December 17 , 2021.
Spain / La Palma , Cumbre Vieja :
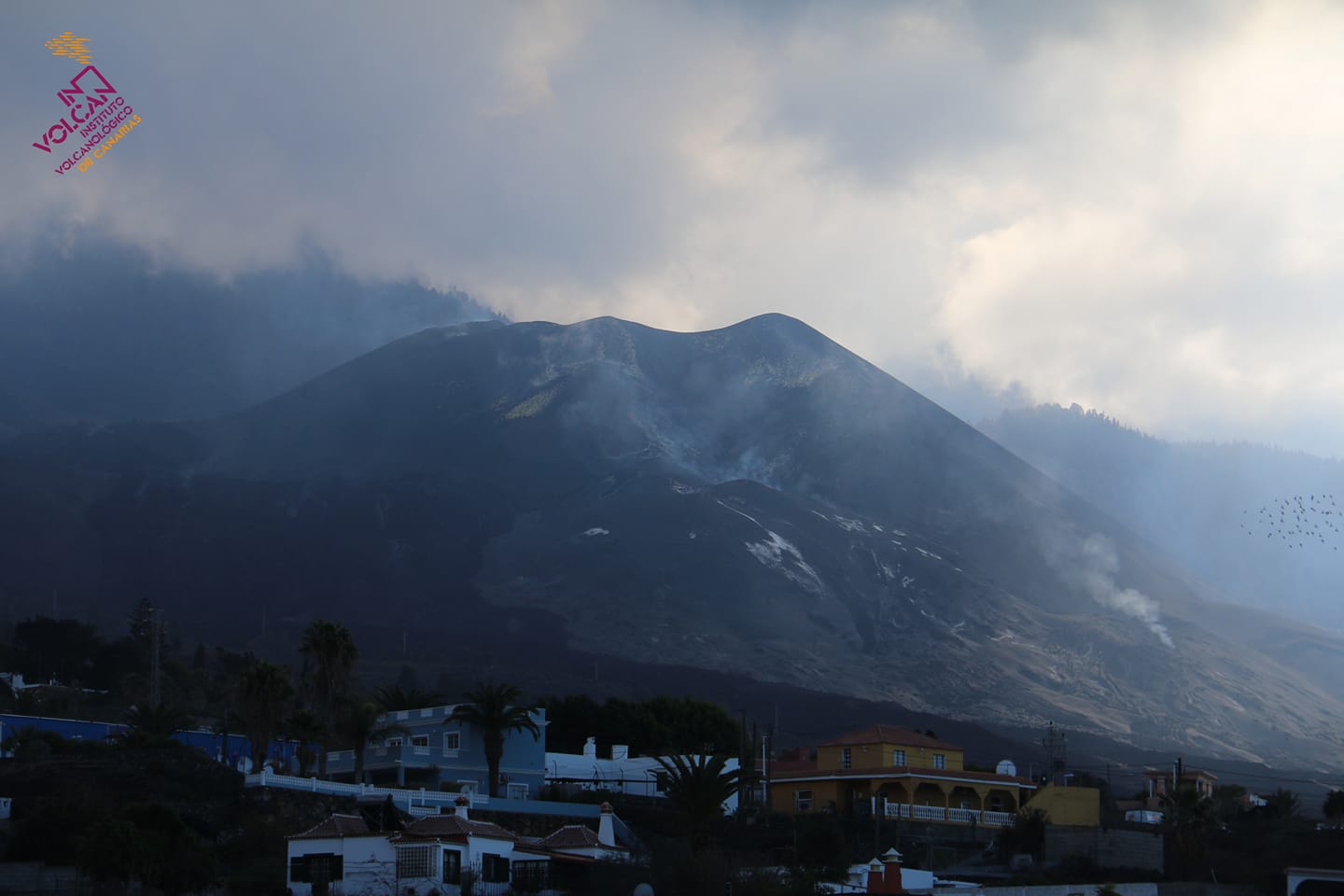
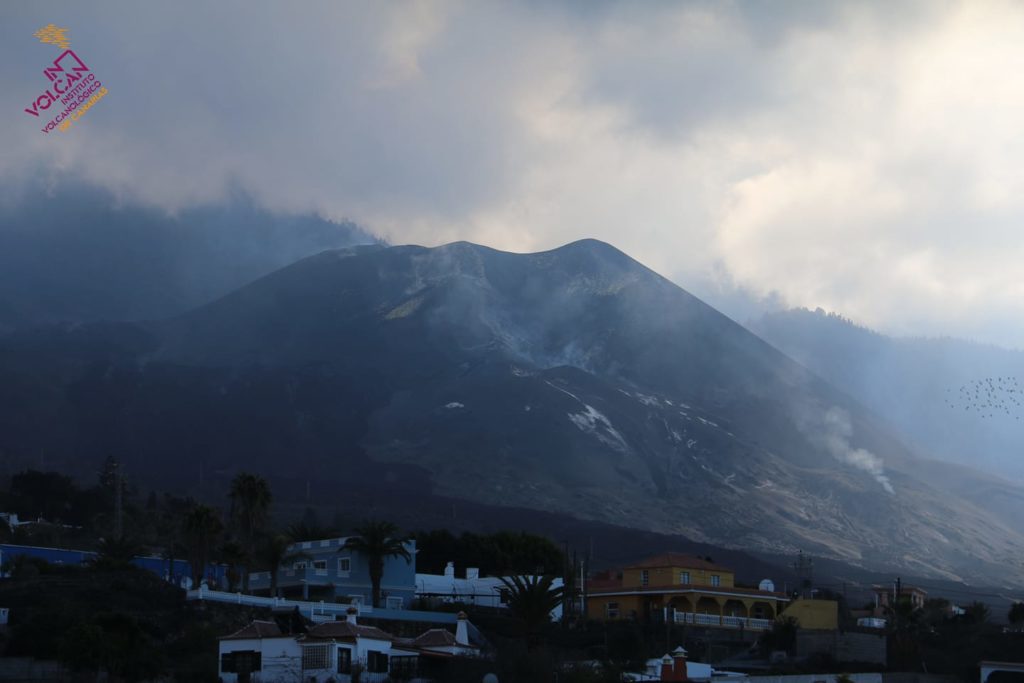
December 16, 2021, 09:00 UTC. Eruptive activity continues on La Palma.
Since the last press release, a total of 56 earthquakes have been located on the island of La Palma, including one felt by the population.
The maximum recorded magnitude is 3.4 (mbLg), corresponding to yesterday’s earthquake at 15:09 UTC, at a depth of 14 km. The minimum magnitude of the localized earthquake was 1.2 mbLg.
Localized seismicity continues under the central area of Cumbre Vieja in the same areas of the last days, with dispersion. Most earthquakes (39) are located at depths between 8 and 17 km. Eleven earthquakes were also located at depths between 33 and 40 km and 6 at depths between 0 and 5 km.
Apart from this localized volcano-tectonic activity, and coinciding with the disappearance of the volcanic tremor, low frequency signals interpreted as LP type events were detected in the seismic stations.
The amplitude of the tremor signal over the past 24 hours has remained at very low levels, close to the pre-eruptive period.
The island’s network of permanent GNSS stations does not show a clear trend in the deformation of the stations closest to the eruptive centers.
In the rest of the seasons, the slight deflation observed previously stabilized.
In view of the image calibrated at 08:45 UTC, no type of emission is visible.
The height of the cone is measured by obtaining a value of 1122 m at sea level.
The sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission « has almost disappeared » compared to the values of the previous days.
The deformation of the surface persists, and the CSIC volcanologist believes it will be permanent, as happened with the eruption of the submarine volcano Tagoro, in El Hierro, ten years ago. Additionally, the drones did not detect any lava flows, « not even any remains. You only see incandescences, ”he says. « It is not excluded that a small overpressure will occur and generate a small activity impulse of short duration. But nothing suggests a reactivation of the volcano, ”explains Soler. Juan Carlos Carracedo corroborates this thesis, noting that all the parameters that measure the energy of the eruption have calmed down or ceased, so it is very difficult for the volcano to enter a phase of greater activity. He agrees that if there was deep or intermediate seismicity, evidence that “there is still lava stored with a tendency to come out,” there could be doubts about that. And he adds that if there was magma in the eruptive conduits, over the days, « it cools down, becomes more pasty and solidifies » and would produce a plug that would require a great deal of energy from below to unblock it. « It doesn’t. there is no sign that this could happen. The logical thing is to think that the rash is over, « says Carracedo.
Sources : IGNes , El Pais .
Photos : I love the world
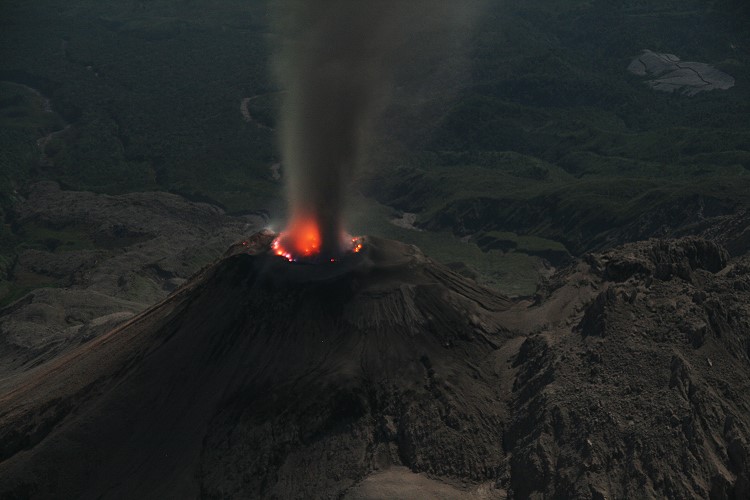
Indonesia , Semeru :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA.
Issued : Décember 16 , 2021
Volcano : Semeru (263300)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Semeru Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2021SMR84
Volcano Location : S 08 deg 06 min 29 sec E 112 deg 55 min 12 sec
Area : East java, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 11763 FT (3676 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
Pyroclastic flow occured from the edge of lava deposit at 08h42 UTC ( 15h42 local )
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Ash-cloud is not visible
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Ash-cloud moving to southeast
Remarks :
Lava flow is observed through the Southeast direction of the Semeru summit crater.
Seismicity is linked to the activity of magma as well as to tectonic activity. We record:
– 8 earthquakes eruptions
– 73 avalanche earthquakes
– 3 distant tectonic earthquakes
– 1 flood earthquake
This Thursday, December 16, 2021, 1. There was an avalanche of hot clouds at 9:01 am WIB up to 4.5 km from the summit. This hot cloud event was recorded on a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 25 mm and a duration of 912 seconds.
2. There was an avalanche of hot clouds at 9:30 AM WIB. This hot cloud event was recorded on a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 17 mm and a duration of 395 seconds, but was not observed visually because the Semeru volcano was covered in fog.
3. There was an avalanche of hot clouds at 3:42 PM WIB up to 4.5 km from the summit. This hot cloud event was recorded on a seismograph with a maximum amplitude of 20 mm and a duration of 400 seconds.
4. Seismicity is dominated by eruption, emission and avalanche earthquakes, with the number of earthquakes increasing over the past three days from 15 to 73 events per day, compared to an average of 8 events per day since. December 1, 2021. Deep volcanic earthquakes and harmonic tremors occur in insignificant numbers.
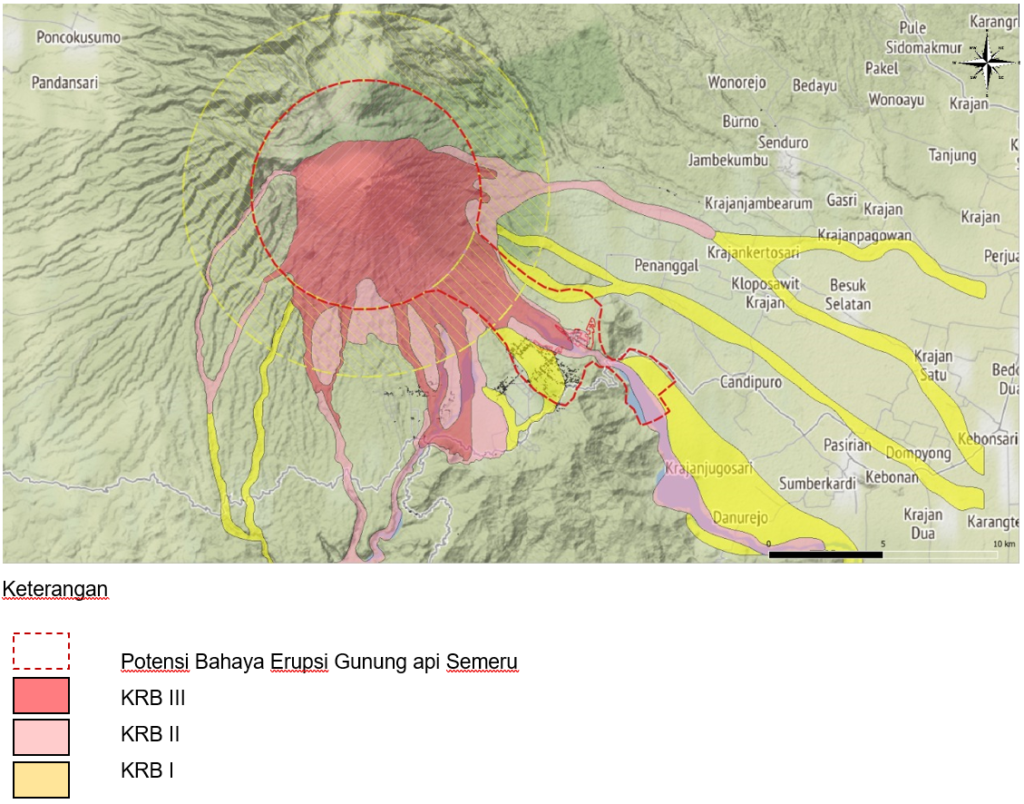
Hot cloud activity still has the potential to occur due to the presence of lava flow deposits (lava tongue) with a flow length of ± 2 km from the center of the eruption. The lava flow is still unstable and can lead to landslides, especially at the end of the flow, so it can cause hot cloud avalanches.
In addition to the potential for hot clouds, the potential for mudslide is also still high given the heavy rainfall on the Semeru volcano. Supported by BMKG data, it is estimated that the rainy season will last for the next 3 months.
Secondary explosions also have the potential to occur along the course of rivers if the hot cloud slides that occurs in / in contact with river water.
Considering that the activities of the Semeru volcano are still high and that there has been an increase in the distance of hot cloud slides and lava flows, the Geological Agency said that the activity level of the Semeru volcano has been statement from WASPADA level (level II) to SIAGA LEVEL (level III) from December 16, 2021 at 11:00 p.m. WIB.
Sources : Magma Indonésie , PVMBG.
Photos : Andi volcanist . Magma Indonésie .
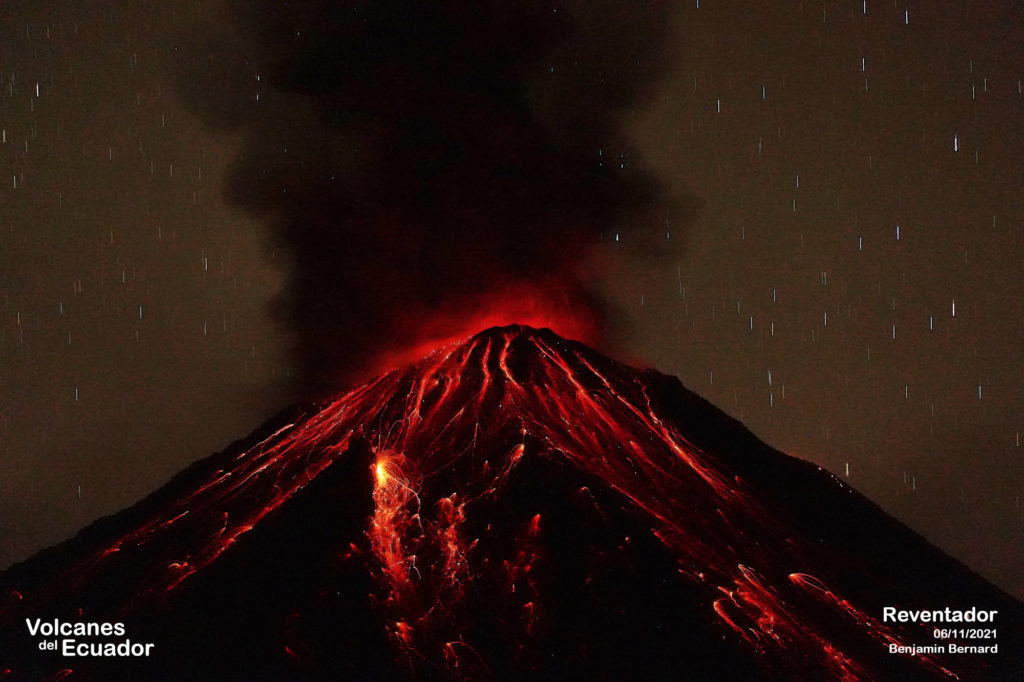
Ecuador , Reventador :
DAILY REPORT OF THE STATE OF THE REVENTADOR VOLCANO, Thursday December 16, 2021.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface activity level: High, Surface trend: No change.
Internal activity level: Moderate, Internal trend: No change.
Seismicity: From December 15, 2021, 11:00 a.m. to December 16, 2021, 11:00 a.m.
Seismic statistics correspond to 16 hours of intermittent data transmission.
Explosion (EXP) 19
Long periods (LP) 21
Emission Tremors (TREMI) 5
Harmonic Tremor (TRARM) 1
Rains / Lahars:
Light rains were recorded, without causing lahars.
Emission / ash column:
Gas emissions were observed at a height of about 700 m at summit level in a westerly direction. 2 VAAC alerts were recorded in a southwest direction with a height of 1338m above the crater level
Other monitoring parameters:
No thermal anomalies have been reported in the past 24 hours.
Observation:
In the afternoon, gas emissions were observed. VAAC alerts were recorded overnight, during which time an incandescence was observed at the summit. The area was seen cloudy today.
Alert level: Orange.
Source : IG-EPN.
Photo : Benjamin Bernard
Alaska , Semisopochnoi :
51°55’44 » N 179°35’52 » E,
Summit Elevation 2625 ft (800 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Low-level eruptive activity and elevated seismicity continue at Semisopochnoi volcano. Small explosions from the north crater of Mount Cerberus were recorded by seismic and infrasound sensors. Low-level ash and steam emissions were observed in partly cloudy satellite and web camera views. Weakly elevated surface temperatures were also seen in the north crater in a clear overnight image.
Small eruptions producing minor ash deposits within the vicinity of the active north crater of Mount Cerberus and ash clouds usually under 10,000 ft above sea level have characterized the recent activity. Small explosions and associated ash emissions may continue and could be difficult to detect, especially when thick cloud cover obscures the volcano.
Semisopochnoi is monitored by local seismic and infrasound sensors, satellite data, web cameras, and remote infrasound and lightning networks.
Source : AVO
Photo : Loewen, Matt / Alaska Volcano Observatory / U.S. Geological Survey.
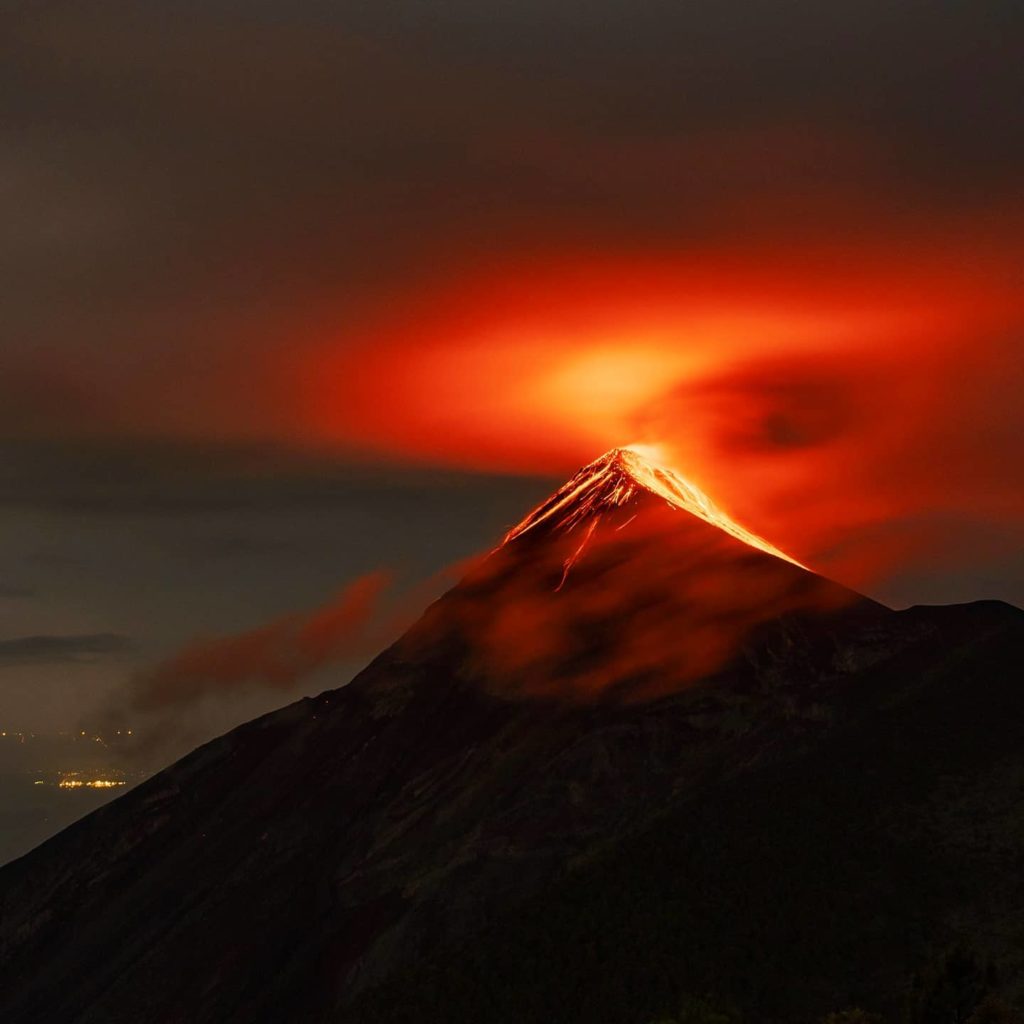
Guatemala , Santiaguito / Fuego :
Santiaguito activity:
The observatory of the volcanic complex of Santa María-Santiaguito reports weak to moderate degassing 200 meters above the Caliente dome, as well as weak explosions that produce rumblings and ash columns that rise to 3000 m from altitude (9842 feet), which scatter southwest up to 15 kilometers.
During the night and early in the morning, an intense incandescence was observed on the western and southwestern edge of the Caliente dome, as well as the descent of numerous weak to moderate avalanches towards the western, southwestern and southern flanks. The extrusive activity remains at a high level and continues to pile material unstably in the lava flow on the western flank, as well as in the Caliente dome, thus maintaining the possibility of some of this material collapsing. and becomes to generate long pyroclastic flows towards the southwest, the south and the east.
Fuego activity:
The Fuego volcano observatory reports 4 to 8 weak, moderate and strong explosions per hour, which raise gray ash columns to heights of 4200 to 4500 m altitude (13,779 to 14,764 feet), which disperse towards West and Northwest up to 40 kilometers, with the probability of ash fall on the surroundings of Yepocapa, Acatenango and San Miguel Pochuta. The explosions produced weak avalanches around the crater and towards the canyons of Ceniza, Taniluyá, Santa Teresa, Seca, Las Lajas and Honda.
During the night and early in the morning, an incandescence was observed in the crater through the cloudiness that covered it. The explosions produce a low, moderate rumble with shock waves that vibrate the roofs and windows of homes in communities near the volcano. Sounds similar to that of a train locomotive were heard at intervals of 1 to 3 minutes.
Source : Insivumeh .
Photos : Marcszeglat , 2009 / wikimedia , Diego Rizzo .