
May 05 , 2022.
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
MONTHLY BULLETIN, APRIL 2022. (issue date 03 May 2022)
ACTIVITY STATUS SUMMARY
In the light of the surveillance data, it is highlighted:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Variable rate degassing activity at the summit craters.
2) SEISMOLOGY: Low fracturing activity. Amplitude of the tremor on mainly low and medium-low values. Sources of tremor located mainly between the Bocca Nuova and Southeast craters.
3) INFRASOUND: There are no significant changes in the rate of occurrence of events, which are mainly located in the Bocca Nuova crater area.
4) GROUND DEFORMATIONS: Ground deformation monitoring networks have not recorded any significant changes over the past month.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: SO2 flux at a medium-low level.
Soil CO2 flux shows a clear increase.
The partial pressure of dissolved CO2 in groundwater shows values in seasonal variability.
The latest available data of the helium isotope ratio show high but stable values (sampling of 11.04.2022).
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: Thermal activity in the summit area was at a low level.
VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS
The monitoring of the volcanic activity of Etna, during the observation period in question, was carried out by analyzing the images of the network of surveillance cameras of the INGV, Osservatorio Etneo (INGV-OE) and through a overflight carried out on April 8 with a helicopter made available to the 2nd Air Unit of the Catania Coast Guard. The alternating weather conditions made the observation of the activity at the level of the summit craters discontinuous thanks to the network of cameras.
In general, over the period under review, the activity of Etna showed no change compared to that observed after the end of the last eruptive episode on February 21 and was characterized by variable degassing of the craters. summits.
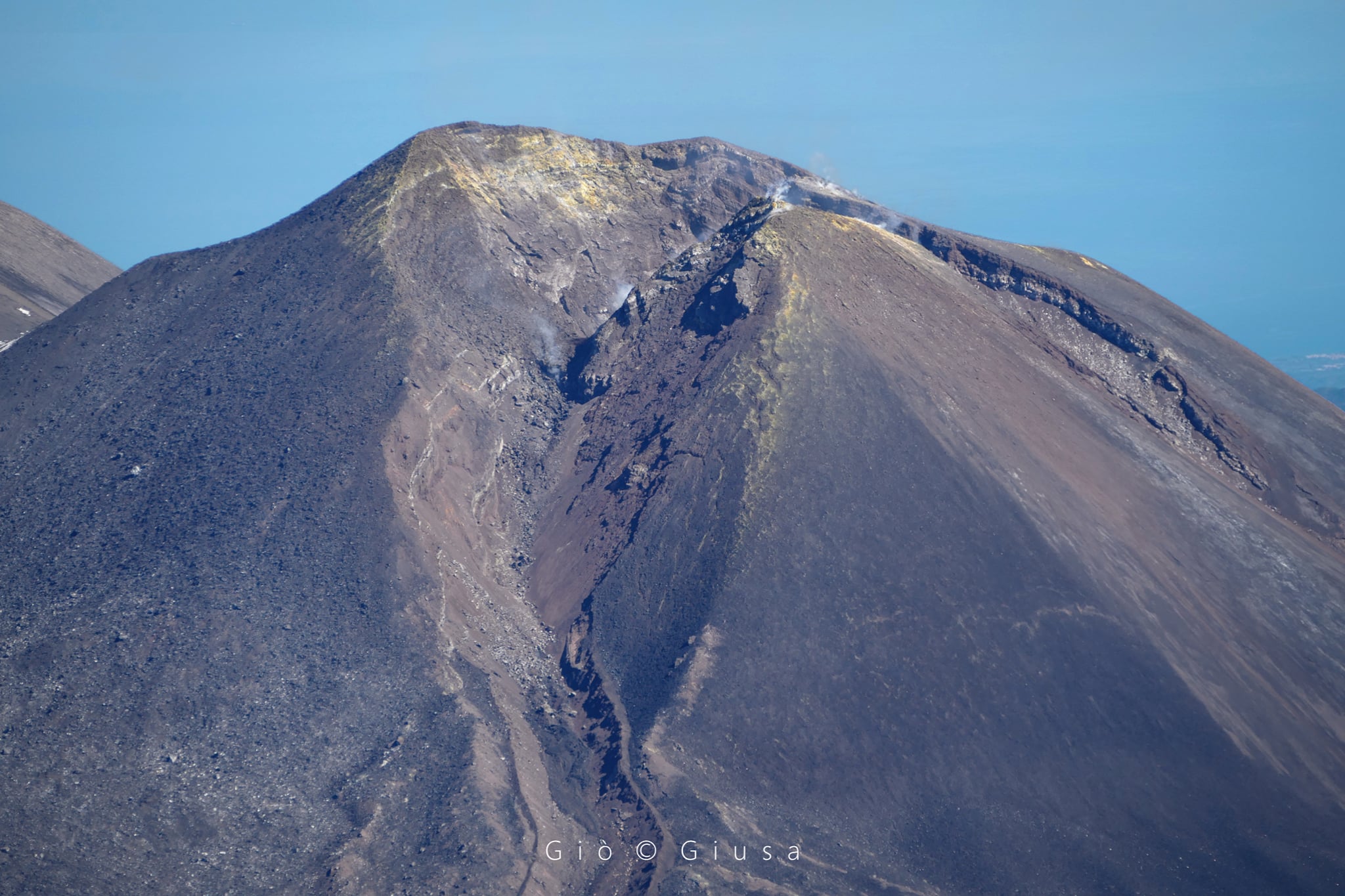
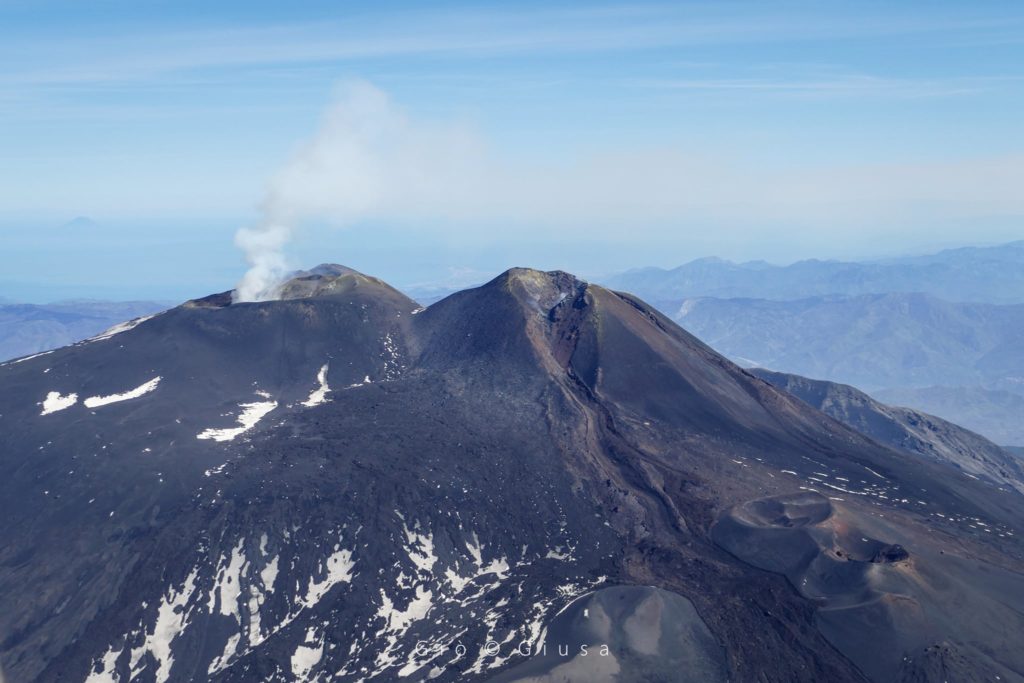
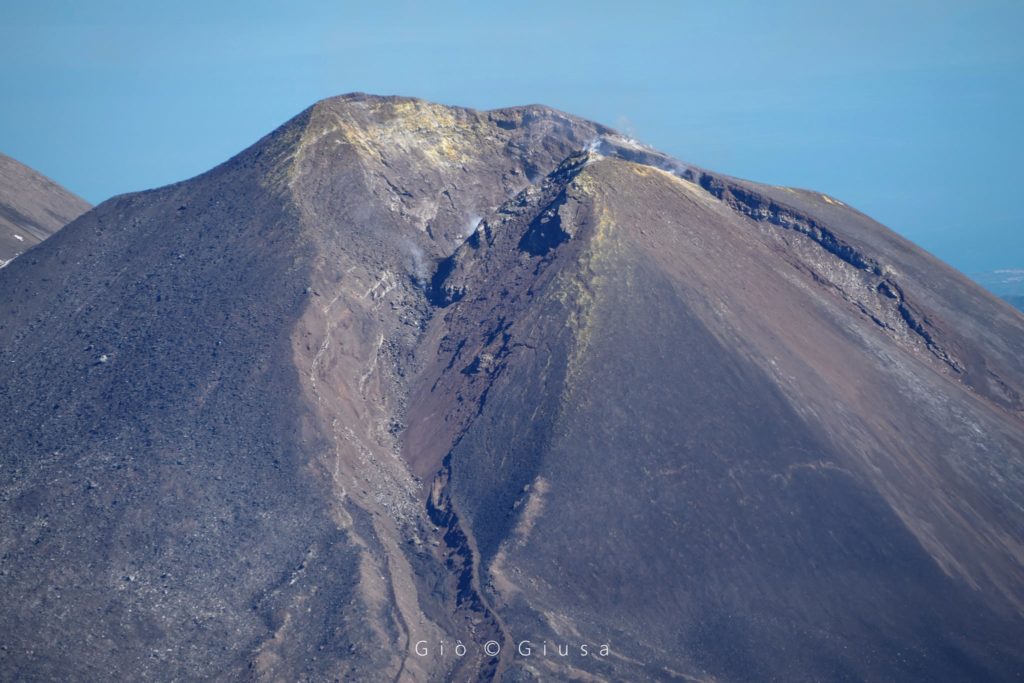
In detail, the Bocca Nuova (BN) crater is characterized by variable and sometimes pulsed intra-crater degassing. According to the surveillance cameras, we observe that the plume consists
mainly from vapor emissions. In the early morning hours of April 27, very faint emissions of reddish ash were observed from the camera array. This observation was confirmed by INGV-OE field staff.
The Southeast crater has degassing of varying intensity, fed mainly by the fumaroles located along the northern edge of the crater and inside the niche formed by the collapse on the side of February 10, 2022. At 09:06 UTC the On April 21, a small landslide occurred on the southern slope of the cone, which produced a modest thermal anomaly visible from the Montagnola camera. Another very modest landslide event occurred at the same site at 21:14 UTC on April 22.
Finally, with regard to the Voragine crater (VOR), no activity, not even degassing, is observed from the surveillance cameras, while the Northeast crater (NEC) shows only a weak degassing activity.
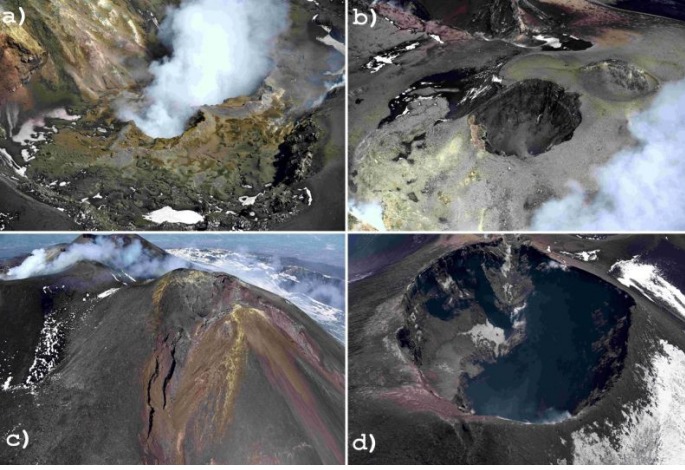
(a) Intense degassing activity of the two collapse craters located in the depression of the Bocca Nuova crater (BN). (b) Interior of the Voragine crater (VOR) with the two coalescing cones, formed during the 2019 activity, completely free of degassing. (c) Southeast Crater (SEC) and the depression formed as a result of the February 10, 2022 lava fountain, inside which a small crater formed. (d) Low degassing activity from the Northeast Crater
During the overflight carried out on April 8 with a helicopter made available to the 2nd Air Unit of the Coast Guard of Catania, it was possible to deepen the observations from a distance.
The Bocca Nuova (BN) crater is affected by intense pulsating outgassing activity from two collapse craters located in the center of the crater depression. The Voragine crater (VOR) shows no degassing activity. The Southeast crater (SEC) is occluded: the degassing activity is very weak and is limited to small fumaroles placed along the edges of the crater. After the last episode of lava fountaining on February 21, 2022, a small collapse crater formed, with a diameter of a few meters, which is affected by very weak degassing. Finally, the Northeast Crater (NEC) shows low degassing activity mainly related to small fumarole systems located along the edge of the crater.
Source : INGV.
Photos : Gio Giusa , INGV.
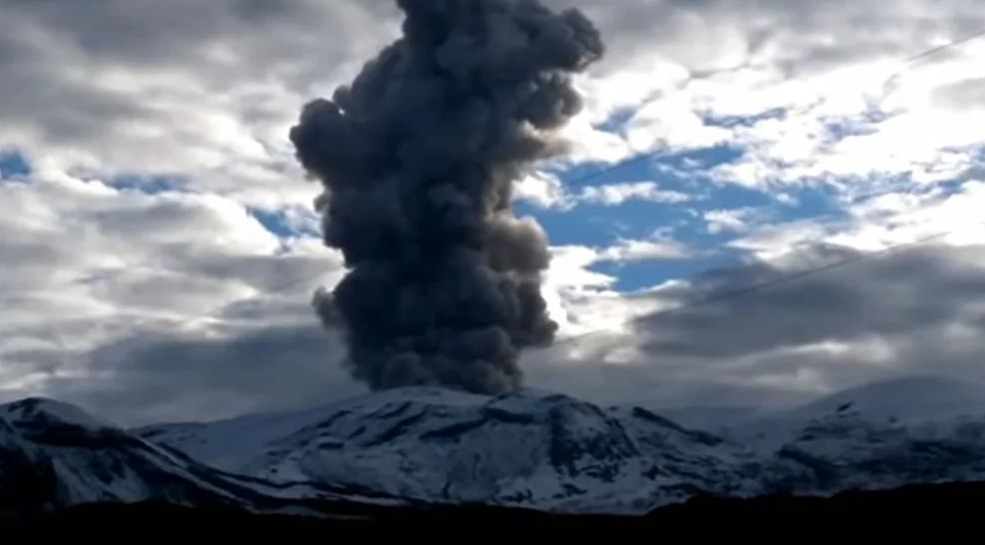
Colombia , Nevado del Ruiz :
Bulletin of activity level of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano.
The activity level continues at the Yellow Activity Level or (III): changes in the behavior of volcanic activity.
Regarding the monitoring of the activity of the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE reports that:
Seismicity associated with rock fracturing decreased in number of earthquakes and seismic energy released, compared to the previous week. This seismic activity was located mainly on the west-northwest and south-west flanks of the volcano and to a lesser extent in the Arenas crater. The depth of the earthquakes varied between 0.4 and 9.0 km. The maximum magnitude recorded during the week was 1.6 ML (Local Magnitude), corresponding to the earthquake which occurred on May 1 at 08:46 (local time), located 6.8 km west-northwest of the crater Arenas, at a depth of 4.5 km.
The recording of low energy « drumbeat » type seismicity, associated with rock fracturing, on April 27 and 28 stands out. This seismicity has been linked to the processes of ascent, emplacement-growth and evolution of a lava dome at the bottom of the Arenas crater.
The seismicity related to fluid dynamics inside the volcanic conduits had a similar level in the number of earthquakes and in the seismic energy released, compared to the previous week. This seismic activity was characterized by the appearance of continuous volcanic tremors, TC, tremor pulses, TR, long-period type earthquakes, LP, and very long period, VLP. In general, these signals exhibited low to moderate energy levels and variable spectral content. Most of these earthquakes were located in the Arenas crater. Some of them were associated with gas and ash emissions that have been confirmed by the cameras installed in the volcano area and by reports from Los Nevados National Natural Park officials, in addition to the visual appreciation at different places around the area of influence of the volcano. Similarly, changes in the relative temperature of the emitted material have been observed using the FLIR cameras (Thermal Cameras) of the SGC’s multi-parameter volcanic monitoring network.
Today, several moderate energetic signals associated with fluid dynamics were accompanied by scattered ash emissions to the West-South-West and West-North-West of the volcano with reports of falling in the municipalities of Santa Rosa, Dosquebradas and Pereira in the department of Risaralda and the municipality of Manizales in the department of Caldas. The emission of 05:36 (local time) stands out with a maximum height of approximately 2126 m measured at the top of the volcano, a value corresponding to the maximum during the week, dispersing towards the West.
Source : SGC.
Photo : infobae.com
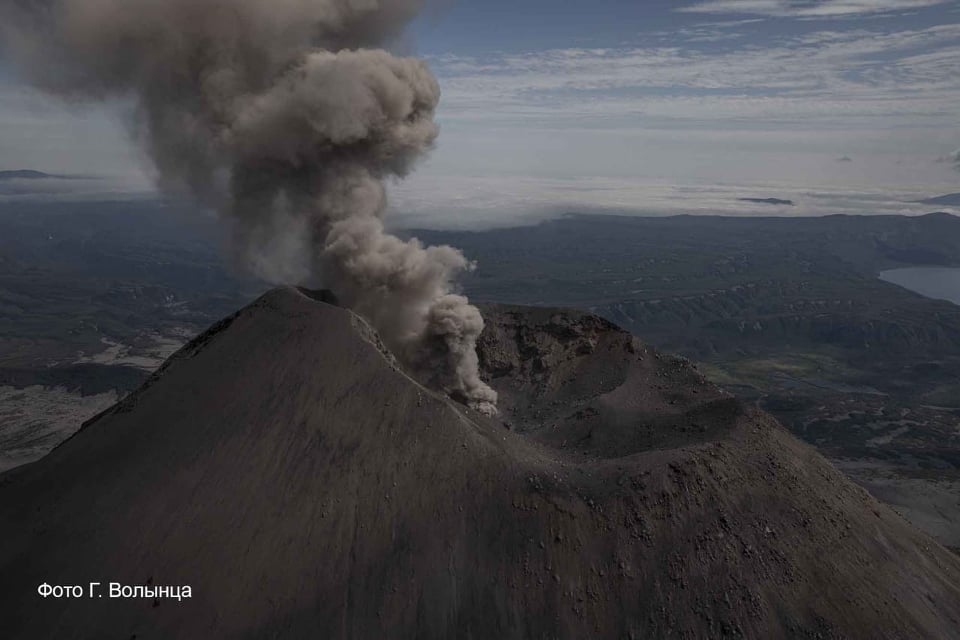
Kamchatka , Karymsky :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Issued: May 04 , 2022 .
Volcano: Karymsky (CAVW #300130)
Current aviation colour code: ORANGE
Previous aviation colour code: orange
Source: KVERT
Notice Number: 2022-32
Volcano Location: N 54 deg 2 min E 159 deg 26 min
Area: Kamchatka, Russia
Summit Elevation: 1486 m (4874.08 ft)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
A moderate activity of the volcano continues. The explosions sent ash up to 3 – 3.2 km a.s.l., the ash plume is extending to the west-southhwest of the volcano.
A moderate activity of the volcano continues. Ash explosions up to 12 km (39,400 ft) a.s.l. could occur at any time. Ongoing activity could affect international and low-flying aircraft.
Volcanic cloud height:
3000-3200 m (9840-10496 ft) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20220504/2050Z – Himawari-8
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 24 km (15 mi)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: WSW / azimuth 241 deg
Time and method of ash plume/cloud determination: 20220504/2050Z – Himawari-8
Start time of explosion and how determined: /1940Z – unknown.
KVERT reported that a thermal anomaly over Karymsky was visible in satellite images on most days during 22-29 April. Explosions during 21-22 April produced ash plumes that rose as high as 5 km (16,400 ft) a.s.l. and drifted around 95 km E and SE. Explosions at 14h10 on 28 April, local time, generated an ash plume that rose to 10 km (32,800 ft) a.s.l., was about 5 x 7 km at it’s top, and drifted WNW. The Aviation Color Code was raised to Red (the highest level on a four-color scale). By 15h50 the ash cloud had spread to 28 x 34 km in size and had drifted almost 290 km WNW at an altitude of 9 km. The Aviation Color Code was lowered to orange because ash was no longer being emitted from the volcano. The plume had drifted more than 1,000 km before dissipating.
Source : Kvert , GVP .
Photo : Kvert , G. Volynets.
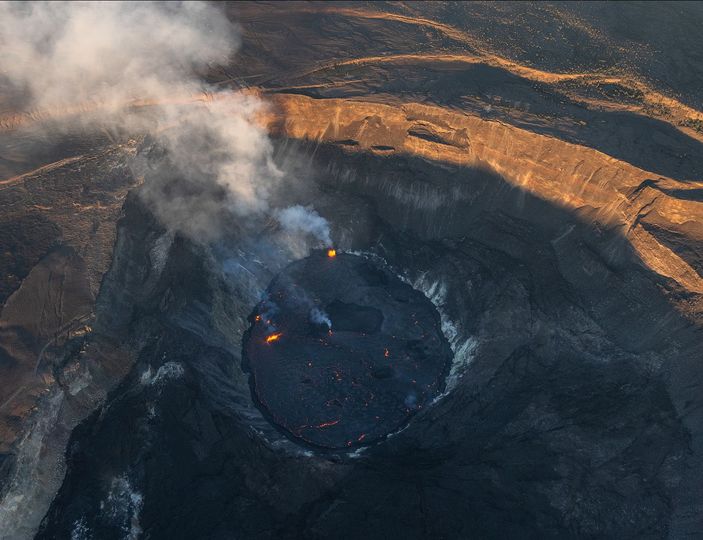
Hawaii , Kilauea :
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Activity Summary:
The summit eruption of Kīlauea Volcano, within Halemaʻumaʻu crater, has continued over the past 24 hours. All recent lava activity has been confined to the crater, and current data indicate that this scenario is likely to continue. No significant changes have been noted in the summit or East Rift Zone.
Halemaʻumaʻu crater Lava Lake Observations:
Eruption of lava from the Halemaʻumaʻu western vent into the active lava lake and onto the crater floor has continued over the past 24 hours. The active lava lake has experienced continuous surface activity, and its surface level has been relatively steady over this period. Sporadic breakouts also continue along the margins of the crater, but these have been relatively weak over the past 24 hours. Overflight measurements on April 6, 2022 indicated that the crater floor had seen a total rise of about 99 meters (325 feet) and that 66 million cubic meters (18 billion gallons) of lava had been effused since the beginning of this eruption on September 29, 2021.
Summit Observations:
Summit tiltmeters recorded only minor fluctuations over the past 24 hours. Volcanic tremor remains above background levels. A sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission rate of approximately 1,800 tonnes per day (t/d) was measured on April 28, 2022.
Source : HVO.
Photo : Bruce Omori / Paradise helicopters .
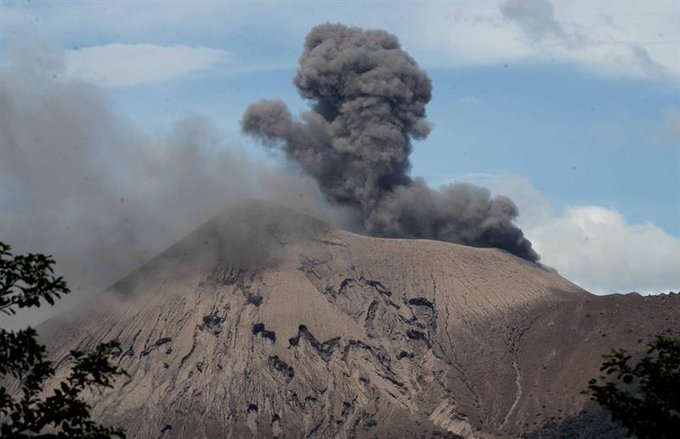
Guatemala , Santiaguito :
Activity :
The observatory of the Santa María-Santiaguito volcanic complex reports a column of moderate degassing 800 meters above the crater moving west, and the descent of weak and moderate avalanches on the southwest flank of the Caliente dome , as well as on the front of the lava flow of 2700 meters in length which is located in the upper part of the ravine of San Isidro. During the night and early in the morning, a constant incandescence was observed in the Caliente dome.
Due to the advance of the lava flow in the San Isidro ravine, this one presents occasional collapses which produce avalanches of blocks and raise columns of ash, so do not stay inside or around said ravine . Due to the dispersal of ash from avalanches, ashfall may occur on Loma Linda. Extruder activity remains at a high level and continues to unstably pile material on the west flank lava flow as well as on the Caliente dome, thus maintaining the possibility that some of this material may collapse and disintegrate generating pyroclastic flows over long distances to the South-West, South and East.
Source : Insivumeh.
Photo : USGS/ Insivumeh.
Nicaragua , Telica :
The Telica volcano, located in the department of León, recorded an explosion of gas accompanied by a small amount of ash, at 3:53 p.m. on Monday, the Nicaraguan Institute for Territorial Studies (INETER) reported.
The fact did not pose a danger to the population, however, there is the possibility of new gas and ash explosions of low to moderate intensity.
It is recommended to the population not to climb the crater and to be attentive to the instructions issued by the authorities.
Regarding the monitoring of other volcanoes in Nicaragua, INETER reports that San Cristóbal, Cerro Negro, Masaya, Momotombo and Concepción fall within the normal ranges of active volcanoes.
Source : nuevaya.com.ni
Photo : Enfoque Noticias .











No comment yet, add your voice below!