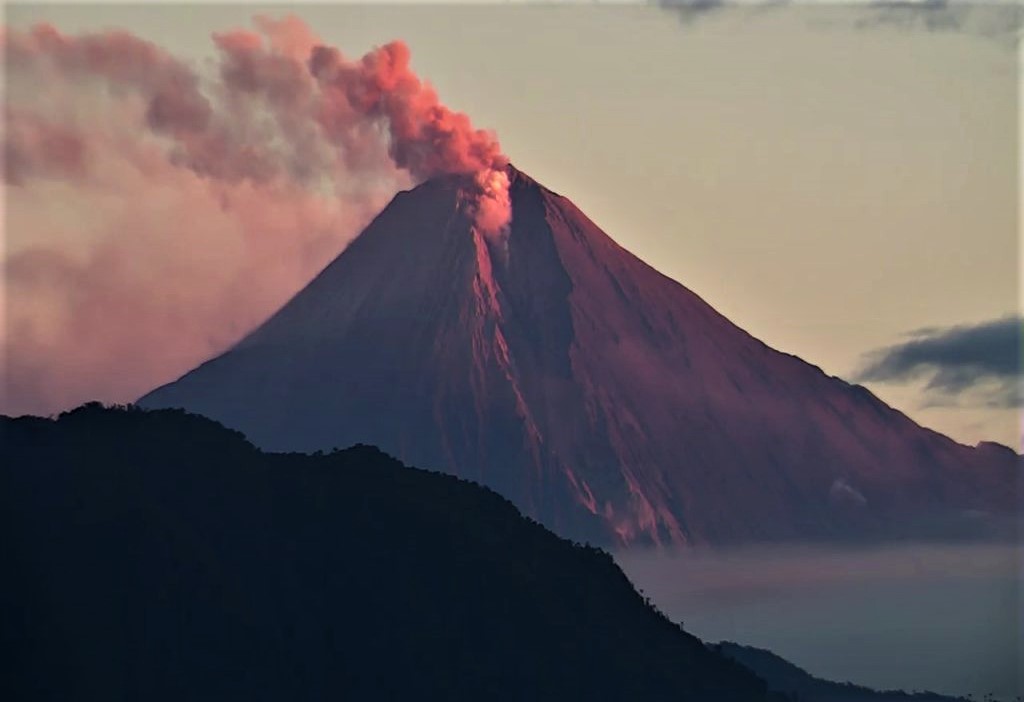
February 10 , 2022.
Tonga Islands , Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai :
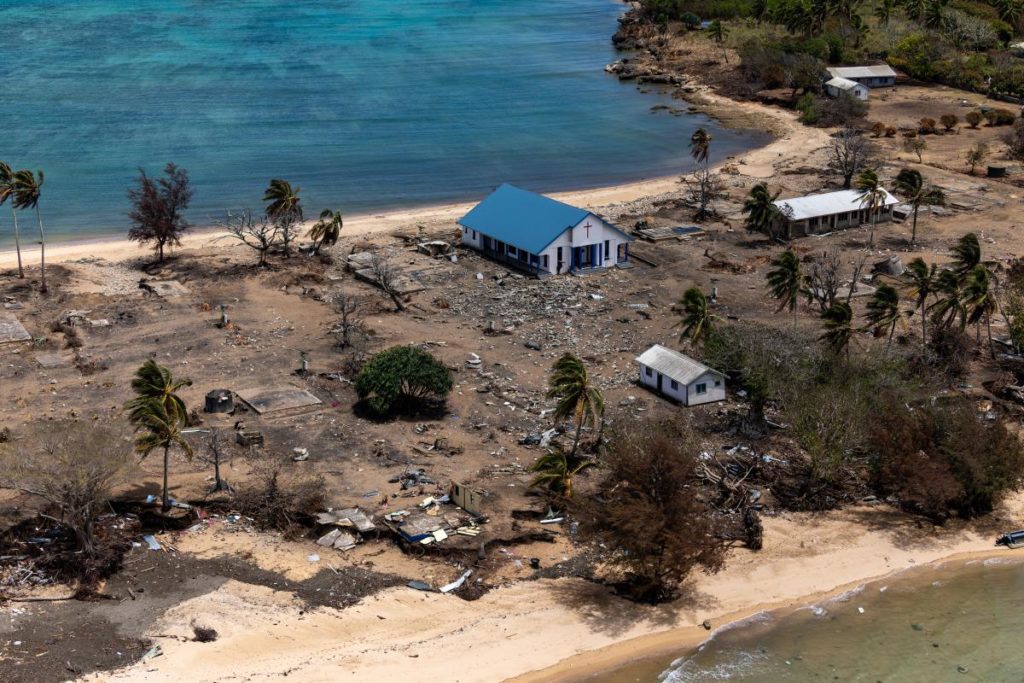
On 4 February the Tonga Geological Services (TGS) posted drone footage of the Good Samaritan Beach, located on the NE side of Tongatapu, showing that tsunamis from the 15 January Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai eruption reached areas at 15 m elevation, 200 m inland. A 6 February post provided details of what happened when tsunamis reached Mango Island (75 km ENE), stating that waves 12 m high went over the church tower, reached 500 m inland, and pushed buildings and structures against the inland wall of trees. Residents fled to an area that was 30 m elevation, 700 m from the coast, and stayed there all night as ash fell. TGS noted that clean-up efforts were continuing on the islands and communications were slowly being restored.
Dozens of earthquakes, M 4.5-5, were centered in the vicinity of the volcano after the eruption, at least through 24 January. The type of earthquake signal was unknown, though they likely represented post-eruption movement along existing faults and not magma movement.
Sources : Tonga Geological Services, Government of Tonga , GVP.
Photo : Petty Officer Christopher Szumlanski.
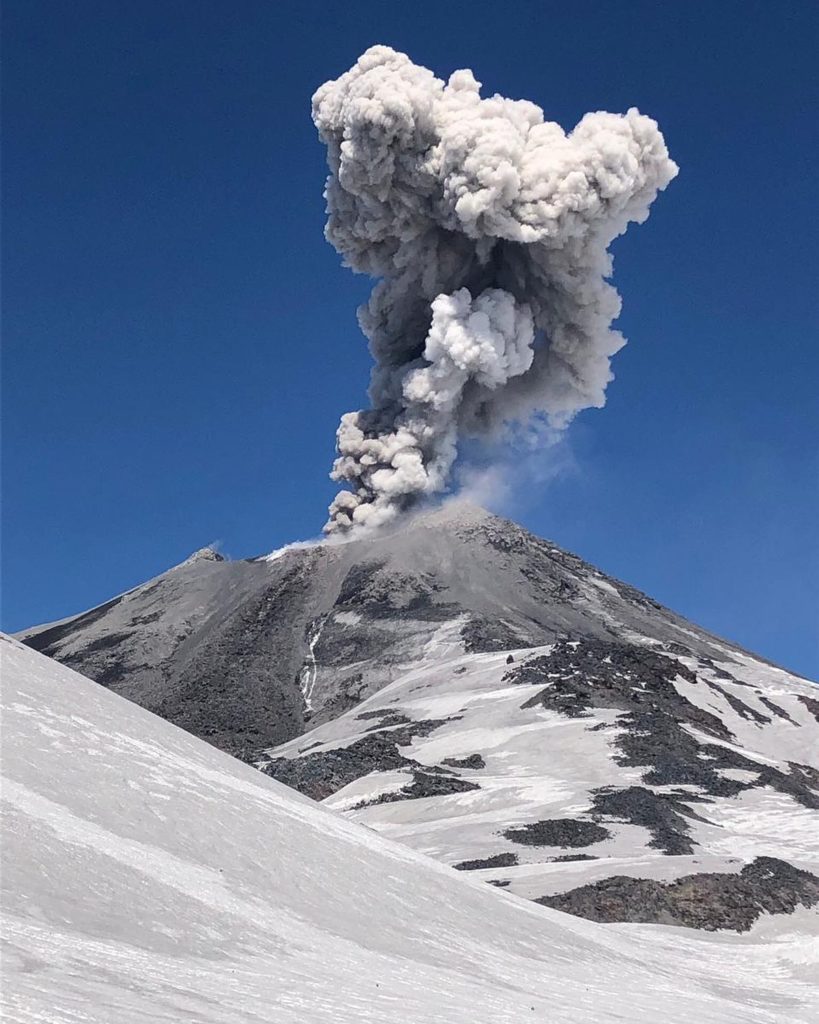
Chile , Nevados de Chillan :
The seismicity parameters associated with the fracturing processes of rigid materials (type VT) presented a significant decrease, returning to values similar to those presented during the month of December 2021, in the same way, the events associated with the dynamics of fluids (LP, VLP and TR type) and explosive type (EX) events remained at similar levels to the previous period.
The higher energy VT-type event had a local magnitude (ML) of 2.3 and was located 3.1 km east-southeast of the volcanic edifice, at a depth of 4.5 km.
From the analysis of the images provided by the surveillance cameras belonging to the OVDAS as well as satellite images, explosions from the active crater were observed, generally characterized by a moderate content of pyroclasts, generally of low impact. The maximum height recorded was 1600 m above crater level on January 19.
The occurrence of pyroclastic flows on January 19, 25 and 26 stands out, with a proximal range of less than 500 m from the crater.
No ongoing extrusive processes or relevant changes in crater morphology were observed.
Episodes of nocturnal incandescence continued to be recorded throughout the period, standing out on January 25 and 26.
According to data obtained by the network of GNSS stations installed on the volcano, no clear or sustained trend has been observed over time. The highest calculated uplift rate corresponds to 0.4 cm / month, in the stations located east of the active crater.
Nine (9) thermal alerts were recorded in the area with a maximum value of 29 MW on January 28, a value considered moderate for this volcano. In turn, luminance anomalies were detected on January 20, 23, 25 and 30 from analysis of Sentinel 2-L2A images.
DOAS gas measurement equipment recorded a maximum sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission value of 526 t/d corresponding to January 16, while the average recorded emission was 285 t/d, remaining at values similar to those displayed in previous months.
Source : Segemar .
Photo : @nluengov ( 2/2021)
Ecuador , Sangay :
IG reported a high level of activity at Sangay during 2-7 February, and seismicity was characterized by daily explosions, long-period earthquakes, and signals indicating emissions. Weather clouds and rain often prevented visual and webcam observations of the volcano, though almost daily ash-and-gas plumes were identified in satellite images by the Washington VAAC or in webcam views; plumes rose as high as 1.5 km above the volcano and drifted in multiple directions. Multiple daily thermal anomalies over the volcano were visible in satellite data. Several ash emissions were observed in satellite images on 8February; at 04h30 an ash plume rose more than 7 km above the summit, the highest a plume had risen since the current eruption started in 2019. Ashfall was reported in areas to the NW, in the provinces of Chimborazo and Bolivar.
DAILY REPORT OF THE STATE OF SANGAY VOLCANO. 09 February 2022.
Surface activity level: High, Surface trend: Ascending.
Internal activity level: High, Internal trend: No change.
Seismicity: From February 08, 2022, 11:00 a.m. to February 09, 2022, 11:00 a.m.:
Information on seismic events was provided by the SAGA and SAG1 stations.
Explosion type (EXP): 45
Long Period Types (LP):2
Emission Tremors (TREMI): 15
Rains / Lahars:
No lahars were recorded. **In the event of heavy rains, these could remobilize the material accumulated in the gullies, generating mudslides and debris that would descend through the drains of the volcano and flow into the adjacent rivers.**
Emission / ash column:
Since yesterday afternoon, emissions of gas, steam and ash have been observed with variable heights between 1000m and 2000m above the level of the crater, with a northwest direction.
Other Monitoring Parameters:
FIRMS registers 3 thermal alerts, while MIROVA registers 1 high thermal alert (208 MW).
Observation:
During the night hours, the release of incandescent materials was observed following some explosions. There are no reports of ash fall so far. The volcano area is cloudy.
Sources : GVP , IGEPN.
Photo : ECU
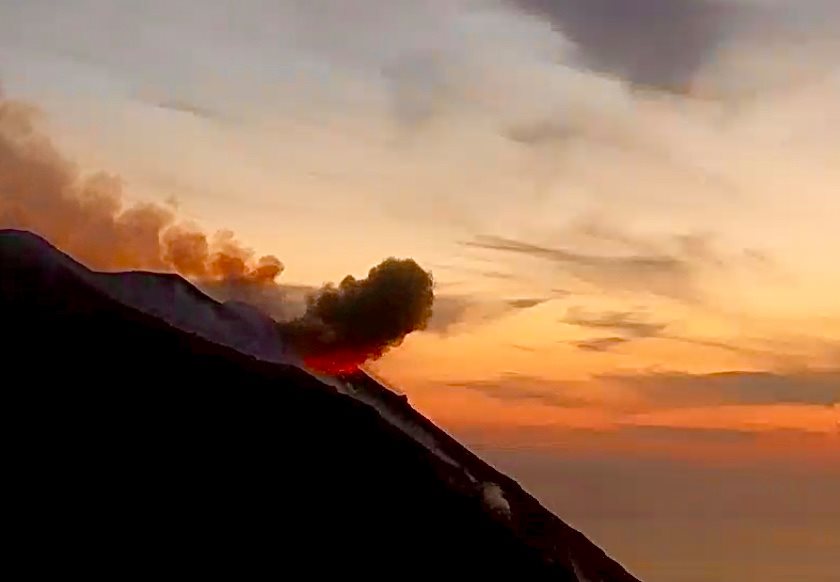
Italy , Stromboli :
WEEKLY BULLETIN from January 31, 2022 to February 06, 2022 (issue date February 08, 2022)
ACTIVITY BULLETIN SUMMARY:
In the light of the surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: During this period, normal explosive activity of the Strombolian type was observed with projection activity in the N zone. The total hourly frequency of the explosions fluctuated between average values (11-14 events / h). The intensity of the explosions was low in the area of the North crater and variable from low to medium in the area of the Center-South crater.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The seismological parameters monitored do not show any significant variations.
3) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: Ground deformation monitoring networks have not detected any significant variations.
4) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO flux at an average level.
CO2 flux in the crater area stable at high values.
C/S ratio up slightly on average values.
The isotopic ratio of helium, slightly decreasing, is established at mean R/Ra values of 4.31.
5) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity observed by satellite was at a low level.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
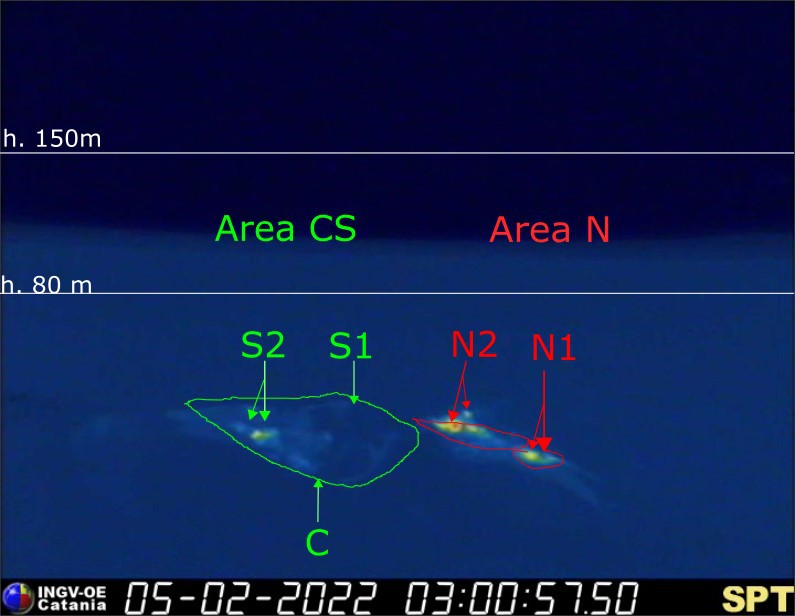
During the observation period, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized through the analysis of images recorded by the INGV-OE surveillance cameras (altitude 190m, Punta Corvi, altitude 400m and Pizzo). The explosive activity was mainly produced by 4 (four) eruptive vents located in the North crater area and 2 (two) eruptive vents located in the Center-South crater area. All the mouths are located inside the depression which occupies the terrace of the crater.
Due to the unfavorable weather conditions of January 31, February 5 and February 6, 2022, the visibility of the crater terrace was insufficient for a correct description of the eruptive activity.
Sector N1, with two emission points, located in the North crater area produced low intensity explosions (less than 80 m high) emitting fine materials (ash) mixed with coarse materials (lapilli and bombs) . Sector N2, with two emission points, showed low intensity explosive activity (less than 80 m in height) emitting coarse materials with intense discontinuous projection activity for short periods from February 2 to 4. The average frequency of explosions was between 9 and 12 events / h.
In the Center-South zone, sectors S1 and C did not show significant explosive activity, while the two vents located in sector S2 produced explosions, even simultaneously, of mainly medium-low intensity (sometimes the products of the explosions exceeded 80 m in height) emitting coarse materials mixed with fine materials. The frequency of the explosions varied between 2 and 3 events/h.
Source : INGV
Photo : webcam / Wolfgang Künker
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
Update on ETNA activity, February 10, 2022, 05:12 (04:12 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo reports that during the night, we observe the resumption of a modest explosive activity at the level of the Southeast Crater, highlighted by visible incandescences on the cameras of the video surveillance network. .
The activity is currently confined inside the crater and generates discontinuous and light ash emissions. According to the forecast model, the volcanic plume is heading southwest.
From 01:30 UTC an increase in the average amplitude of the tremor is observed up to average values with an increasing trend. The source is located in the Southeast Crater area at a depth of about 3000 m above sea level. At the same time, infrasound activity also showed an increase and is located below the South Crater -East.
There are no significant variations in the time series of the tilt and GNSS network data
Further updates will be communicated soon.
Source : INGV.
Photo : Giuseppe Tonzuso via Boris Behncke.