November 19 , 2023.
Iceland , Reykjanes Peninsula :
High likelihood of volcanic eruption continues. Updated 18 November at 15:00 UTC
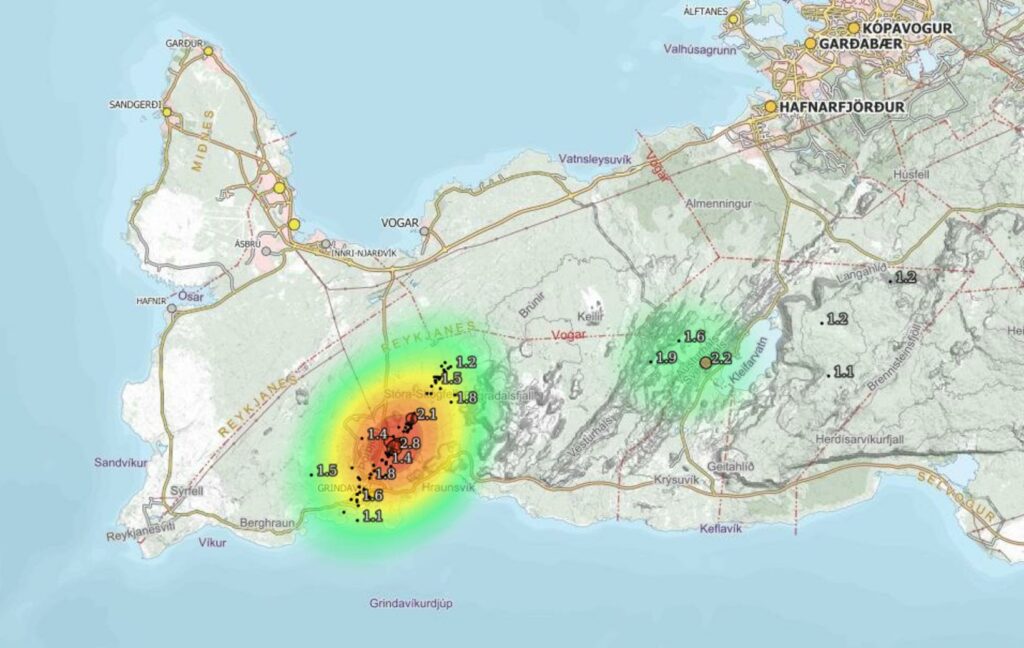
Seismicity related to the magma intrusion that formed suddenly a week ago remains high and constant. Approximately 1,700 earthquakes have been recorded in the last 24 hours, 1.000 of those recorded since midnight. The largest earthquake during the last 24 hours had a magnitude of 2.8 and occurred near Hagafell, 3.5 km NNE of Grindavík.
Signs of magma being closer to the surface.
Kristín Jónsdóttir, the director of natural-monitoring at the Icelandic Met Office, said at a Civil protection meeting this afternoon that the situation is in line with the past few days and the earthquake activity and deformation rate have decreased.
Jónsdóttir says that the number of earthquakes associated with the magma movement is both lower and slower with each passing day.
“The magma channel continues to expand and deepen, but it has expanded and deepened less in the past day than in the previous days.”
Signs of magma being closer to the surface.
Kristín Jónsdóttir, the director of natural-monitoring at the Icelandic Met Office, said at a Civil protection meeting this afternoon that the situation is in line with the past few days and the earthquake activity and deformation rate have decreased.
Jónsdóttir says that the number of earthquakes associated with the magma movement is both lower and slower with each passing day.
“The magma channel continues to expand and deepen, but it has expanded and deepened less in the past day than in the previous days.”
The seismic activity in the last 24 hours.
Magma has come closer to the surface
This decreasing activity indicates that the magma has entered the crust very high, as it is already very fractured and does not require much conflict to reach the surface.
While probability calculations still indicate that magma flows into the magma channel, it must be considered probable that it will erupt and that this increased probability will last at least for the next few days.
The data indicate that the most widening of the tunnel is around its center, in the area west of Hagafell. Therefore, scientists believe that this area is the most likely location for a volcanic eruption.
“But if lava comes up in the area in question, it can flow towards Svartsengi power plant or Grindavík, but also towards the north and east, depending on where exactly the lava comes up.”
Fastest event in 30 years of measurement history
According to Jónsdóttir, we are still in the middle of a chain of events, of all the many events on the Reykjanes peninsula in the past three years, which began in mid-October with a lands rise at Mt. Þorbjörn. The activity took a new direction on November 10, when tremors began to be detected at Sundhnúkar crater row.
“Then the signs of the upheavals that came with the formation of the magma channel one of the fastest events we’ve seen in 30 years of measurement,” she says, adding that the breakthrough was a major challenge for residents, scientists and responders. The time it takes for the earth to recover will possibly be proportional to the size of the breakthrough.
Sources : IMO , Icelandmonitor.
Photo : map/Map.is
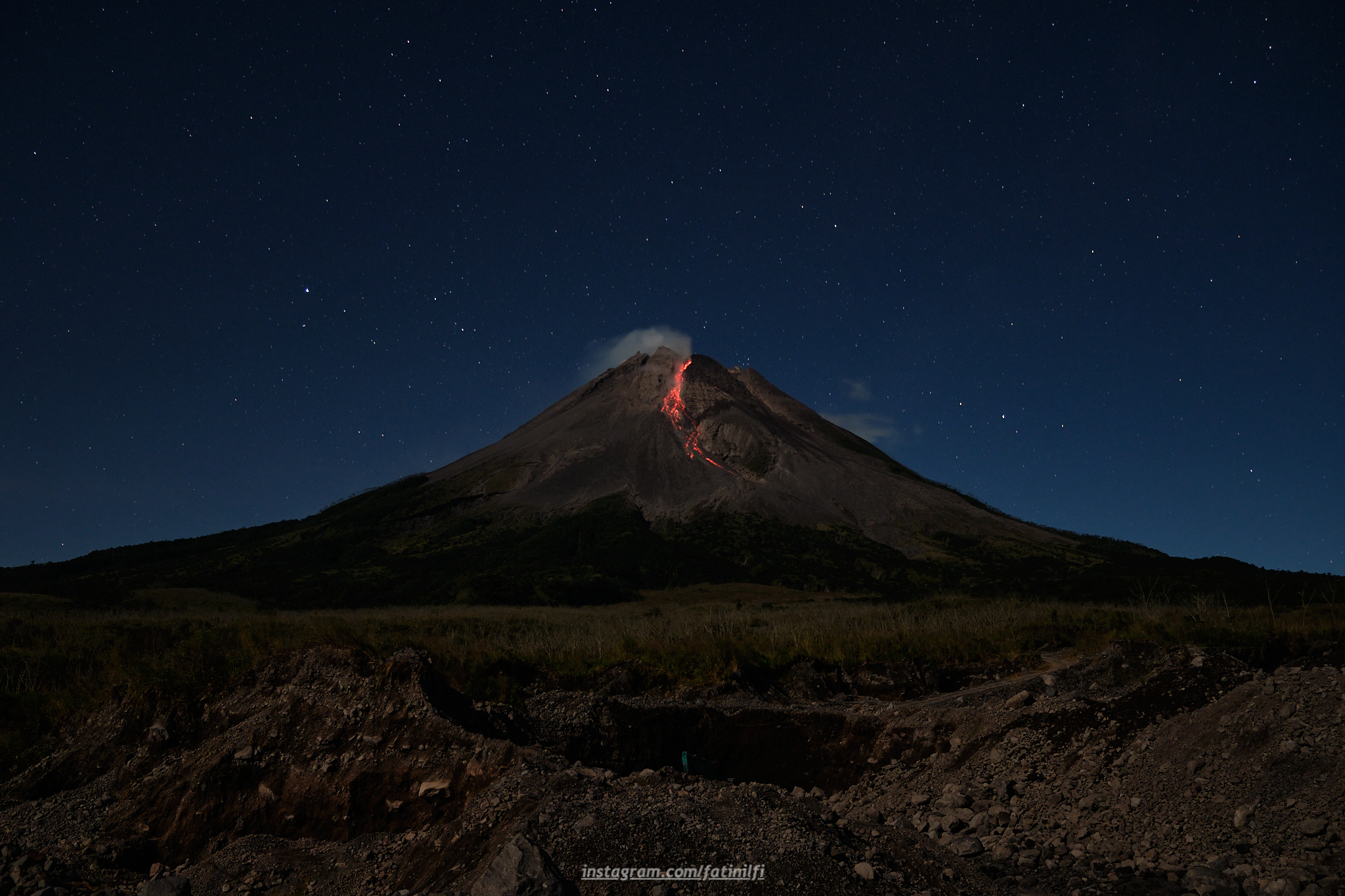
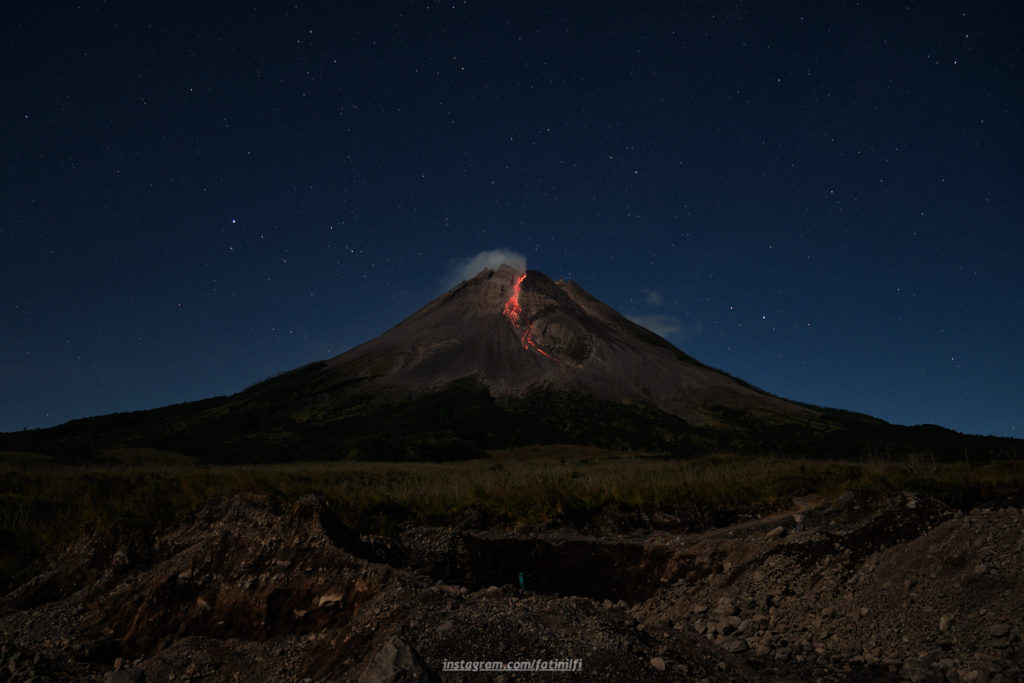
Indonesia , Merapi :
Report on the activity of Mount Merapi from November 10, 2023 to November 16, Published on November 17, 2023.
OBSERVATION RESULTS
Visual
The weather around Mount Merapi is generally sunny in the morning and afternoon, while the evening is foggy. White smoke, fine to thick, low to medium pressure and 150 m high was observed from the observation post of Mount Merapi in Badaban on November 11, 2023 at 5:30 a.m.
This week, lava avalanches were observed 69 times towards the South and Southwest, including 10 times upstream of the Boyong River up to 1500 m and 59 times upstream of the Bebeng River up to a maximum of 1700 m. The sound of avalanches was heard 30 times from the Babadan post with low to moderate intensity.
Thanks to the thermal images taken by drone on November 16, 2023, it was possible to analyze the situation of the summit domes.
The highest hot spot in the southwest dome area reaches 292°C. For the central dome, no significant changes were observed. The highest hotspot reached 165°C higher than the temperature measured during the previous period.
Based on the analysis of aerial photos from September 28, 2023, the volume of the southwest dome was measured at 3,348,600 cubic meters and that of the central dome at 2,358,000 cubic meters.
Seismicity
This week, the seismicity of Mount Merapi showed:
2 shallow volcanic earthquakes (VTB)
1956 multi-phase (MP) earthquakes,
814 avalanche earthquakes (RF)
9 tectonic earthquakes (TT).
The intensity of seismicity this week is lower than last week, but the number of earthquakes is still quite high.
Deformation
The deformation of Mount Merapi that was monitored using EDM this week showed a shortening of steepening distance of 0.01 cm/day.
Rain and lahars:
There was rain this week at Mount Merapi observation post in Kaliurang with an intensity of 67 mm/hour for 70 mins on November 12, 2023. There were no reports of additional flows or lahars from of rivers that descend from Mount Merapi.
Conclusion
Based on the results of visual and instrumental observations, it is concluded that:
-Mount Merapi’s volcanic activity is still quite high in the form of effusive eruption activity. The activity status is defined at the “SIAGA” level.
The current danger potential is in the form of lava avalanches and hot clouds in the South-South-West sector including the Boyong river for a maximum of 5 km, the Bedog, Krasak, Bebeng rivers for a maximum of 7 km. In the South-East sector, it includes the Woro river for a maximum of 3 km and the Gendol river for 5 km. While the ejection of volcanic material in the event of an explosive eruption can reach a radius of 3 km from the summit.
Source : BPPTKG
Photo : , merapi_uncover
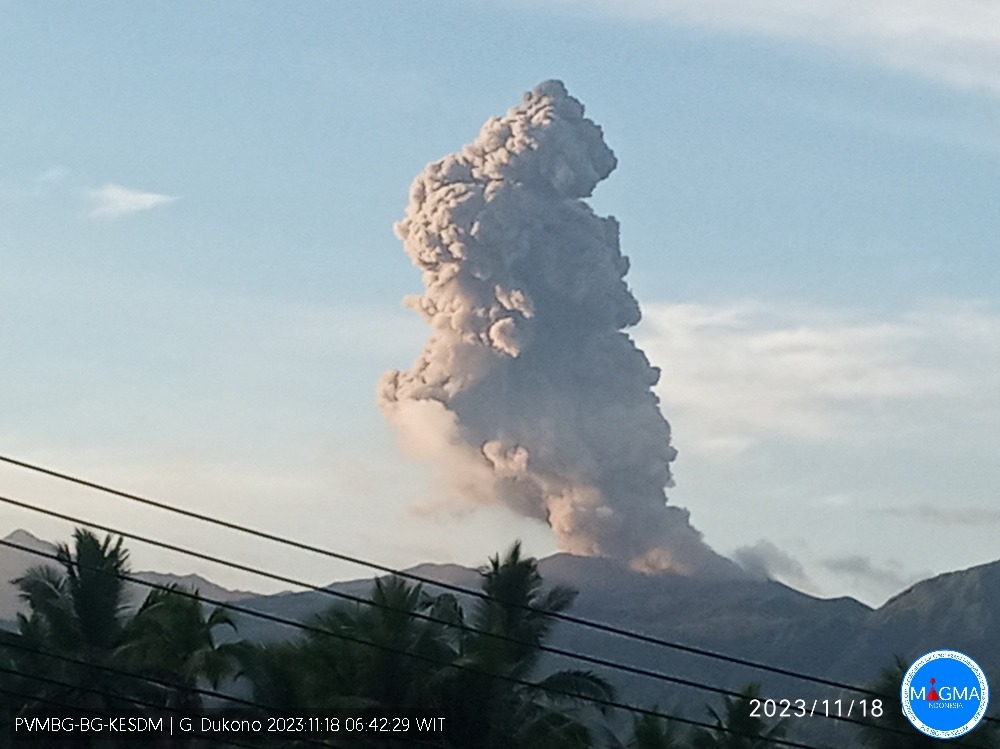
Indonesia , Dukono :
Dukono erupted on Sunday, November 19, 2023, at 07:24 WIT. The height of the eruptive column was observed to be ±2,600 m above the peak (±3,687 m above sea level). The ash column was observed to be white, gray to black, with thick intensity, oriented towards the Northeast and East. At the time of writing, the eruption was still ongoing.
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : November 18 ,2023
Volcano : Dukono (268010)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Dukono Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2023DUK024
Volcano Location : N 01 deg 41 min 35 sec E 127 deg 53 min 38 sec
Area : North Maluku, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 3933 FT (1229 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 22h24 UTC (07h24 local).
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 12253 FT (3829 M) above sea level or 8320 FT (2600 M) above summit. May be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash cloud moving from northeast to east. Volcanic ash is observed to be white to dark. The intensity of volcanic ash is observed to be thick.
Remarks :
Eruption and ash emission is continuing.
Source et photo : Magma indonésie
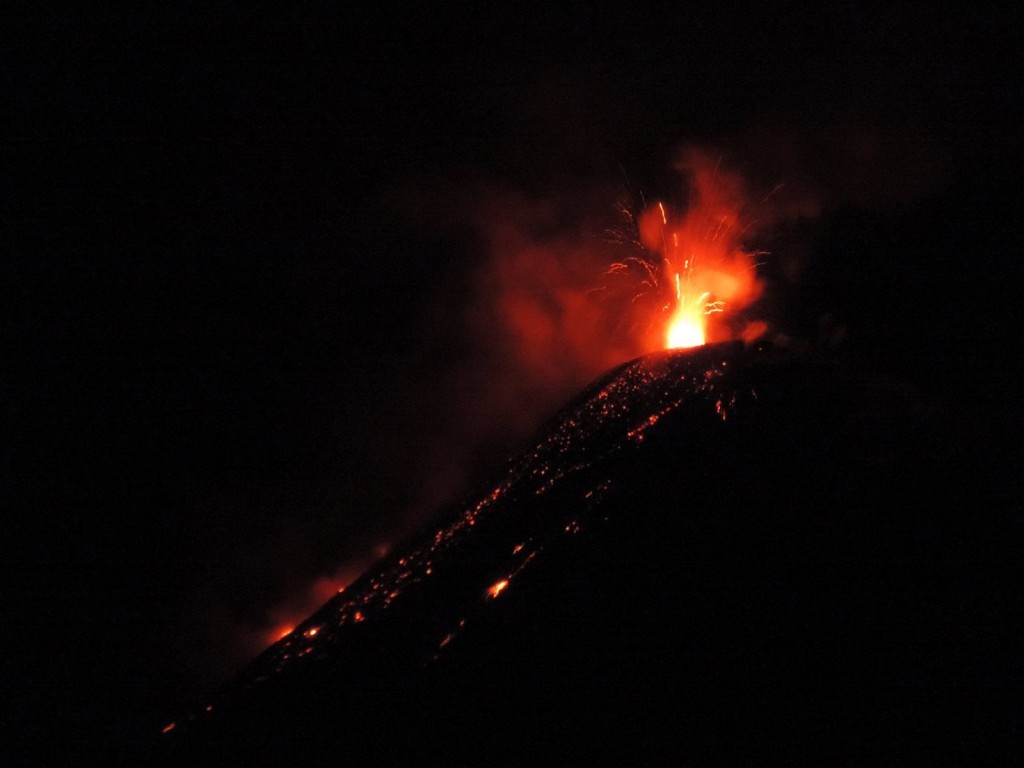
Ecuador , Reventador :
DAILY REPORT ON THE STATE OF THE REVENTADOR VOLCANO, Saturday November 18, 2023.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface activity level: Moderate, Surface trend: No changes
Internal activity level: Moderate, Internal trend: No changes
Seismicity: From November 17, 2023, 11:00 a.m. to November 18, 2023, 11:00 a.m.:
The following table shows the number of seismic events from the reference station in the last 24 hours.
Explosion (EXP) 59
Long Period (LP) 9
Transmitting Tremor (TREMI) 14
Harmonic Tremor (VT) 8
Precipitation/Lahars:
Rainfall is not recorded. **In the event of heavy rains, these could remobilize the accumulated materials, generating mud and debris flows which would descend the sides of the volcano and flow into adjacent rivers.
Emissions/ash column:
From yesterday afternoon until today morning, thanks to the surveillance camera system, several gas and ash emissions were recorded with heights between 500 and 1000 meters above the level of the crater in the directions West and North-West. In addition, the VAAC in Washington reported an emission of gas and ash at a height of 1,010 meters above the level of the crater, in a southeast direction.
Other monitoring parameters:
The MIROVA-MODIS satellite system recorded 1 moderate thermal anomaly and 1 weak thermal anomaly and the MIROVA-MODIS satellite system recorded 1 moderate thermal anomaly in the last 24 hours. While the WORLDVIEW satellite system recorded 2 thermal anomalies in the last 12 hours.
Observation:
During the night of yesterday and early today, several episodes of incandescence were recorded with the descent of incandescent material along the flanks of the volcano, up to 800 meters below the level of the crater. Since yesterday afternoon until this morning, the volcano has remained generally clear. At the time of publishing this report, the volcano is cloudy.
Alert level: Orange.
Source : IGEPN.
Photo : Hosteria ( archive).
Alaska , Great Sitkin :
52°4’35 » N 176°6’39 » W,
Summit Elevation 5709 ft (1740 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Slow eruption of lava in the summit crater of Great Sitkin Volcano continues. Seismic activity was quiet over the past day. No unusual activity was observed in mostly cloudy satellite and web camera views over the past day.
The current lava flow began erupting in July 2021. No explosive events have occurred since a single event in May 2021.
Local seismic and infrasound sensors, web cameras, regional infrasound and lightning networks, and satellite data are used to monitor the volcano.
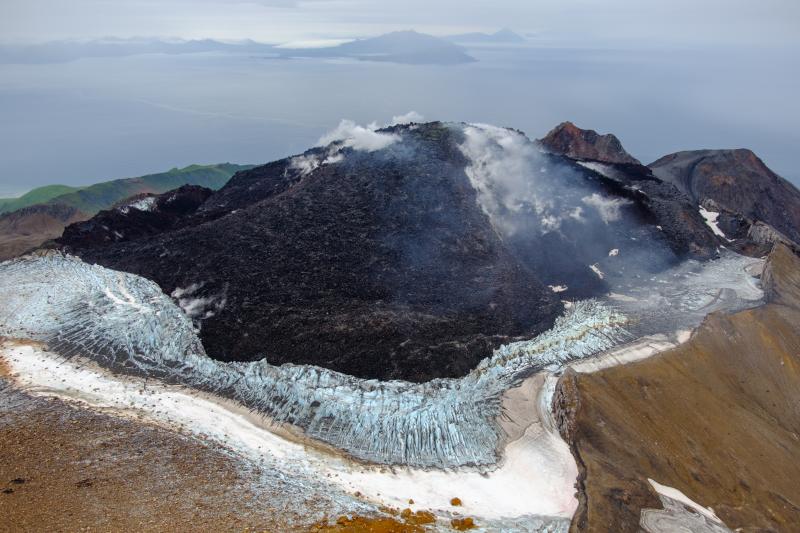
Great Sitkin Volcano on September 3, 2023, during helicopter approach for sampling efforts by AVO geologists. Image is looking west, with Adak and Kanaga Islands visible on the horizon.
Great Sitkin Volcano is a basaltic andesite volcano that occupies most of the northern half of Great Sitkin Island, a member of the Andreanof Islands group in the central Aleutian Islands. It is located 26 miles (43 km) east of the community of Adak. The volcano is a composite structure consisting of an older dissected volcano and a younger parasitic cone with a ~1 mile (1.5 km)-diameter summit crater. A steep-sided lava dome, emplaced during the 1974 eruption, occupies the center of the crater. That eruption produced at least one ash cloud that likely exceeded an altitude of 25,000 ft (7.6 km) above sea level. A poorly documented eruption occurred in 1945, also producing a lava dome that was partially destroyed in the 1974 eruption. Within the past 280 years a large explosive eruption produced pyroclastic flows that partially filled the Glacier Creek valley on the southwest flank.
Source : AVO
Photo : Loewen, Matt / AVO / U.S. Geological Survey.