November 07 , 2021.
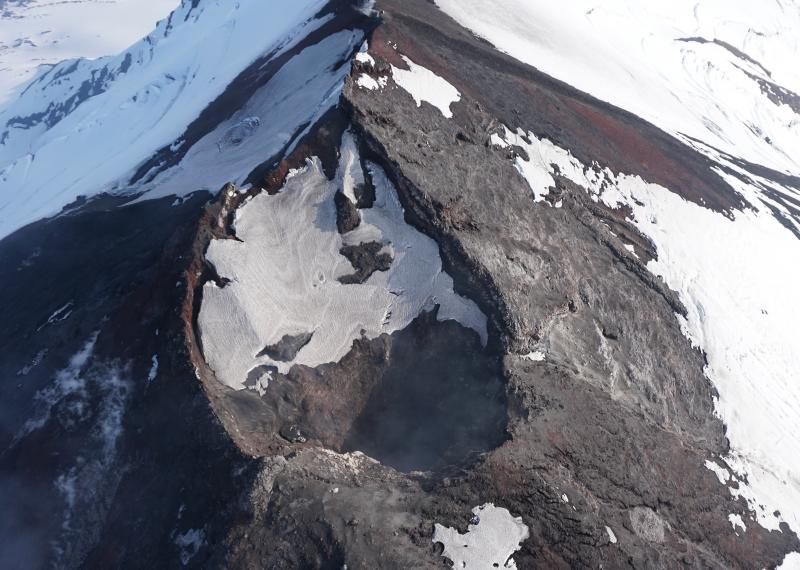
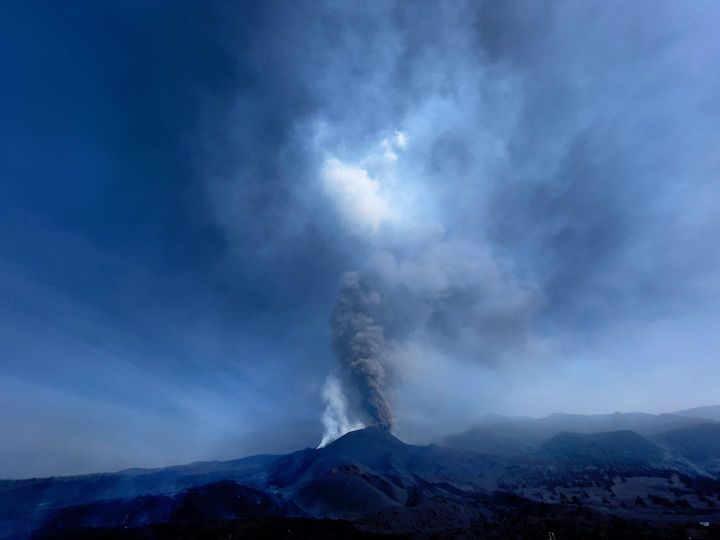
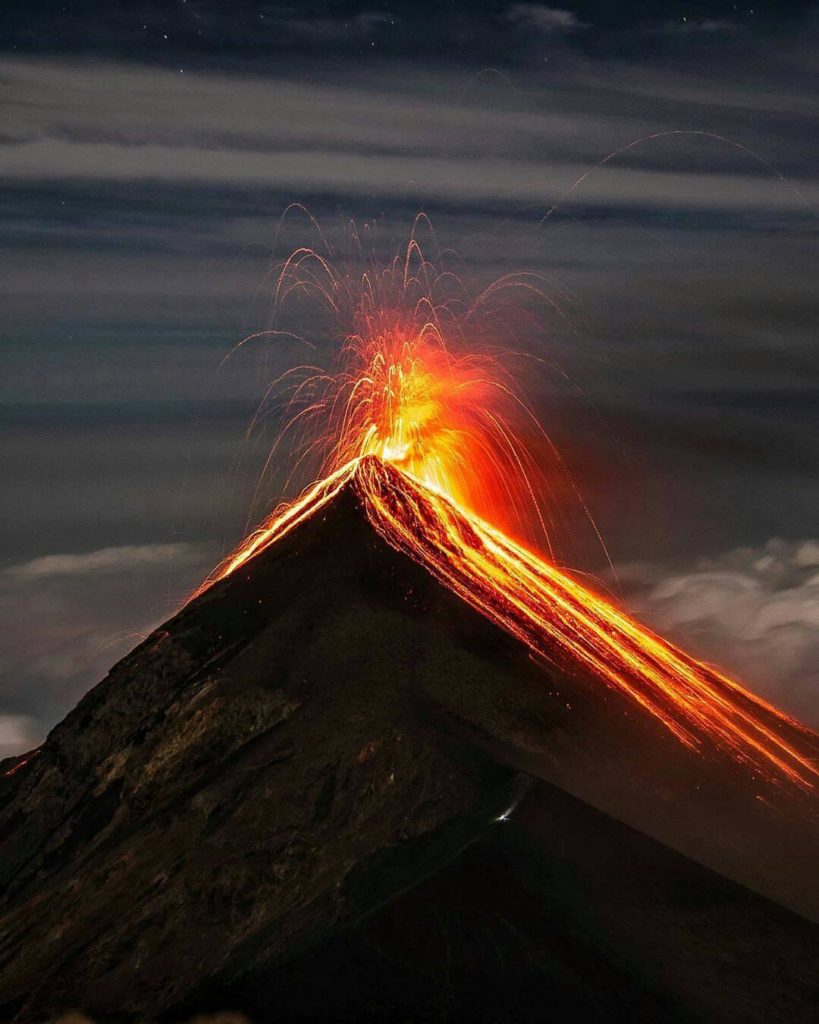
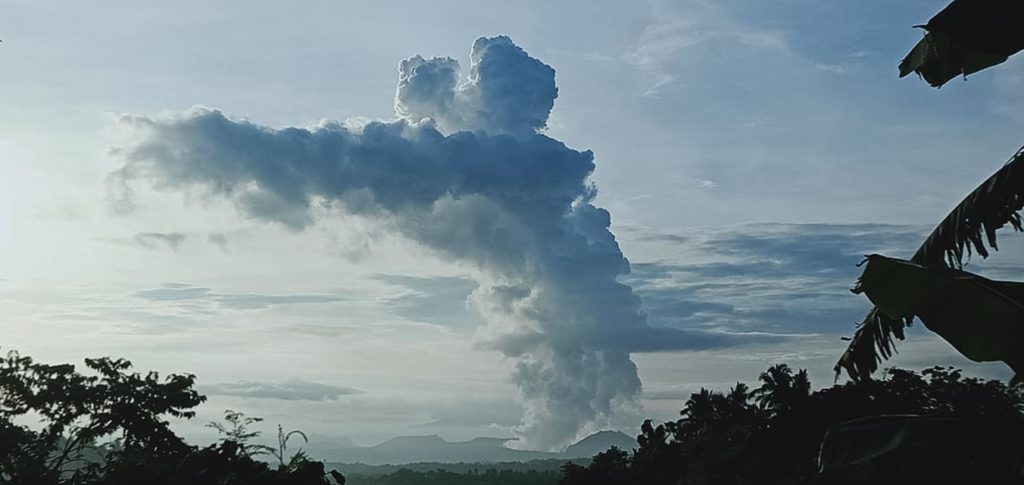
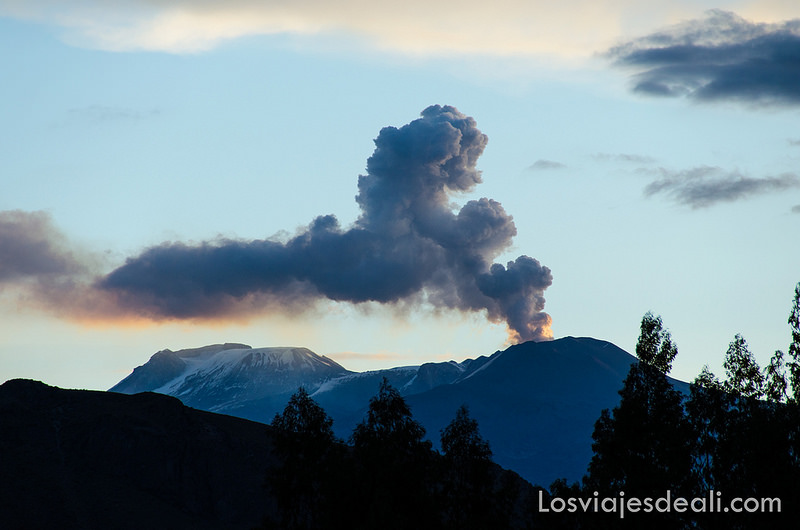
Indonesia , Merapi :
Merapi activity report, from October 29 to November 4, 2021.
– The weather around Mount Merapi is generally sunny in the morning and evening, while it is foggy in the afternoon.
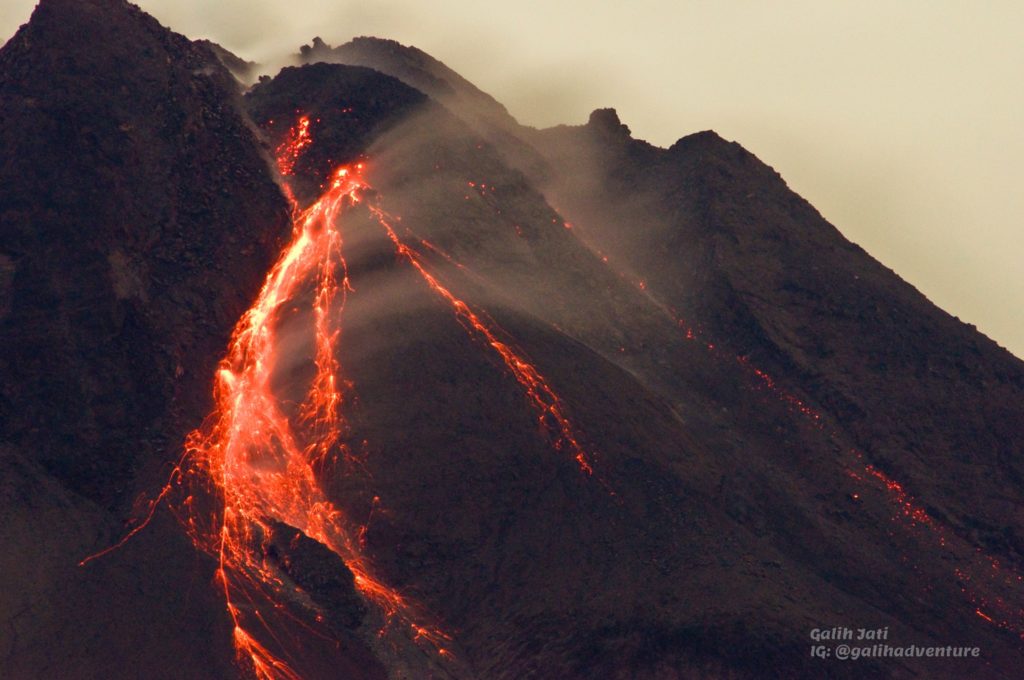
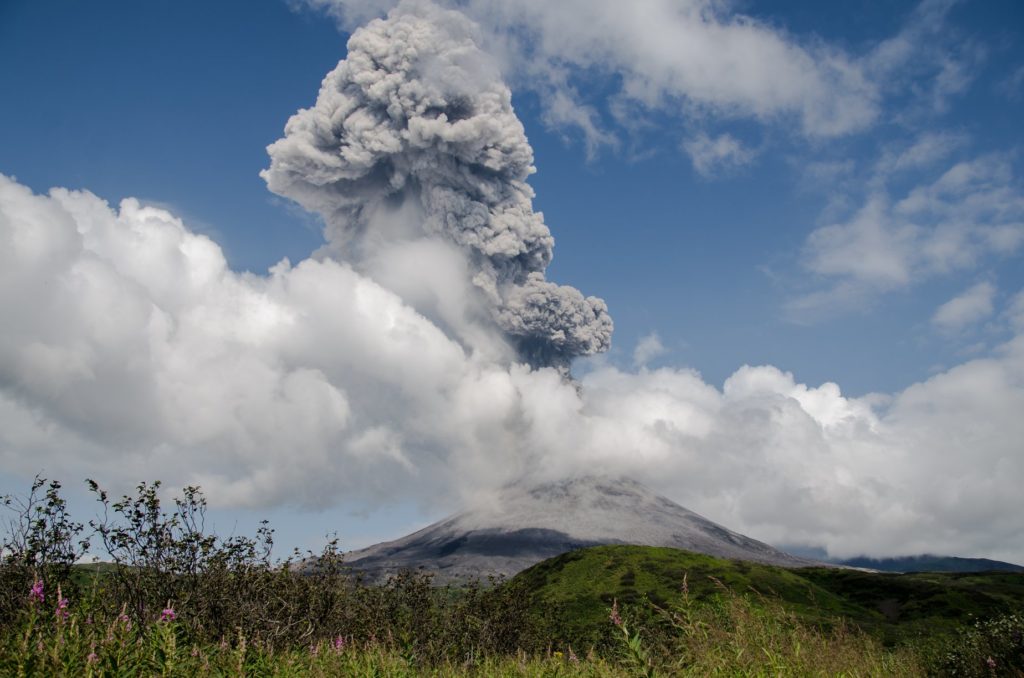
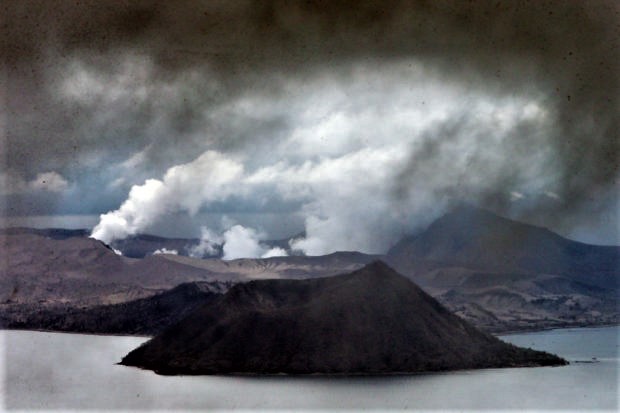
– This week, there was 1 avalanche of hot clouds towards the southwest with a sliding distance of 2000 m. Lava avalanches have been observed 106 times to the southwest with a maximum slide distance of 2000 m.
– No significant morphological change was observed in either the southwest dome or the central dome. The volume of the southwest lava dome is 1,610,000 m3 and the central dome is 2,927,000 m3.
According to the seismographs of November 5, 2021, it was recorded:
159 avalanche earthquakes
16 earthquakes of emissions
18 hybrid earthquakes
3 shallow volcanic earthquakes
2 distant tectonic earthquakes
– This week’s seismicity intensity was lower than last week.
The deformation of Mount Merapi which was monitored using EDM and GPS this week showed no significant changes.
– A rainfall intensity of 49 mm / hour for 220 minutes was recorded at the Kaliurang post on November 2, 2021. No additional lahar or flow was reported in the rivers that originate on Mount Merapi.
Conclusion:
– The volcanic activity of Mount Merapi is still quite high in the form of effusive eruption activity. The status of the activity is defined in the “SIAGA” level.
– The current potential danger consists of lava avalanches and hot clouds in the South-East / South-West sectors over a maximum of 3 km to the Woro river and 5 km to the Gendol and Kuning rivers , Boyong, Bedog, Krasak, Bebeng and Putih. During this time, the ejection of volcanic material in the event of an explosive eruption can reach a radius of 3 km from the summit.
Source : BPPTKG.
Photo : Yohannes Tyas Galih Jati
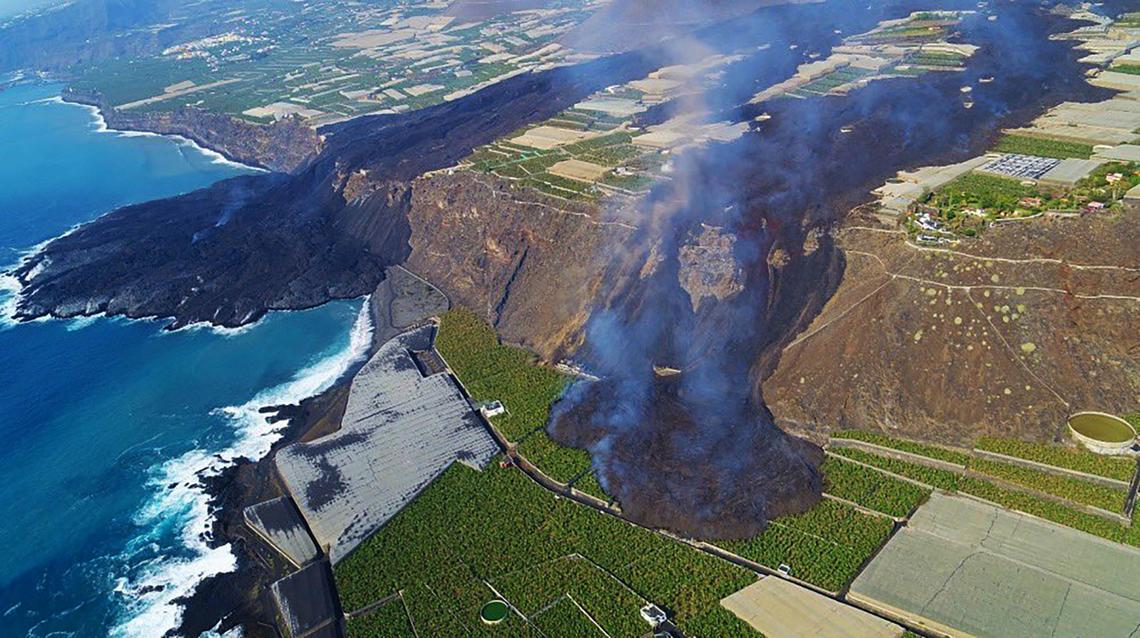
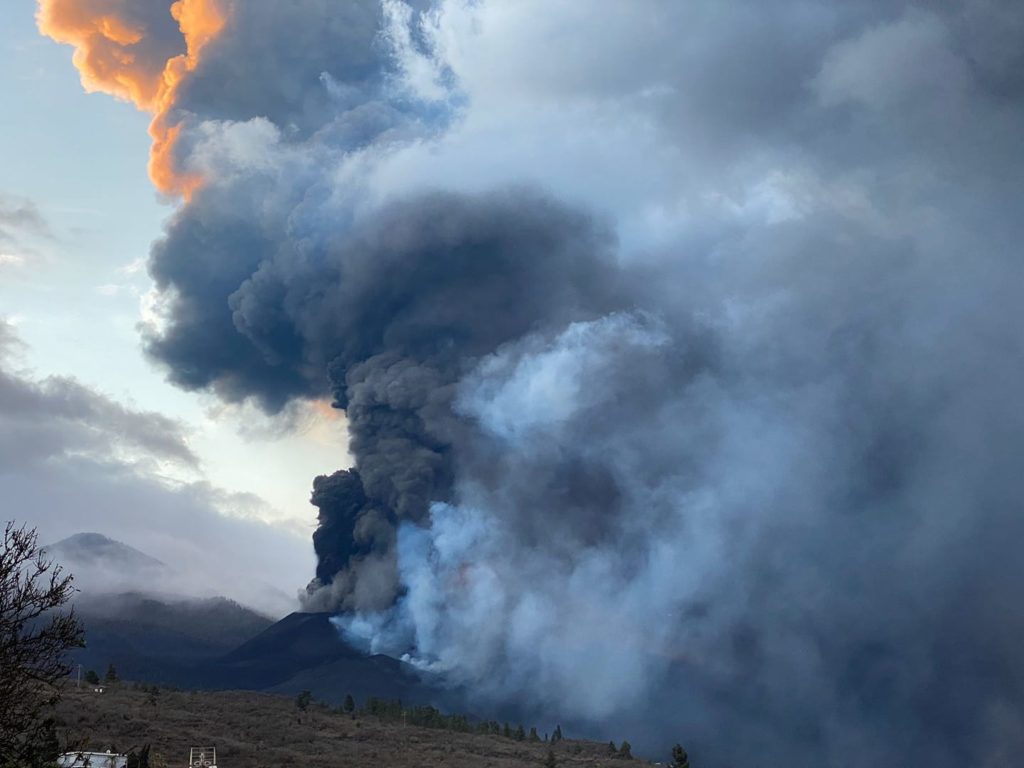
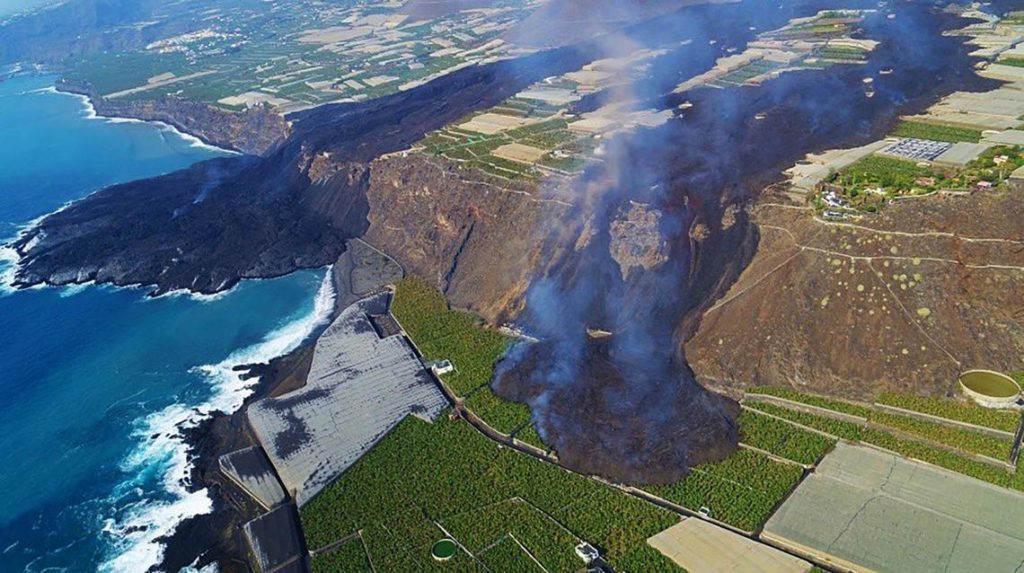
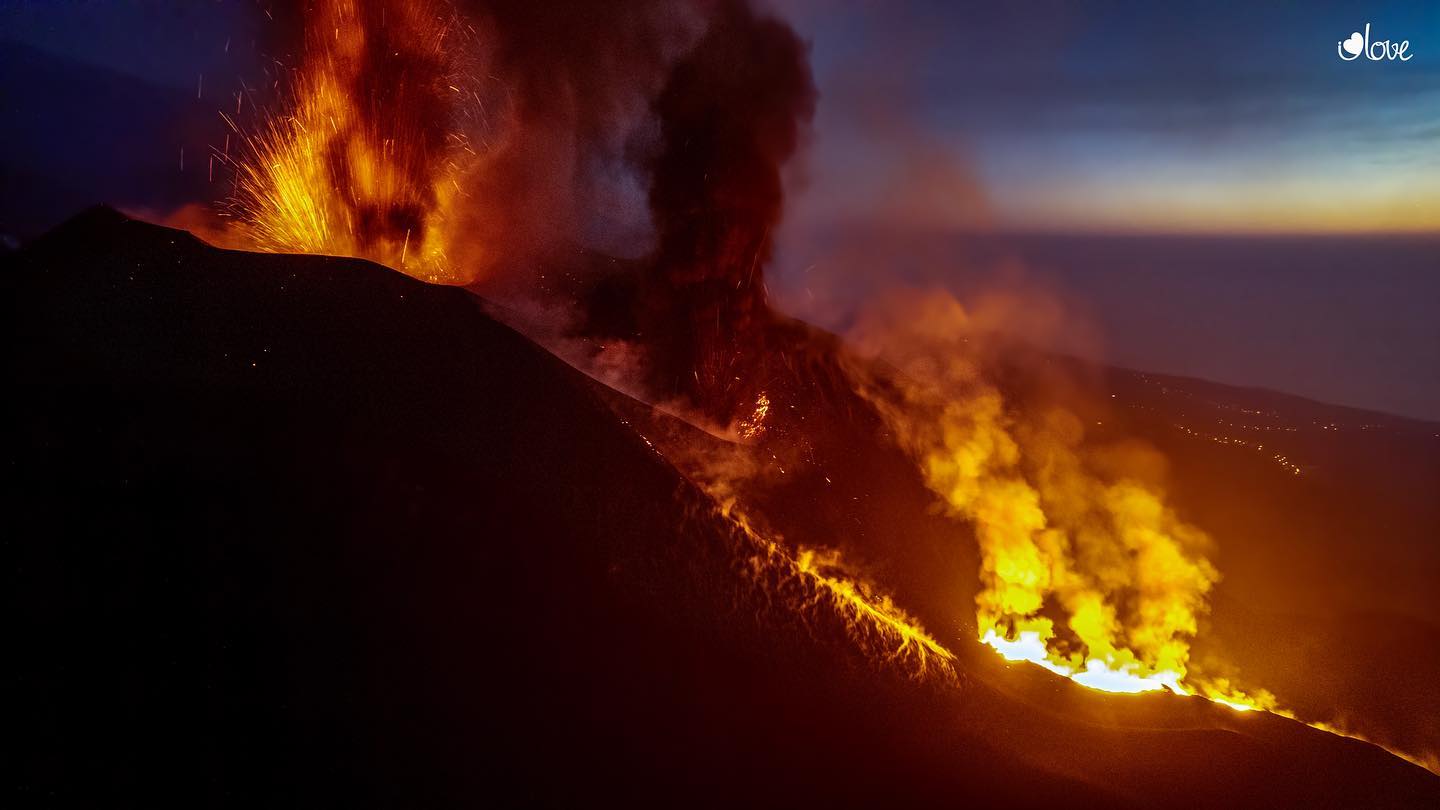
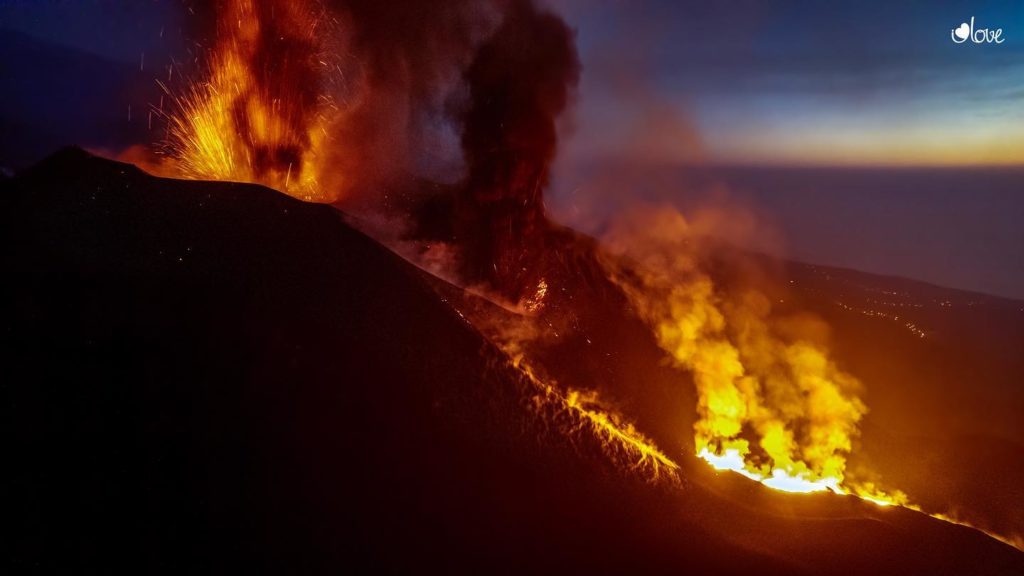
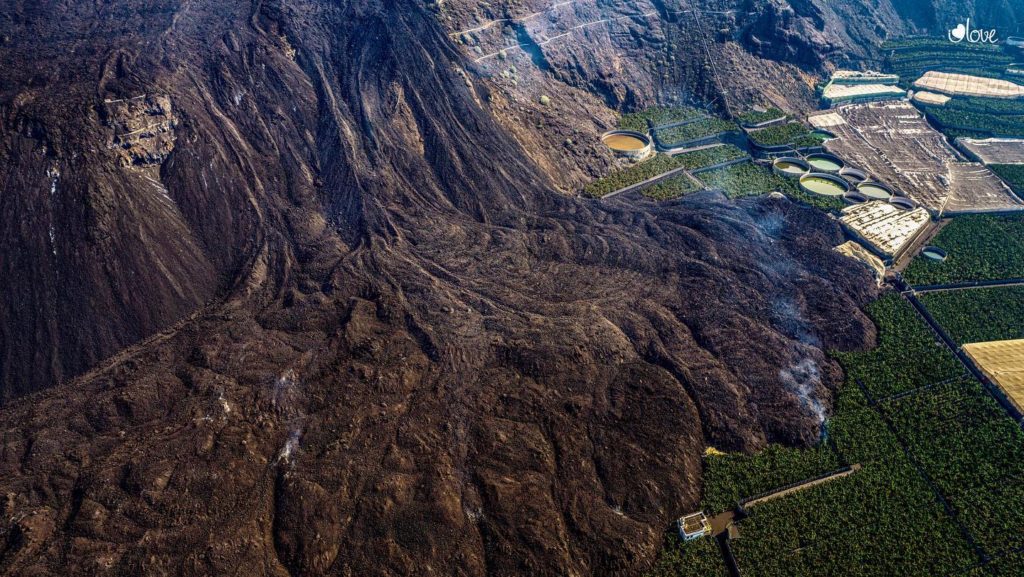
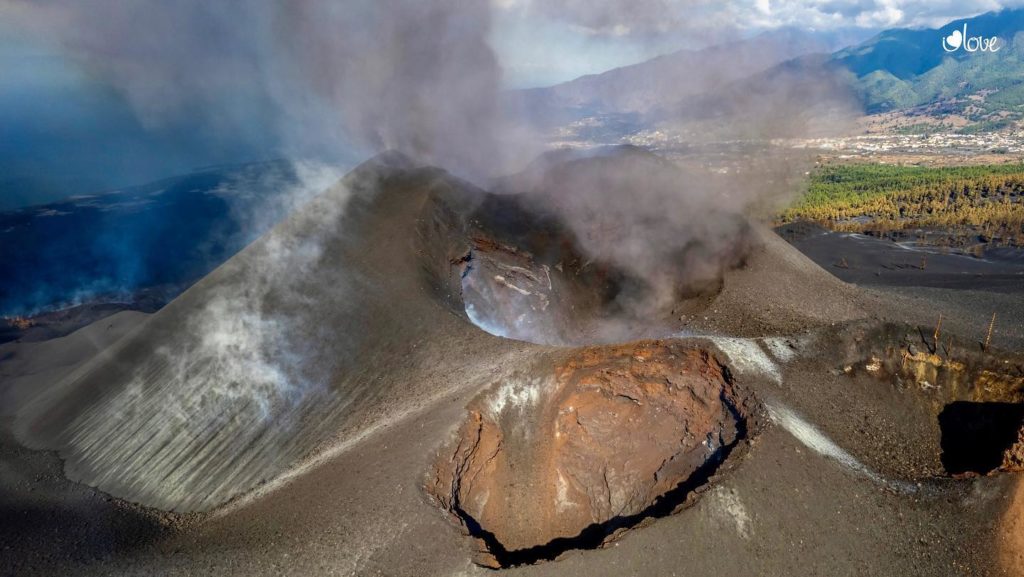
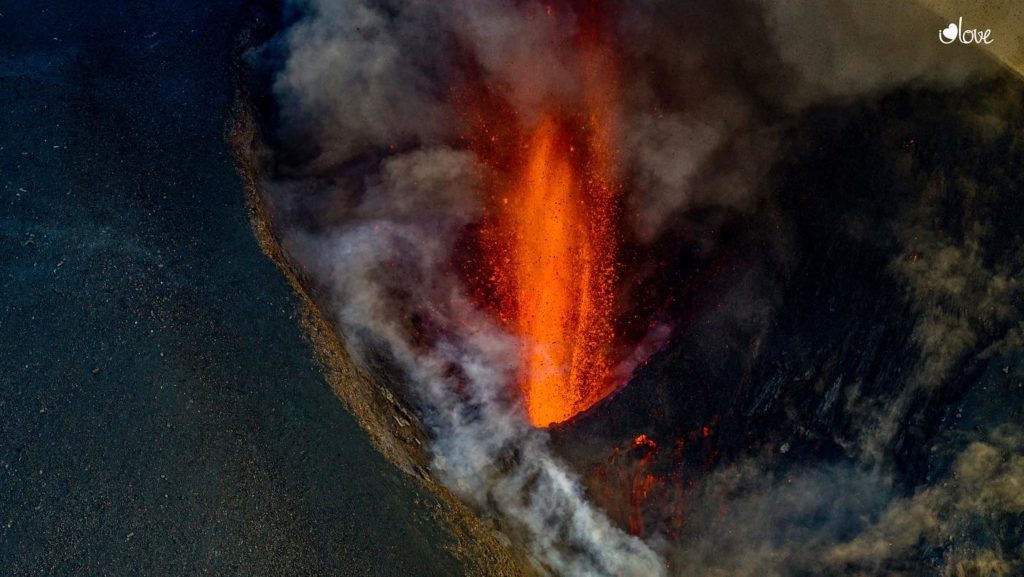
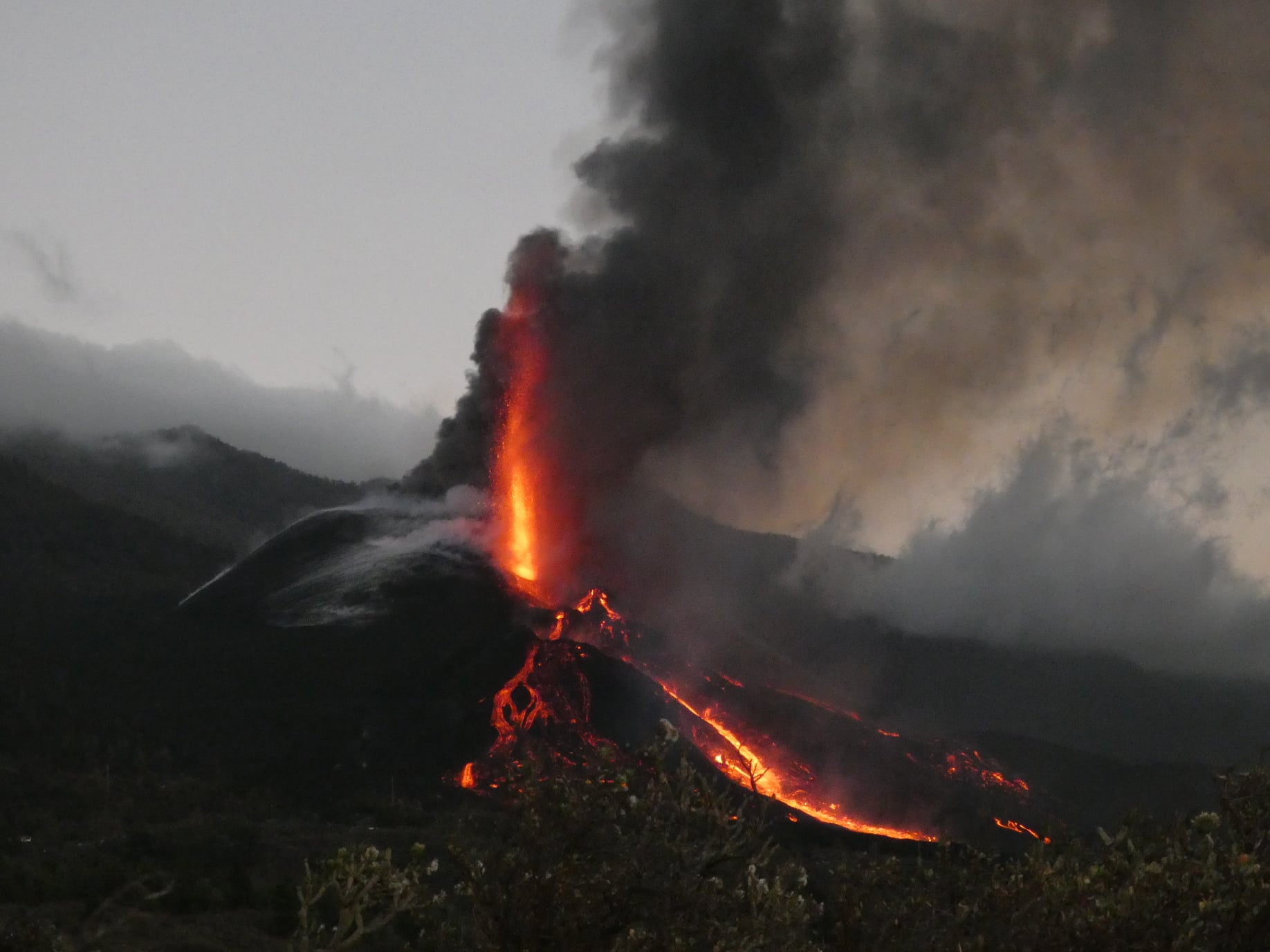
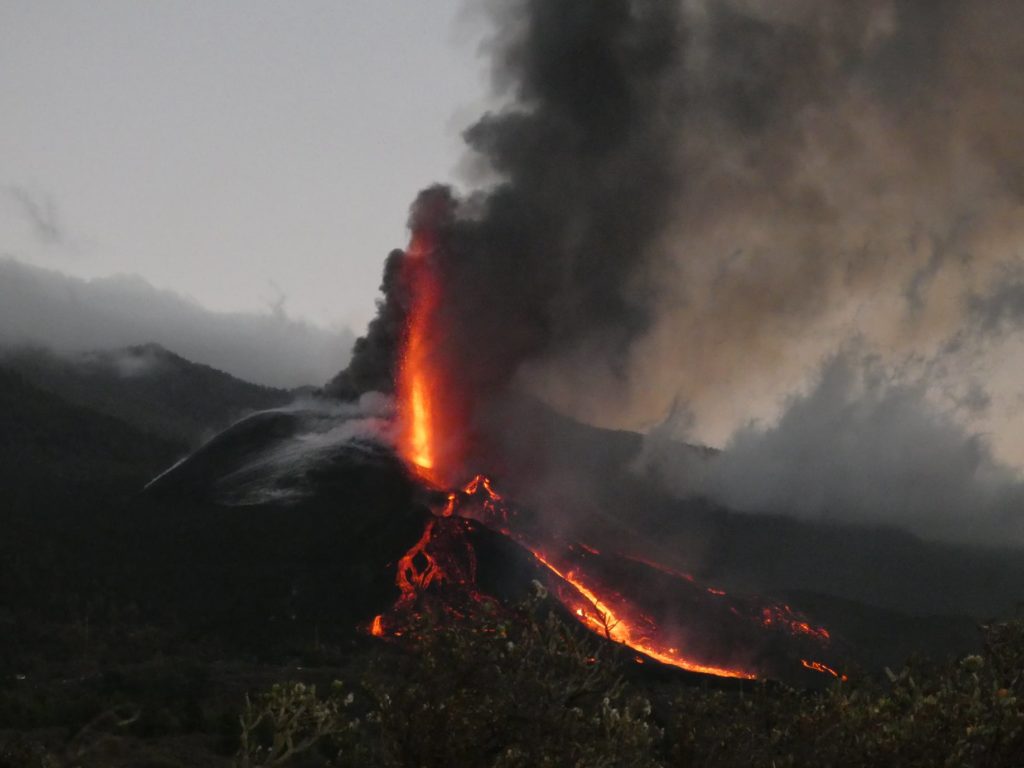
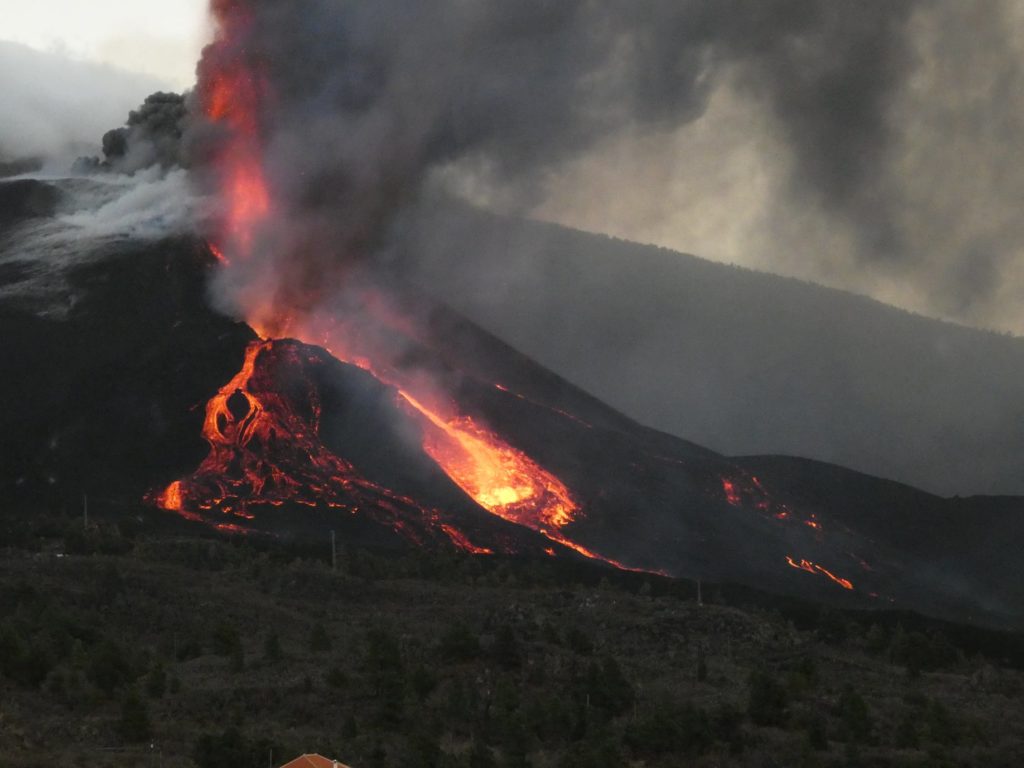
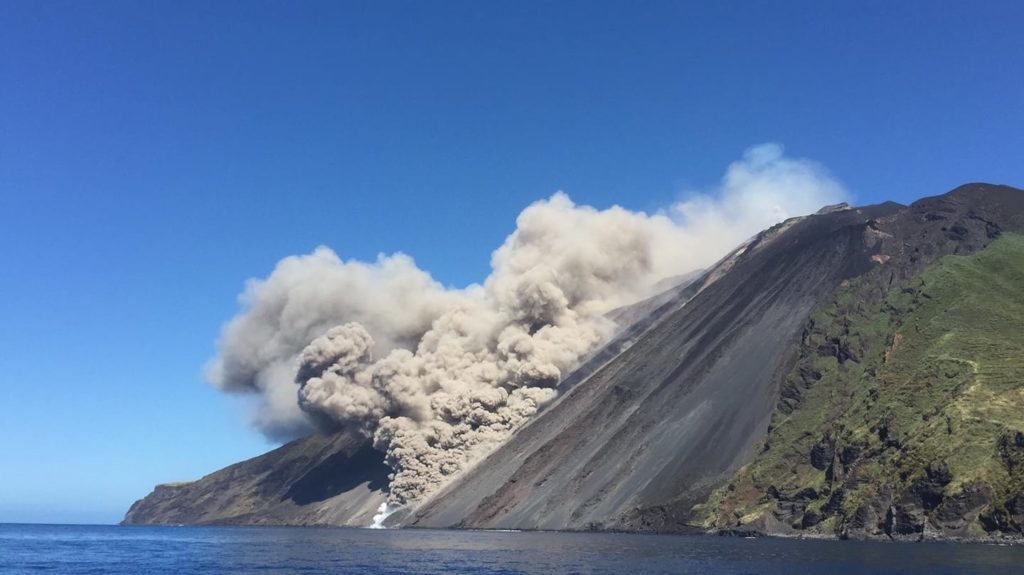
Spain / La Palma , Cumbre Vieja :
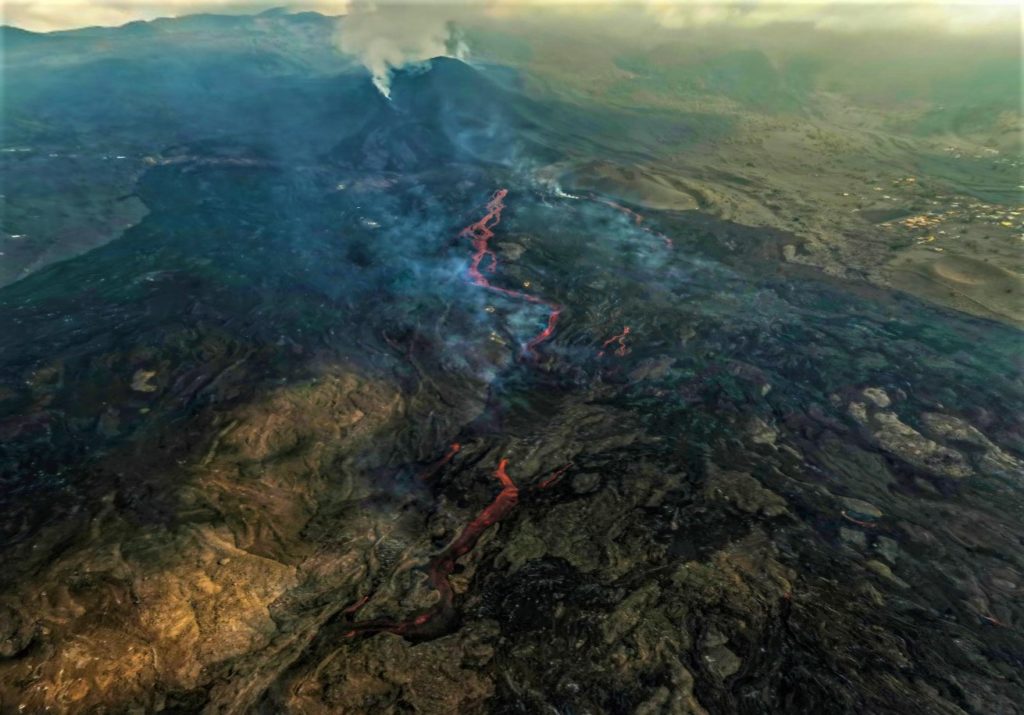
November 06, 2021, 09:00 UTC. Eruptive activity continues on La Palma.
Since the last declaration, only 26 earthquakes have been located in the area affected by the volcanic reactivation of Cumbre Vieja, one of these earthquakes was felt by the population, having reached the maximum intensity in the epicentral area of III-IV (EMS98).
The most significant earthquake is the one which occurred at 01:39 (UTC) today, with a magnitude of 4.0 mbLg at 11 km depth and felt with an intensity III-IV on the island of La Palma. In the period considered, 2 earthquakes were located at depths of about 30 km, the rest of the hypocenters of the period are located at a shallower depth, about 12 km.
The amplitude of the volcanic tremor signal is at low average levels, with intensifying pulses.
The island’s network of permanent GNSS stations shows an elevation of around 10 cm as well as a southwestward deformation between November 3 and 5 at station LP03, which is closest to the eruptive centers.
On the other hand, at the most distant stations, a slight deflation was maintained, possibly linked to deep seismicity.
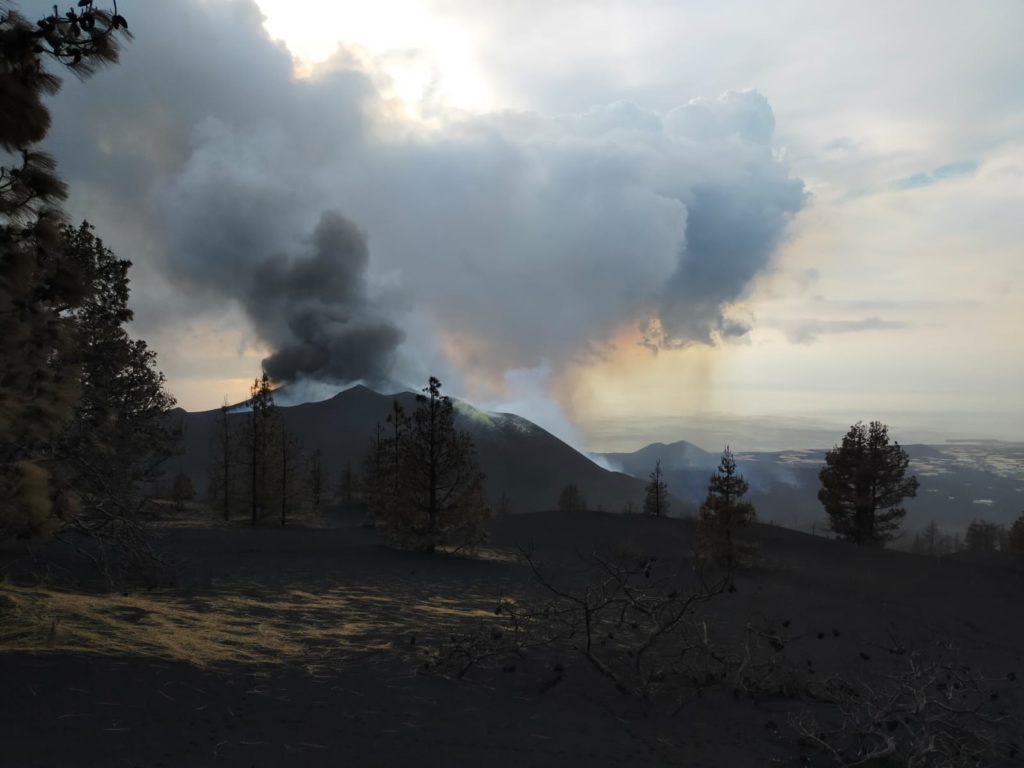
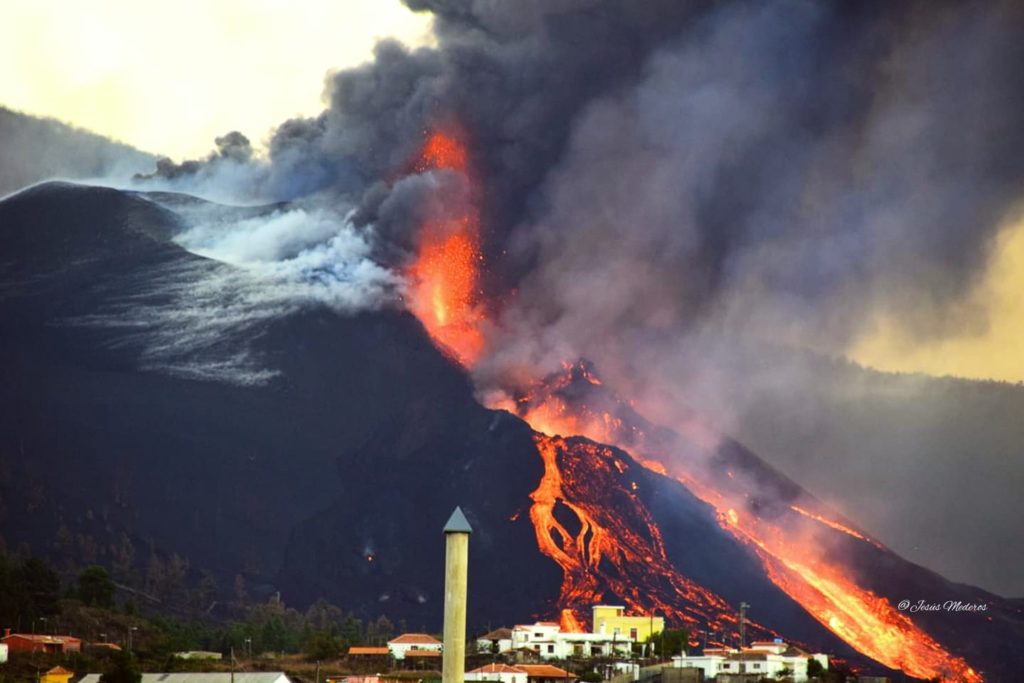
In view of the calibrated image, a column height of 2,500 m was estimated at 08:48 UTC with a West-South-West direction.
Today at 10:30 UTC, due to the decrease in the height of the eruptive column, IGN issued a new VONA (Volcano Observatory Notice for Aviation) message informing that the maximum height of the eruptive column was 2,700 m on sea level.
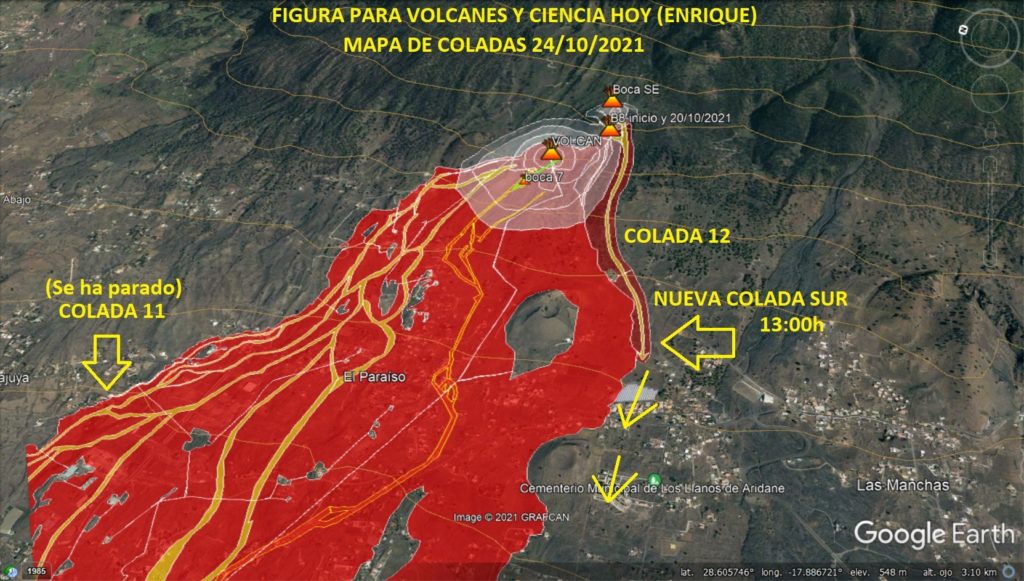
Canary Islands Volcanic Emergency Plan (Pevolca) Scientific Committee spokeswoman Carmen López said on Saturday that there was no scientific data indicating that the volcano’s eruption « in the short term » Cumbre Vieja, in La Palma, would end. “We have to be careful. What is useful are trends and trends need several days to be robust, ”López insisted. The seismic swarm continues the downward trend recorded during this week, although it remains active south of the Cumbre Vieja volcano.
The Department of Homeland Security (DSN) published on Sunday on its official Twitter account its daily report on the situation of the Cumbre Vieja volcano, on the island of La Palma. This organism reminds us that the eruptive process continues and that the lava continues to flow towards the North-West, but without affecting new surfaces. « In general, all the flows are almost motionless, » explains the DSN, which also points out that the air quality is particularly unfavorable in the municipalities of Paso, Tazacorte, Puntagorda, Tijarafe and Los Llanos de Aridane.
Sources : IGN es ,
Photos : IGN, Jesus Mederos via Mónica Acosta Delgado.
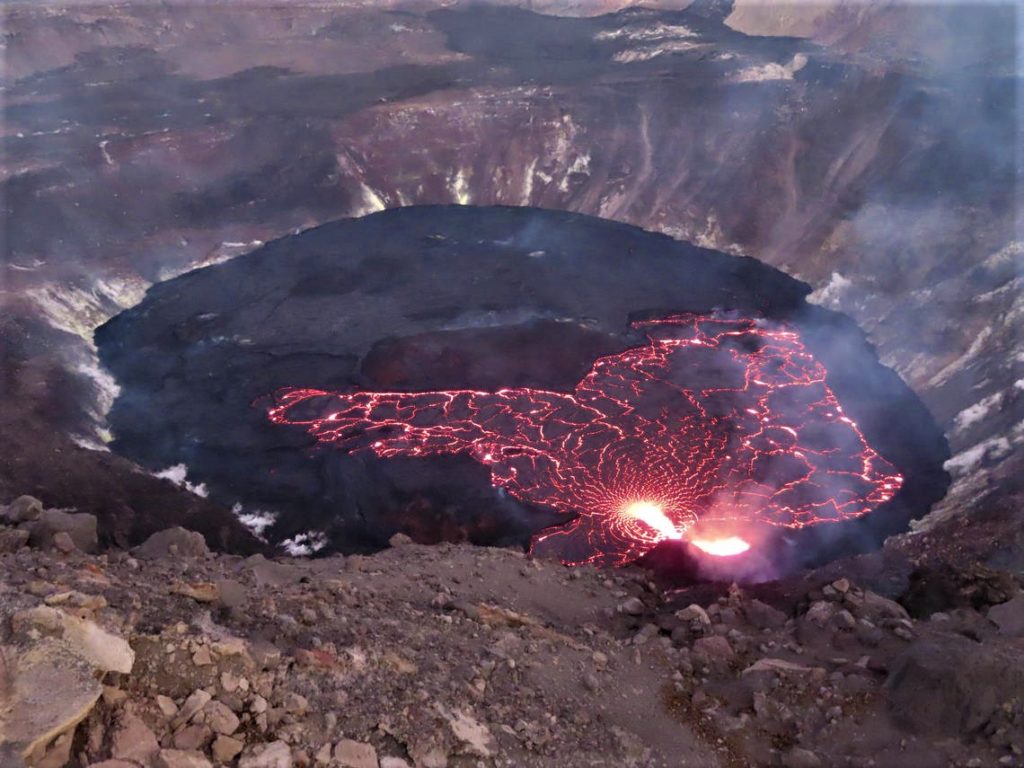
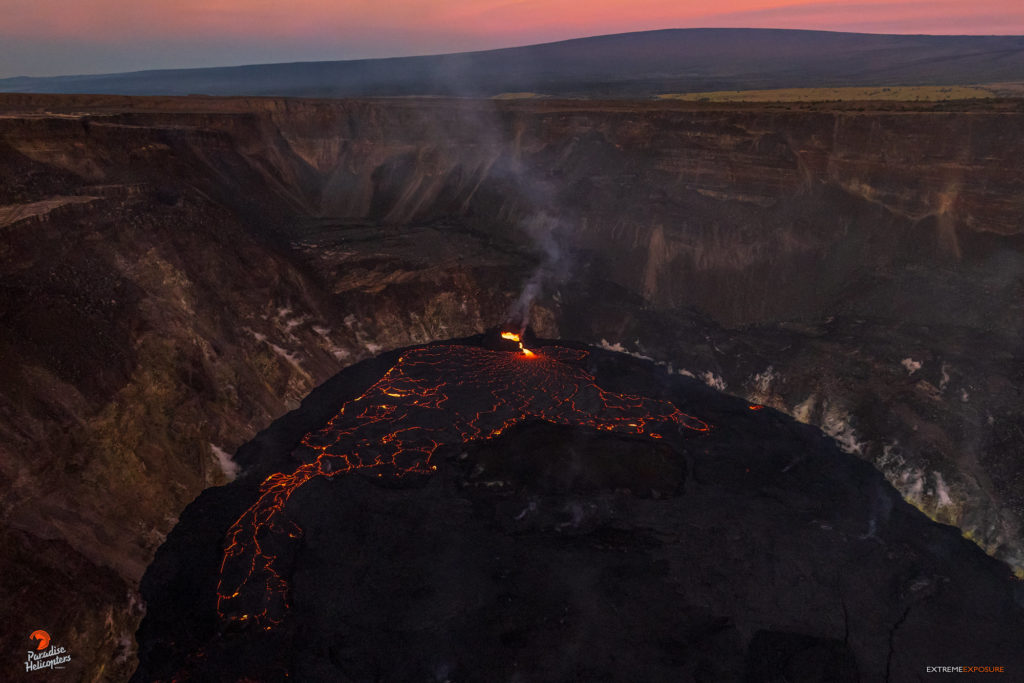
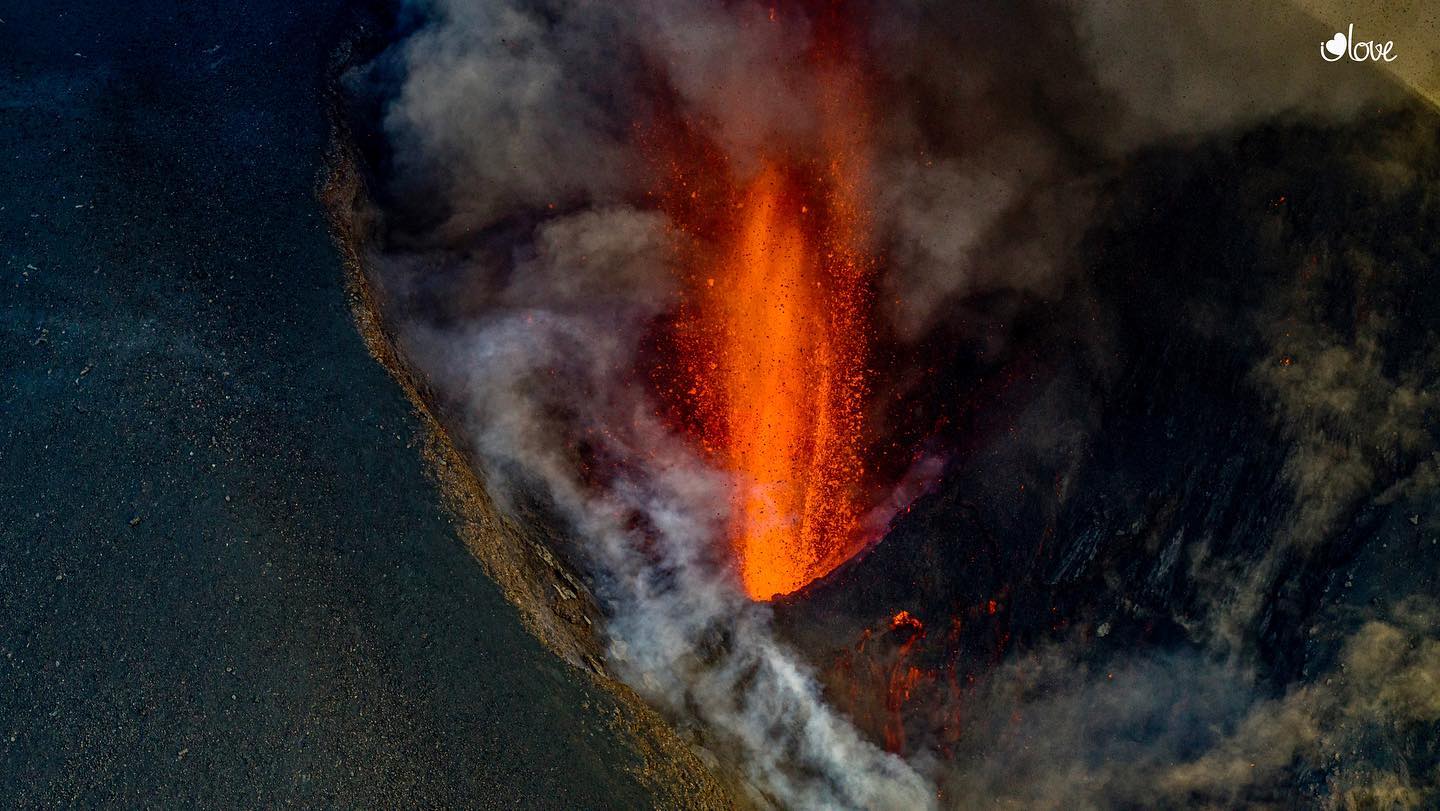
Hawaii , Kilauea :
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Activity Summary:
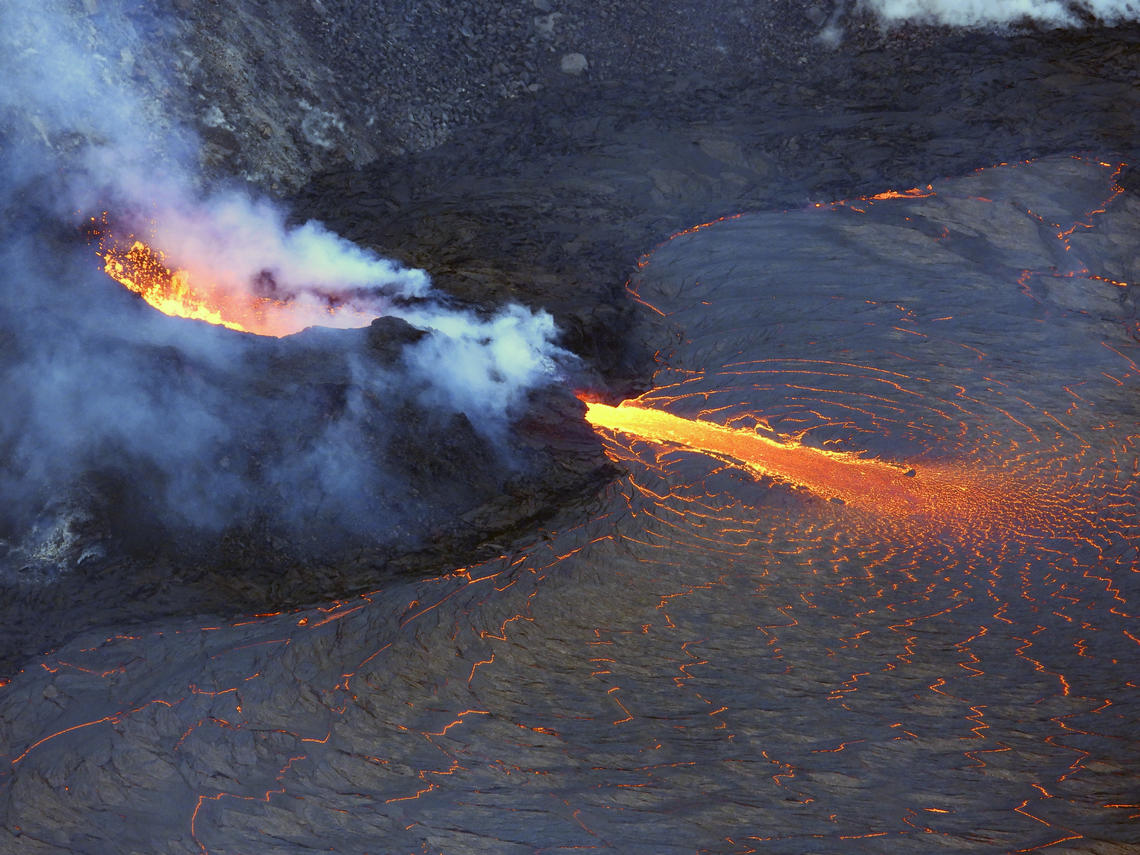
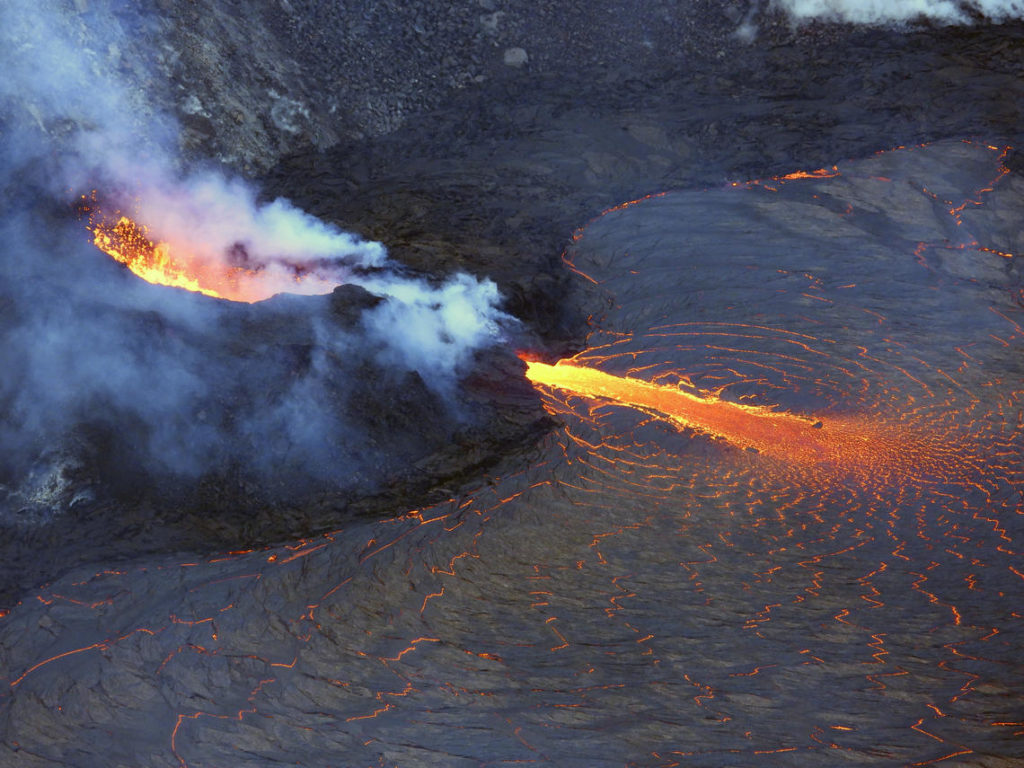
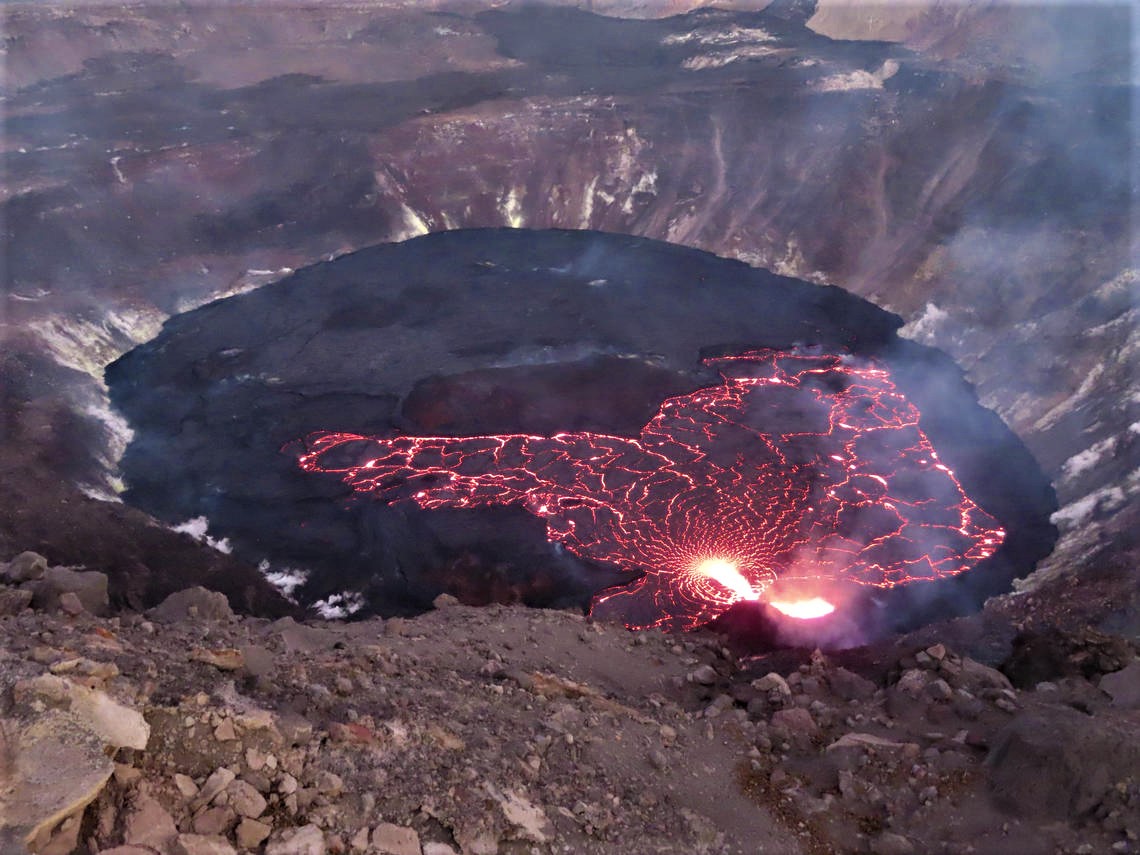
Kīlauea volcano is erupting. As of this morning, November 5, 2021, lava continues to erupt from a single vent in the western wall of Halemaʻumaʻu crater. All lava activity is confined within Halemaʻumaʻu crater in Hawai‘i Volcanoes National Park. Seismic activity and volcanic gas emission rates remain elevated.
Summit Observations:
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission rates remain high, with an emission rate for November 4, 2021, of approximately 1,700 tonnes per day. Summit tilt and GPS observations show no or minimal deformation over the past week. Earthquake activity remains below background and volcanic tremor remains elevated since the beginning of the eruption.
A telephoto image of the west vent in Halema‘uma‘u crater at the summit of Kīlauea. Ponded lava within the spatter cone supplies lava into the lava lake through the tubed-over spillway. The fast-moving lava stream is incandescent as it enters into the lava lake at the base of the cone. As the lava slows and cools, a thin crust begins to form on the surface (center right).
Halemaʻumaʻu Lava Lake Observations:
Lava continues to erupt from a single vent in the western wall of Halemaʻumaʻu crater. The western end of the lake showed a maximum elevation of approximately 799.5 meters (2623 ft) above sea level by HVO’s permanent laser rangefinder on November 5, 2021, which is about 1 m (3 ft) above the previous day, and a total increase of about 56 meters (184 ft) since lava emerged on September 29. The lava lake is not level across its surface due to the location of the vent on the western side. There is about 6 meters (20 feet) elevation difference between the active west and stagnant east part of the lake. The eastern edge of the lake is now level with and has begun to advance onto the lowest of the down-dropped blocks remaining from the 2018 collapse event. Field crews on November 4, 2021, observed roiling and low spattering in the lava pond within the western vent. The total erupted volume since the beginning of the eruption was estimated to be about 19.9 million cubic meters (5.3 billion gallons) on October 15.
Source : HVO.
Photo : USGS / L. DeSmither.
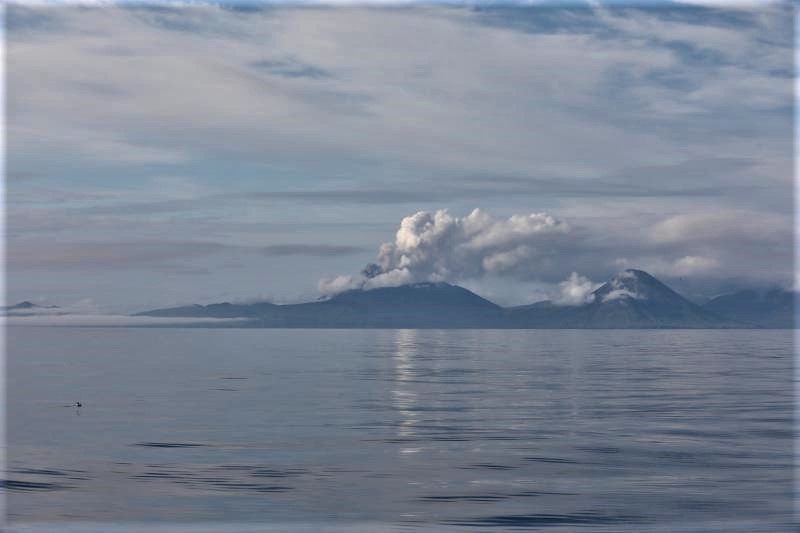
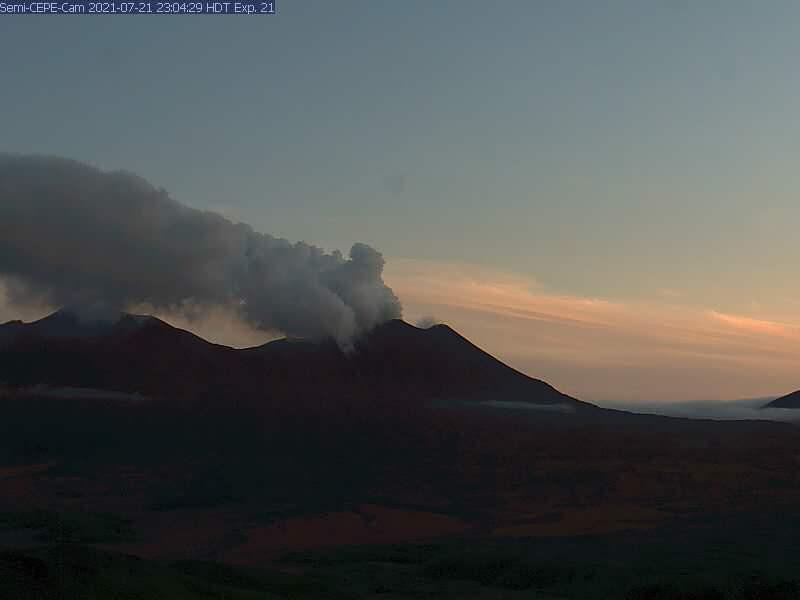
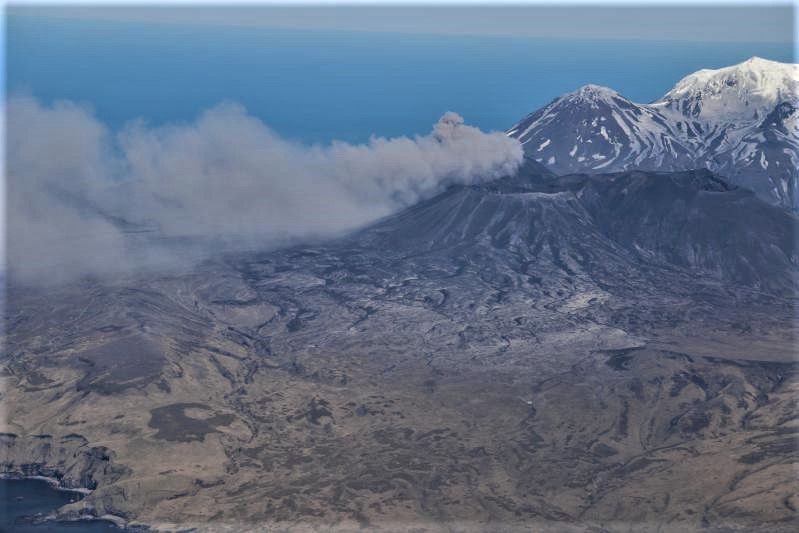
Alaska , Semisopochnoi :
51°55’44 » N 179°35’52 » E,
Summit Elevation 2625 ft (800 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
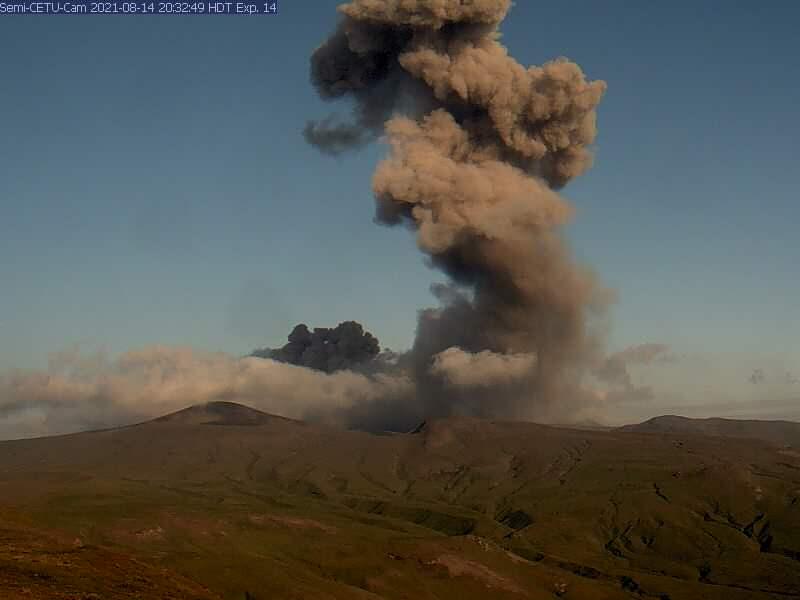
Eruptive activity continues at the north crater of Mount Cerberus. Explosions and tremor were detected in seismic and infrasound data over the past day. Low-level ash emissions were observed in web camera data during periods of clear weather. High meteorological clouds obscured the volcano and no ash emissions were observed in satellite data rising above the meteorological cloud deck, which had an estimated cloud top altitude of 10,000 to 20,000 ft asl. The seismic and infrasound amplitudes of the explosions were typical of those observed during this eruption, suggesting that ash emissions were likely rising 5,000 to 10,000 ft asl.
Small eruptions producing minor ash deposits within the vicinity of the active north crater of Mount Cerberus and ash clouds usually under 10,000 feet above sea level have characterized the recent activity, which shows no signs of abating. Small explosions may continue to occur and could be difficult to detect, especially during poor weather conditions.
Semisopochnoi is monitored by local seismic and infrasound sensors, satellite data, web cameras, and remote infrasound and lightning networks.
Source : AVO
Photo : AVO/USGS.
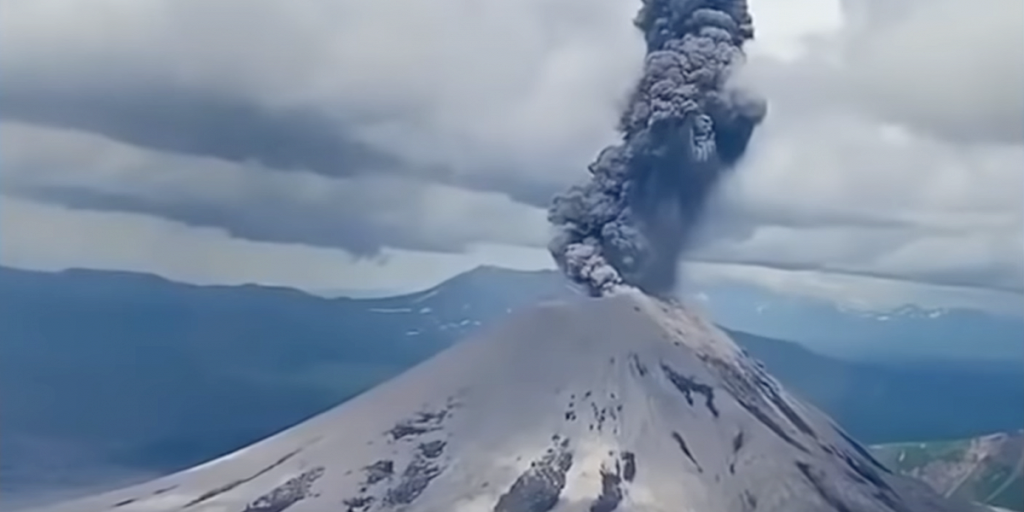
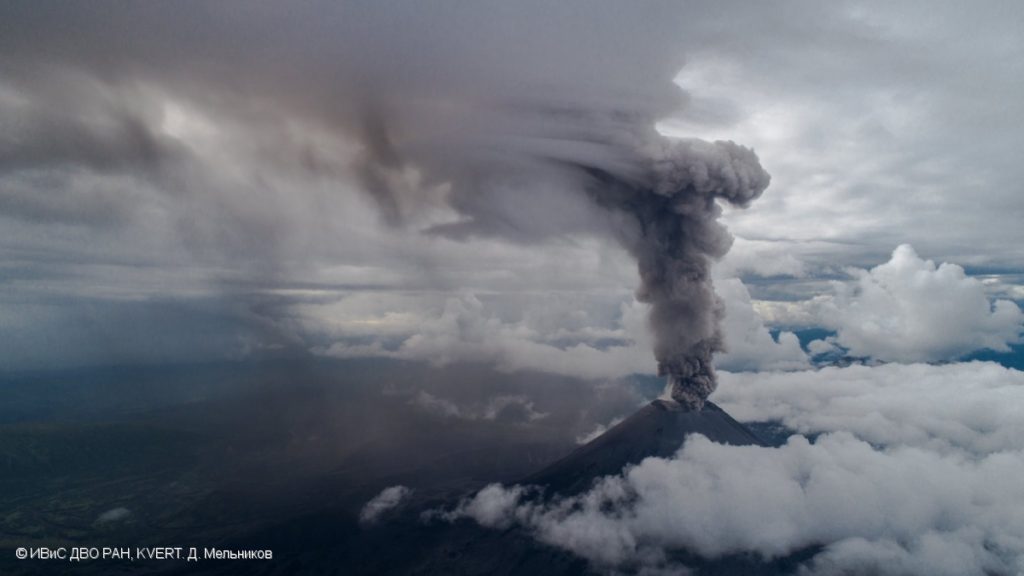
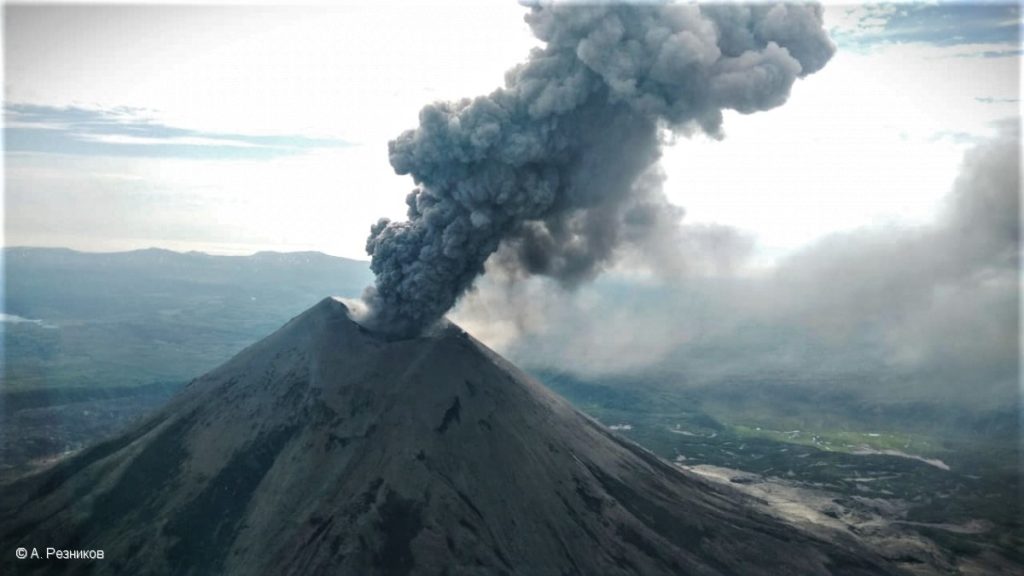
Kamchatka , Ebeko :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Issued: November 07 , 2021
Volcano: Ebeko (CAVW #290380)
Current aviation colour code: ORANGE
Previous aviation colour code: orange
Source: KVERT
Notice Number: 2021-142
Volcano Location: N 50 deg 41 min E 156 deg 0 min
Area: Northern Kuriles, Russia
Summit Elevation: 1156 m (3791.68 ft)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
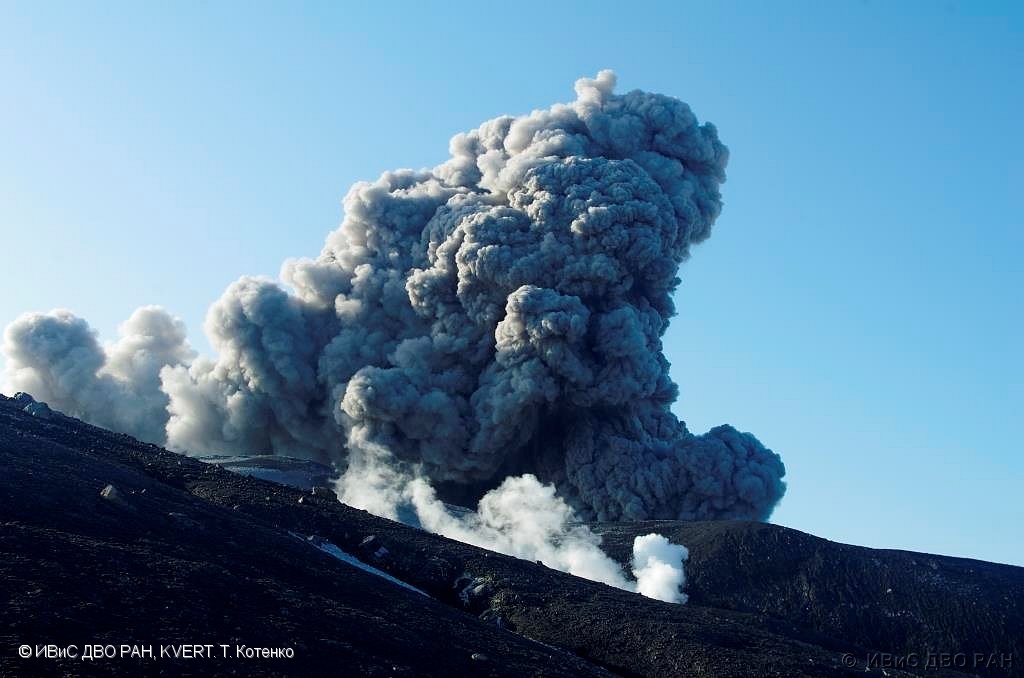
A moderate eruptive activity of the volcano continues. According to visual data by volcanologists from Severo-Kurilsk, an explosion sent ash up to 2.2 km a.s.l., an ash cloud is drifting to the north-east of the volcano.
This activity continues. Ash explosions up to 6 km (19,700 ft) a.s.l. could occur at any time. Ongoing activity could affect low-flying aircraft and airport of Severo-Kurilsk.
Volcanic cloud height:
2200 m (7216 ft) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20211107/0317Z – Visual data
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 5 km (3 mi)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: NE / azimuth 50 deg
Time and method of ash plume/cloud determination: 20211107/0317Z – Visual data
Source : Kvert.
Photo : T. Kotenko, IVS FEB RAS, KVERT
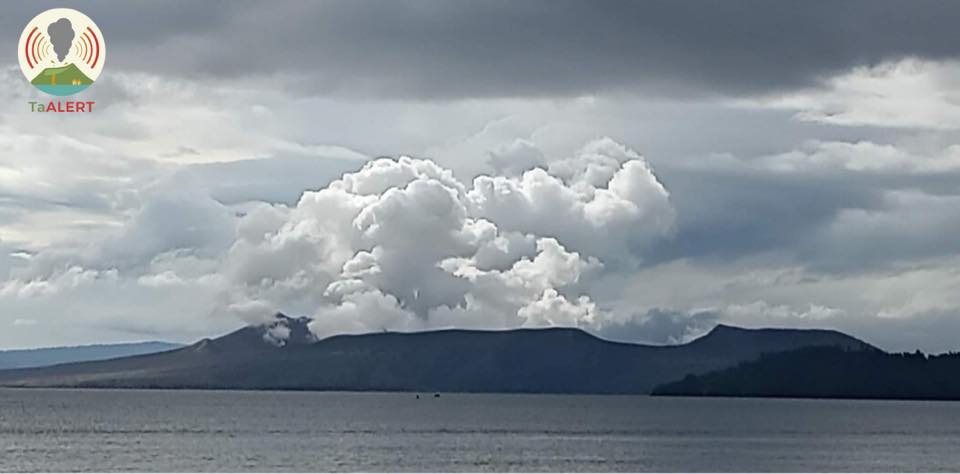
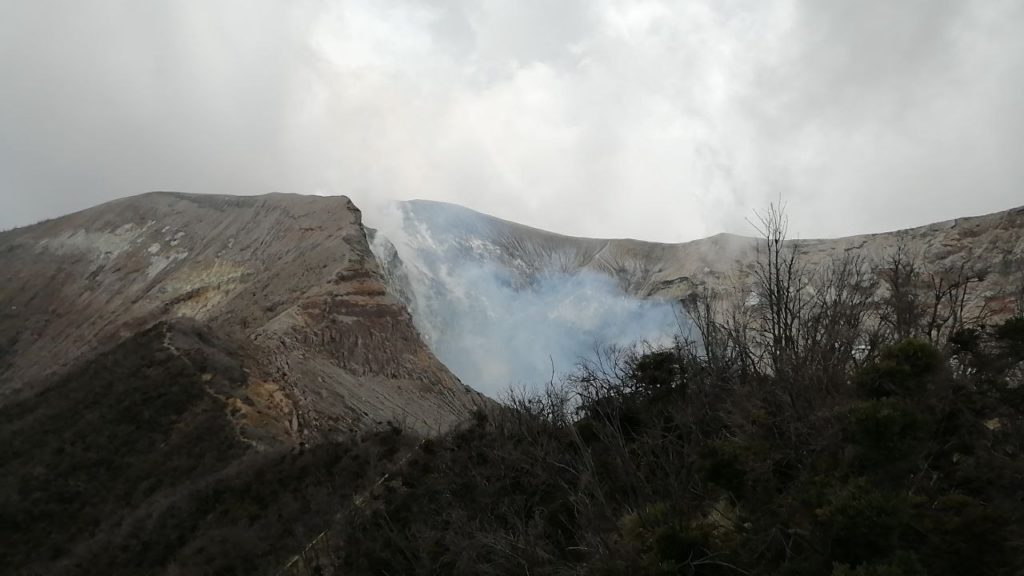
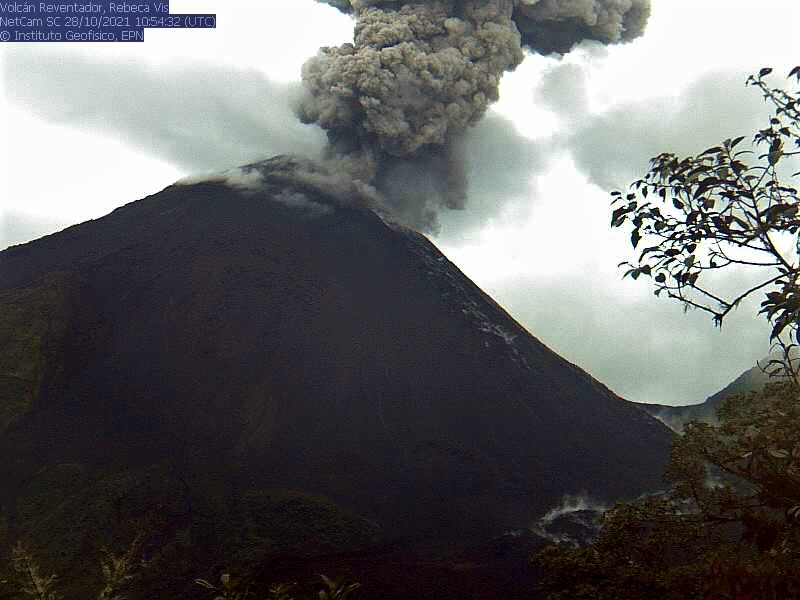
Costa Rica , Turrialba / Poas / Rincon de la Vieja :
Daily report of the state of volcanoes. Date: November 03, 2021. Updated at: 11:04:00.
Turrialba volcano
At 06:46:00 local time on November 3, 2021, an eruption was recorded on the Turrialba volcano, with a column that rose 200 meters above the height of the crater and to 3,540 m. (meters above sea level, 11611.2 feet).
Duration of activity: 1 minute.
Seismic activity is higher than yesterday.
At the time of this report, the winds are blowing from the west.
Low frequency and low magnitude volcanic earthquakes are observed. Gas ratios remain stable. No significant deformation of the volcanic building is observed.
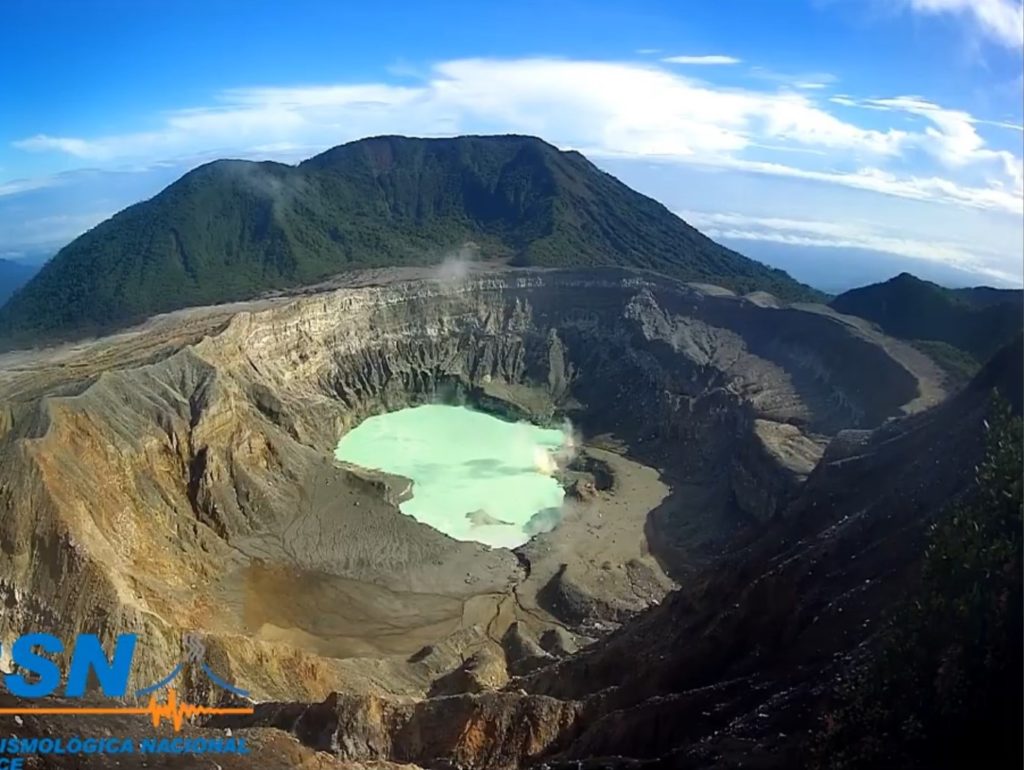
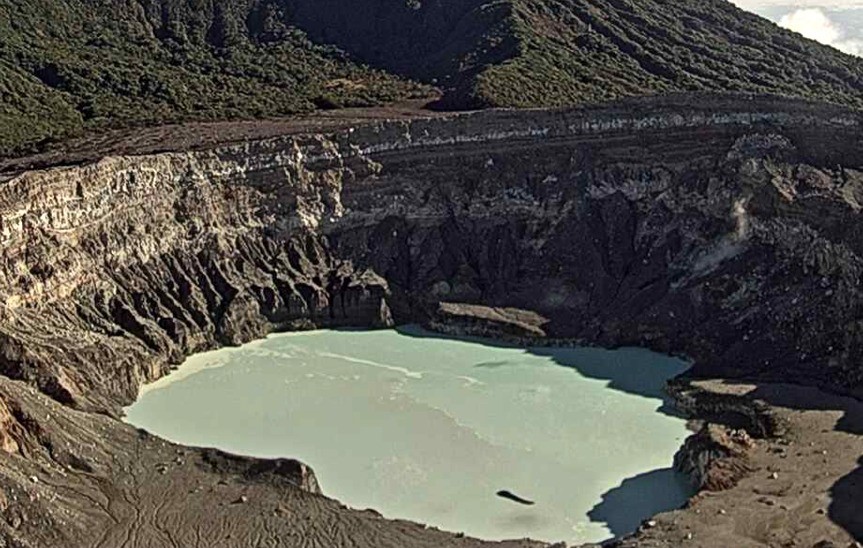
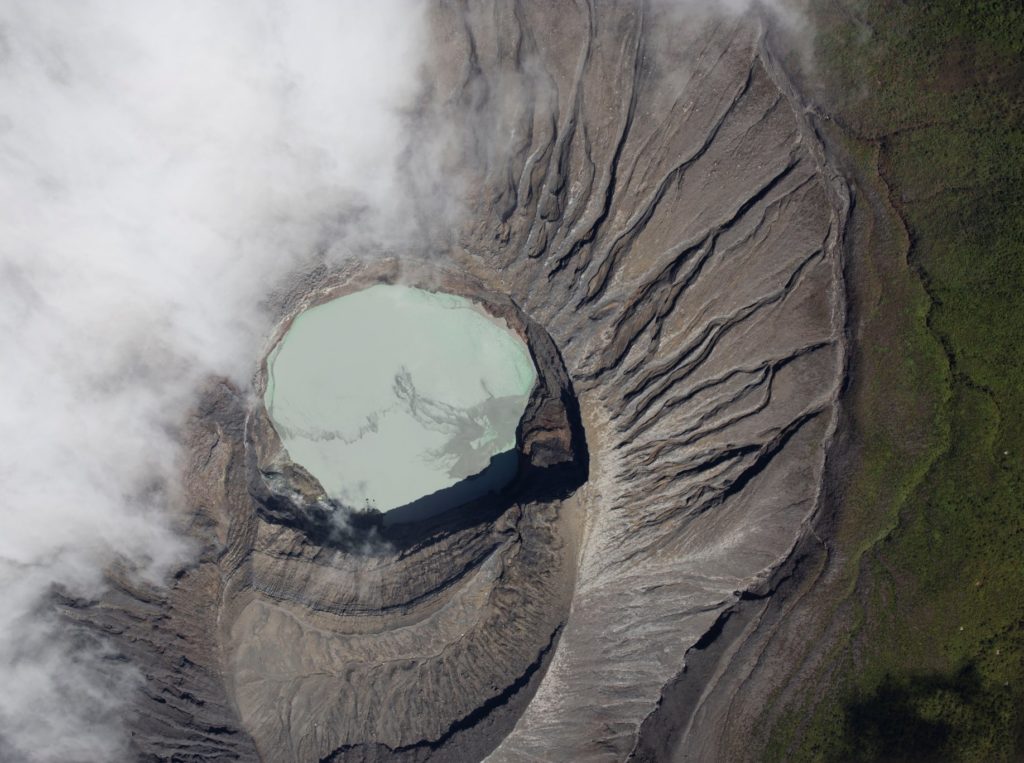
Poas volcano
At 6:16 a.m. local time on November 3, 2021, an eruption was recorded on the Poas volcano, with a column at least 50 meters above the crater.
Duration of activity: 1 minute.
Seismic activity is similar, compared to yesterday.
At the time of this report, the winds are blowing from the west.
There was a small eruption pouring a large amount of sediment and sulfur into the lake which changed its coloring. It seems that material is still coming out of the bottom of the lake. Weak fumarolic activity was maintained on the north and east walls. Low frequency and very low magnitude volcanic earthquakes are recorded. Gas ratios remain stable. No significant deformation of the volcanic building is observed.
Rincón de la Vieja volcano
No eruption is reported.

Seismic activity is similar, compared to yesterday.
At the time of this report, the winds are blowing from the west.
Low frequency and low amplitude volcanic earthquakes are recorded. No significant deformation of the volcanic building is observed.
Source : Ovsicori.
Photos : RSN ( Archive, les trois )