April 12 , 2019.
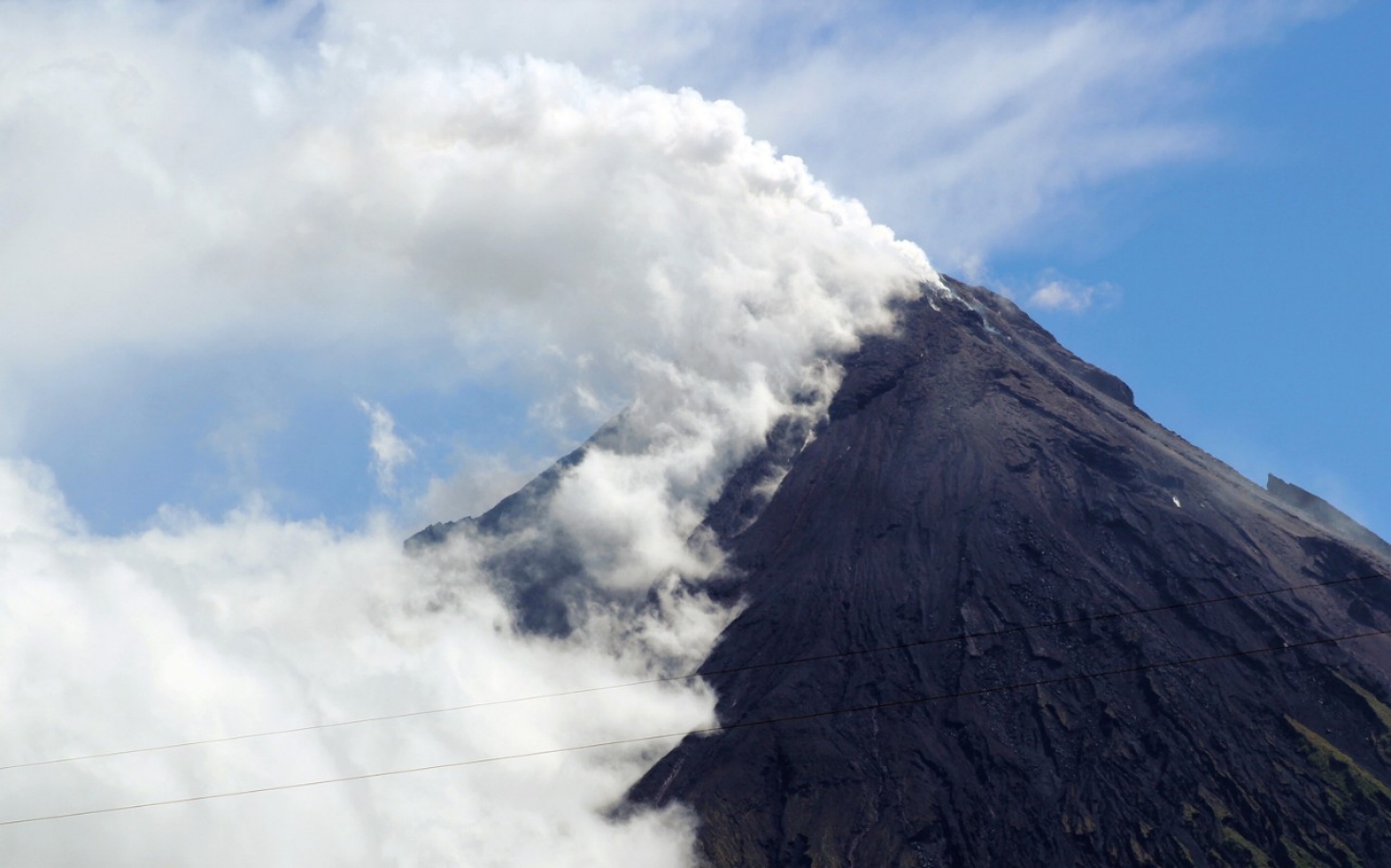
Indonesia , Agung :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA.
Issued: April 11 , 2019
Volcano: Agung (264020)
Current Aviation Colour Code: ORANGE
Previous Aviation Colour Code: orange
Source: Agung Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2019AGU15
Volcano Location: S 08 deg 20 min 31 sec E 115 deg 30 min 29 sec
Area: Bali, Indonesia
Summit Elevation: 10054 FT (3142 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
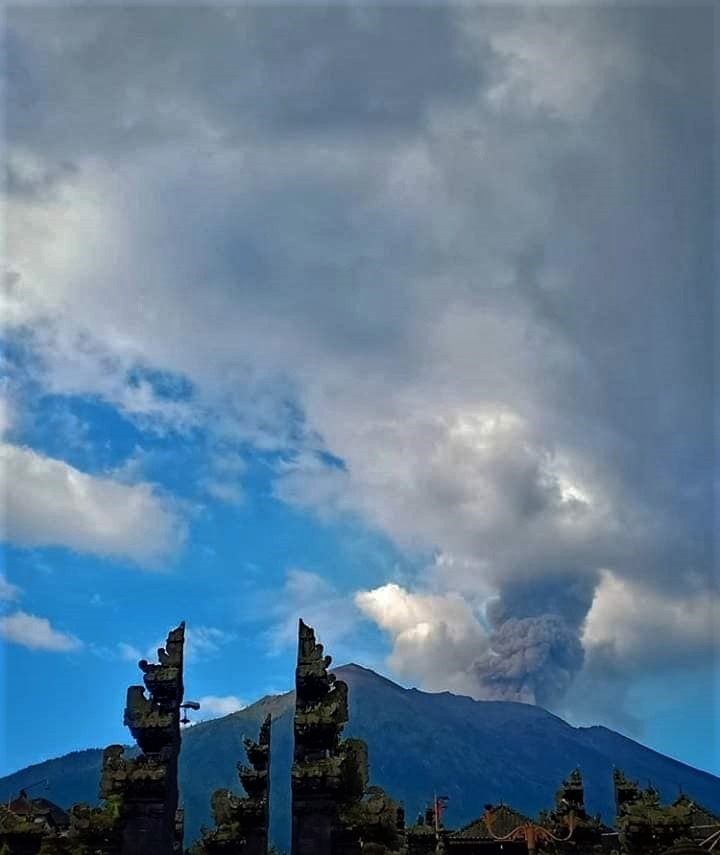
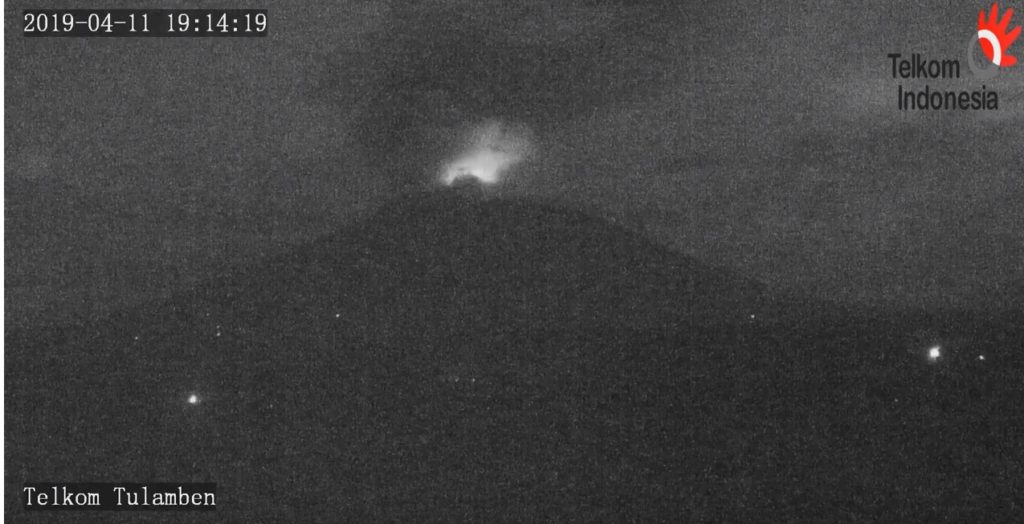
Eruption with volcanic ash cloud at 10h47 UTC (18h47 local). Eruption and ash emission is not continuing.
Volcanic Cloud Height:
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 16454 FT (5142 M) above sea level, may be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information:
Ash-cloud moving to west
Remarks:
Seismic activity is characterized by volcanic earhquake
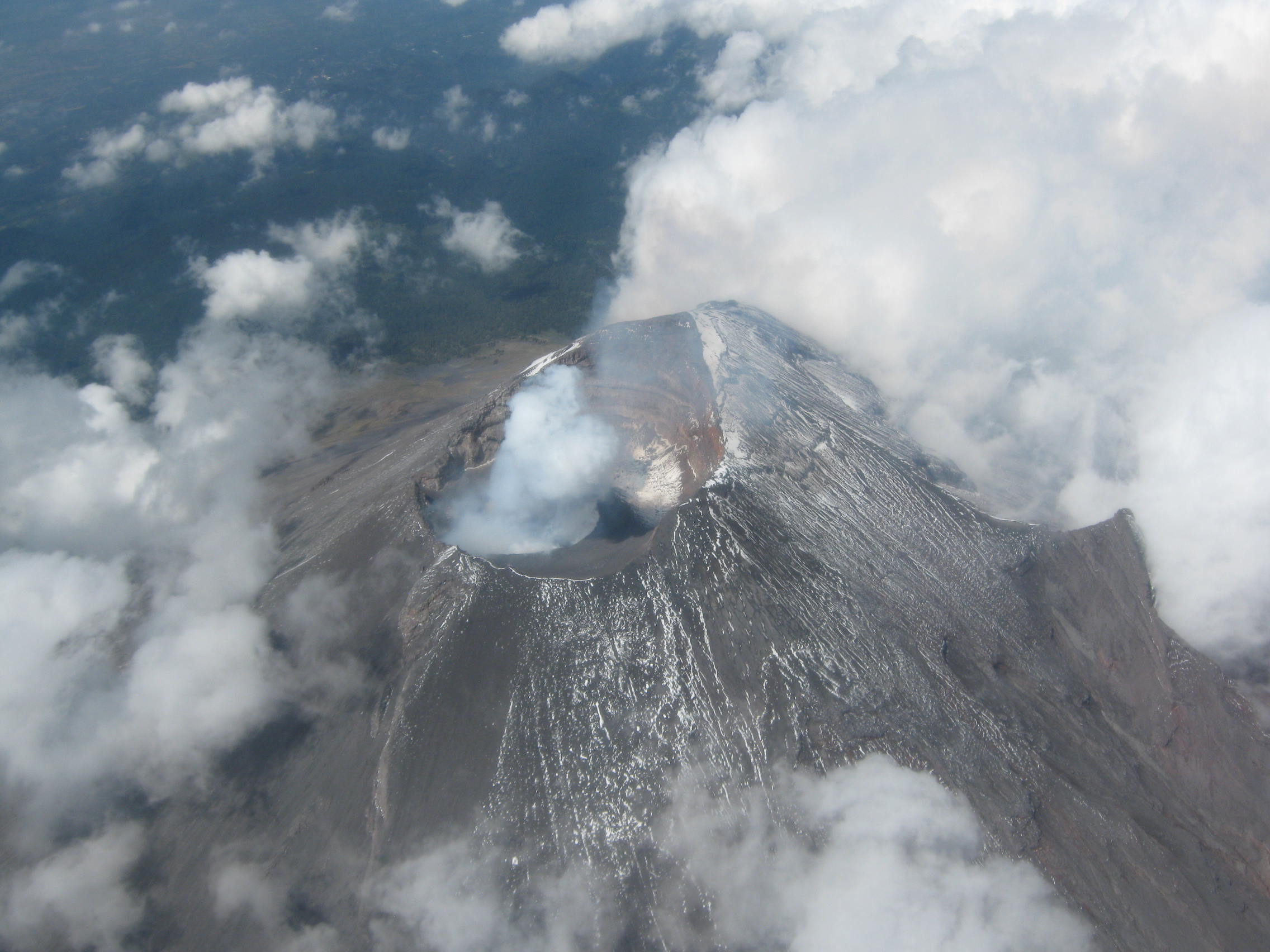
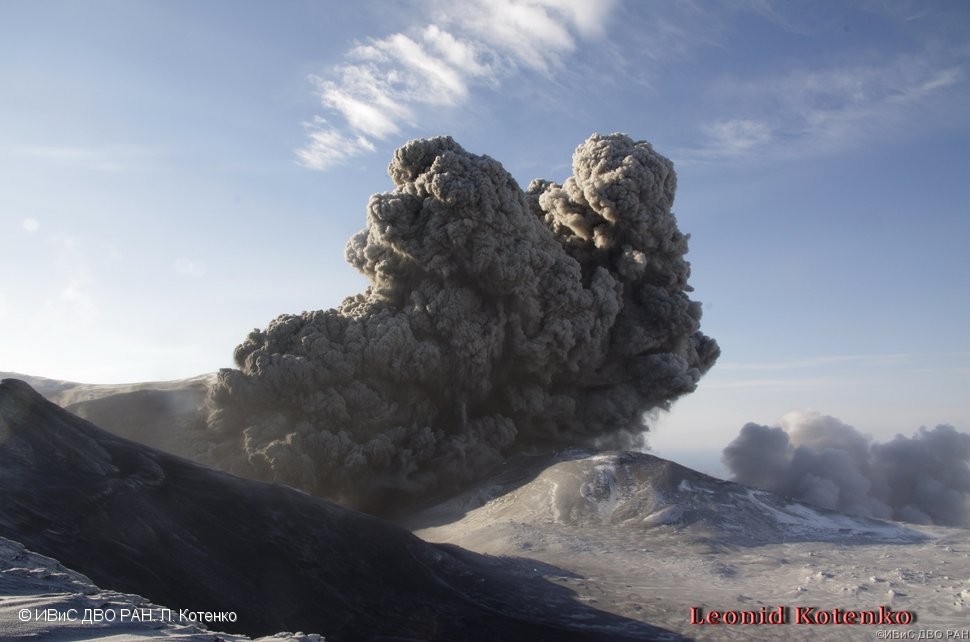
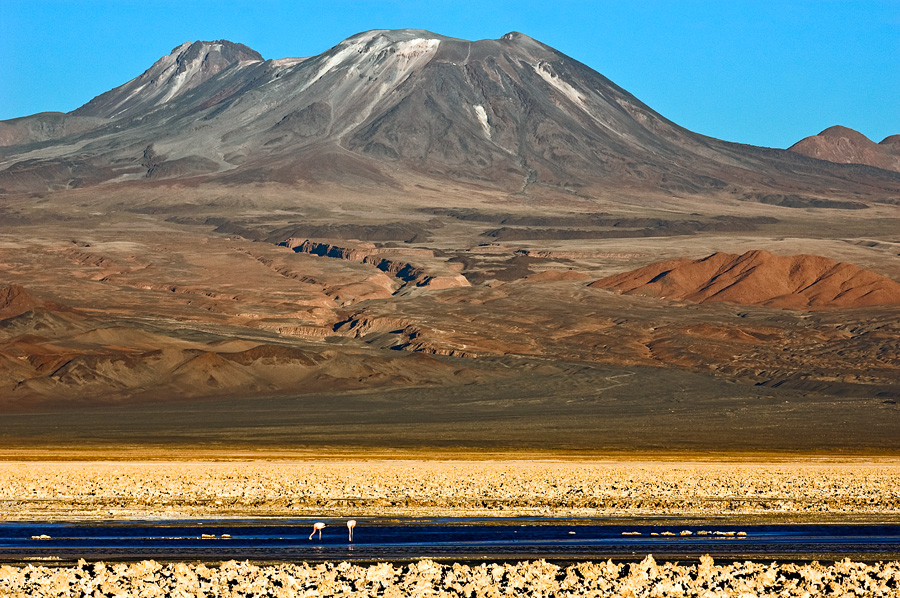
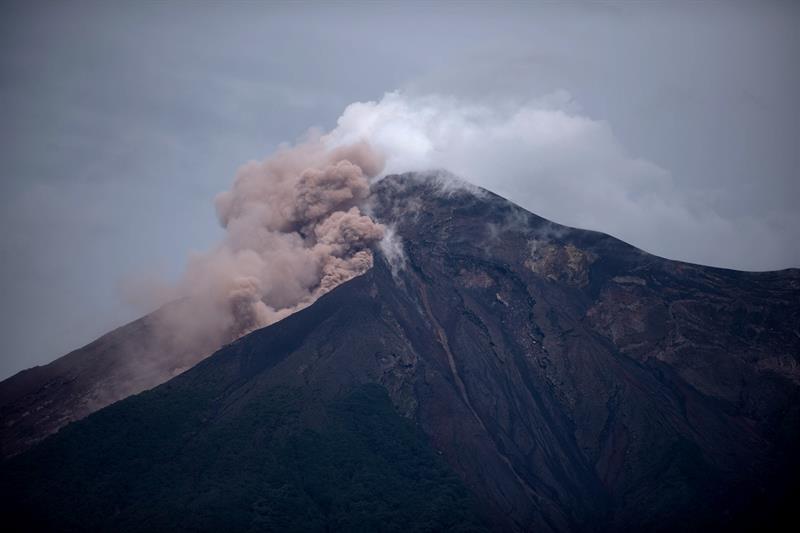
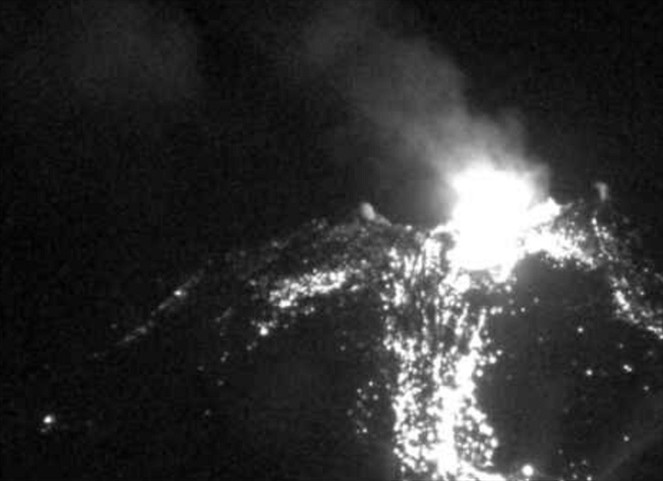
Information on the eruption of G. Agung, April 11, 2019.
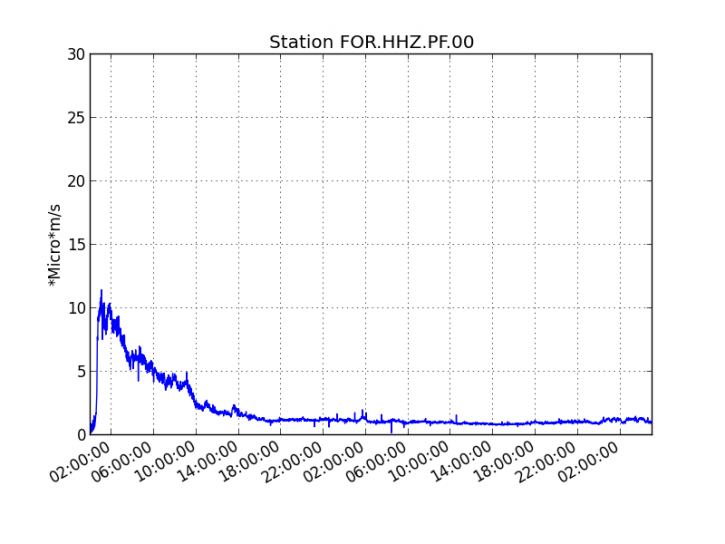
The eruption of Mount Agung occurred on April 11, 2019 at 18:47 with the height of the ash column observed at ± 2,000 m above the summit (± 5,142 m above sea level). The column of ash was gray, of thick intensity and inclined towards the West. This eruption was recorded on a seismogram of maximum amplitude of 25 mm and a duration of ± 2 minutes 8 seconds. A low roar was heard from the Rendang station.
Currently, G. Agung is at Level III (SIAGA) with recommendations:
Communities around Mount Agung and mountaineers / visitors / tourists must not climb or carry out any activity in the estimated risk zone within 4 km of Mount Agung. The estimated risk area is dynamic and continues to be evaluated. It can be modified at any time to follow the most recent G. Agung observation data.
Communities that live and move around rivers that are downstream of Gunung Agung are sensitized to potential secondary hazards in the form of lahar descent that can occur especially during the rainy season and if the eruption material is still exposed in the area of the summit.
Source : Magma Indonésie, PVMBG .
Photos : Peter rendez vous ( Archives ) , Telkom indonesia .
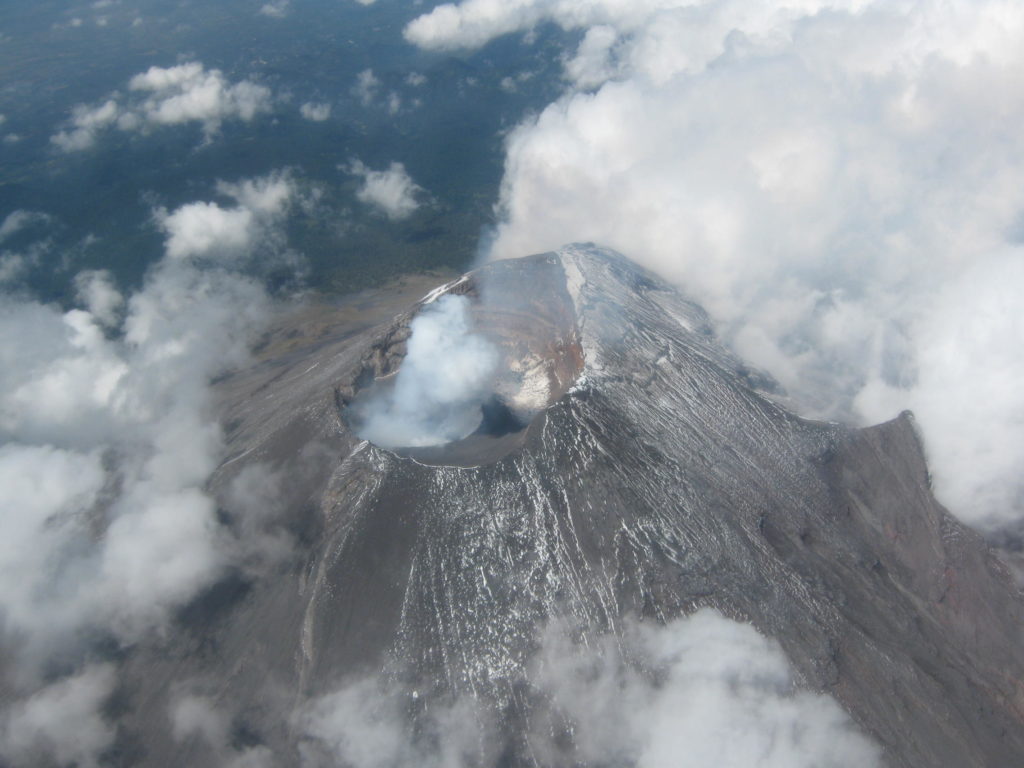
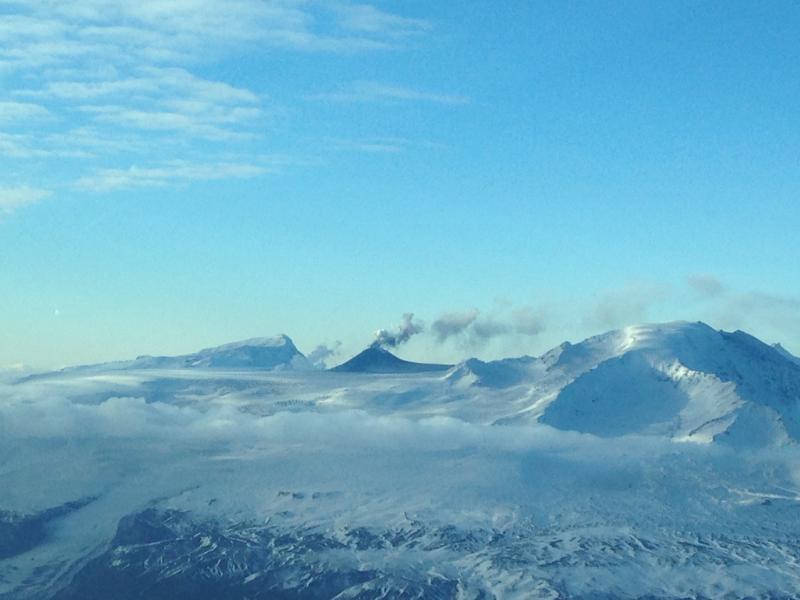
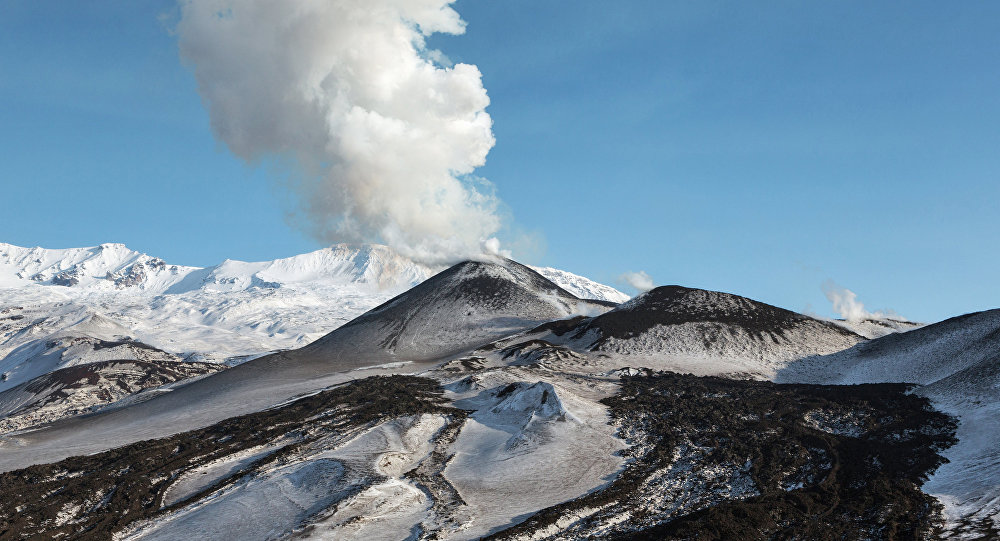
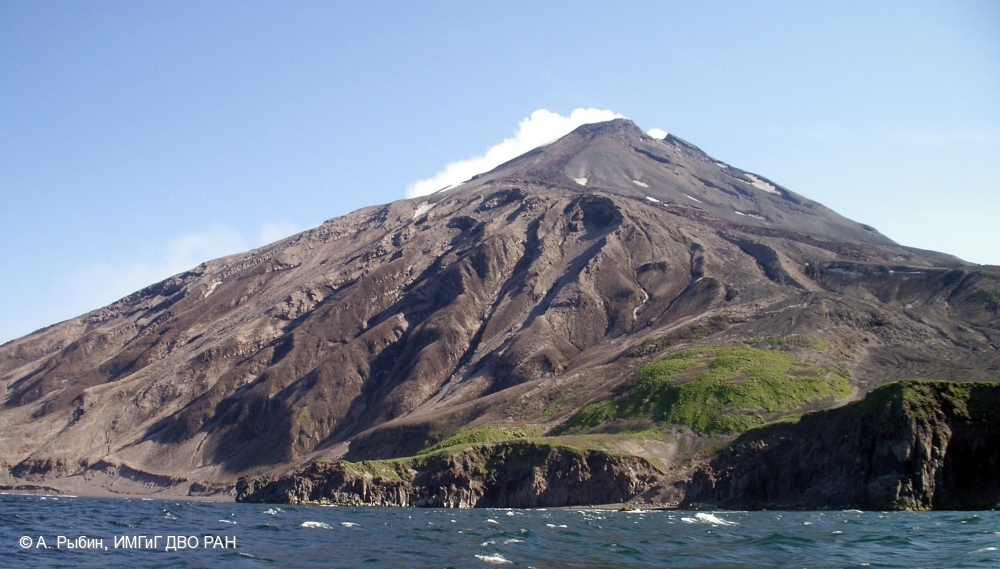
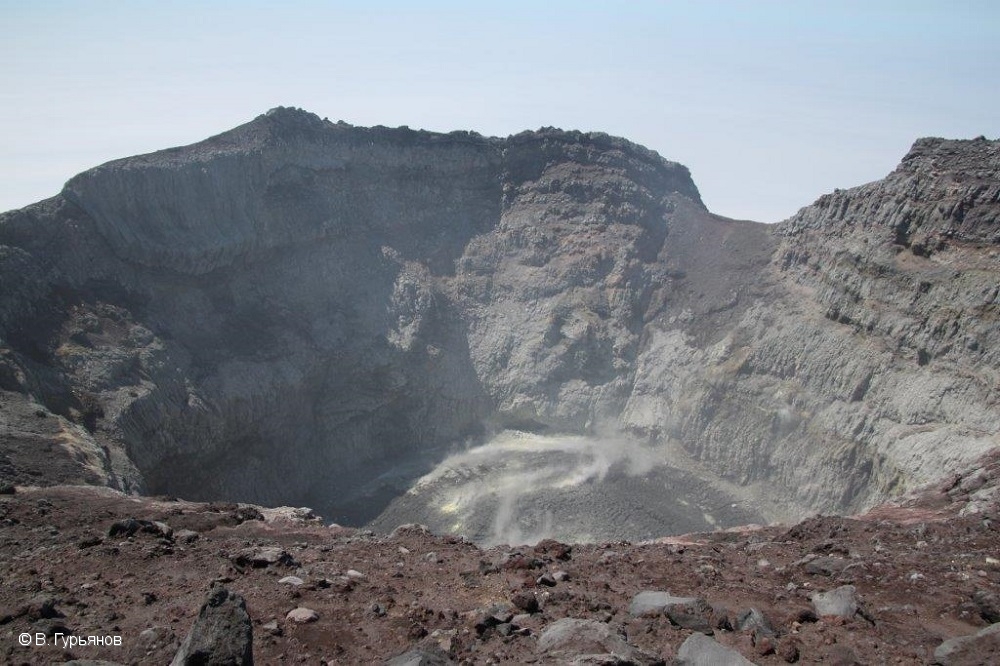
Kurile Islands , Ebeko :
50.69 N, 156.01 E;
Elevation 3792 ft (1156 m)
Aviation Colour Code is ORANGE
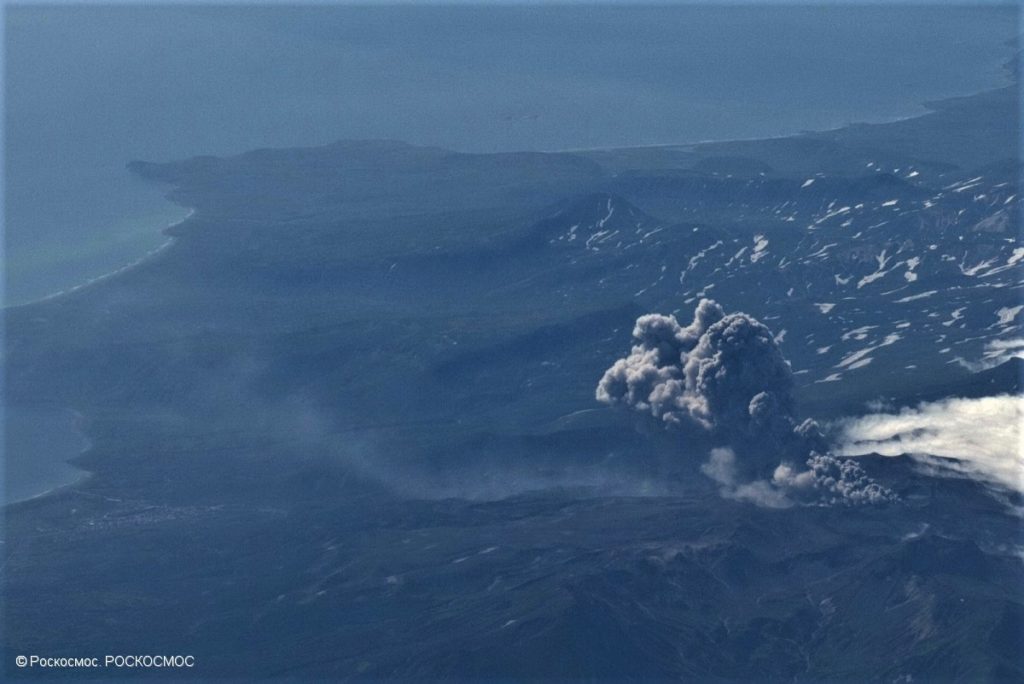
A moderate eruptive activity of the volcano continues. Ash explosions up to 19,700 ft (6 km) a.s.l. could occur at any time. Ongoing activity could affect low-flying aircraft and airport of Severo-Kurilsk.
A moderate explosive activity of the volcano continues. According to visual data by volcanologists from Severo-Kurilsk, explosions sent ash up to 2.2 km a.s.l. on 09 April. Satellite data by KVERT shows the volcano was obscured by clouds.
Source : Kvert
Photo : roskosmos
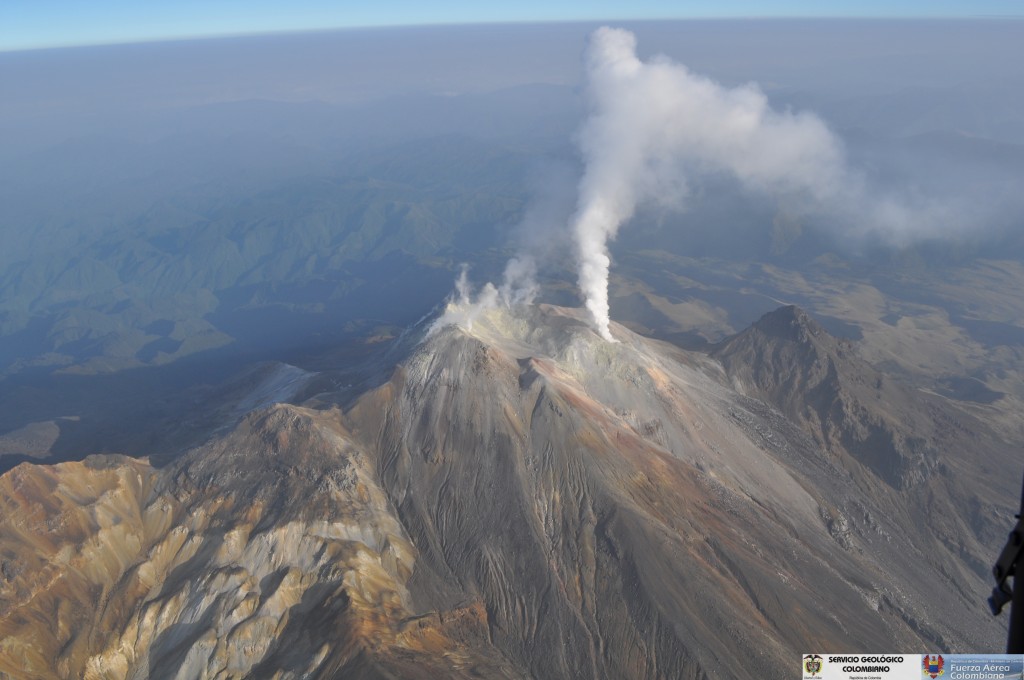
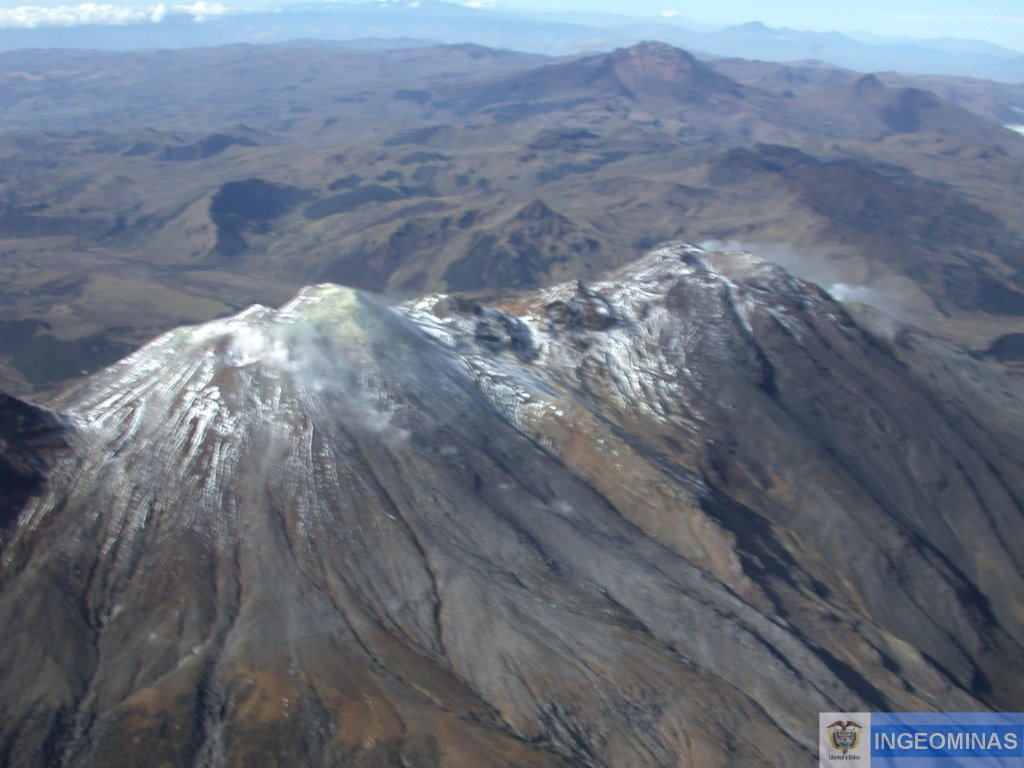
Colombia, Cumbal :
Weekly activity bulletin of the volcanic complex of Cumbal.
The level of activity of the volcano continues at the level: YELLOW LEVEL ■ (III): CHANGES IN THE BEHAVIOR OF THE VOLCANIC ACTIVITY.
Following the activity of the CUMBAL VOLCANIC COMPLEX, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE (SGC) reports that:
For the period evaluated between April 2 and 8, 2019, seismic activity was maintained at values similar to those reported in previous periods, from 316 to 334 earthquakes. The events associated with the fracture of solid materials inside the volcano were scattered in the area of influence of the Cumbal volcanic complex at depths less than 2 km from its summit (4700 m altitude) and a magnitude less than 0.1 on the Richter scale.
Favorable climatic conditions made it possible to observe gas emissions coming mainly from the El Verde fumarol field north-northeast of the volcanic complex. These emissions were white, of low height and of direction variable according to the action of the winds.
The COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE is attentive to the evolution of the volcanic phenomenon and will continue to inform in a timely manner of the observed changes.
Source : SGC
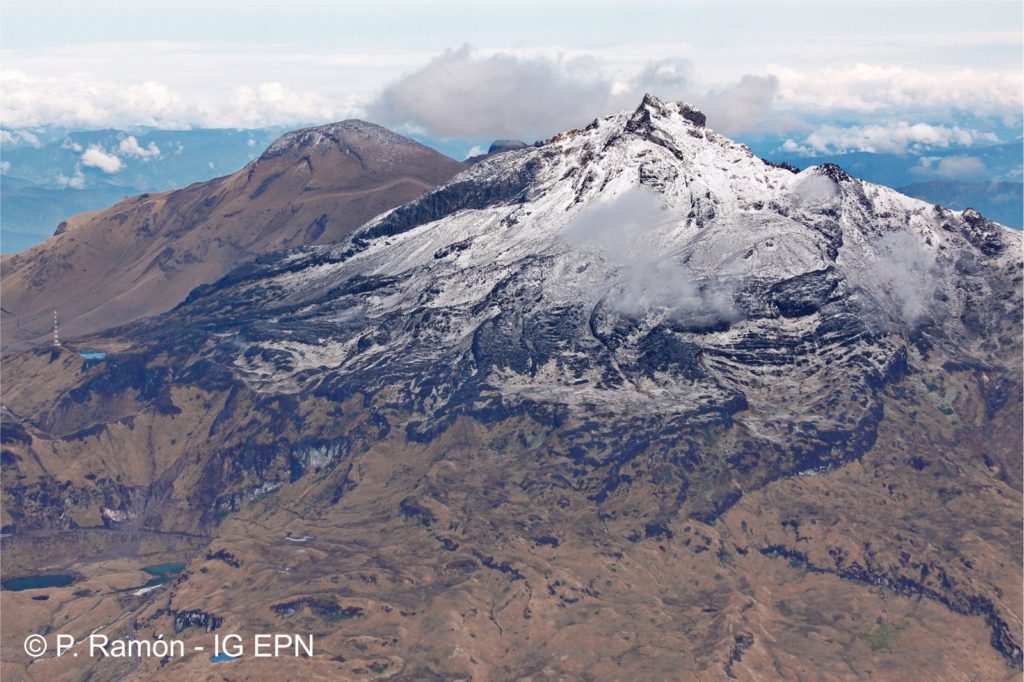
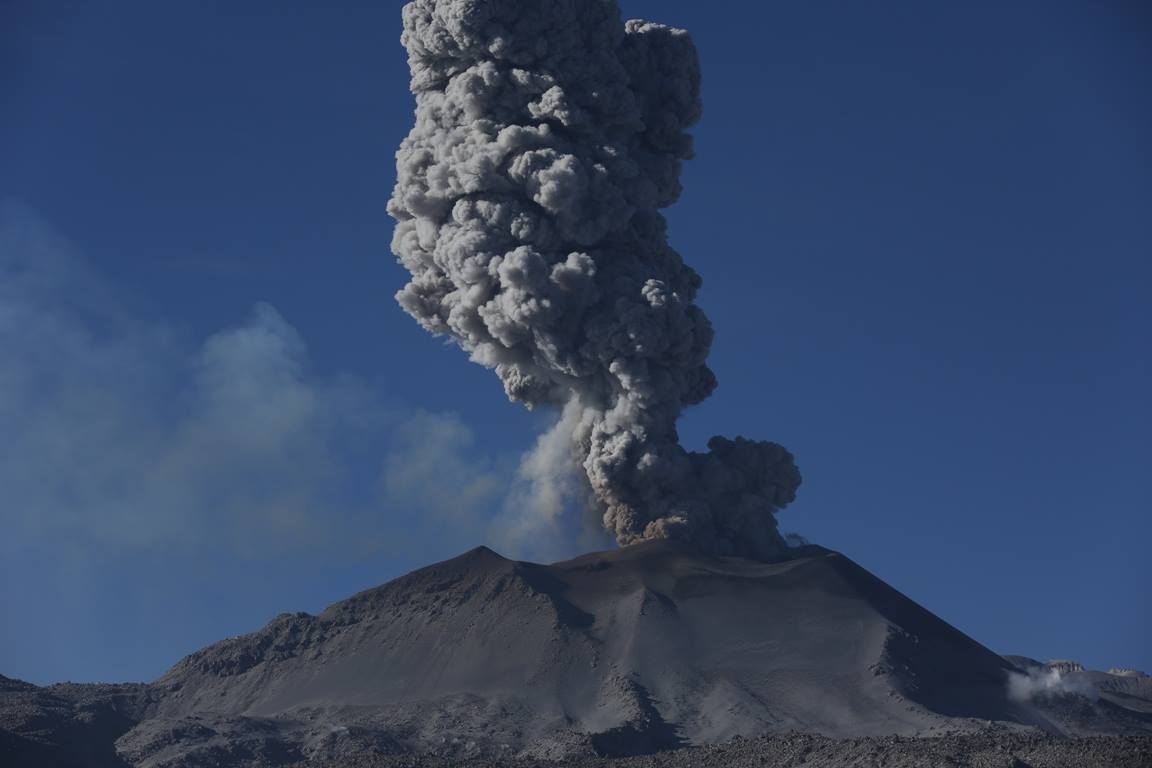
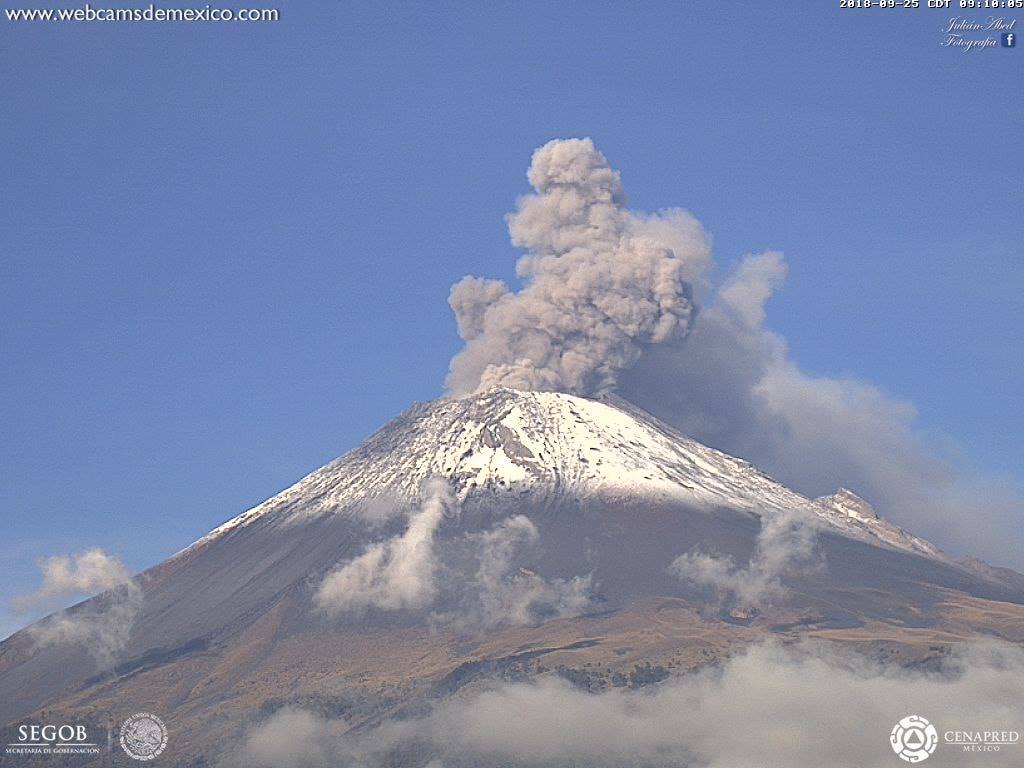
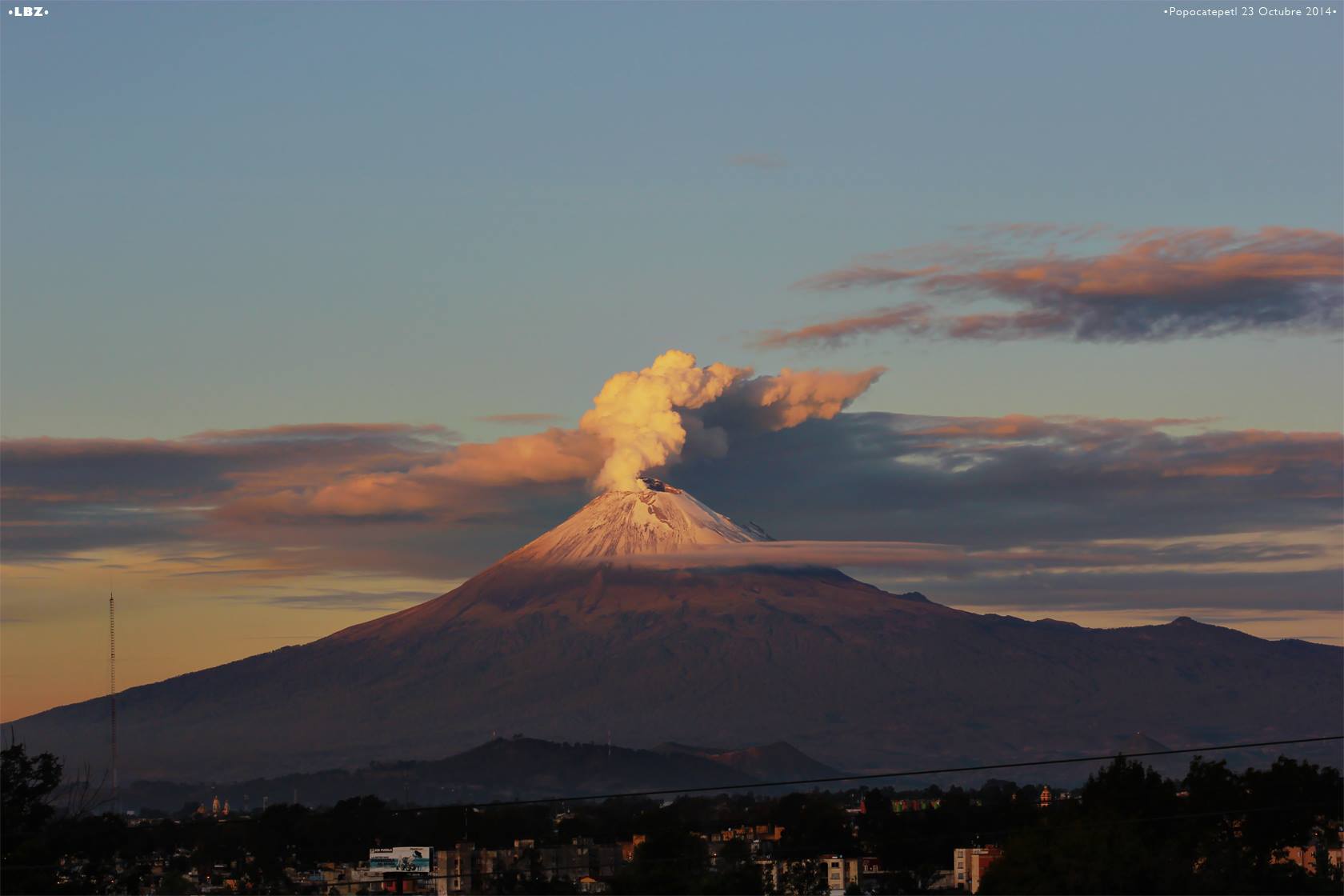
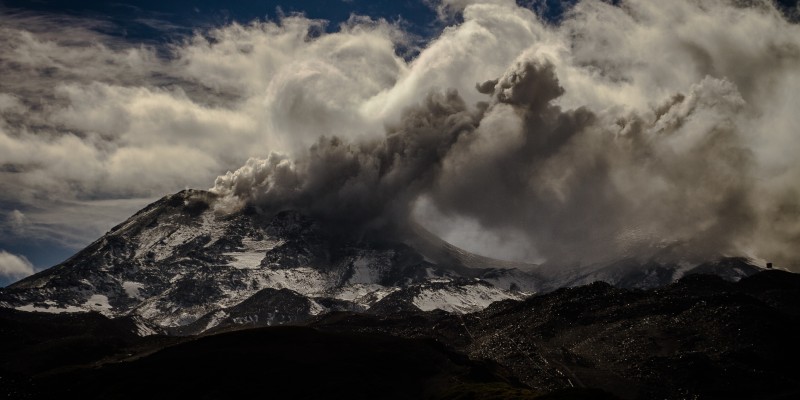
Mexico , Popocatepetl :
April 11, 11:00 am (April 11, 16:00 GMT)
In the last 24 hours, thanks to the monitoring systems of the Popocatépetl volcano, 16 exhalations have been identified, some of which accompanied by volcanic gases and light amounts of ash.
In addition, yesterday at 11:19, an episode of tremor began, accompanied by an emission of ashes, generating a column of a maximum height of 1 km above the crater, which dispersed mainly South-South-East . Is. A total of 110 minutes of low amplitude tremor were recorded.
Since the afternoon of yesterday and during the early hours of this morning, a slight emission of volcanic gases has been observed, which has spread north-east, which continues until this moment.
On April 8, with the support of the Federal Police (PF), experts from the National Center for Disaster Reduction (CENAPRED) and the Institute of Geophysics of the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM), flew of recognition, to evaluate the conditions of the crater Popocatepetl.
During the overflight, it was not possible to corroborate or rule out the presence of a new lava dome due to intense cloudiness, in addition to high vapor and gas emissions in the crater area . However, monitoring of the Popocatépetl volcano is carried out continuously over 24 hours. Any change of activity will be reported quickly.
It should be noted that since December 1, 2018, nine overflights have already been made, providing more accurate and up-to-date data on the volcano. The determination to fly over is derived from the risk analysis previously performed to determine crew safety conditions. Analyzing the videos of the explosions, it was determined that the ballistic fragments reached a height of between 500 m and one kilometer in about 8 to 10 seconds and that their horizontal range was 1 to 3 km.
The flight takes place at 20 000 feet (about 6 100 m altitude), that is to say more than 1 km above the crater floor, and obliquely not to be above that of the crater. -this. The pilot knows that if an explosion is detected, he must immediately change the route to get away from the volcano quickly.
CENAPRED urges NOT to approach the volcano and especially the crater, because of the danger of falling ballistic fragments, and in case of heavy rains to stay away from ravine bottoms due to the danger of mudslides and debris.
The Popocatepetl volcanic alert semaphore is located in PHASE 3 YELLOW.
Source : Cenapred
Photos : Cenapred , Felipe Pérez Fotoblog.
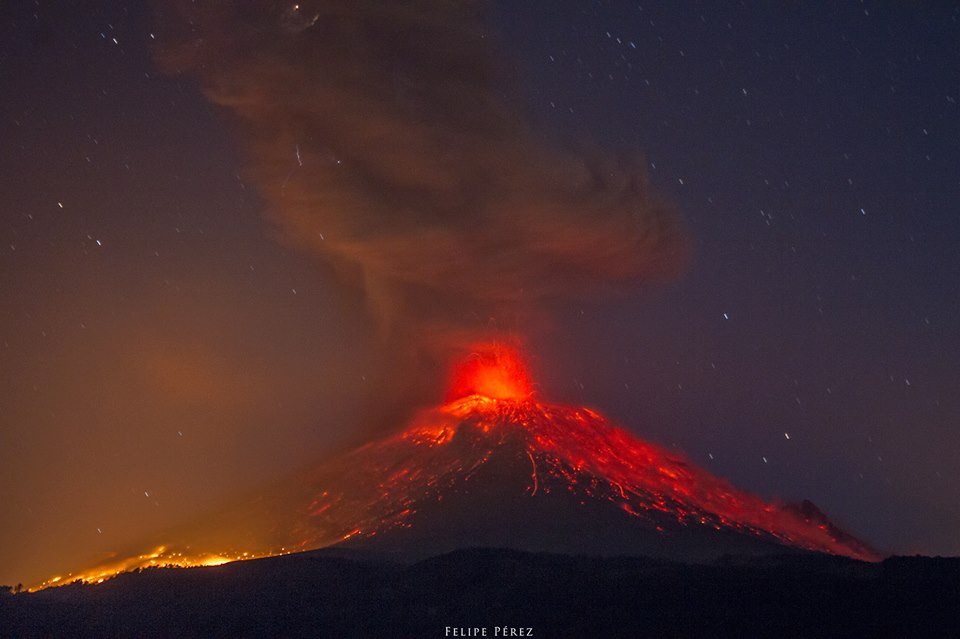
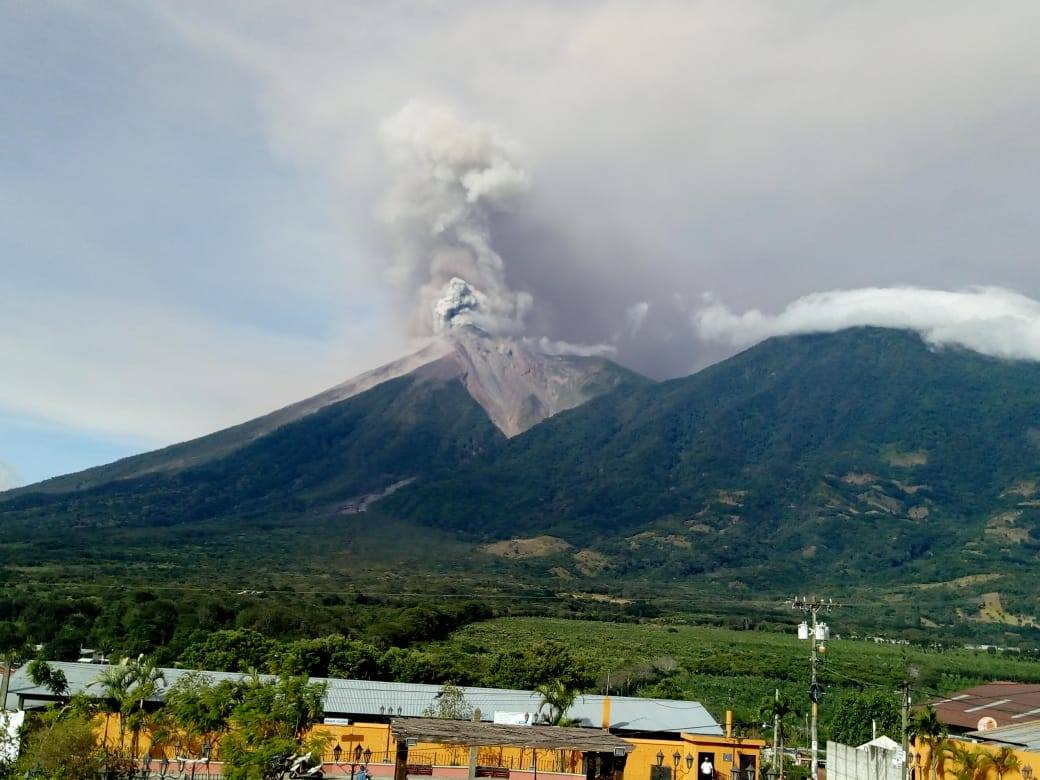
Guatemala , Fuego :
Type of activity: Vulcanian
Morphology: Composite Stratovolcano
Geographical location: 14 ° 28’54˝ Latitude N; 90 ° 52’54˝Longitude W.
Height: 3,763 meters above sea level.
Weather conditions: Clear
Wind: from the west at 5 km / h
Precipitation: 2.1 mm
Activity:
Presence of degassing fumarole of white color. The volcano observatory and the seismic stations record between 18 and 22 explosions between weak, moderate and a little strong per hour that expel columns of gray ash at a height of 4500 – 4800 m (14765-15750 feet) scattered over 15 to 20 km to the east, at night and early morning, incandescent impulses were observed at an altitude of 200 to 300 m with weak to moderate avalanches on the contour of the crater towards the ravines of Seca, Taniluya, Ceniza Trinidad, Las Lajas and Honda. In the Seca Canyon, a lava flow is observed 500 meters long. Some explosions generate moderate rumblings that cause shock waves that cause vibrations in the roofs of homes near the volcano. It is also possible to hear sounds similar to those of train locomotives with an interval of 15 minutes, causing the fall of fine ash particles in Alotenango, Ciudad Vieja, La Reunión. There is a probability of ash falling in Antigua Guatemala.
Source : Insivumeh
Photo : elinformador.com