June 18 , 2022.
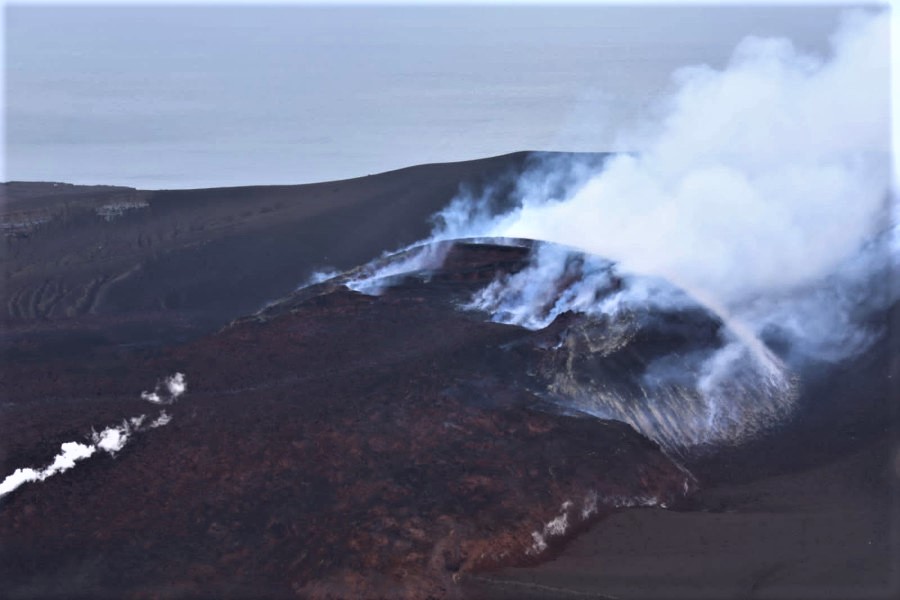
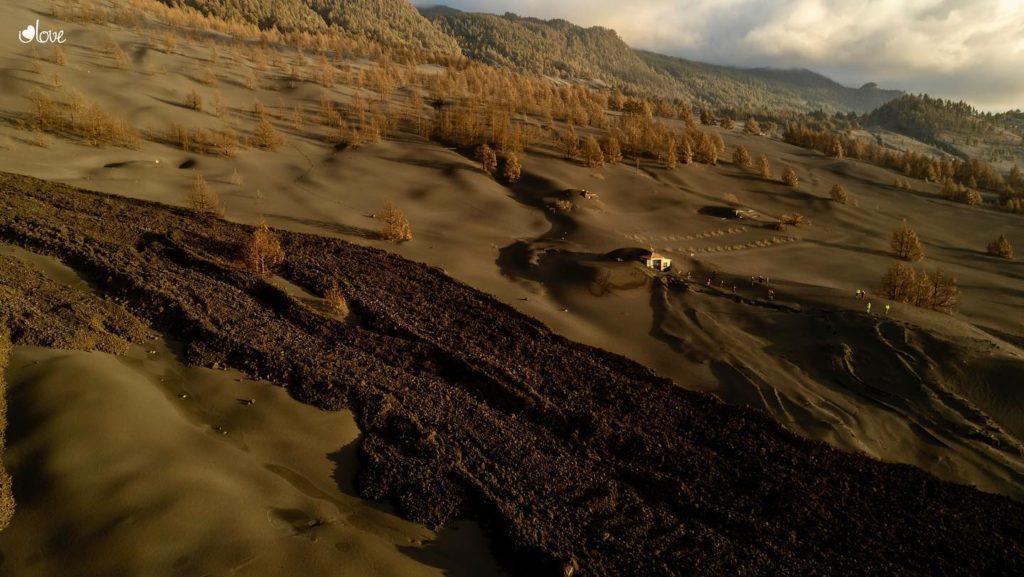
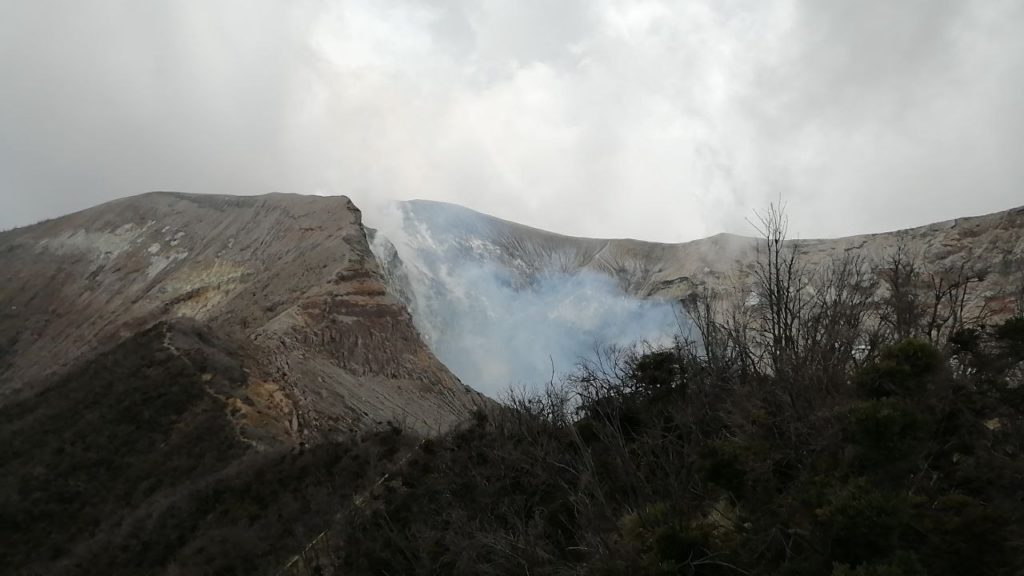
Indonesia , Anak Krakatau :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA
Issued : June 17 , 2022 .
Volcano : Anak Krakatau (262000)
Current Aviation Colour Code : ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code : orange
Source : Anak Krakatau Volcano Observatory
Notice Number : 2022KRA52
Volcano Location : S 06 deg 06 min 07 sec E 105 deg 25 min 23 sec
Area : Lampung, Indonesia
Summit Elevation : 502 FT (157 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary :
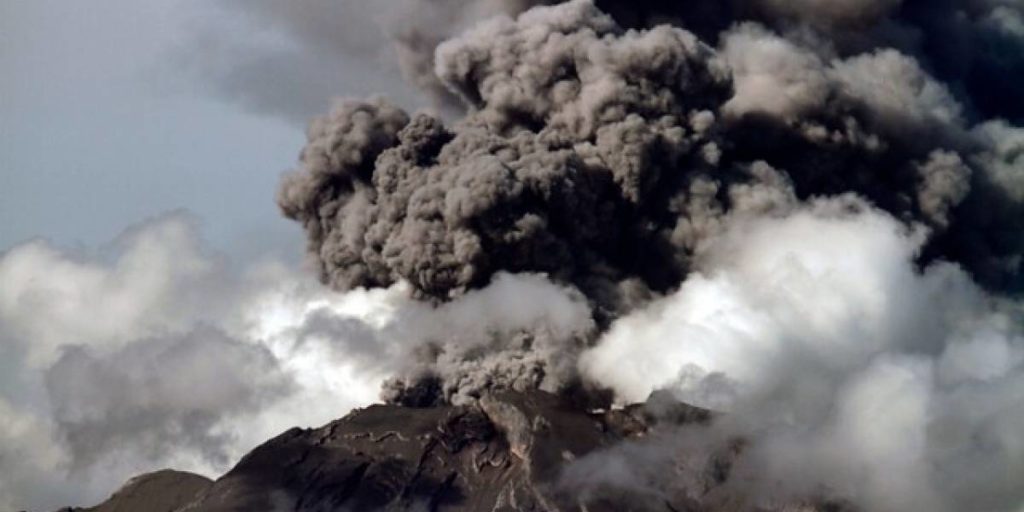
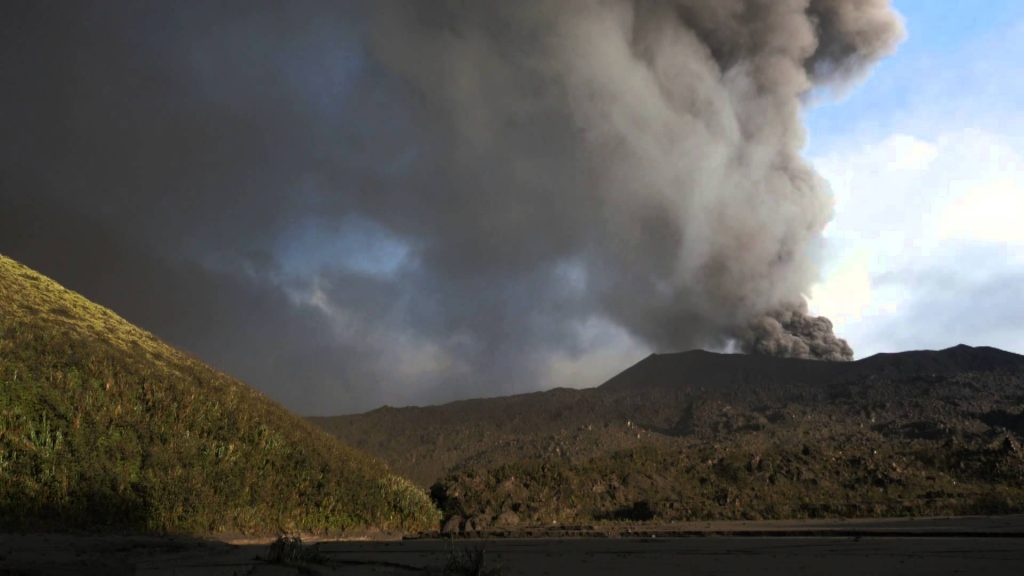
-Eruption with ash clouds at 07:45 UTC (14:45 local time). The eruption lasted for 71 seconds.
-Eruption with ash clouds at 11:39 UTC (18:39 local time). The eruption lasted for 84 seconds.
Volcanic Cloud Height :
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 2742 FT (857 M) above sea level, may be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information :
Visuals directly from the cctv were observed eruptions with the color of the thick black eruption smoke 700m from the top of the volcano, the wind direction slowly to the south.
Remarks :
-Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 58 mm and maximum duration 71 second.
-Eruption recorded on seismogram with maximum amplitude 60 mm and maximum duration 84 second.
Source : Magma Indonésie .
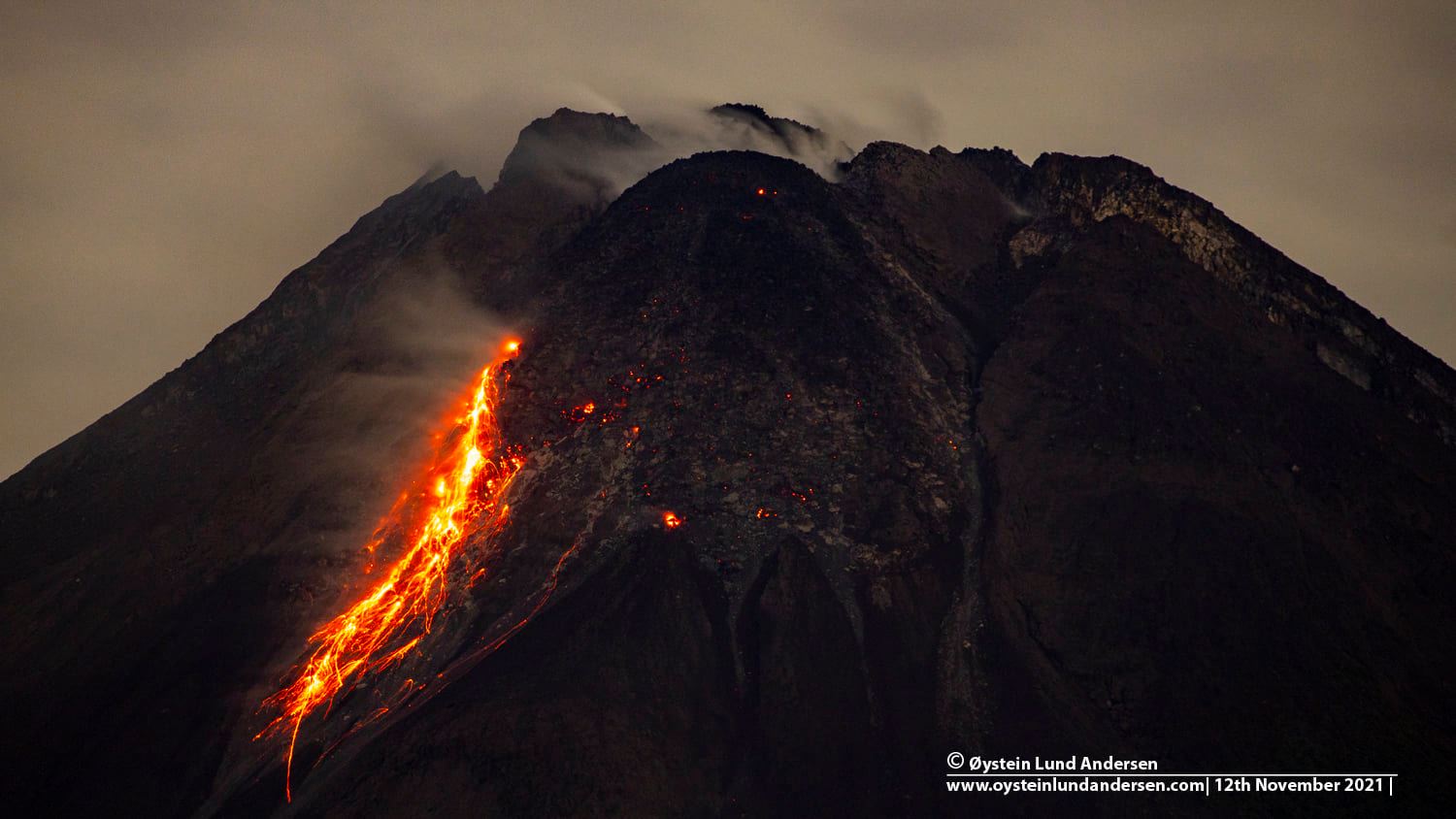
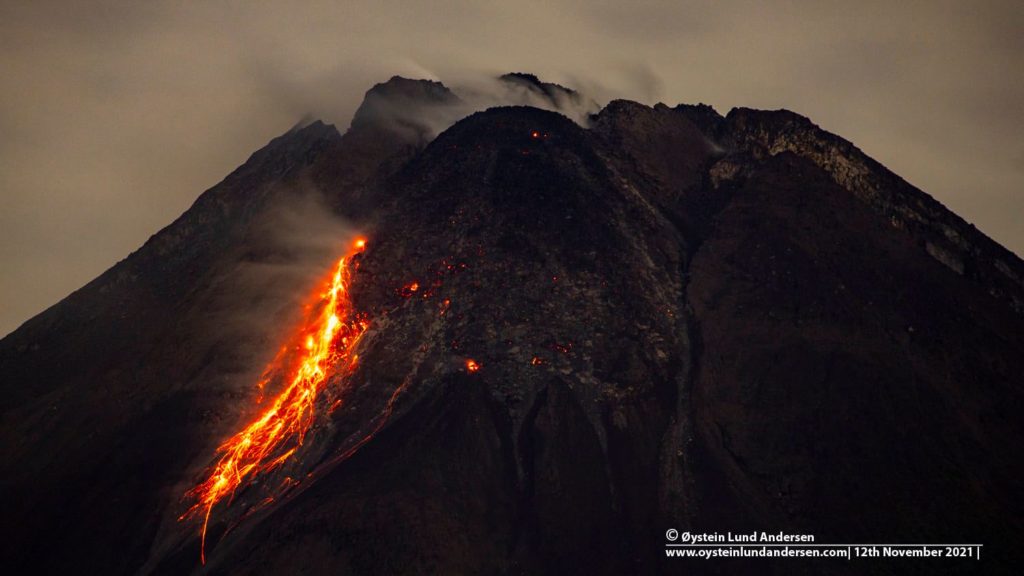
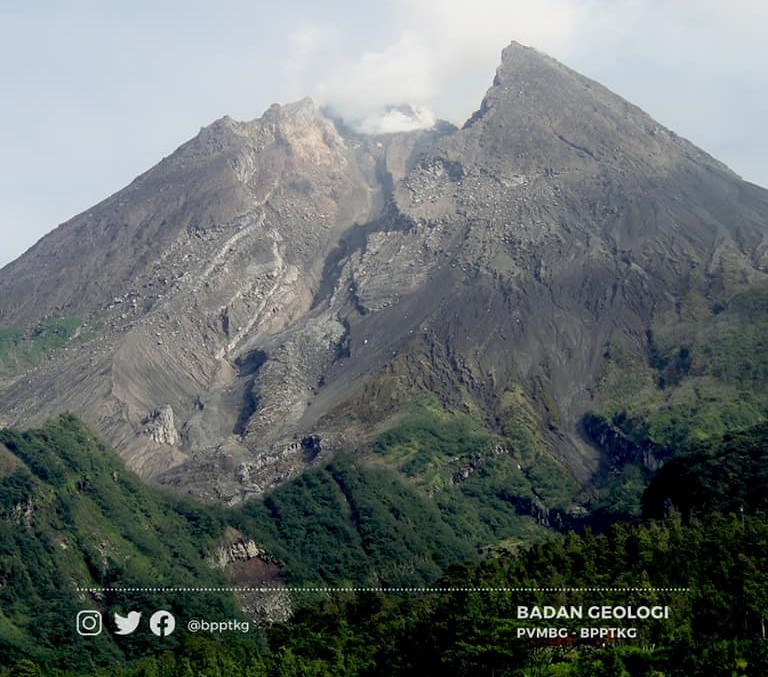
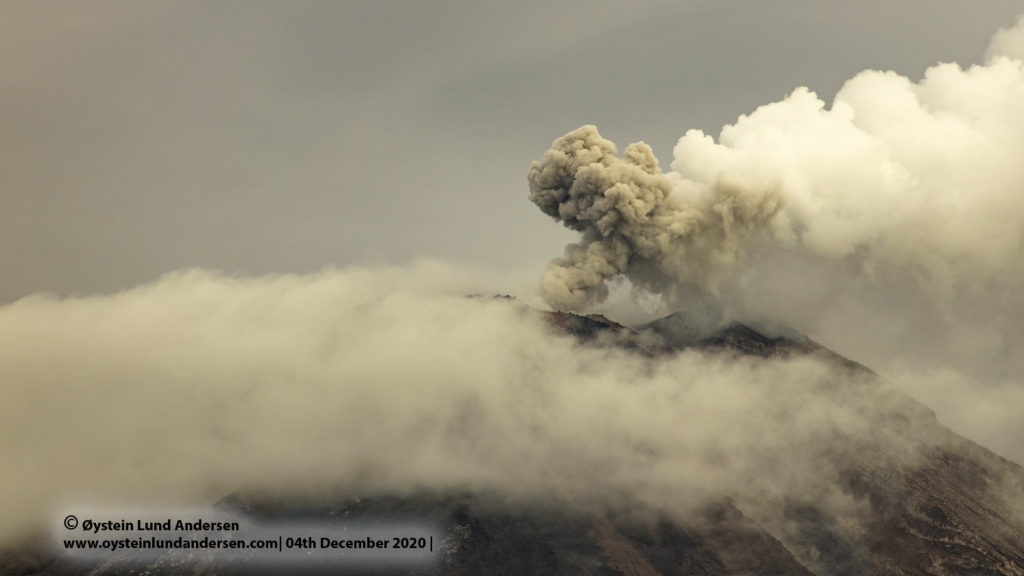
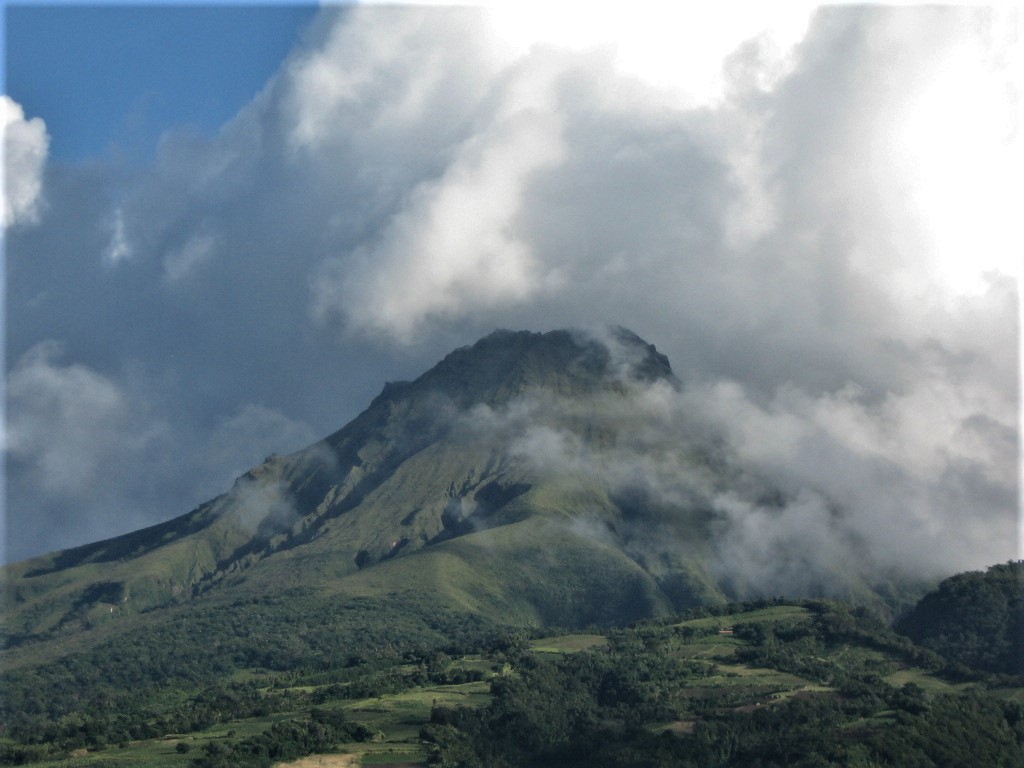
Indonesia , Merapi :
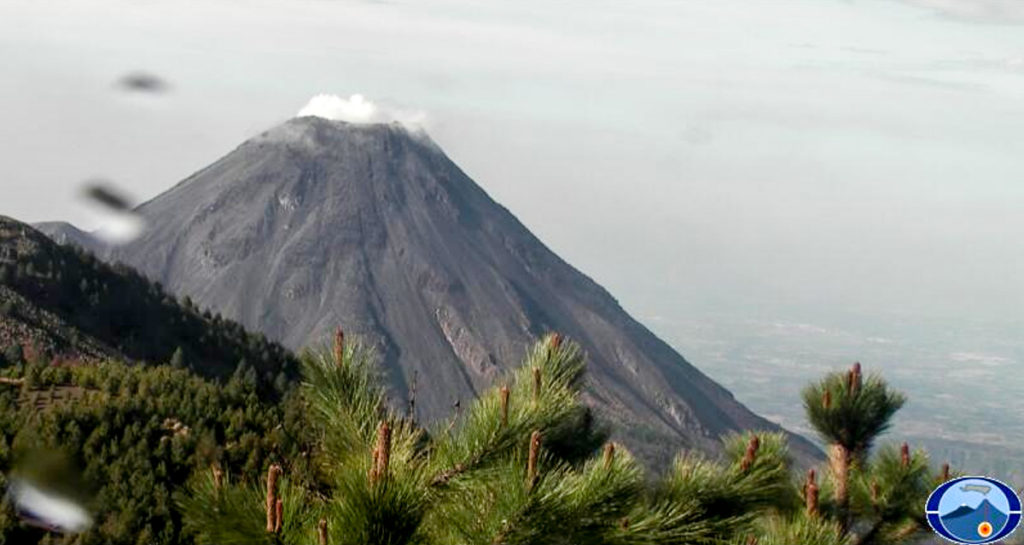
Mount Merapi activity report from June 10 to 16, 2022
– This week, 58 lava avalanches were observed in a southwesterly direction, descending the Bebeng River with a maximum sliding distance of 1800 m.
– For the southwest dome, there is no change in the height of the dome. For the central dome, no significant morphological change was observed. According to photo analysis, the volume of the Southwest lava dome is 1,551,000 m3 and that of the central dome is 2,582,000 m3.
Seismicity:
This week, the seismicity of Mount Merapi recorded:
27 shallow volcanic earthquakes (VTB),
81 multi-phase earthquakes (MP),
584 avalanche earthquakes (RF),
5 emission earthquakes (DG),
7 tectonic earthquakes (TT).
– The intensity of seismicity this week is still quite high.
Mount Merapi’s deformation, which was monitored using EDM this week, showed a distance shortening rate of 0.4 cm/day.
Rainfall intensity of 40 mm/hour for 85 minutes is recorded at Kaliurang Post on June 10, 2022. No reports of lahars or additional flow in rivers that originate at Mount Merapi.
Conclusion:
1. Merapi volcanic activity is still quite high in the form of effusive eruption activity. The state of the activity is defined at the « SIAGA » level.
2. The current potential danger is lava avalanches and hot clouds in the South-South-West sector covering the Boyong River for a maximum of 5 km, the Bedog River, Krasak, Bebeng for a maximum of 7 km. The Southeast sector covers the Woro River for a maximum of 3 km and the Gendol River for a maximum of 5 km. Meanwhile, the ejection of volcanic material in the event of an explosive eruption can reach a radius of 3 km around the summit.
The public should not carry out any activity in potentially dangerous areas, anticipate disturbances due to volcanic ash from the Merapi eruption and be aware of the dangers of lahars, especially when it rains around Merapi.
Source : BPPTKG.
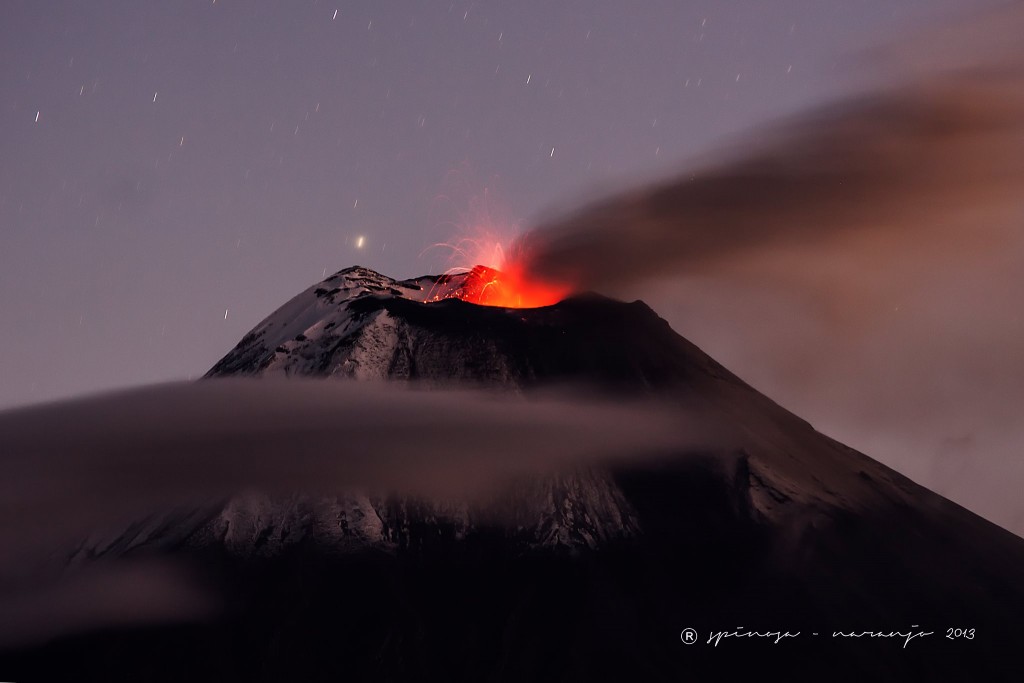
Photo : Oystein Lund Andersen
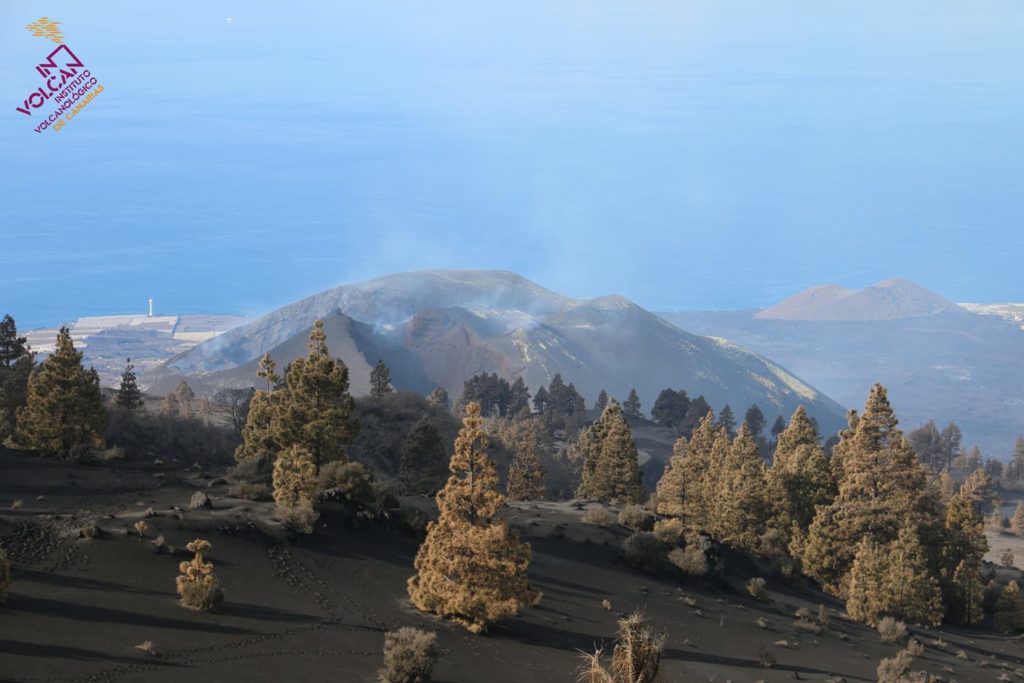
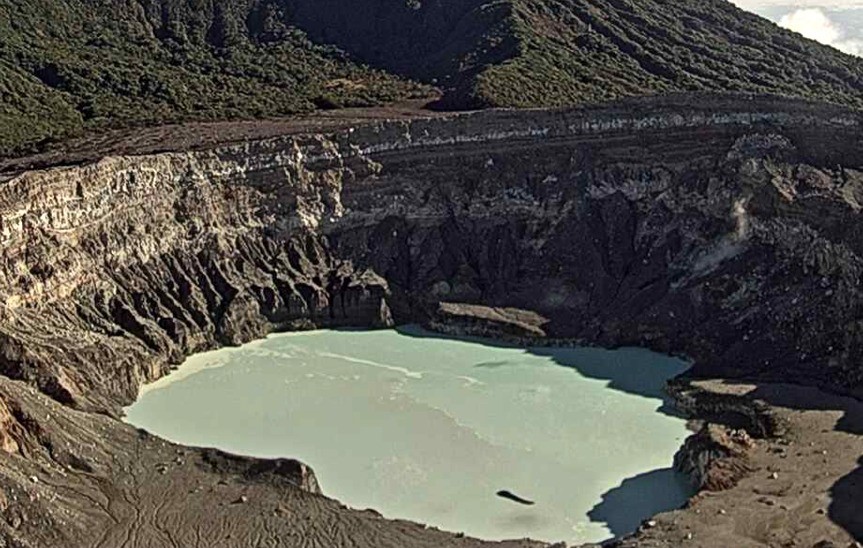
Canaries Islands , Tenerife :
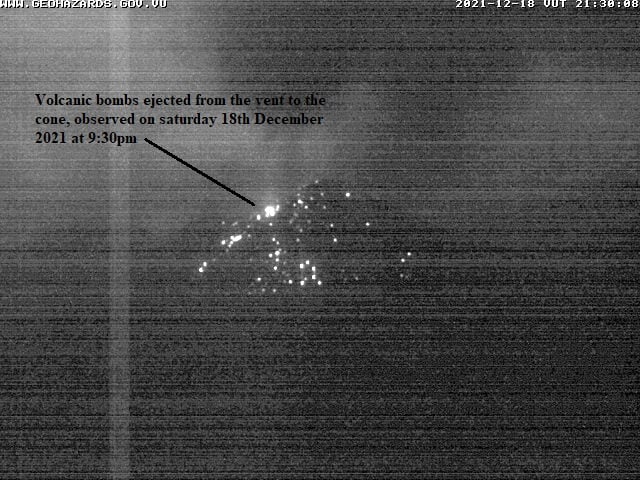
This Friday, June 17, 2022, between 01:50 a.m. and 04:10 a.m. (Canarian time), the Canarian seismic network – operated by the Volcanological Institute of the Canary Islands (INVOLCAN) – recorded a swarm of hybrid events of very low magnitude under the Teide volcano. In this time interval of 2 hours and 20 minutes, at least 300 seismic events have been identified.
This seismic swarm has very similar characteristics to the swarms that were recorded on October 2, 2016 and June 14, 2019. The most likely origin of this type of swarm is the movement of fluids such as steam, gas or l water, inside the hydrothermal system of the Teide volcano. This swarm does not imply a higher probability of an eruption in the short/medium term, but it reminds us that Tenerife is still a volcanically active island.
This does not mean a new magma intrusion, but looks like a movement in one of the reservoirs, namely the phonolithic reservoir area of this area between 11 and 15 km. To find out if there has been a new magma intrusion, we will need to monitor GPS and how the composition of gases such as CO2 and Helium is changing in the coming months to give confirmation of what exactly happened.
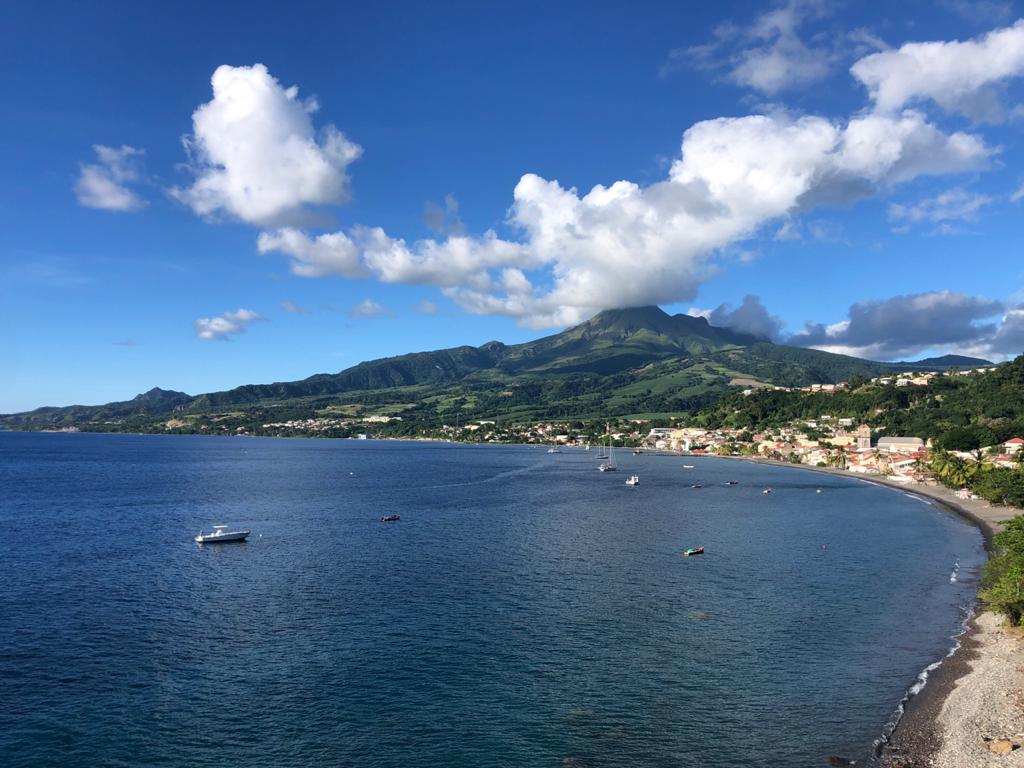
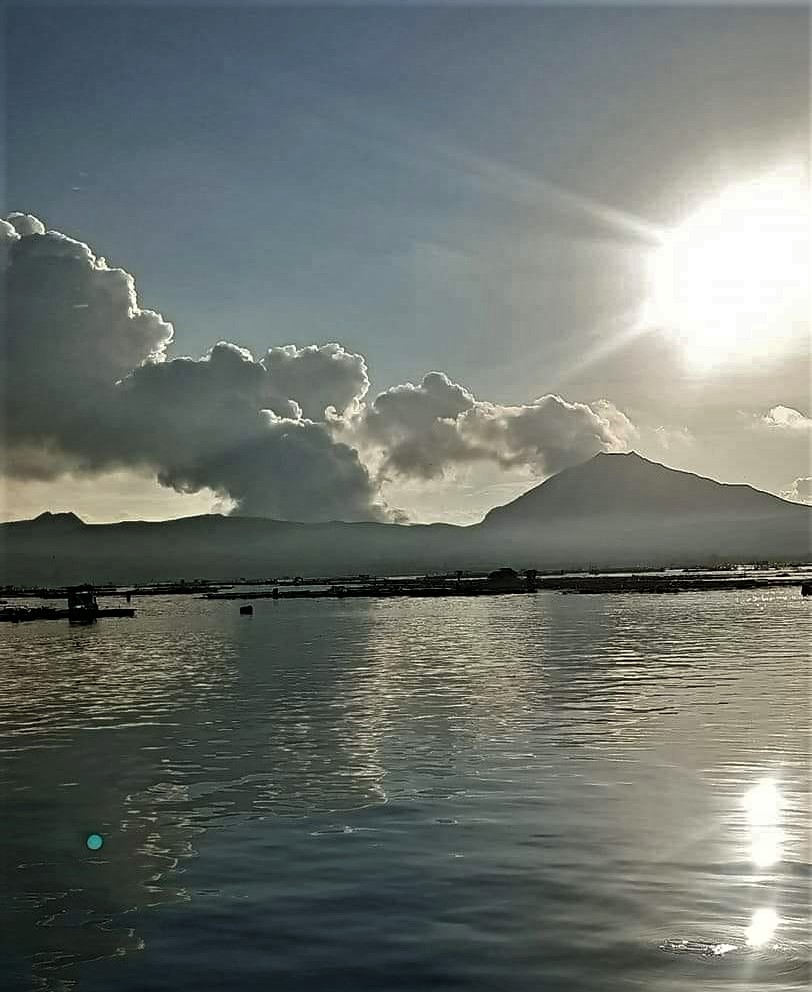
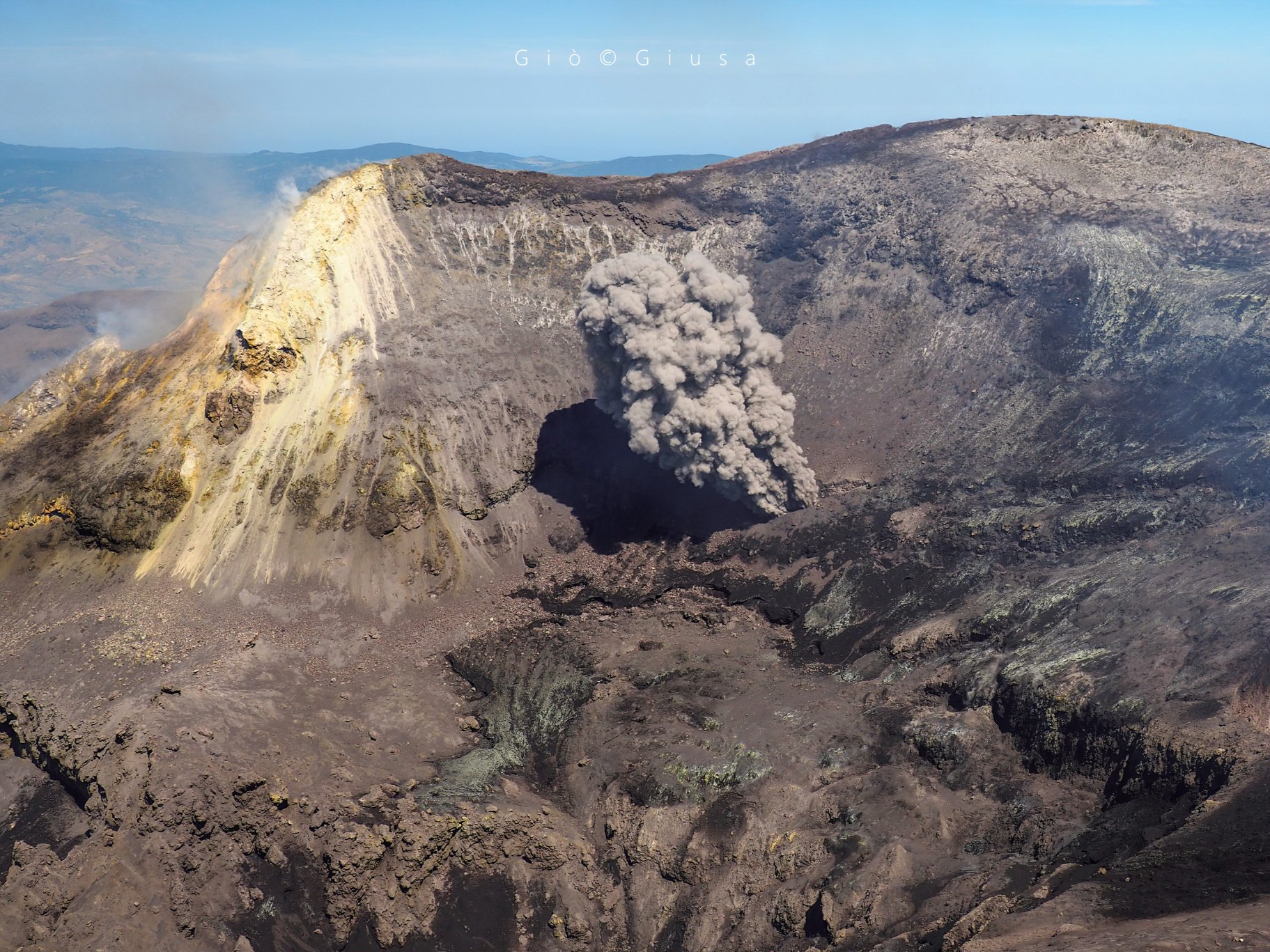
La Martinique , Mount Pelée :
Weekly report on the activity of Mount Pelée for the period from June 10, 2022 to June 17, 2022.
Between June 10, 2022 at 4 p.m. (UTC) and June 17, 2022 at 4 p.m. (UTC), the OVSM recorded at least 3 volcano-tectonic earthquakes including:
2 Earthquakes of magnitude less than 0.1. These low-energy earthquakes were located inside the volcanic edifice between 0.5 and .9 km deep below the surface. This superficial volcano-tectonic seismicity is associated with the formation of micro-fractures in the volcanic edifice.
1 earthquakes with a magnitude of 1.6, located 13.8 km deep below the surface, about 8 km away north-northwest of Le Prêcheur. This earthquake could be associated with fracturing inside the Caribbean plate located under the volcanic edifice.
None of these earthquakes were felt by the population.
The zone of degassing at sea at shallow depth between St Pierre and le Prêcheur is still observed. The IGP took fluid samples in order to understand the origin of this degassing and to assess its possible relationship with the Mount Pelée hydrothermal system.
An extension of two areas of degraded vegetation located between Morne Plumé and the Rivière Chaude was observed during a helicopter flight carried out on February 9, with the support of the Dragon 972, and confirmed by analysis of satellite images.
The alert level remains YELLOW: vigilance.
Source : Direction de l’OVSM IPGP.
Photo : Rci.fm
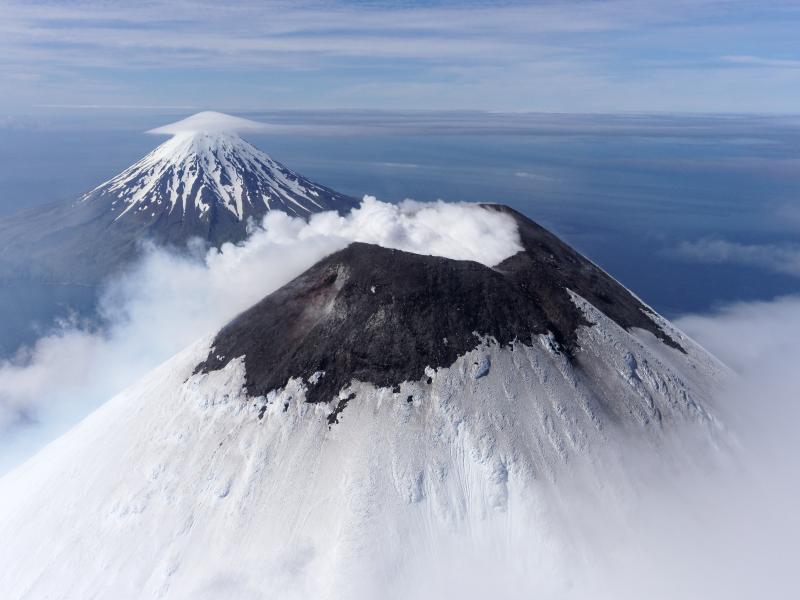
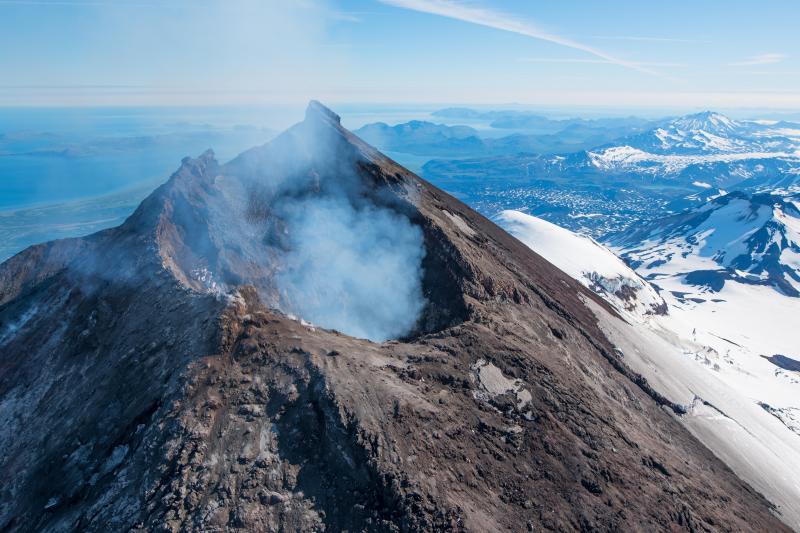
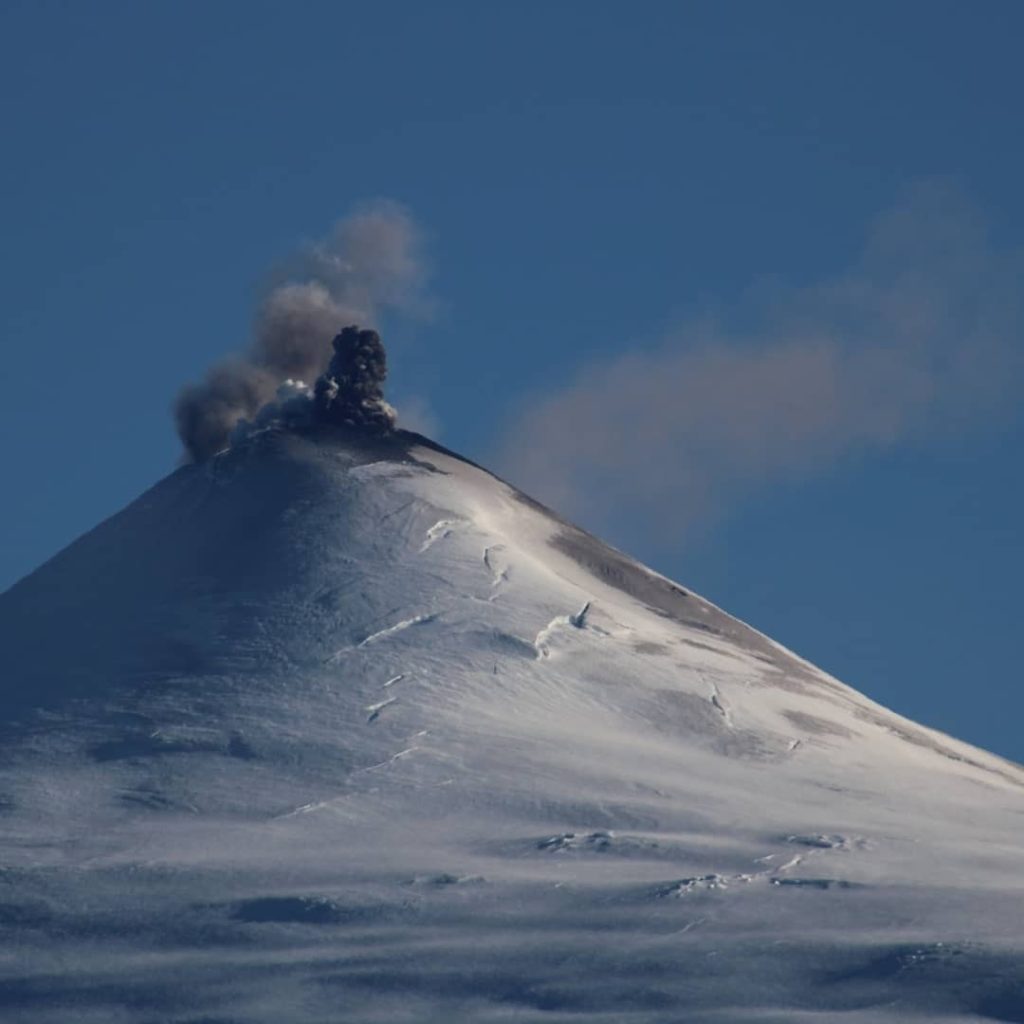
Alaska , Cleveland :
52°49’20 » N 169°56’42 » W,
Summit Elevation 5676 ft (1730 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Unrest continues at Cleveland volcano. Moderately elevated surface temperatures from hot degassing in the summit crater were observed in satellite data early in the week. Cloudy weather conditions prevented clear views on Thursday and Friday, June 16 and 17. Sulfur dioxide gas emissions from the voclano were detected on Saturday, June 11 and Wednesday, June 15. Analysis of satellite radar data images collectred over the past several weeks shows continued subsidence within the summit crater, possibly reflecting subsurface changes within the upper ediface. Seismic actiivty remains low and there have been no observations of explosive activity detected in local and regional seismic and infrasound data over the past week.
Episodes of lava eruption and explosions can occur at Cleveland without advance warning. Explosions are normally short duration and only present a hazard to aviation in the immediate vicinity of the volcano. Larger explosions that present a more widespread hazard to aviation are possible but are less likely and occur less frequently.
Cleveland volcano is monitored by only two seismic stations, which restricts AVO’s ability to precisely locate earthquakes and detect precursory unrest that may lead to an explosive eruption. Rapid detection of an ash-producing eruption may be possible using a combination of seismic, infrasound, lightning, and satellite data.
Source : AVO.
Photo : Herstand, Malcolm / Alaska Volcano Observatory / Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys