08 Mars 2022 .
Guatemala , Fuego :
BULLETIN SPECIAL VOLCANOLOGIQUE, 7 mars 2022, 21h56 heure locale .
MISE À JOUR SUR L’ÉRUPTION STROMBOLIENNE
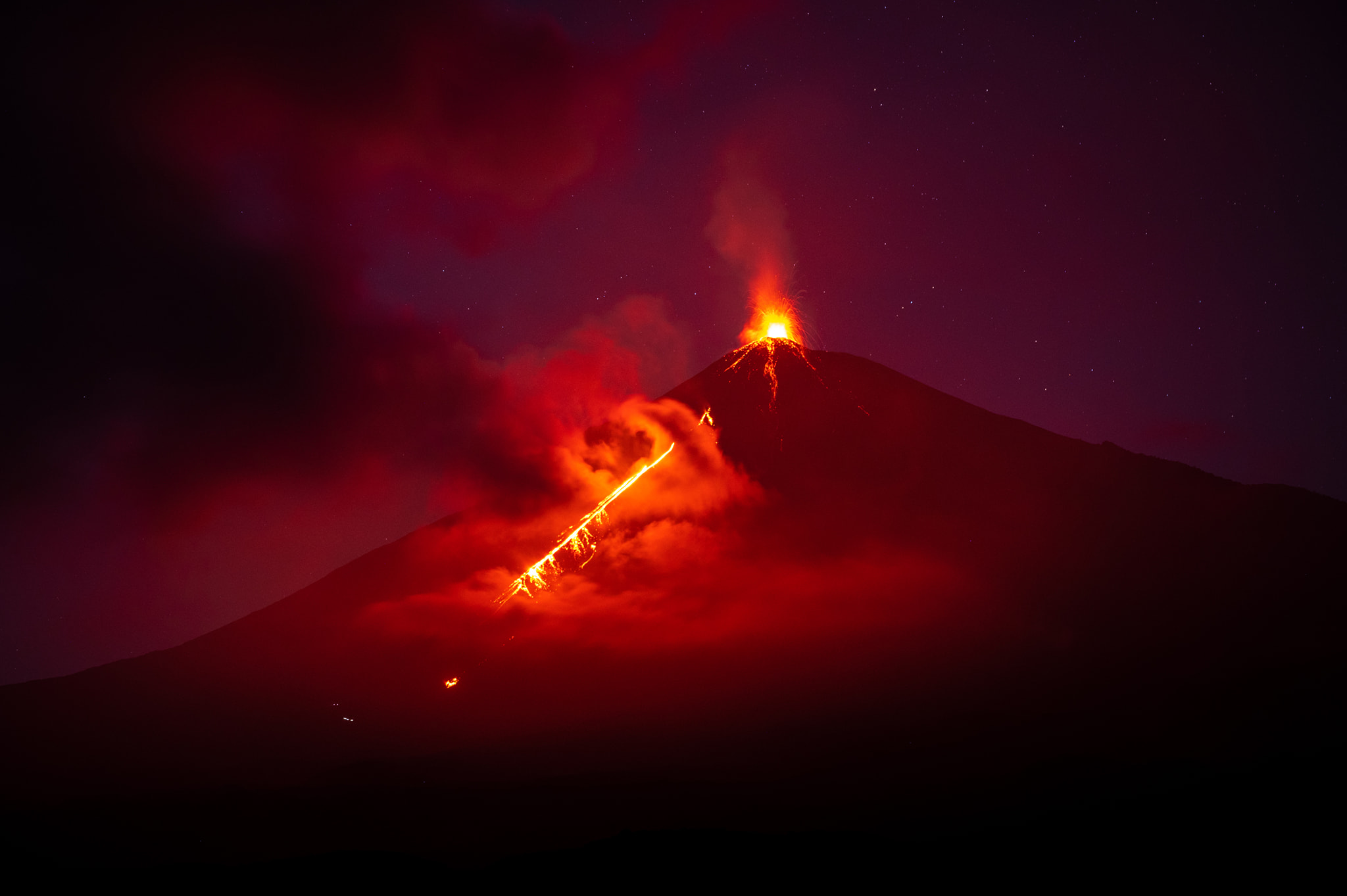
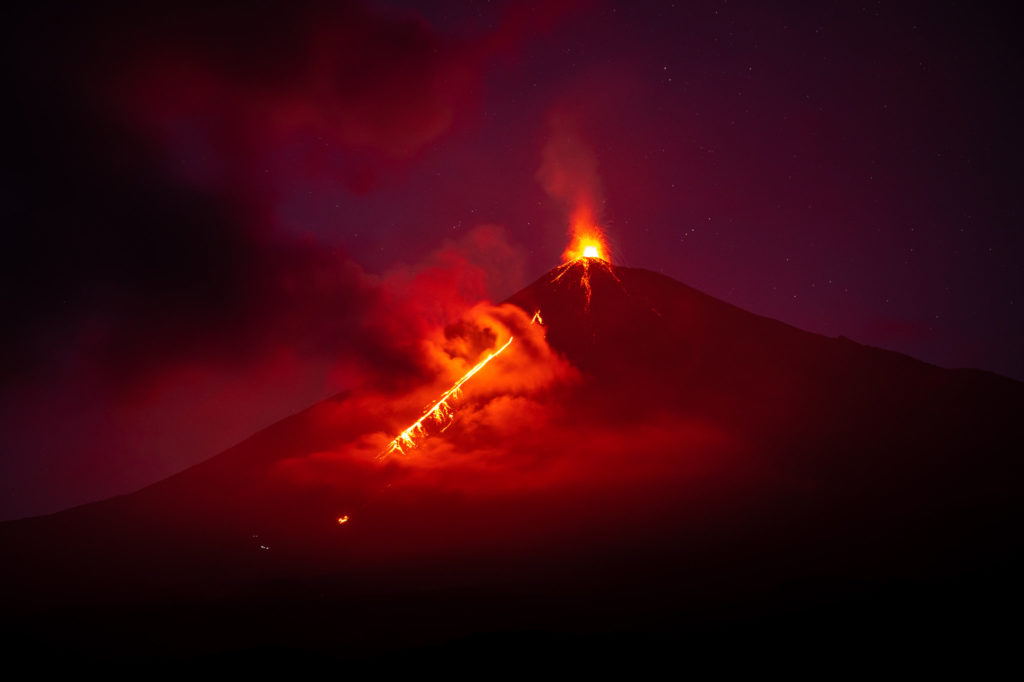
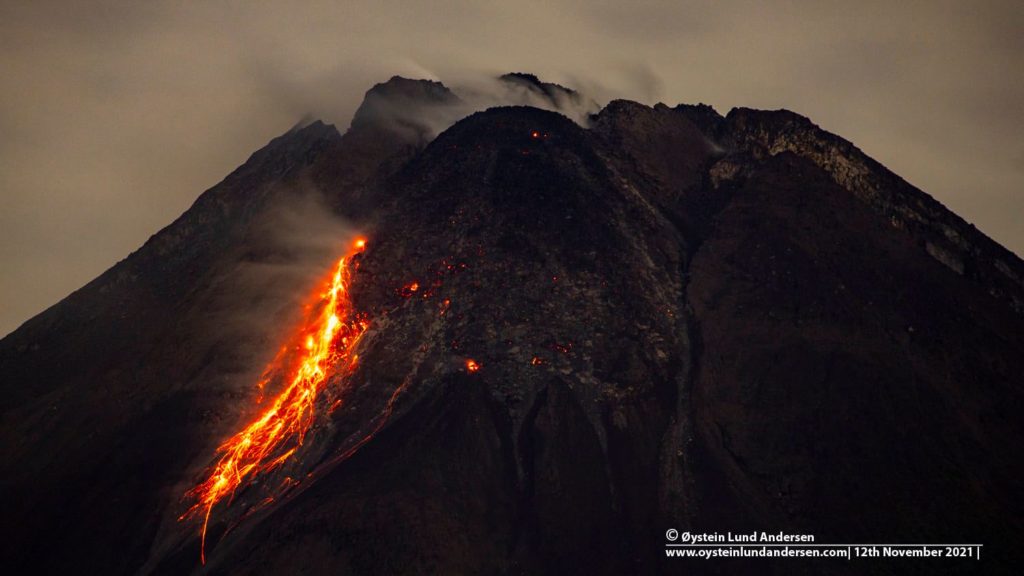
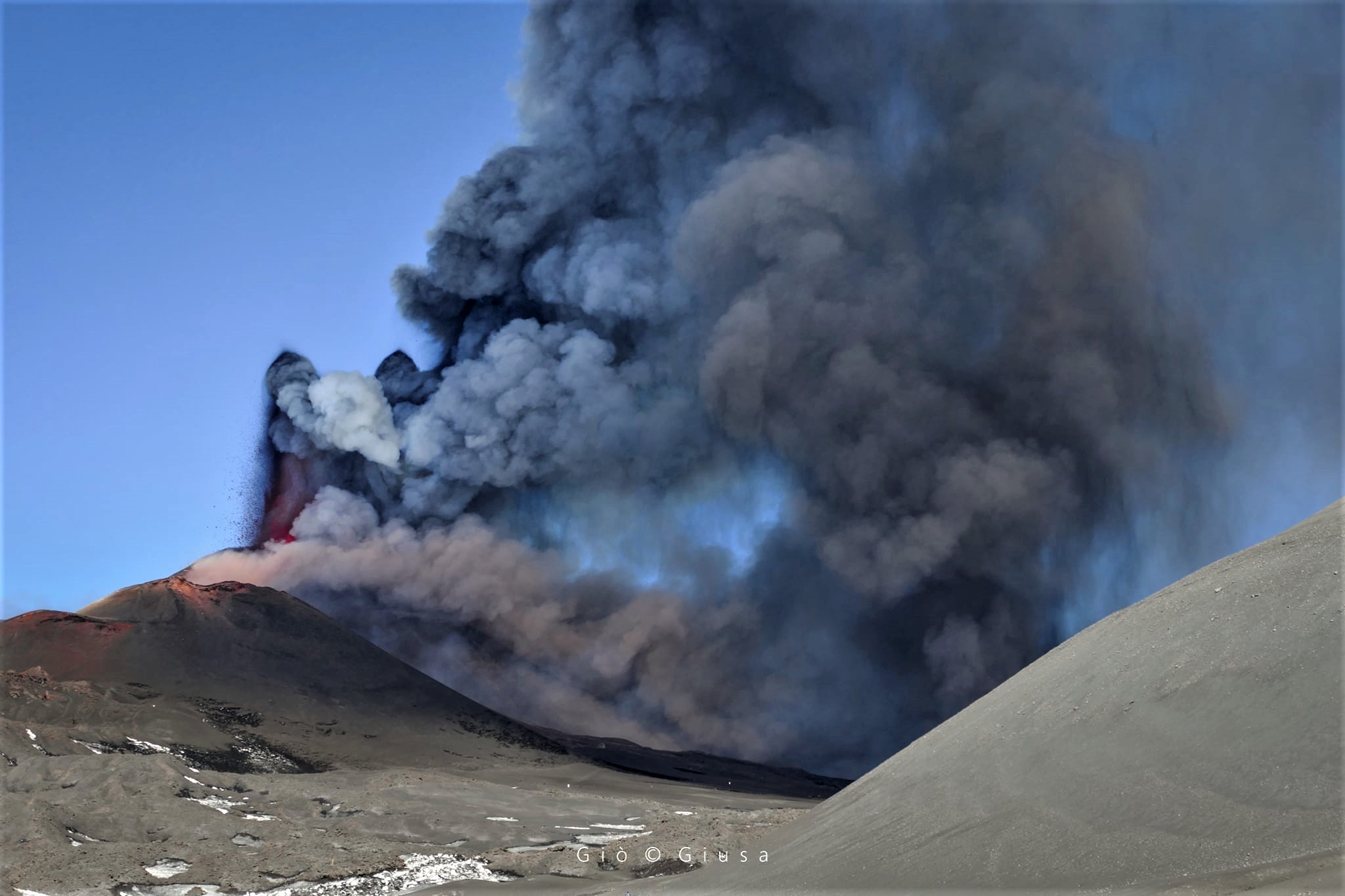
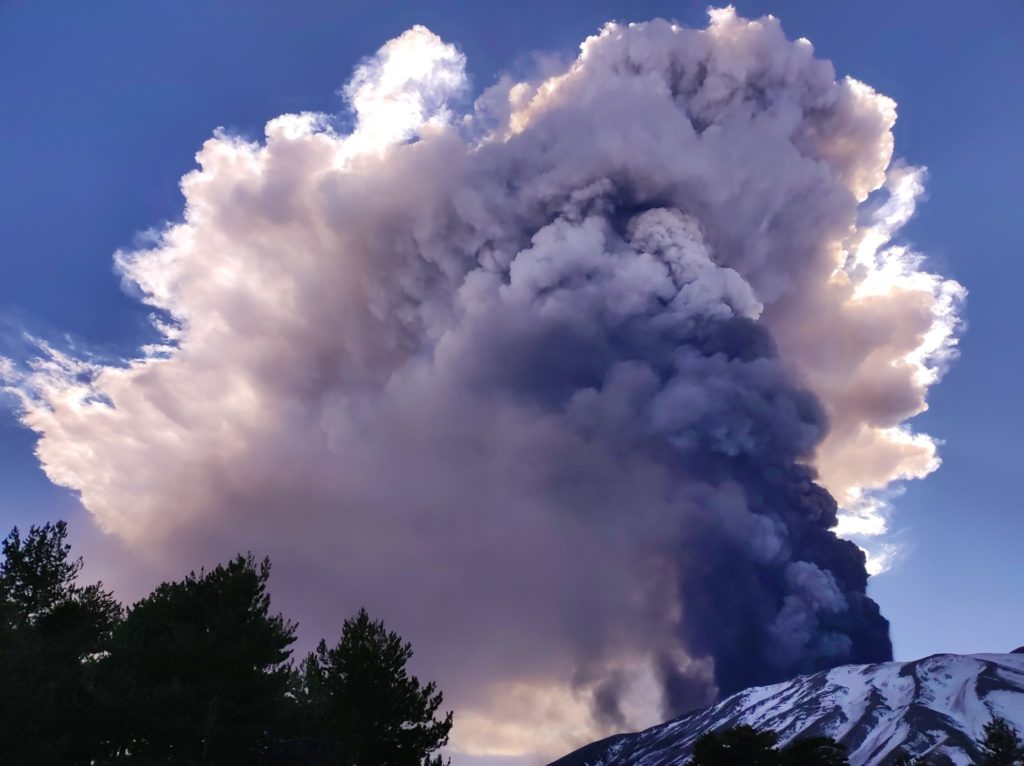
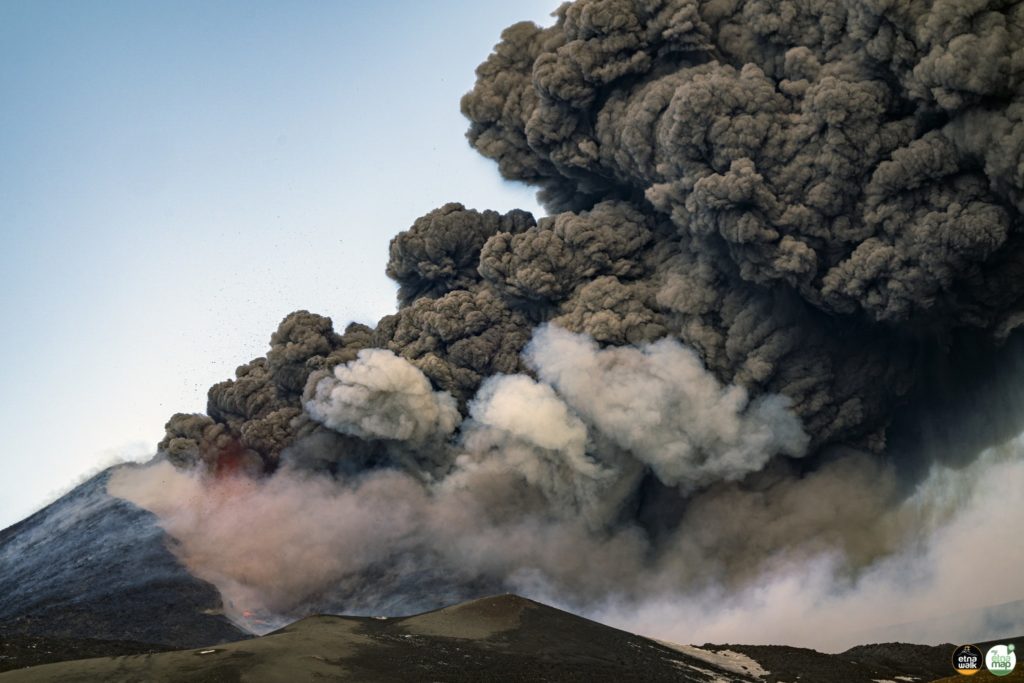
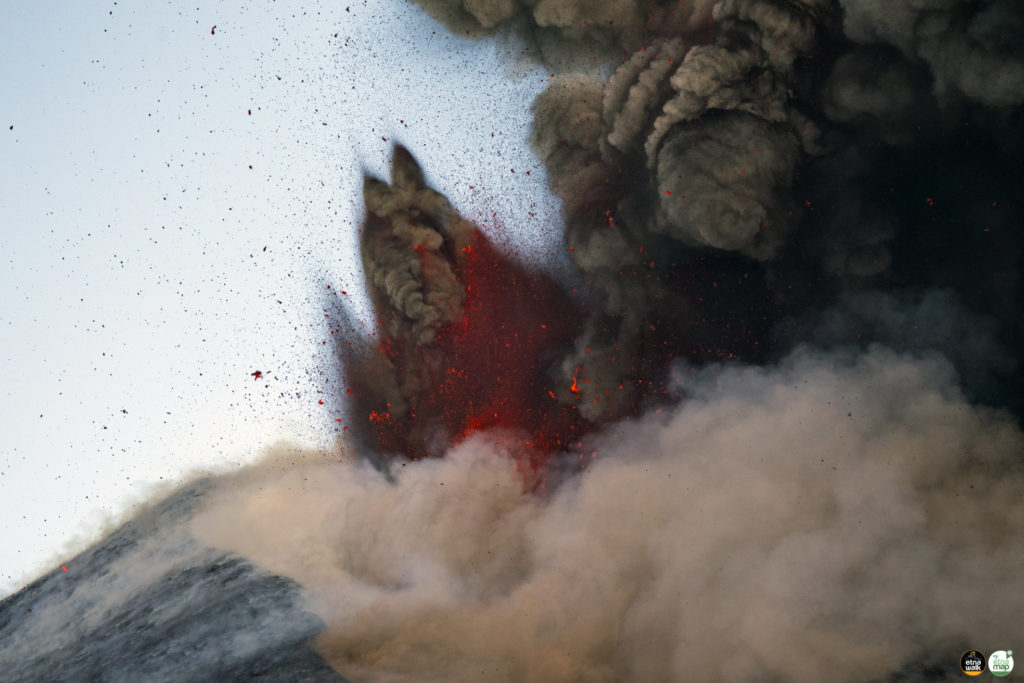
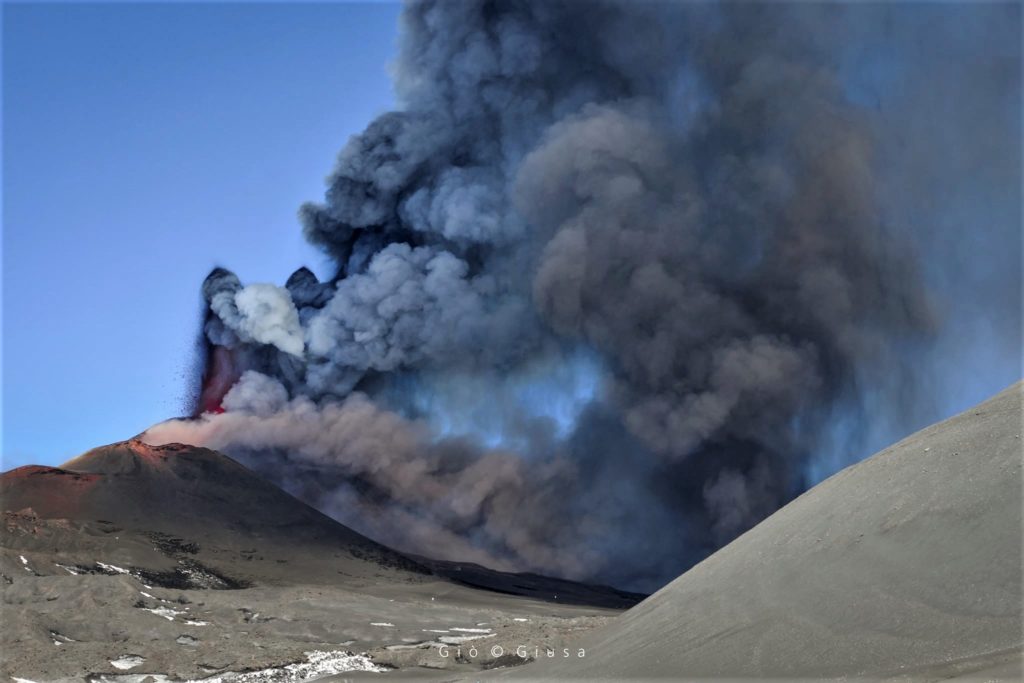
Suite à l’éruption du volcan Fuego et au bulletin spécial , il est rapporté qu’au cours des dernières heures les paramètres sismiques ont enregistré une augmentation d’activité supérieure à celle observée au cours des dernières 24 heures. Il en résulte une augmentation des quantités de flux pyroclastiques, d’incandescence et de chute de cendres. Des sons identiques à ceux des locomotives et de turbine d’avion continuent d’être modérés et l’odeur de soufre est signalée à proximité de l’édifice volcanique. Dans les dernières heures, les conditions atmosphériques dans la partie supérieure de l’édifice volcanique ont été favorables pour observer que la descente des coulées pyroclastiques se poursuit vers la Barranca Ceniza et qu’elle s’étend également à d’autres flancs du volcan, en l’occurrence des avalanches modérées et éventuellement de faibles coulées pyroclastiques vers la Barranca Las Lajas.
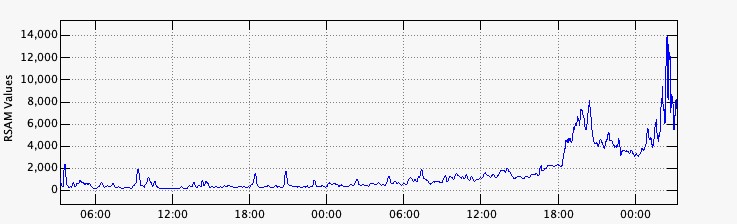
FIGURE 1. Graphique des dernières heures d’activité sismique, enregistrées à la station FG16.
Il n’est pas exclu que de nouvelles coulées de lave soient générées vers d’autres ravins, ainsi que de violentes explosions chargées de cendres et générant continuellement plus de coulées pyroclastiques vers l’un des ravins du volcan Fuego, raison pour laquelle il ne faut pas rester à proximité ou à l’intérieur des canyons du volcan.
L’INSIVUMEH maintient une surveillance visuelle et instrumentale de l’activité volcanique grâce à des stations sismiques, des observateurs du volcan et des caméras Web.
Activité :
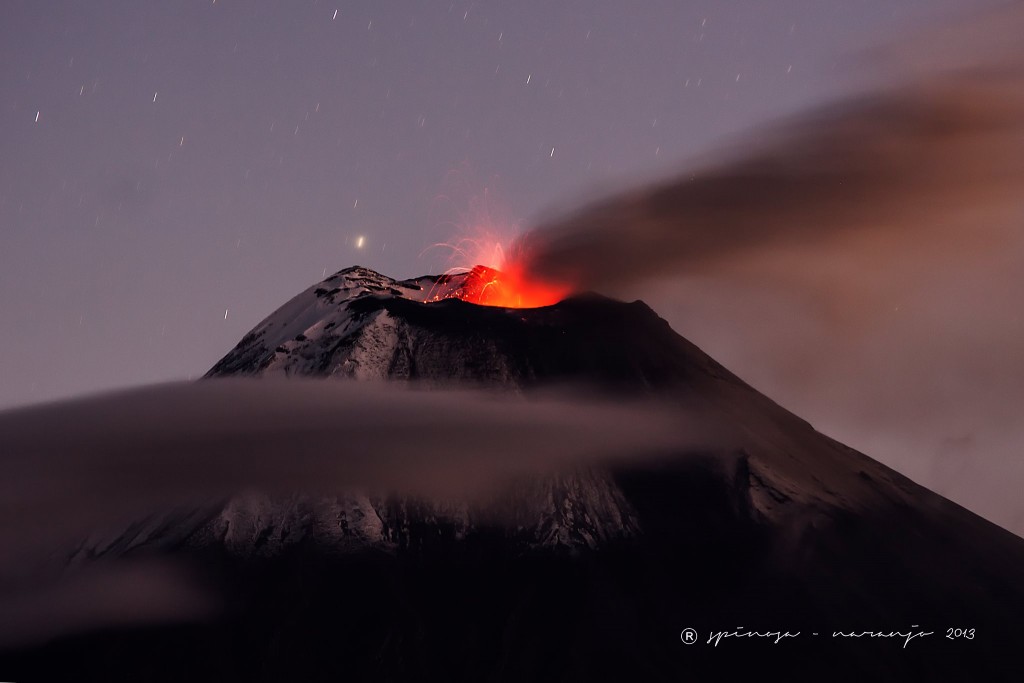
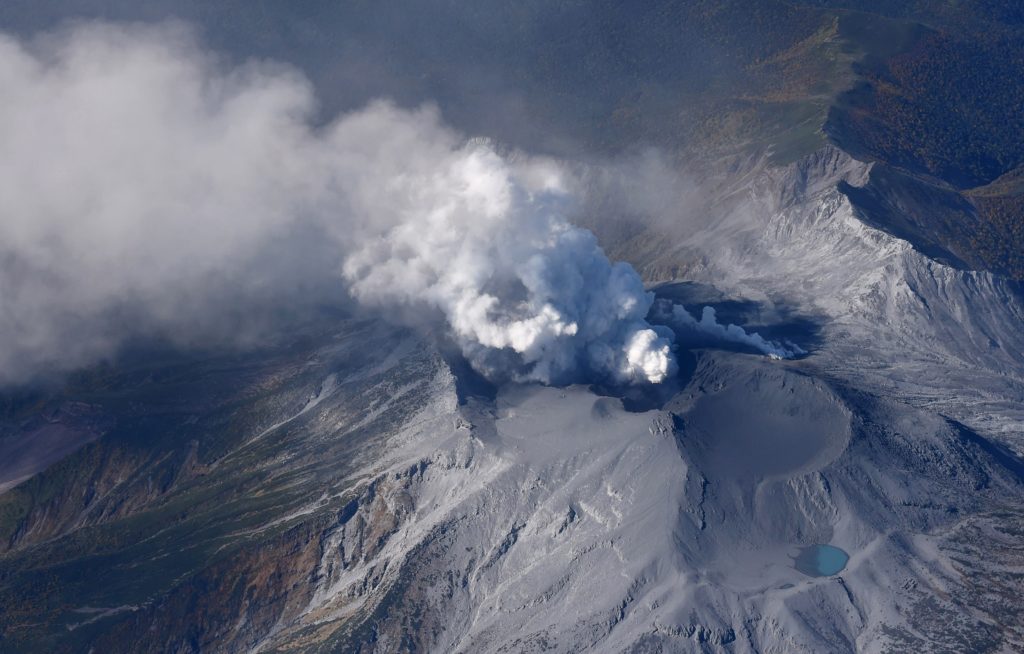
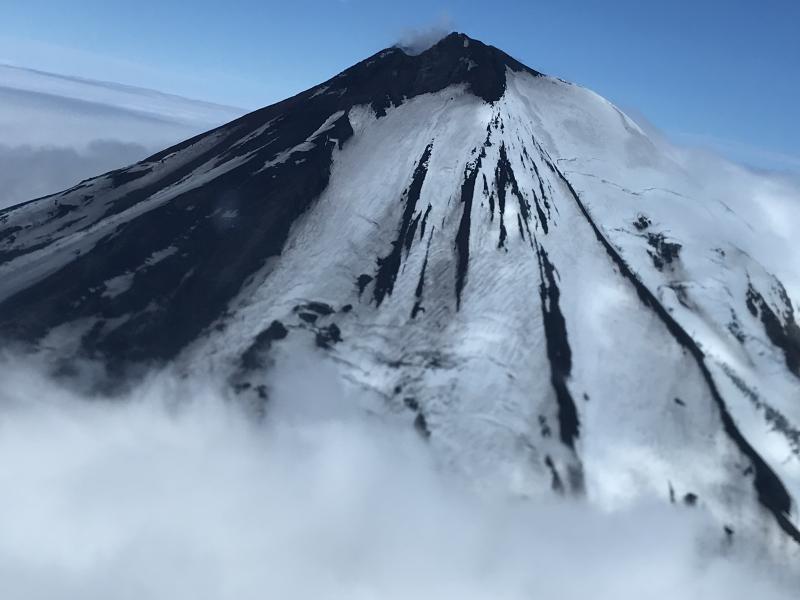
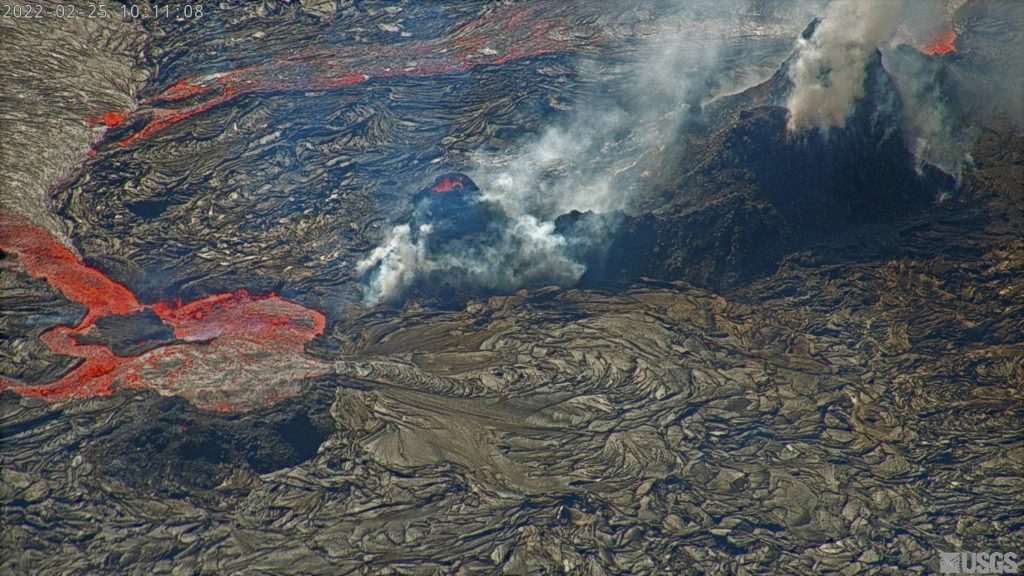
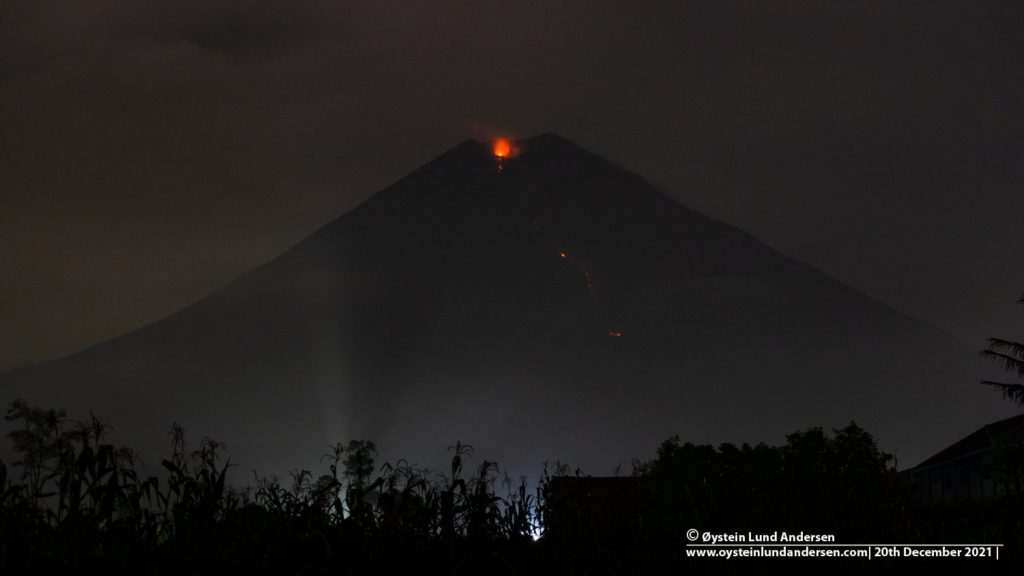
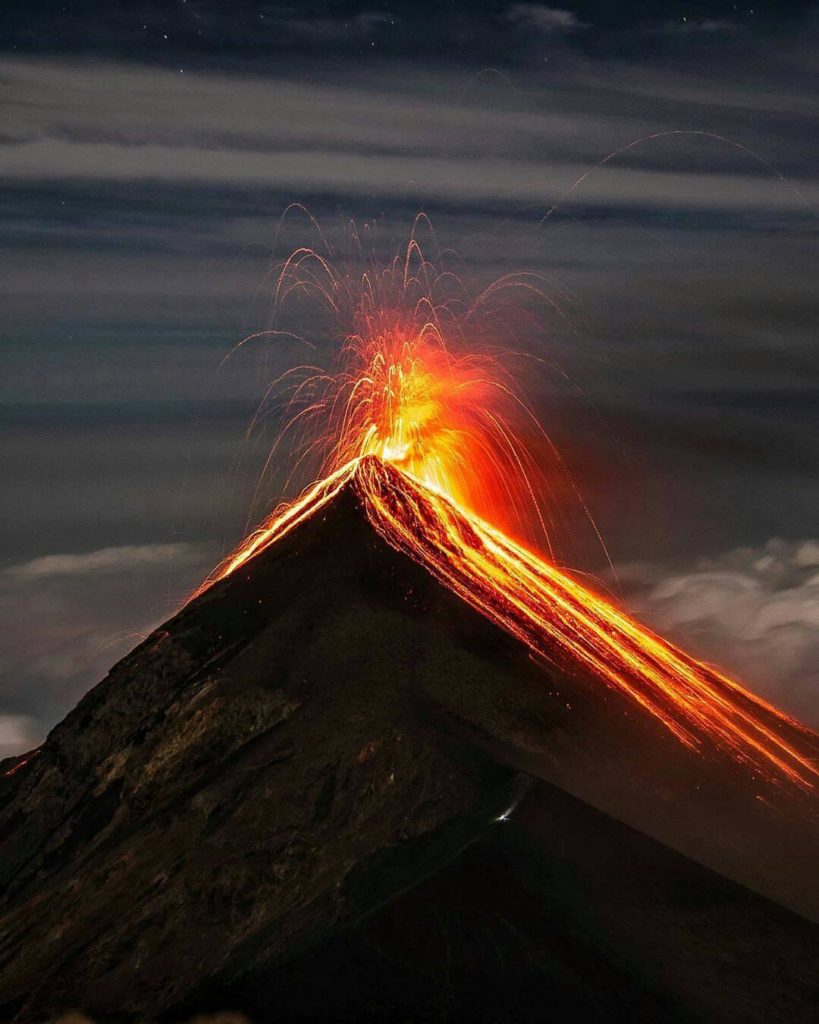
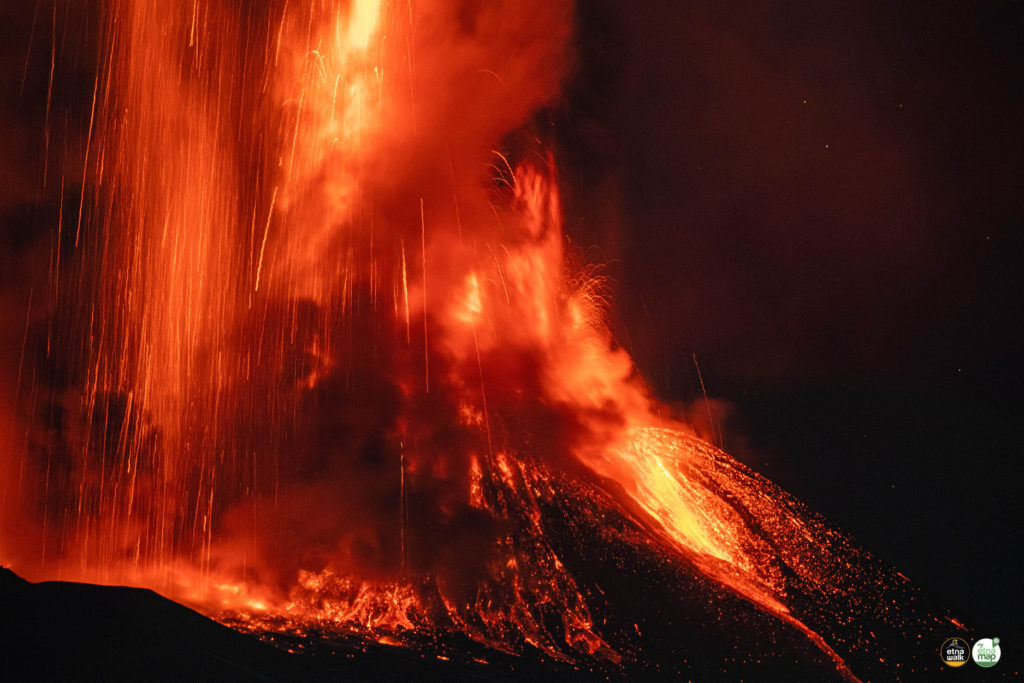
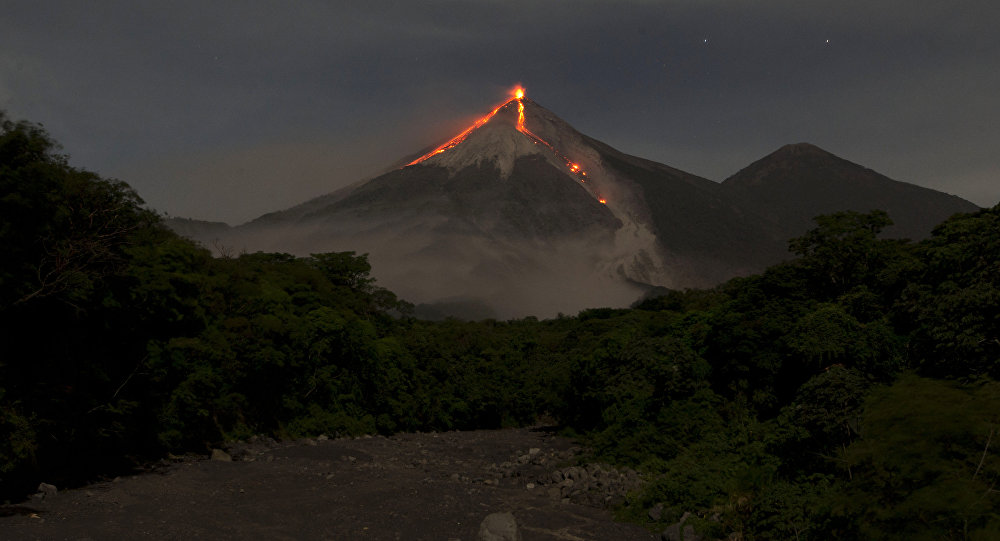
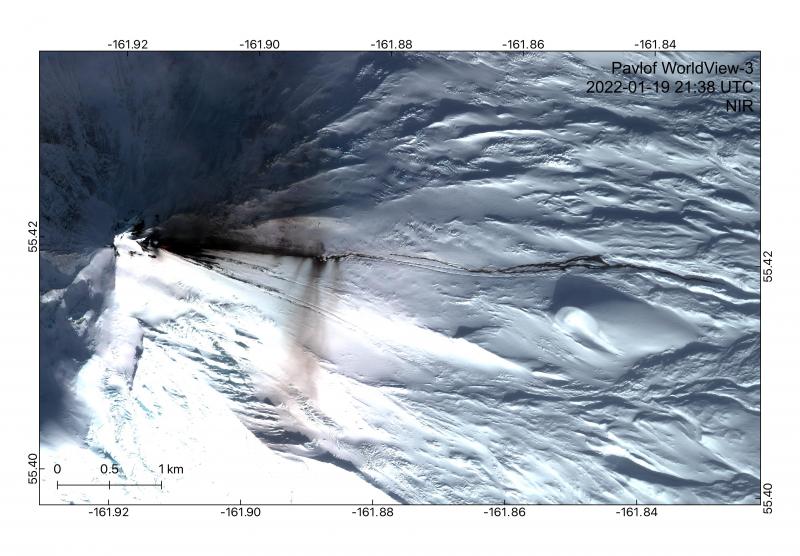
L’observatoire du volcan Fuego signale une source incandescente de 100 à 200 mètres au-dessus du cratère, des périodes de dégazage constant et deux coulées de lave en direction du ravin Ceniza et du ravin Santa Teresa avec une longueur de 250 mètres et 100 mètres respectivement, des avalanches modérées à fortes sur le contour du cratère, vers les ravins Ceniza et Trinidad et faibles et modérées en direction des ravins Las Lajas et Santa Teresa, plusieurs d’entre elles atteignant la lisière de la végétation. La colonne éruptive est située à une hauteur de 4900 mètres d’altitude (16076 pieds) se dispersant dans une direction Sud-Ouest et Ouest sur une distance de 20 kilomètres, 10 à 15 grondements faibles et modérés par heure sont signalés avec de faibles ondes de choc qui font vibrer les plafonds et les fenêtres des maisons proches du volcan. Des chutes de cendres sont signalées dans les communautés de Panimaché I, Panimaché II, Morelia, Santa Sofía, Yucales, El Porvenir et d’autres dans cette direction. Le volcan est dans un stade effusif élevé, donc les recommandations données dans le bulletin BEFGO 006-2022 sont toujours actives.
Source : Insivumeh.
Photo : Diego Rizzo Photo .
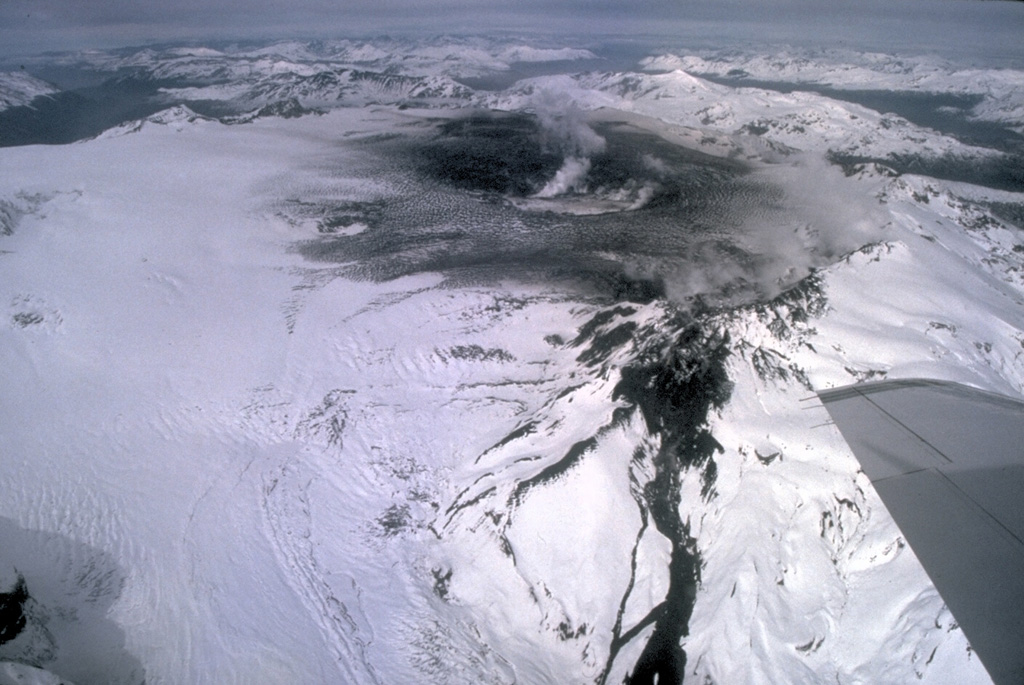
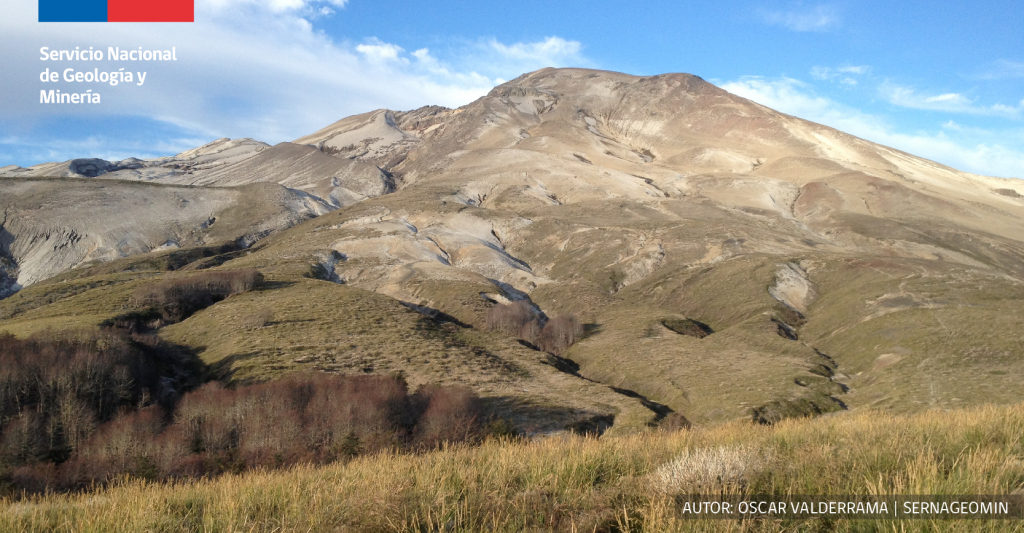
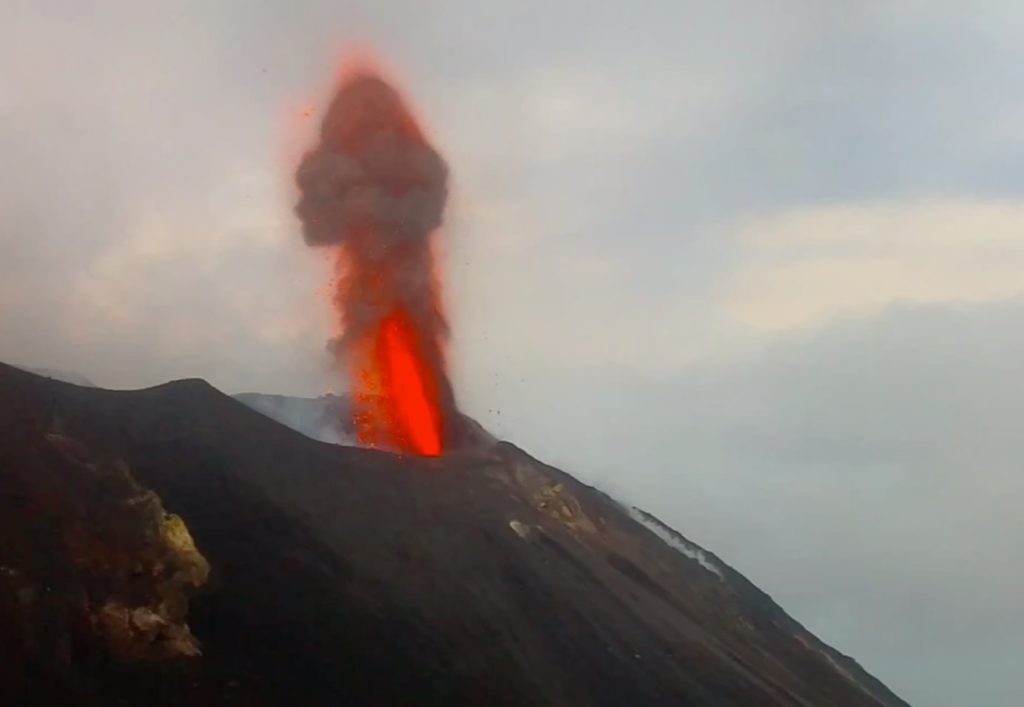
Chili , Hudson :
Rapport spécial sur l’activité volcanique (REAV), région De Aysén Del Général Carlos Ibanez Del Campo , volcan Hudson , 06 Mars 2022, 19 h 50, heure locale (Chili continental).
Le Service National de Géologie et des Mines du Chili (Sernageomin) publie les informations PRÉLIMINAIRES suivantes, obtenues grâce à l’équipement de surveillance du Réseau National de Surveillance Volcanique (RNVV), traitées et analysées à l’Observatoire Volcanologique des Andes du Sud (Ovdas):
Le Dimanche 06 Mars 2022, à 18h49 heure locale (21h49 UTC ), les stations de surveillance installées à proximité du volcan Hudson ont enregistré un séisme associé à la fois à la fracturation des roches et à la dynamique des fluides (type hybride) dans le système volcanique.
Les caractéristiques des séismes après leur analyse sont les suivantes:
HEURE D’ORIGINE: 18h49 heure locale (21h49 UTC ).
LATITUDE: 45.958 ° S
LONGITUDE: 72,966 ° W
PROFONDEUR: 5,2 km
DEPLACEMENT REDUIT: 1101,8 cm2
OBSERVATIONS :
Après l’événement signalé, une activité sismique de plus faible énergie continue d’être enregistrée. Les conditions météorologiques dans la région ne permettent pas de voir le bâtiment volcanique.
L’alerte technique volcanique reste au niveau Vert .
Source : Sernageomin.
Photo : Norm Banks, 1991 (U.S. Geological Survey).
Pérou , Sabancaya :
Période d’analyse: du 28 Février 2022 au 06 Mars 2022 , Arequipa, 07 Mars 2022.
Niveau d’alerte: ORANGE
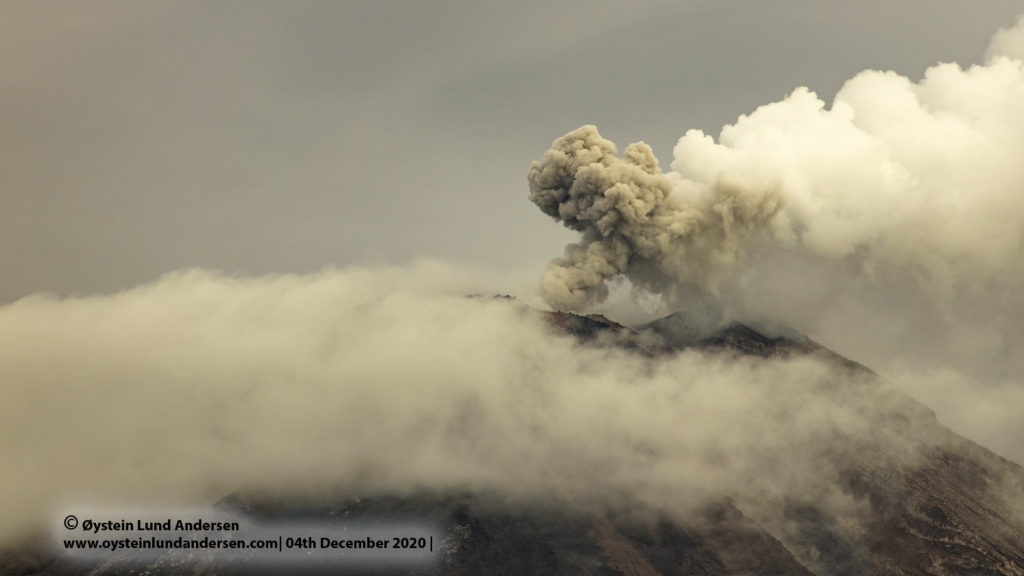
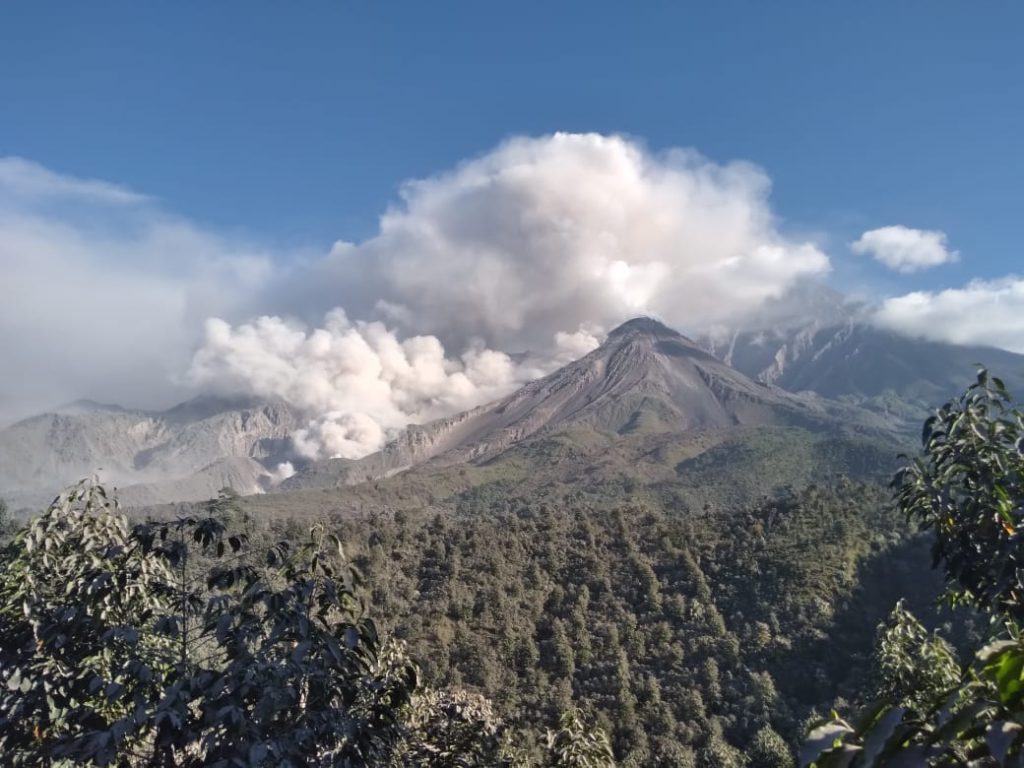
L’Institut géophysique du Pérou (IGP) rapporte que l’activité éruptive du volcan Sabancaya reste à des niveaux modérés, c’est-à-dire avec l’enregistrement d’une moyenne de 15 explosions quotidiennes , avec des colonnes de cendres et de gaz jusqu’à 1,0 km d’altitude au dessus du sommet du volcan et leur dispersion consécutives . Par conséquent, pour les jours suivants, aucun changement significatif n’est attendu concernant l’ activité éruptive.
L’IGP a enregistré et analysé l’occurrence de 108 tremblements de terre d’origine volcanique, associés à la circulation de fluides magmatiques à l’intérieur du volcan Sabancaya. Une moyenne de 15 explosions a été enregistrée quotidiennement . Au cours de cette période, les tremblements de terre de type Volcano-Tectoniques (VT) associés à des fracturations rocheuses ont été localisés principalement dans le Nord-Est et le Nord-Ouest du Sabancaya et ont présenté des magnitudes de M 2,5 .
Le suivi de la déformation de la structure volcanique à l’aide de techniques GNSS (traitées avec des orbites rapides) ne présente pas d’anomalies significatives. Cependant, de manière générale, un processus d’inflation a été observé dans le secteur Nord ( environs du volcan Hualca Hualca ). La surveillance visuelle a permis d’identifier des colonnes de gaz et de cendres jusqu’à 1,0 km d’altitude au dessus du sommet du volcan , qui étaient dispersées vers les secteurs Ouest , Sud et Sud-Ouest du Sabancaya. Les enregistrements par satellites ont identifiés la présence de 2 anomalies thermiques , avec une valeur maximale de 14 MW , associées à la présence d’un corps de lave à la superficie du cratère du volcan.
RECOMMANDATIONS
• Garder le niveau d’alerte volcanique en orange.
• Ne pas s’ approcher dans un rayon de moins de 12 km du cratère.
Source : CENVUL
Photo : Ingemmet
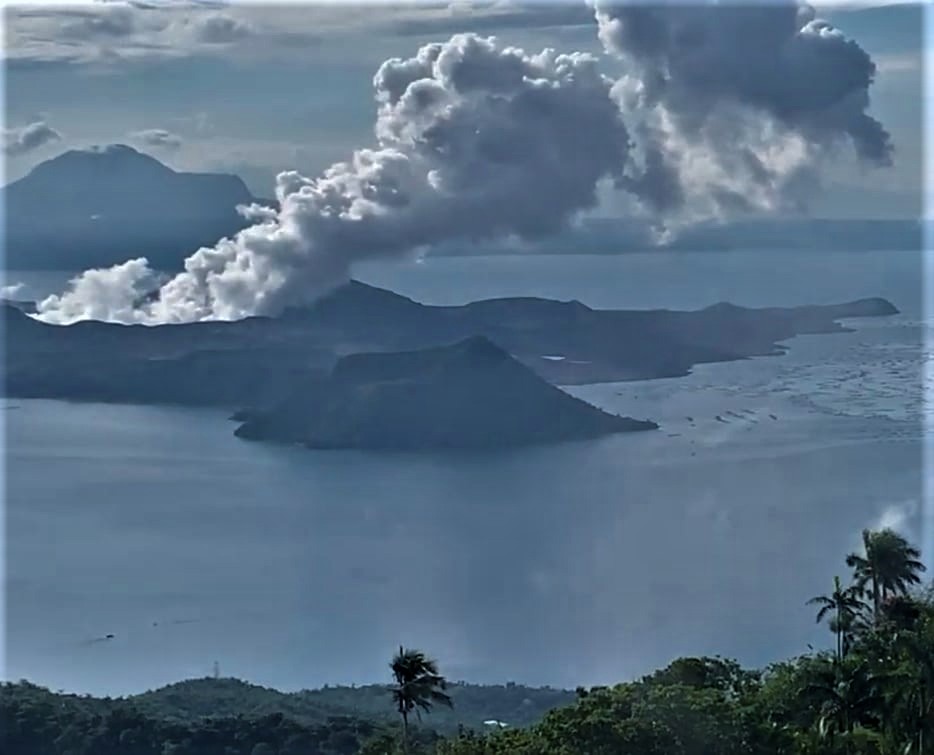
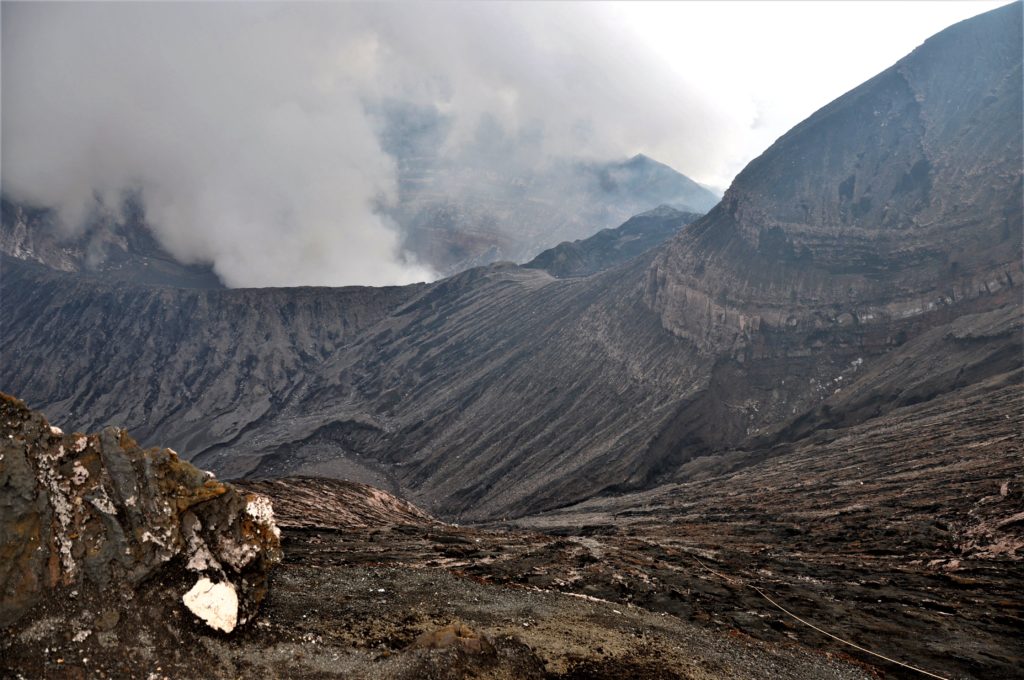
Philippines , Taal :
BULLETIN D’ACTIVITE DU VOLCAN TAAL , 08 Mars 2022 , 08:00 .
Au cours des dernières 24 heures, le réseau de capteurs du volcan Taal n’a détecté aucun tremblement de terre volcanique. L’activité du cratère a été dominée par la remontée de fluides volcaniques chauds dans le lac qui a généré des panaches de 900 mètres de haut qui ont dérivé vers le Sud-Ouest. Les émissions de dioxyde de soufre (SO2) étaient en moyenne de 7 695 tonnes / jour le 07 mars 2022. Des températures maximales de 63,7 ° C ont été mesurées pour la dernière fois dans le lac de cratère le 25 février 2022. Sur la base des paramètres de déformation du sol , des mesures électroniques de l’inclinaison , du GPS continu et de la surveillance InSAR, L’île du volcan Taal et la région du Taal ont commencé à se dégonfler en octobre 2021.
Le niveau d’alerte 2 (agitation accrue) prévaut sur le volcan Taal. Le DOST-PHIVOLCS rappelle au public qu’au niveau d’alerte 2, des explosions soudaines de vapeur ou de gaz, des tremblements de terre volcaniques, des chutes de cendres mineures et des accumulations ou expulsions mortelles de gaz volcanique peuvent se produire et menacer les zones à l’intérieur et autour de TVI. Le DOST-PHIVOLCS recommande fortement que l’entrée dans l’île du volcan Taal, la zone de danger permanent ou PDZ du Taal soit strictement interdite, en particulier aux alentours du cratère principal et de la fissure Daang Kastila, ainsi que les séjours prolongés sur le lac Taal.
Source : Phivolcs .
Photo : Kyle Aranza
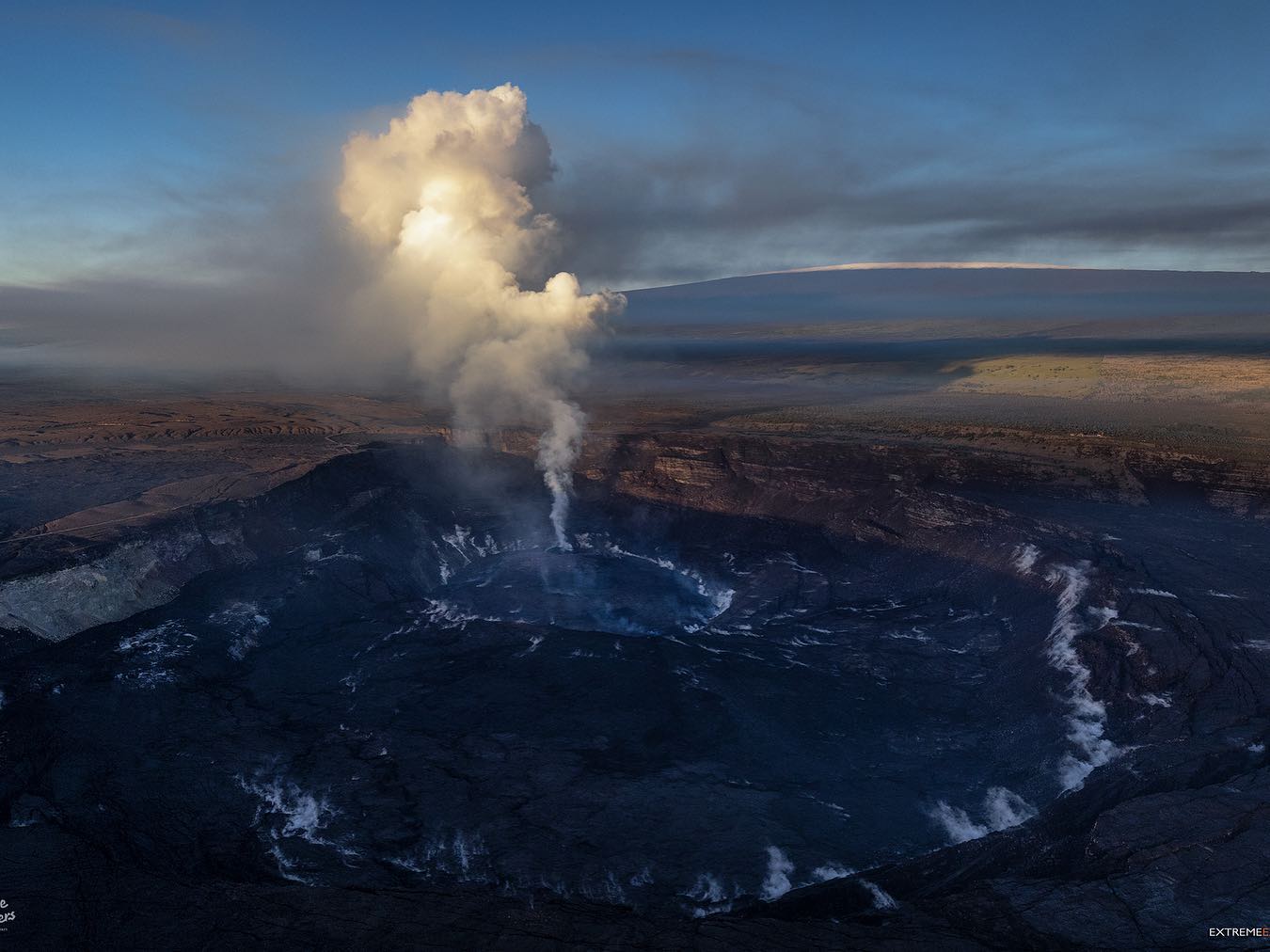
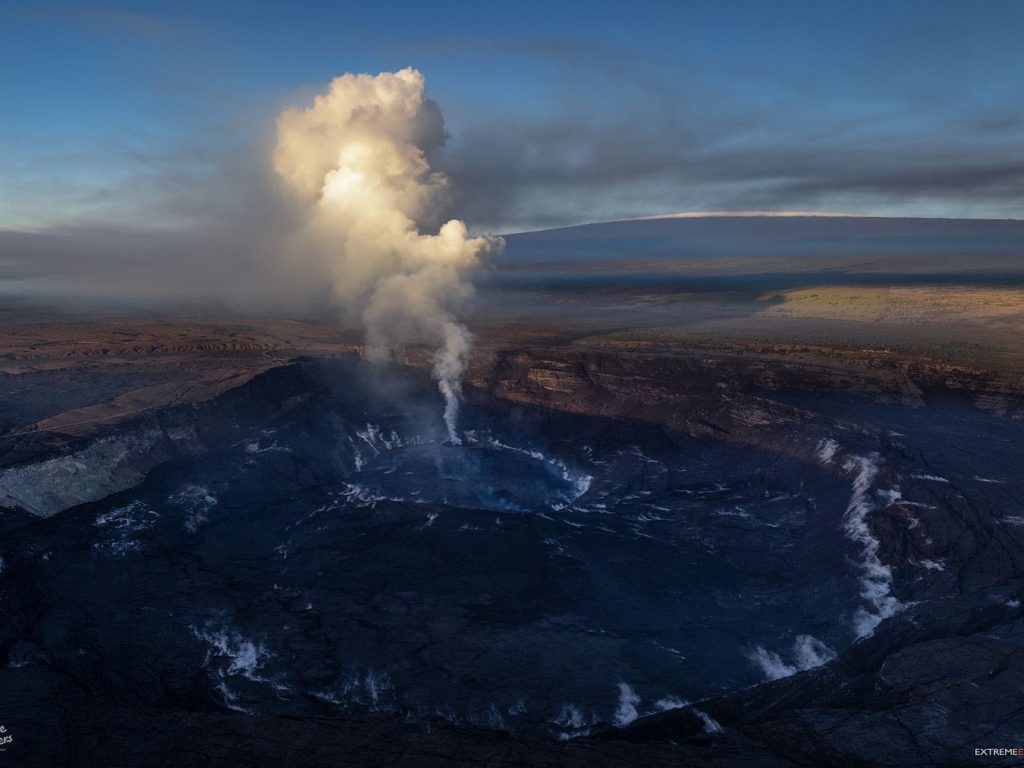
Hawaii , Mauna Loa :
19°28’30 » N 155°36’29 » O,
Altitude du sommet :13681 pieds (4170 m)
Niveau d’alerte volcanique actuel : AVIS
Code couleur actuel de l’aviation : JAUNE
Résumé de l’activité :
Le volcan Mauna Loa n’est pas en éruption. Les taux de sismicité restent légèrement élevés au-dessus des niveaux de fond à long terme, mais n’ont pas changé de manière significative au cours de la semaine dernière. Les autres flux de données de surveillance du Mauna Loa – déformation du sol, concentrations de gaz, apparence visuelle dans les webcams – ne montrent aucun changement significatif.
Observations :
Au cours de la semaine dernière, les sismomètres du HVO ont enregistré environ 50 tremblements de terre de faible magnitude (inférieure à M2,5) sous le sommet et les flancs supérieurs du Mauna Loa. La majorité de ces tremblements de terre se sont produits à des profondeurs peu profondes inférieures à 10 kilomètres (6 miles) sous le niveau de la mer.
Les mesures du système de positionnement global (GPS) montrent des taux de déformation très faibles dans la région du sommet qui se sont poursuivis au cours de la semaine dernière.
Les concentrations de gaz et les températures des fumerolles au sommet et à Sulphur Cone sur la zone de rift Sud-Ouest restent stables.
Les vues de la webcam n’ont montré aucun changement dans le paysage volcanique du Mauna Loa au cours de la semaine dernière.
Source et photo: HVO.
Mexique , Popocatepetl :
07 mars, 11h00 (07 mars, 17h00 GMT)
Au cours des dernières 24 heures, grâce aux systèmes de surveillance du volcan Popocatépetl, huit expirations de faible intensité ont été détectées. De plus, des épisodes de tremors de faible amplitude ont été enregistrés qui ont totalisé 1 045 minutes, accompagnés d’émissions de vapeur d’eau, de gaz et parfois de légères quantités de cendres. De plus, un tremblement de terre volcano-tectonique a été enregistré aujourd’hui à 02h11, avec une magnitude calculée de 1,2.
Au cours de la matinée et au moment de ce rapport, une émission intermittente de vapeur et de gaz volcaniques est observée, se dispersant vers le Nord-Ouest.
Sur la base des différents paramètres qui sont surveillés, il est considéré comme probable que les émissions de cendres continueront de se produire. Finalement, certaines explosions pourraient être enregistrées qui ne dépassent pas en intensité celles déjà observées. Ces scénarios sont envisagés dans le niveau jaune de la phase 2 du feu de signalisation d’alerte volcanique.
Le CENAPRED exhorte à NE PAS APPROCHER le volcan et surtout le cratère, en raison du danger de chute de fragments balistiques et, en cas de fortes pluies, de rester à l’écart du fond des ravins en raison du danger de coulées de boue et de débris.
Le feu de circulation d’alerte volcanique du Popocatépetl est en JAUNE PHASE 2.
Source : Cenapred .