popocatépetl volcanic alert semaphore is at YELLOW PHASE 2.
Source : Cenapred .
Photo : Archive webcamdemexico