
June 08 , 2022.
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
Communication on the activity of Etna, 07 June 2022/, 20:43 (18:43 UTC).
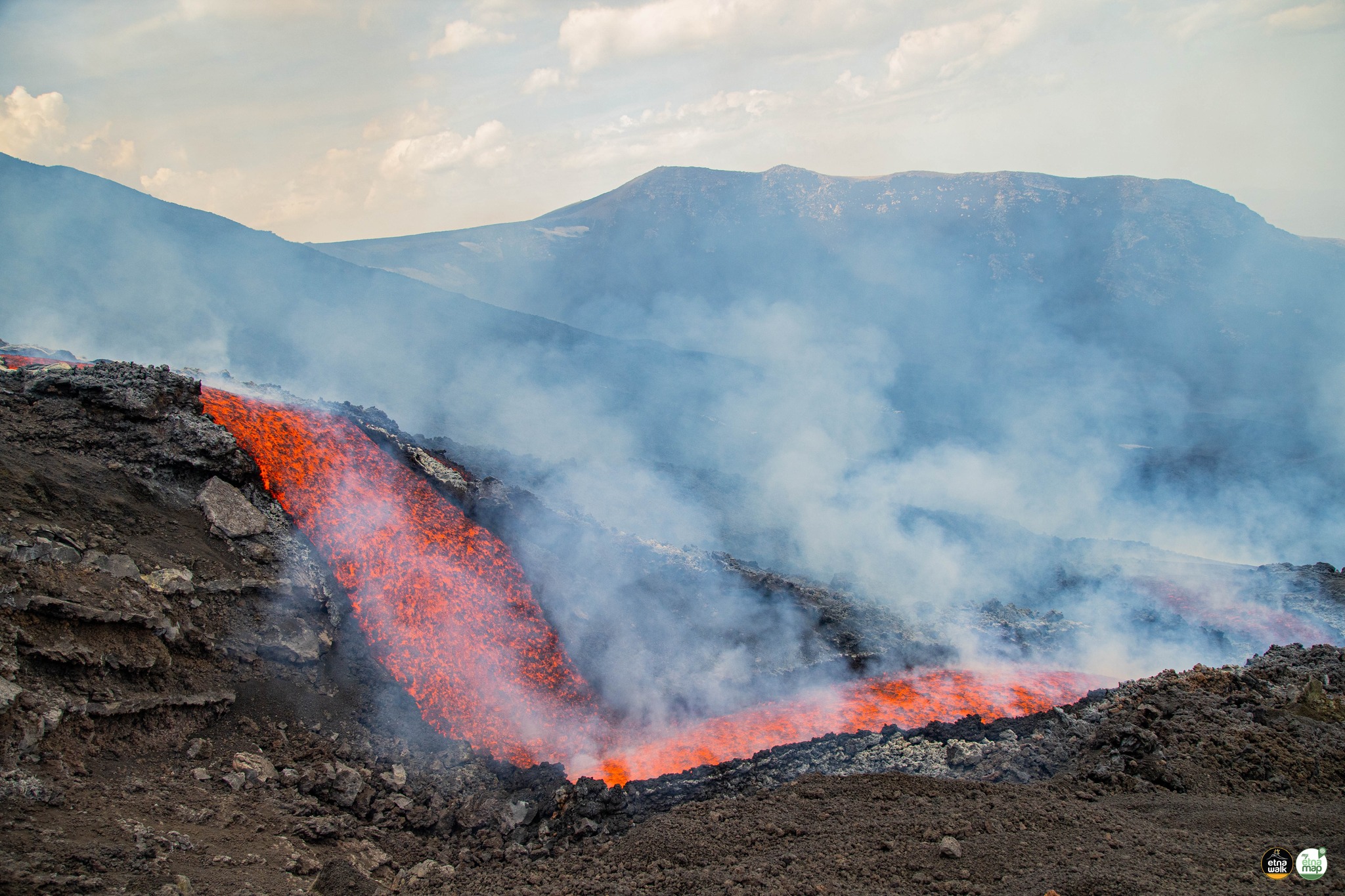
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, reports that new fractures have been observed at the base of the northern wall of the Valle del Bove, in the Serracozzo region, from the most downstream part of this system of fracture, lava is released. The emission point is located at an altitude of about 1800 m.
An inspection by INGV staff is in progress. Regarding the average amplitude of the volcanic tremor, since late yesterday evening, there is a phase of gradual decrease which has increased this parameter from high to medium-high values. The sources of the tremor are located in the area of the Southeast Crater at an altitude of approximately 2900 meters above sea level. The infrasound activity is weak, however the strong wind this morning may have affected the detection infrasonic events. From the analysis of the ground deformation signals, no noise-free variation in the last hours at the inclinometer stations and the GNSS network is deduced.
Communication on the activity of Etna, 08 June 2022/, 00:32 (22:32 UTC).
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that the inspection carried out by the staff of the INGV-OE shows that the effusive vent opened at the end of the afternoon of June 7, 2022 is located at a altitude of about 1900-1950 m (therefore higher than the altitude previously communicated). The flow it emits is poorly fed and the lava flow has expanded by a few tens of meters. On the other hand, the effusive activity of the vents opened on May 29 continues unchanged, between 2900 and 2700 m, the active lava fronts reaching an altitude of about 2000 m.
From a seismic point of view, there are no significant changes compared to what was communicated in the previous update at 8:43 p.m. local time.
The stations of the inclinometric and GNSS network do not show any significant deformations of the ground.
Further updates will be communicated soon.
WEEKLY NEWSLETTER, from May 30, 2022 to June 05, 2022. (issue date June 07, 2022)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY:
In the light of the surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Strombolian activity at the level of the Southeast Crater, sometimes accompanied by the formation of ash clouds and effusive activity with the development of lava flows in the Valle del Bove.
2) SEISMOLOGY: Low seismic activity of fracturing. The sources of the tremor are located in the Southeast Crater area
3) INFRASOUND: moderate infrasound activity.
4) DEFORMATIONS OF THE GROUND: The analysis of the deformations of the ground shows a weak deflation these last weeks. In general, no significant change is observed.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux at an average level
Soil CO2 flux shows average values.
The partial pressure of dissolved CO2 in groundwater shows values in seasonal variability.
The latest data available from 01/06/2022 showed high values.
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity in the summit zone was of a high level in correspondence with the current effusive activity.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
The monitoring of Etna’s volcanic activity during the observation period was carried out through the analysis of images from the INGV surveillance camera network, Osservatorio Etneo (INGV-OE) and through various site inspections carried out by INGV staff. -OE.
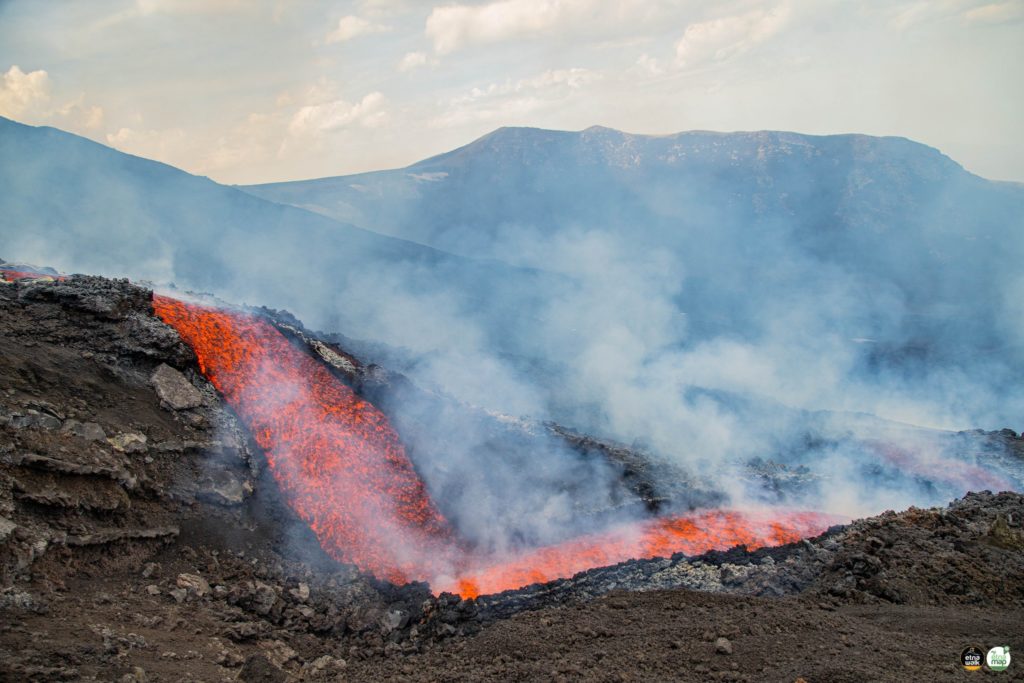
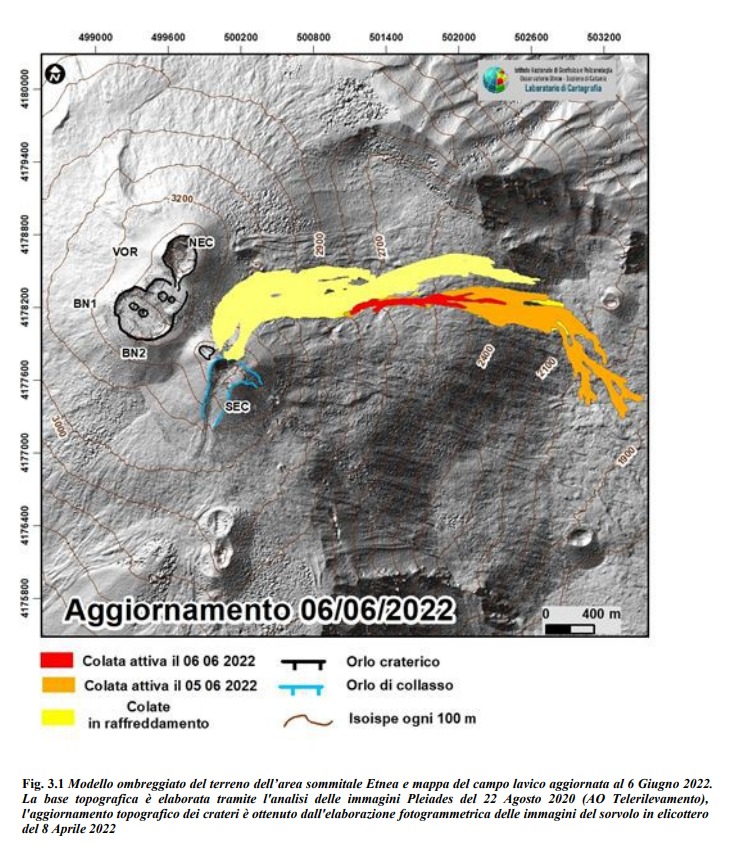
During the period, the effusive activity produced by the eruptive fissure that opened on May 29 continued in a variable and pulsating manner. in the upper part of the Valle del Bove, at an altitude between 2700 and 2900 m and with an approximately East-West orientation (Fig 3.1). Over time, the variability in the effusive rate was reflected in the development of a branching lava field with overlapping lava flows and in some cases and for short stretches, even collapsed. The flow fronts peaked at about 1900 m a.s.l. on June 5 and stopped on June 6 at 2380 m a.s.l. Figure 3.1 shows the summit area of Etna with the updated mapping of the lava field produced through the analysis of satellite images, Planetscope of June 5 and Sentinel of June 6.
The average eruptive rate (TADR) since May 12 was estimated with the CLHOTSAT system thanks to the processing of infrared satellite images from the SEVIRI sensor. Data updated at 3:00 GMT on June 6 indicates a TADR with flows between 2 and 4 m3/s between May 13 and 28, increasing from May 29 with flows even exceeding 10 m3/s, and decreasing from June 3. By integrating the values of the effusive rate throughout the eruptive period, the cumulative volume curve was calculated, which is between 3.8 and 7.8 million m3.
The dynamics of the lava field and the placement of the lava flow have been reproduced digitally with the new model GPUFLOW. Effusive activity was simulated from four eruptive vents placed at an altitude of approximately 3200 m (from May 12), 3300 m (from May 20), 2850 and 2730 m (from May 29 ). The simulation was carried out on the 4-meter DEM updated in July 2021 and obtained from the processing of Pléiades and WorldView3 images.
Source : INGV.
Photos : INGV , Etna walk /Giuseppe Distefano / Marco Restivo / Marco Di Marco .
Italy , Vulcano :
WEEKLY NEWSLETTER, from May 30, 2022 to June 05, 2022. (issue date June 07, 2022)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
In the light of the surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) Temperature of the crater fumaroles: Maximum stable emission temperatures around 382°C. The weekly average is 379°C.
2) Flux of CO2 in the area of the crater: The flux of CO2 from the ground in the summit area displays an average value of approximately 6000 g/m2/day.
3) SO2 flux in the crater area: SO2 flux at a medium-high level
4) Geochemistry of fumarolic gases: No update since the last bulletin.
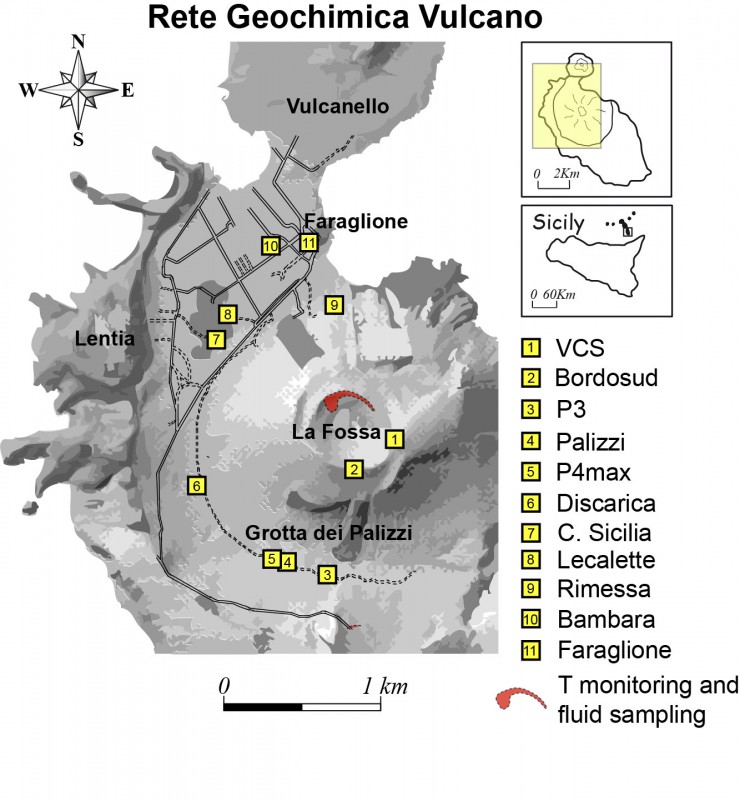
5) CO2 fluxes at the base of the La Fossa cone and in the Vulcano Porto area: The CO2 fluxes recorded in the C. Sicilia and P4max sites remain at medium-high values; at Rimessa there is a slight downward trend, at the Faraglione site the values are stable.
6) Geochemistry of thermal aquifers: The physico-chemical parameters of thermal aquifers show stable values. There are no significant changes.
7) Local seismicity: the phase of general increase in local micro-seismicity continues, linked to the dynamics of hydrothermal fluids.
8) Regional seismicity: No earthquake with Ml >= 1 in the Vulcano area.
9) Deformations – GNSS: Data from the permanent GNSS network did not show any significant changes during the week.
10) Deformations – Clinometrics: The data from the network of clinometric stations on the island did not show any significant changes during the week.
11) Other observations: Gravimetry: No significant variation was recorded.
Monthly CO2 flux campaign: a slight decrease in CO2 emissions is observed in the Vulcano Porto area; average CO2 emissions from soils still remain at abnormal levels.
Monthly well campaign: a decrease in the supply of fluids of fumarolic origin to the thermal water table is generally observed, which still remains at abnormal levels in certain sites for certain monitored parameters.
CRATER FUMAROLES TEMPERATURE
Along the upper edge, the maximum emission temperature has extremely stable values, with a maximum of 382°C and a weekly average of 379°C (T1). The fumarolic field presents homogeneous emission temperatures all along the summit fracture line, confirming a thermal anomaly still maintained by a stable vapor flow.
The thermal signal of the sensor placed T3 and on the internal side has been restored: T3 (fumerola F5) overlaps the temperatures recorded in T2 (fumarole F5AT) and the site restored on the internal side has the same variability before the failure, with obvious disturbances (dominant modulation) of exogenous nature and maximum temperature equal to 112°C.
LOCAL SEISMICITY
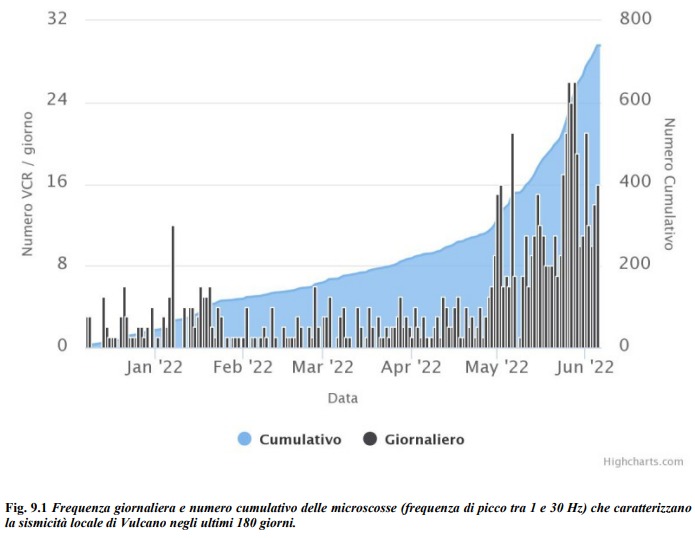
The phase of general increase in the rate of occurrence of local micro-shocks, linked to the dynamics of hydrothermal fluids, continues, although discontinuously.
In particular, as can be seen in Fig. 9.1, this phase involved local high frequency events (dominant peak > 1Hz) from April 30 and is not yet complete. Regarding low frequency type events (VLP; dominant peak 1 Hz), also on the increase since May 22, there are no significant changes compared to what was reported last week.
Source : INGV.
Photos : INGV , Filippo Parisi .
Colombia , Chiles / Cerro Negro :
Weekly activity bulletin of the Chiles and Cerro Negro volcanoes.
Volcano activity continues at YELLOW LEVEL or (III): CHANGES IN THE BEHAVIOR OF VOLCANIC ACTIVITY.
From monitoring the activity of the CHILES AND CERRO NEGRO VOLCANOES, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE (SGC) reports that:
For the week between May 31 and June 6, 2022, seismic activity maintains the increase in occurrence and released energy, reported in the bulletin of May 31, 2022, increasing from 2,805 to 8,147 events per compared to the previous period. The most frequent earthquakes were those associated with a fracture of the cortical material inside the volcano, which were located mainly towards the southern sector of the zone of influence of the Chiles volcano, at distances of up to 3, 7 km, depths between 2 and 5 km from its summit (4700 m above sea level) and with a maximum magnitude of 2.5.
No manifestation of surface activity was observed, nor significant variations in other parameters of volcanic monitoring.
The possibility of high-energy earthquakes, which can be felt by residents of the volcanic influence zone, as has happened in the past, is not excluded.
Source : SGC.
Photo : Ingeominas
Iceland , Reykjanes Peninsula :
About 2600 earthquakes were detected by IMOs SIL seismic network this week. Around 1150 of them have been manually located. Overall there were 4 eathquakes mesured larger or equal to M3.0, one in Reykjanesskagi, 2 on Húsavíkur and Flateyjarfault zone where the largest earthquake of the week was detected and one out on Kolbeinseyjarhrygg. Largest part of last weeks activity was on Reykjanes Peninsula, mostly by Svartsengi.
There is still ongoing seismic activity on Reykjanes, however the newest GPS and sattilite data shows that the inflation has now stopped. A small seismic swarm was detected on Húsavíkur and Flateyjarfault zone between 30-31st of May where about 200 earthquakes was detected.
Earthquake activity on the Reykjanes peninsula is ongoing, in the past days the activity has been fluctuating.
Uplift is no longer observed on GPS measurements on the Reykjanes peninsula.
Source : Vedur is
Ecuador , Sangay :
DAILY REPORT OF THE STATE OF SANGAY VOLCANO, Tuesday June 07, 2022.
Information Geophysical Institute – EPN.
Surface Activity Level: High, Surface Trend: No change.
Internal activity level: High, Internal trend: No change.
Seismicity: From June 06, 2022, 11:00 a.m. to June 07, 2022, 11:00 a.m.:
Explosion (EXP) 6
Long Periods (LP) 93
Emission tremor (TREMI): 54
Rains / Lahars:
No rain was reported in the area in the past 24 hours. **In the event of heavy rains, these could remobilize the accumulated materials, generating mudslides and debris that would descend on the flanks of the volcano and flow into the adjacent rivers.**
Emission / ash column:
Several emissions of steam, gas and ash were observed at heights greater than 1500 meters above the level of the crater, with directions oscillating between the North-West and the North-East. The Washington VAAC published 3 reports of ash emission with heights of 870 to 1,470 meters above crater level, heading west and northwest.
Other Monitoring Parameters:
The FIRMS system records 98 thermal alerts and MIROVA records 1 moderate thermal alert in the last 24 hours.
Observation:
For the moment, the volcano remains cloudy.
Alert level: Orange.
Source : IGEPN
Photo : ECU 911
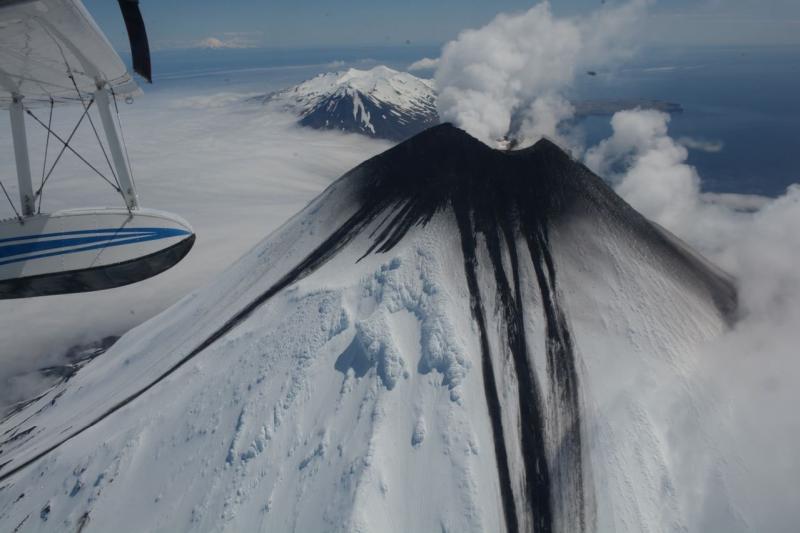
Alaska , Cleveland :
52°49’20 » N 169°56’42 » W,
Summit Elevation 5676 ft (1730 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Unrest continues. Satellite images continue to show elevated surface temperatures in the summit crater. Recent subsidence in the summit crater was observed using a comparison of satellite radar images the were collected on 19 and 30 May (and only recently released). Subsidence in the summit crater is not unusual at this volcano. No significant seismic or infrasound activity was detected over the past day.
Episodes of lava effusion and explosions can occur without advance warning. Explosions from Cleveland are normally short duration and only present a hazard to aviation in the immediate vicinity of the volcano. Larger explosions that present a more widespread hazard to aviation are possible, but are less likely and occur less frequently.
When operational, Cleveland volcano is monitored by only two seismic stations, which restricts AVO’s ability to precisely locate earthquakes and detect precursory unrest that may lead to an explosive eruption. Rapid detection of an ash-producing eruption may be possible using a combination of seismic, infrasound, lightning, and satellite data.
Source : AVO.
Photo : Mees, Burke











No comment yet, add your voice below!