
October 25 , 2021 .
Spain / La Palma , Cumbre Vieja :
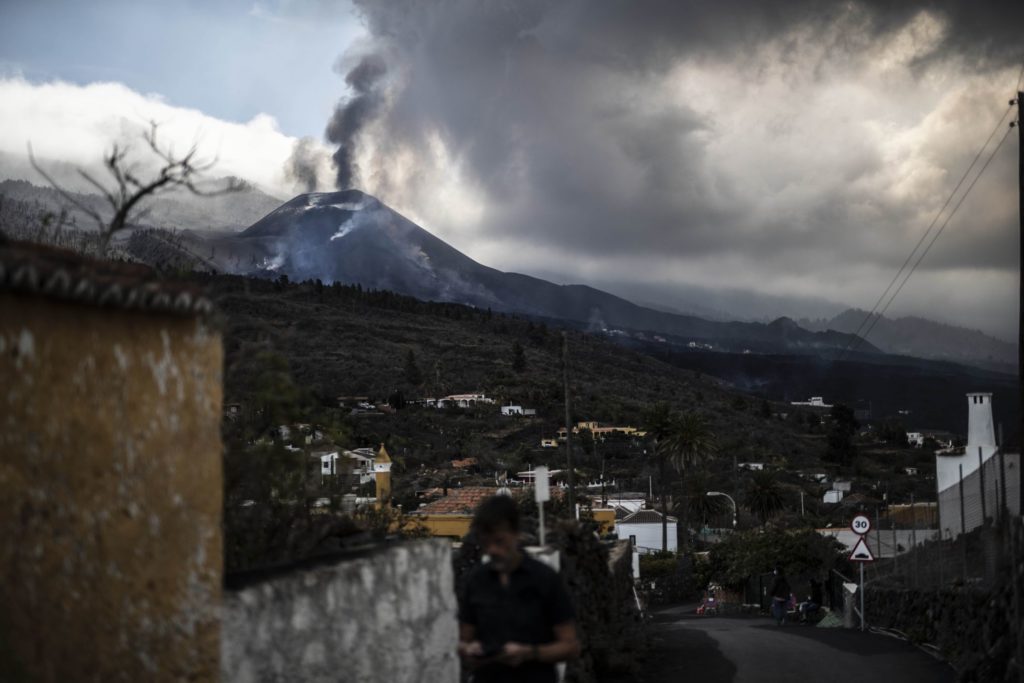
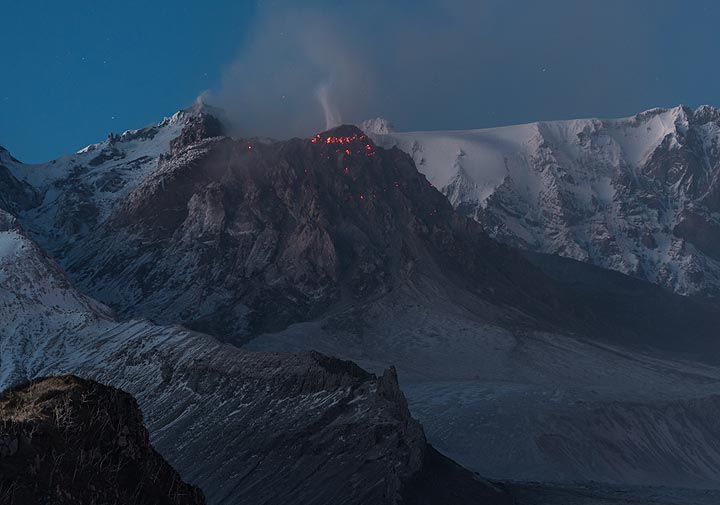
October 24, 2021, 08:00 UTC. Eruptive activity continues on La Palma.
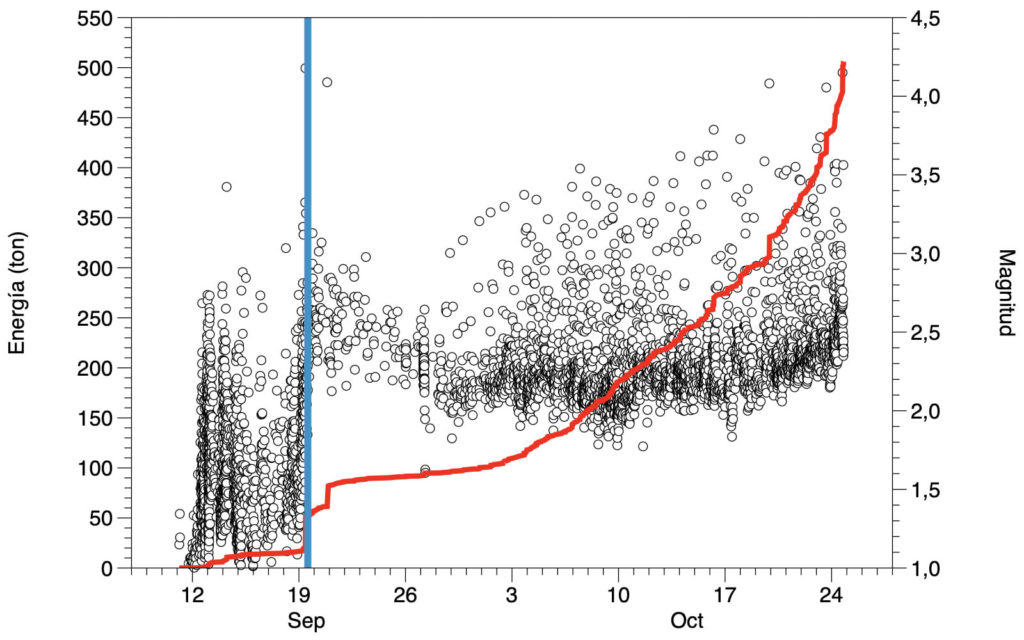
Since the last declaration, 135 earthquakes have been located in the area affected by the volcanic reactivation of Cumbre Vieja, 20 of these earthquakes were felt by the population, the maximum intensity in the epicentral zone IV (EMS98) being for 4 earthquakes.
The earthquake that occurred at 15:34 UTC on the 23rd, with a magnitude of 4.9 mbLg at a depth of 38 km, so far is the largest earthquake since the start of the eruption, it was widely felt throughout the island of La Palma and with intensity II, weakly by some populations of the islands of La Gomera and Tenerife.
During the period considered, a total of 9 earthquakes were located at depths of about 30 km, the rest of the hypocenters of the period are located at a shallower depth, around 12 km.
The volcanic tremor signal maintains a high average amplitude, with intensifying pulses.
The height of the emission column measured at 07:45 UTC is estimated at 3200 m.
The island’s network of permanent GNSS stations still does not show a clear tendency to warp from stations closest to eruptive centers, while at more distant stations a slight deflation is maintained, possibly related to deep seismicity. .
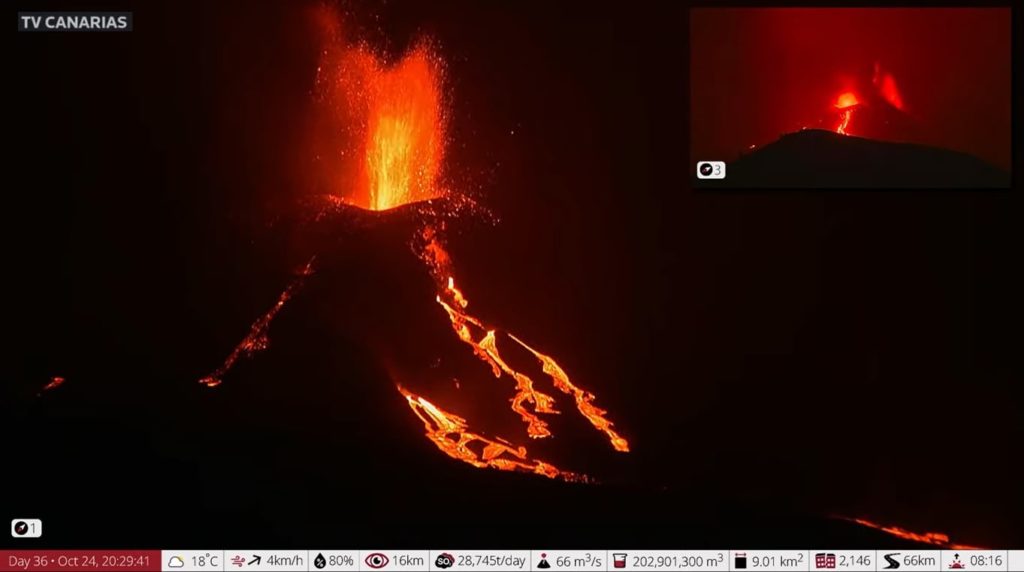
The Canary Islands Volcanological Institute (Involcan) reported this morning the appearance of a new flow in the south-eastern area of the volcano of La Palma which has created a new magmatic front. Lava began to emerge through the cone which was reactivated on October 15 and which so far only emitted pyroclasts. On Saturday, part of the volcano’s main cone suffered a landslide, according to Involcan, who also explained how lava overflowed from that mouth with low emission.
The volcano of La Palma experienced another day of unrest this Sunday. During the afternoon, the island registered an increase in earthquakes and saw a fifth mouth open, as confirmed by the volcanologist of the National Geographical Institute Rubén López. The eruption, in this way, has three mouths in the main cone and two more in the west, reports López. Opening this fifth mouth increased the flow of magma that emerged to the surface, causing the lava to overflow by mid-afternoon.
This was not the only relevant event throughout the day in regards to volcanic activity. The cone which was reactivated on the 15th, and which until now only emitted pyroclasts, began to expel lava in the afternoon of Saturday and was reactivated on Sunday. The technical director of the Canary Islands Volcanic Emergency Plan (Pevolca), Miguel Ángel Morcuende, explained that « this is important information, because in the end there is a redistribution of the magma to other points ».
Source : IGN es
Photo : Alvaro García / El Pais .
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
Paroxysm of the Southeast Crater of Etna, October 23, 2021.
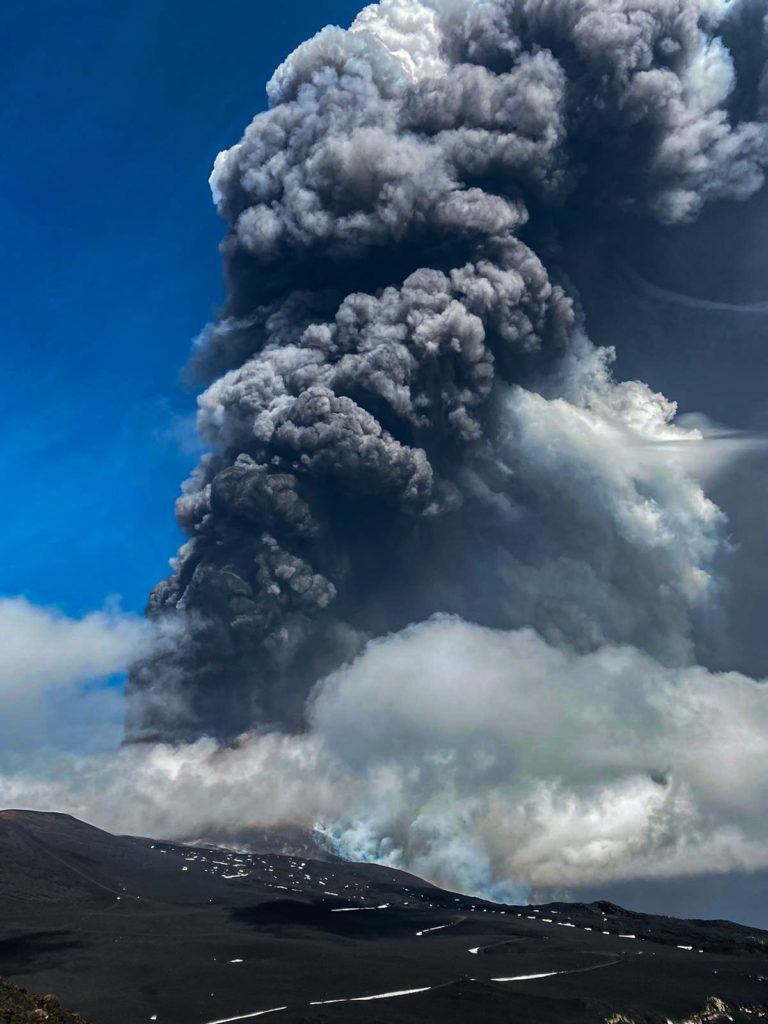
After a little over a month of relative calm, the Southeast Crater of Etna produced a new paroxysmal episode during the morning of October 23, 2021. This is the 52nd climax in the streak that began on February 16, 2021.
Weak Strombolian activity had already started in the early hours of October 20, and gradually intensified from the evening of October 22. At the same time, the amplitude of the volcanic tremor increased. Modest ash emissions accompanied Strombolian activity starting at 08:00 UTC (10:00 local time) on the 23rd. Ash production gradually increased, stopping abruptly at 08:35 UTC. A few minutes later a sequence of very strong explosions took place, which generated visible pressure waves, and which were followed by the resumption of the emission of ash. The activity intensified very quickly, producing an eruptive column several kilometers high and bent by the wind towards the east-northeast.
At 08:48 UTC, a pyroclastic flow broke away from the eastern flank of the Southeast Crater cone, which flowed into the western wall of the Valle del Bove, stopping after traveling just under 1.5 km. A second pyroclastic flow traveled 1.5 km at 09:00 UTC; subsequently, several smaller flows were observed, still under the eastern flank of the Southeast Crater. These flows were generated during the opening of a fracture in the south-eastern flank of the cone, from the lower part of which a lava flow originated, also directed towards the western side of the Valle del Bove. .
At 09:58 UTC, a new pyroclastic flow spilled in two branches towards the Southeast and the South, stopping after a few hundred meters.
The eruptive vents at the top of the Southeast Crater produced lava fountains which, in the phase of maximum intensity, reached about 800 m in height. In the short intervals of partial visibility of the cone, sporadic and small explosions were observed from the area of the « saddle mouth » and the southwest side of the cone.
The eruptive column rose, during the culminating phase of the paroxysm, to more than 10 km above sea level. Relapses of pyroclastic material have occurred towards the East-North-East, along an axis that starts from the South-East Crater passes to the Citelli refuge and crosses the towns of Vena, Presa, Piedimonte Etneo, Taormina and up to to the province of Reggio Calabria. Lapilli and ash relapses have also been reported in Mascali and Linguaglossa.
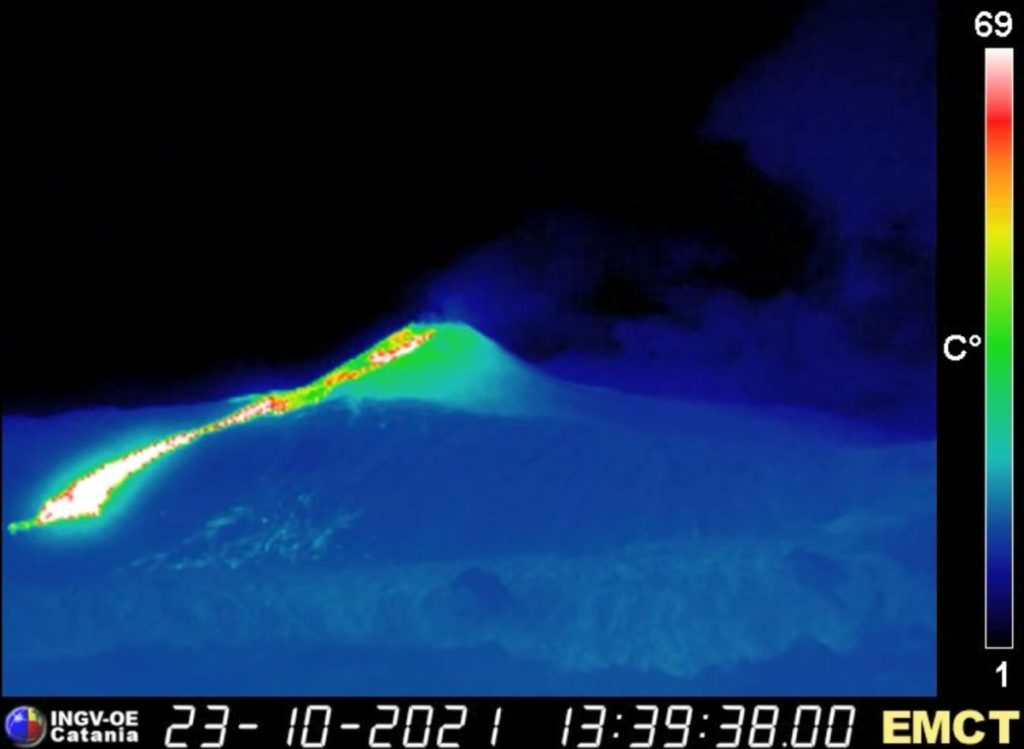
Lava flow directed towards the Valle del Bove, taken by the thermal surveillance camera in Monte Cagliato (east side of Etna), after the end of the paroxysmal activity on October 23, 2021.
Explosive activity began to wane around 10:00 UTC and essentially ended at 10:30 a.m., as landslides and hot material slides continued in the fracture formed in the southeast flank of the Southeast Crater. ; the lava flow emitted by the lower part of the fracture was still advancing on the western flank of the Valle del Bove, having reached an altitude of about 2300 m.
The cone of the Southeast Crater underwent important morphological changes during this paroxysm. While the summit seems to have grown further in height, the south-eastern flank is now cut by the deep niche from which the pyroclastic flows and the lava flow originate.
Source : INGV.
Photos : Guide Alpine Vulcanologiche Etna , INGV.
Hawaii , Kilauea :
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: WATCH
Current Aviation Color Code: ORANGE
Activity Summary:
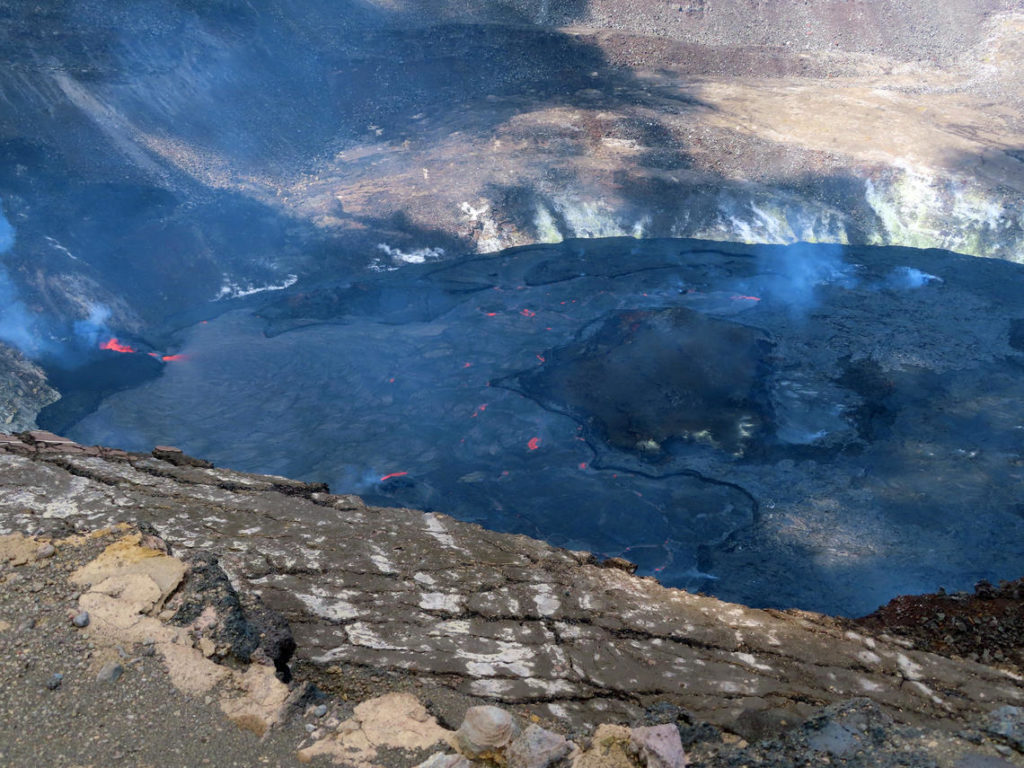
Kīlauea volcano is erupting. As of this morning, October 23, 2021, lava continues to erupt from a single vent in the western wall of Halemaʻumaʻu crater. All lava activity is confined within Halemaʻumaʻu crater in Hawai‘i Volcanoes National Park. Seismic activity and volcanic gas emission rates remain elevated.
Summit Observations:
Sulfur dioxide (SO2) emission rates remain high, with a preliminary emission rate for October 22, 2021, of approximately 3,200 tonnes per day. No significant changes seen in summit tilt or GPS observations. Earthquake activity remains below background and volcanic tremor remains elevated since the beginning of the eruption.
On October 19, 2021, the lava lake in Halema‘uma‘u crater—at the summit of Kīlauea—showed surface activity by crustal foundering, where warm lava flows on top of older, cooler surface crust that then sinks back into the lake. A 1 m (3 ft) high edge separates the active surface to the west from the stagnant surface to the east.
Halemaʻumaʻu Lava Lake Observations:
Lava continues to erupt from a single vent in the western wall of Halemaʻumaʻu crater. The western end of the lake showed a maximum elevation of approximately 792 meters (2598 ft) above sea level by HVO’s permanent laser rangefinder on October 24, 2021, which is the same as yesterday, and a total increase of about 48 meters (157 ft) since lava emerged on September 29. The total erupted volume since the beginning of the eruption was estimated to be about 19.9 million cubic meters (5.3 billion gallons) on October 15. Fountaining is generally confined to within the active western vent, with occasional bursts over the top as observed by field crews on October 23, 2021. The lava lake is not level across its surface due to the location of the vent in the western end. There is about 9 meters (30 feet) elevation difference between the active west and stagnant east part of the lake as measured by field crews on October 22, 2021. Field conditions precluded observation of this difference by field crews on October 23, 2021.
Source : HVO.
Photo : USGS / J. Schmith
Kamchatka , Sheveluch :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA)
Issued: October 24 , 2021
Volcano: Sheveluch (CAVW #300270)
Current aviation colour code: ORANGE
Previous aviation colour code: orange
Source: KVERT
Notice Number: 2021-126
Volcano Location: N 56 deg 38 min E 161 deg 18 min
Area: Kamchatka, Russia
Summit Elevation: 3283 m (10768.24 ft), the dome elevation ~2500 m (8200 ft)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
The activity of the volcano continues. Satellite data showed a gas-steam plume containing some amount of ash extending 33 km to the north-east from the volcano.
The extrusive eruption of the volcano continues. Ash explosions up to 10-15 km (32,800-49,200 ft) a.s.l. could occur at any time. Ongoing activity could affect international and low-flying aircra
Volcanic cloud height:
4000 m (13120 ft) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20211024/0310Z – Himawari-8
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 33 km (21 mi)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: NE / azimuth 51 deg
Time and method of ash plume/cloud determination: 20211024/0310Z – Himawari-8
Source : Kvert.
Photo : Tom Pfeiffer / VolcanoDiscovery.
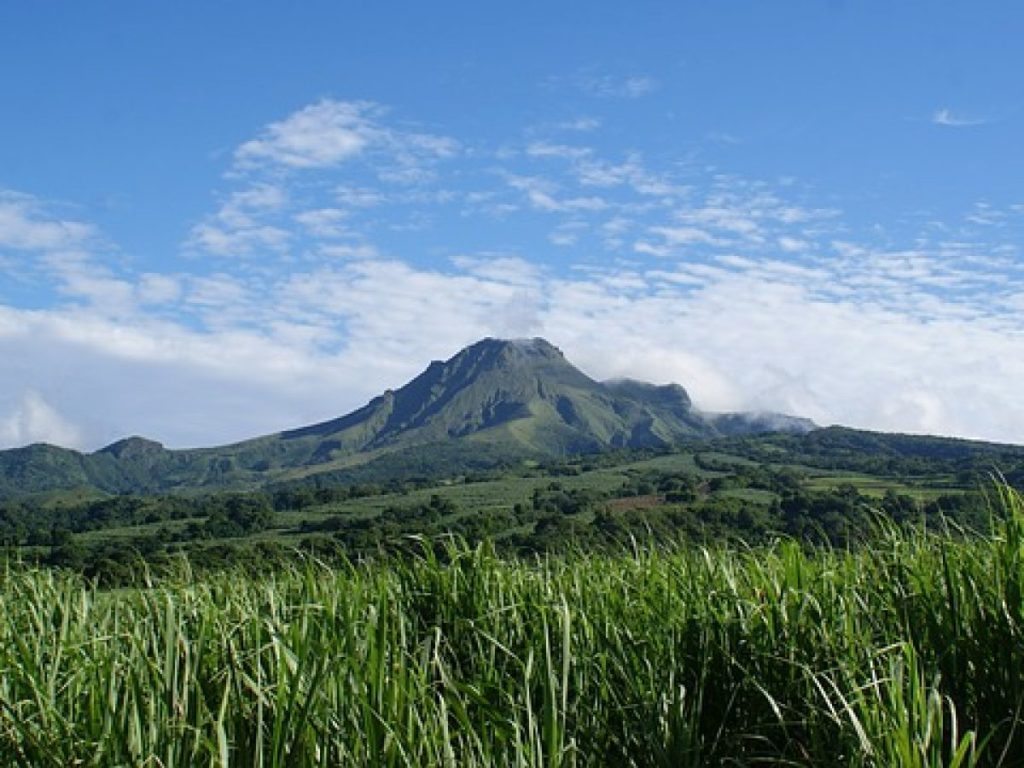
La Martinique , Mount Pelée :
Weekly report on the activity of Mount Pelée for the period from 01 to 08 October 2021.
Between October 15, 2021 at 4 p.m. (UTC) and October 22, 2021 at 4 p.m. (UTC), OVSM recorded at least 44 volcano-tectonic earthquakes of magnitude less than or equal to 0.1. These earthquakes were located inside the volcanic edifice between 1 km and 0.1 km below the surface. None of these earthquakes were felt by the population. This volcano-tectonic-type superficial seismicity is associated with the formation of micro-fractures in the volcanic edifice.
A degassing zone at sea was detected at shallow depth (between St Pierre and le Prêcheur). The IGP is currently setting up experiments to map this gas emanation zone, carry out physicochemical measurements of the fluids and samples of these fluids in order to understand the origin of this degassing and to assess its possible relationship. with the hydrothermal system of Mount Pelée. This kind of manifestation is frequent on active or not active underwater volcanic sites. The analyzes underway by the OVSM-IPGP will make it possible to determine the possible relationship of this underwater degassing with the activity of Mount Pelée recorded by the OVSM since 2019.
A main area of heavily degraded vegetation is still observed on the southwest flank of Mount Pelée, between the upper Claire River and the Chaude River.
The alert level remains YELLOW: vigilance.
Source : Direction of OVSM IPGP.
Photo : Antilles prestige










No comment yet, add your voice below!