April 17 , 2020 .
Alaska , Shishaldin :
AVO/USGS Volcanic Activity Notice
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Previous Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Previous Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Issued: Thursday, April 16, 2020, 11:44 AM AKDT
Source: Alaska Volcano Observatory
Location: N 54 deg 45 min W 163 deg 58 min
Elevation: 9373 ft (2857 m)
Area: Aleutians
Volcanic Activity Summary:
Seismicity at Shishaldin Volcano has decreased over the past two weeks to levels slightly above background. Similarly, satellite views show no lava or changes within the crater since the start of April, accompanied by a decrease in surface temperatures. Eruptive activity therefore appears to have ended or paused. Due to this decrease in activity, the Alaska Volcano Observatory is decreasing the Aviation Color Code for Shishaldin Volcano to YELLOW and the Alert Level to ADVISORY.
Eruptive activity at Shishaldin paused after the explosion on January 19, 2020, before resuming at a low level mid-March. It is therefore possible for eruptive activity to resume with little warning and AVO will continue to monitor the volcano closely.
Shishaldin is monitored by local seismic and infrasound sensors, satellite data, a web camera, a telemetered geodetic network, and distant infrasound and lightning networks.
Recent Observations:
[Volcanic cloud height] na
[Other volcanic cloud information] na
Remarks:
Shishaldin volcano, located near the center of Unimak Island in the eastern Aleutian Islands, is a spectacular symmetric cone with a base diameter of approximately 16 km (10 mi). A 200-m-wide (660 ft) funnel-shaped summit crater typically emits a steam plume and occasional small amounts of ash. Shishaldin is one of the most active volcanoes in the Aleutian volcanic arc, with at least 54 episodes of unrest including over 24 confirmed eruptions since 1775. Most eruptions are relatively small, although the April-May 1999 event generated an ash column that reached 45,000 ft above sea level.
Source : AVO.
Photo : Fischer, Ed.
Indonesia , Anak Krakatau :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA.
Issued: April 17 , 2020 .
Volcano: Anak Krakatau (262000)
Current Aviation Colour Code: ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code: orange
Source: Anak Krakatau Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2020KRA18
Volcano Location: S 06 deg 06 min 07 sec E 105 deg 25 min 23 sec
Area: Lampung, Indonesia
Summit Elevation: 502 FT (157 M)
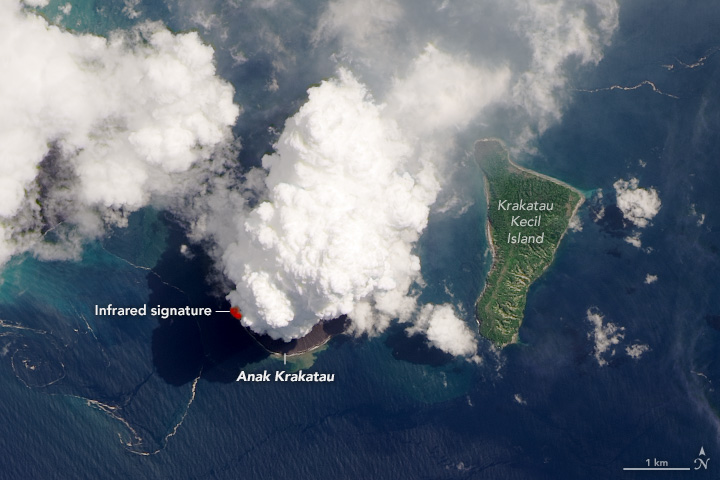
On April 13, 2020, the Operational Land Imager (OLI) on Landsat 8 acquired this natural-color image (OLI bands 4-3-2) of the volcano as a plume towered over the peak. The natural-color image is overlaid with the infrared signature detected by OLI of what is possibly molten rock.
Volcanic Activity Summary:
Eruption with ash clouds at 00:49 UTC (07:49 local time). The eruption lasted for 50 seconds.
Volcanic Cloud Height:
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 662 FT (207 M) above sea level, may be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information:
Visuals directly from the cctv were observed eruptions with the color of the thick gray eruption smoke 50m from the top of the volcano, the wind direction slowly to the south west.
Remarks:
Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 40 mm and maximum duration 50 second.
Source : Magma Indonésie .
Photo : Landsat 8 / Nasa.
Indonesia , Semeru :
Press release on the activity of the Semeru volcano, April 17, 2020.
Visual observation by G. Semeru, April 17, 2020 at 6:10 am. Warm clouds observed towards Besuk Bang.
The level of activity of G. Semeru since May 2, 2012 is at level II (Waspada).
Monitoring data:
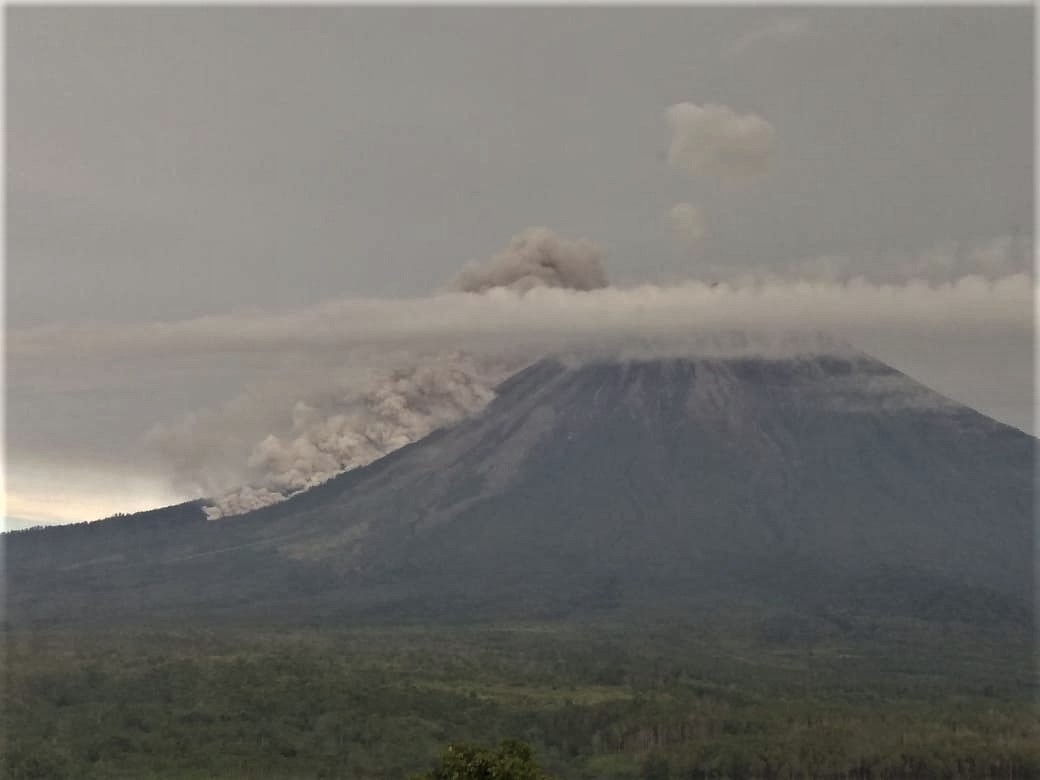
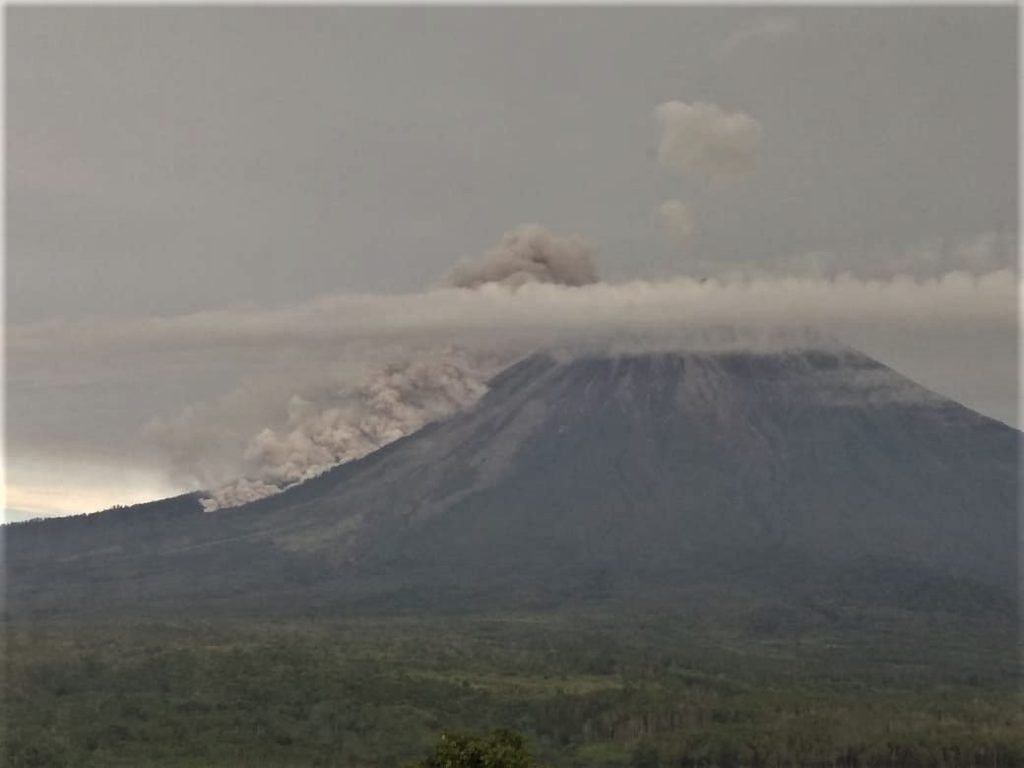
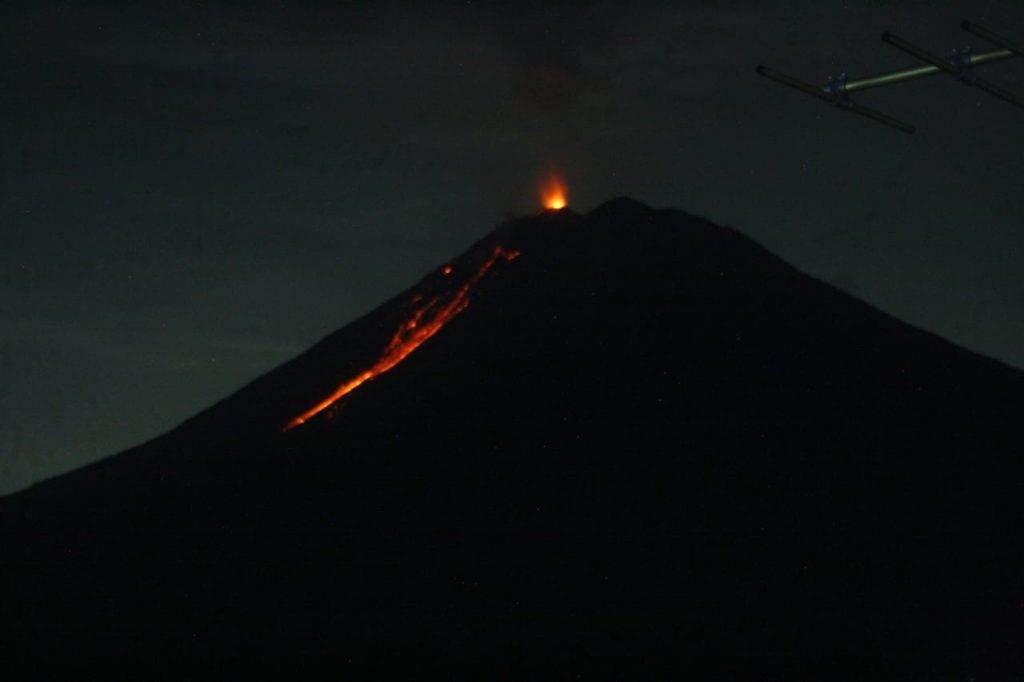
1) Visual: during the period from April 1 to 16, 2020, the activity was dominated by lava avalanches and continuous eruptions. The eruption produces gray columns reaching 400 to 600 meters above the peak. During non-eruption periods, the gases from the gas in Jonggring Seloko crater are gray-white with a height of 200 to 400 m. Glowing lava avalanche activities were observed towards Besuk Bang, Besuk Kobokan and Besuk Kembar over a sliding distance of 500 to 1000 meters from the center of the avalanche. Silent incandescent rays have been observed up to 10-20 meters above the crater. On April 17, 2020 at 06:08 WIB, there was an avalanche of hot clouds up to 2000 m towards Besuk Bang.
2) Seismicity: from April 1 to 16, 2020, the seismic activity of Mount Semeru was still high, dominated by earthquakes of eruption, avalanche and emission. Eruption earthquakes were recorded on average at 25 events / day, avalanche earthquakes at 19 events per day and emission earthquakes at 6 events / day. The number of earthquakes has increased since April 5, 2020, while the eruption has increased in activity since April 8, 2020. In addition, volcanic earthquakes (harmonic tremors, non-harmonic tremors, shallow volcanics and volcanics deep) were recorded in insignificant quantities. On April 17, 2020, an earthquake with a maximum amplitude of 7 mm and a duration of 300 seconds was recorded.
Visual observation by G. Semeru, April 17, 2020 at 6:10 am. Warm clouds observed towards Besuk Bang.
Analysis:
The activity of the eruption and continuous gas bursts in the Jonggring Seloko crater of G. Semeru shows that there is a supply or pressure of magma accompanied by an increase in fluid (gas, liquid and solids) at shallower depth. The appearance of harmonic tremors without accompanying volcanic earthquakes (shallow volcanic or deep volcanic) indicates that the system is now open. The gray color in the eruption column indicates the presence of rocky materials brought to the surface. The intervals of seismic eruption are quite dense and show that so far, there has been no accumulation of energy having the potential of eruptions with greater intensity.
Potential danger:
The potential for continuous eruption is always present with the projection of eruption materials in the form of lava flow, heavy rain of ash and stone throw (incandescent) around the crater within a radius of 1 km around the center of the eruption, and hot clouds descending for 4 km on the South-East and South slopes.
One must be aware of the increase in avalanches which indicate the instability of the tip of the lava flow which has the potential to become a hot cloud of avalanches.
There is an accumulation of eruptive material around the peak, slopes and upstream of Besuk Bang, Besuk Kembar and Besuk Kobokan, with the potential to become mudslides in the event of heavy precipitation. During the period from April 1 to 16, 7 floods were recorded (almost every 2 days), as well as the start of heavy precipitation in East Java.
Source : PVMBG
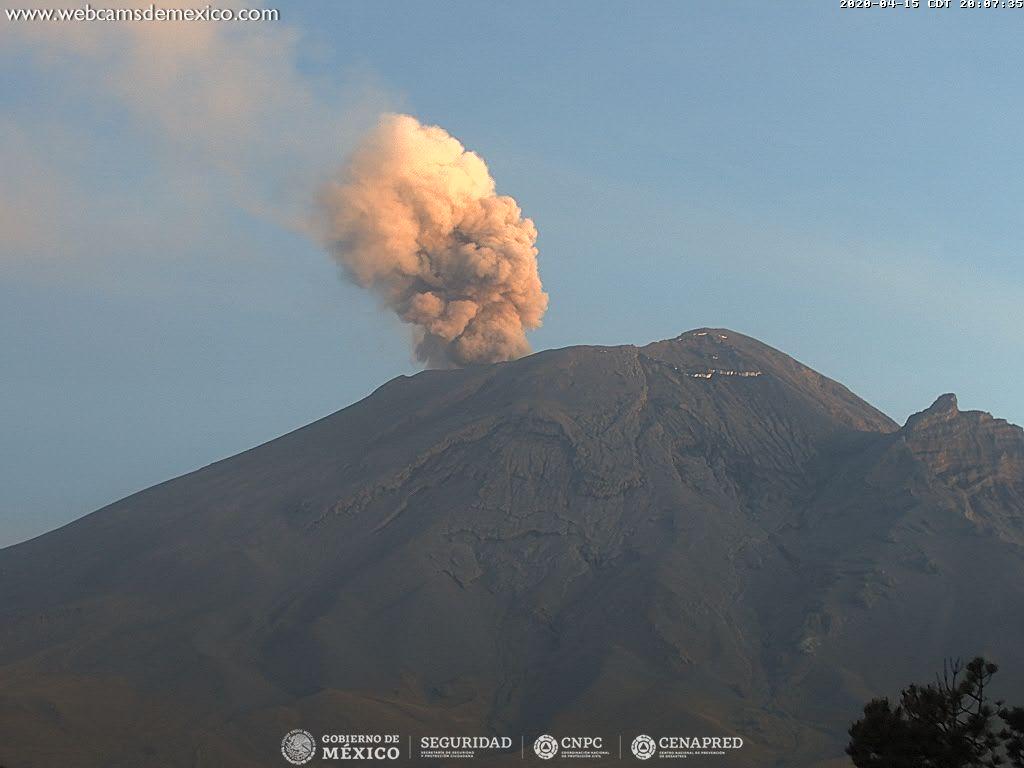
Mexico , Popocatepetl :
April 16, 11:00 a.m. (April 16, 4:00 p.m. GMT)
Over the past 24 hours, 113 exhalations accompanied by volcanic gases and sometimes ash have been identified thanks to the Popocatépetl volcano monitoring system. In addition, 84 minutes of tremors were recorded.
At the time of this report, we observe the constant emission of volcanic gases dispersed towards the Northeast.
CENAPRED urges NOT to get close to the volcano and especially the crater, because of the danger involved in the fall of ballistic fragments and, in the event of heavy rain, to move away from the bottom of the ravines because of the danger of mud and rubble.
The Popocatépetl volcanic alert signaling light is in YELLOW PHASE 2.
Source : Cenapred .