
May 30 ,2021.
Democratic Republic of Congo , Nyiragongo :
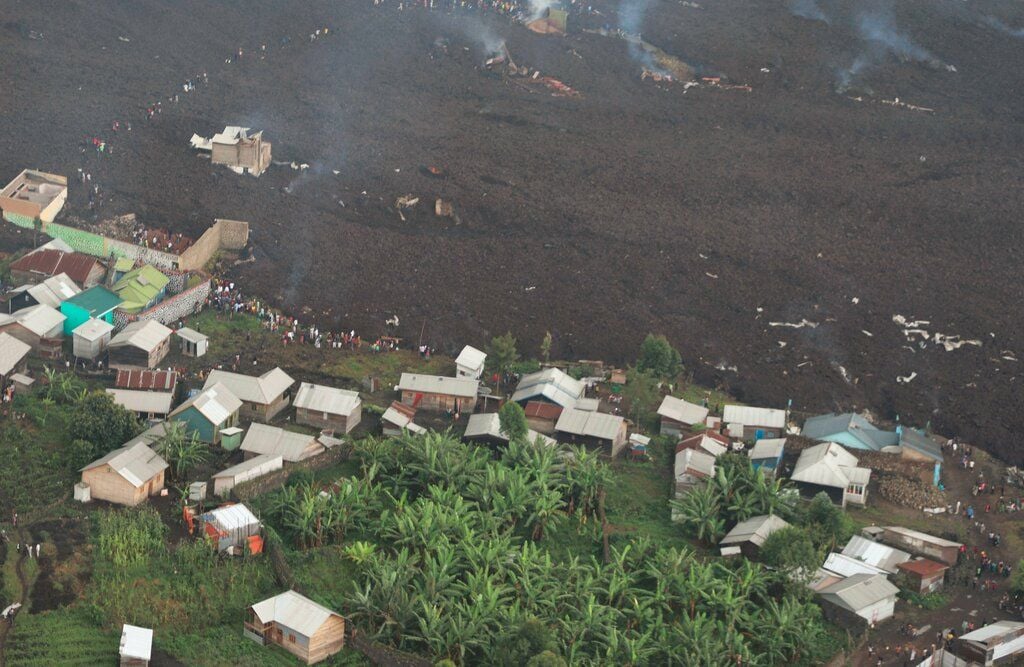
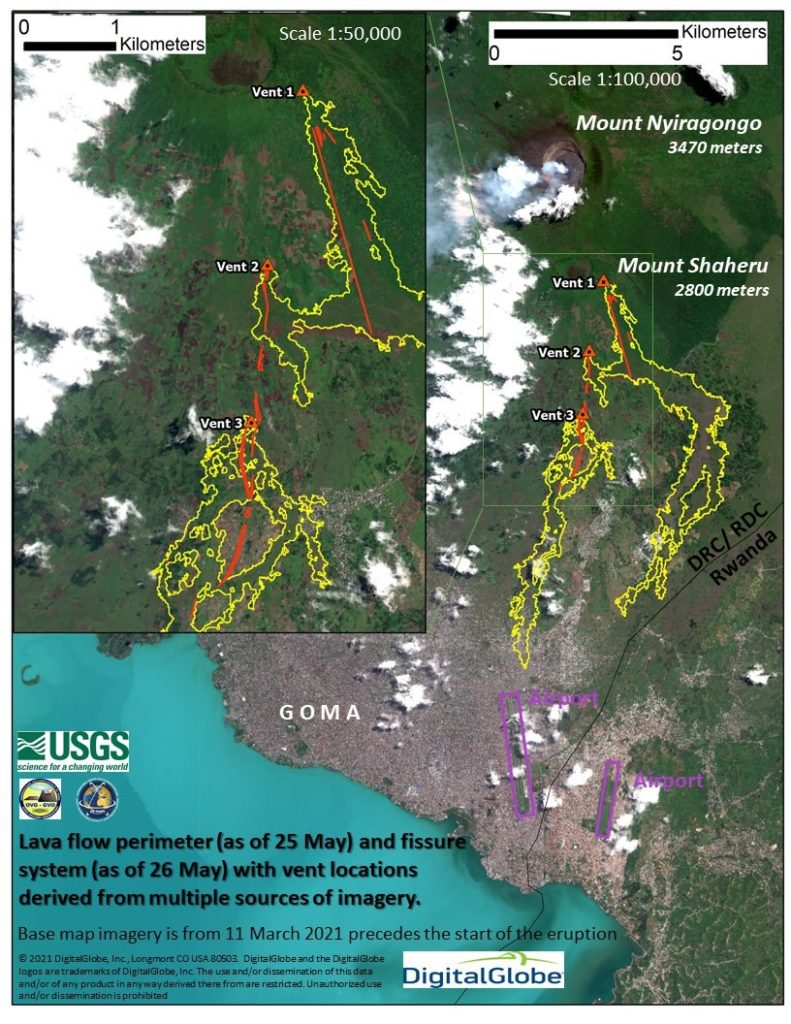
At around 1815 on 22 May seismicity at Nyiragongo spiked, around the same time observers reported at least two fissures opening on the lower S flanks, NW of Kibati (8 km SSE) and Rukoko (10 km S). Lava from the first fissure, originating near the Shaheru crater, flowed E over a major road (N2) and then S. The second fissure produced lava flows that traveled S, overtaking and setting fire to many houses and structures in communities north of Goma, just W of Monigi (12 km S). Video posted on social media showed lava fountaining from the fissures, a glowing red sky, and residents running through the streets. About 1,000 homes and buildings were destroyed and about 25,000 people were displaced. The lava cut off electricity and water supplies to some areas. The flow may have been as wide as 1 km and stopped 1.25 km from the Goma International Airport, in the SE part of the city, during 22-23 May. According to the Toulouse VAAC ash plumes may have initially rose to 13.7 km (45,000 ft) a.s.l., though subsequent estimates put the ash plumes mostly at 6.1-9.1 km (20,000-30,000 ft) a.s.l. during 22-23 May. Satellite images and local scientists indicated that the summit lava lake had drained before the flank fissures had opened, but began refilling afterward; collapses in the summit crater were the likely cause of the ash plumes.
The lava flows stopped in the village of Buhene on the outskirts of Goma City. An aerial photo shows that part of the lava spit, about 50 m wide and spanning several hundred meters, resurfaced and wiped out part of the inhabited area.
Initial reports indicated that about 32 people had died: about 12 from lava and gas asphyxiation while crossing lava flows, and most of the rest from accidents while fleeing. Several people, including many children, remained missing, though families were continuing to be reunited
Map showing 4 day old lava flows (yellow) and the fissure and vent system (red) associated with the May 22-23 flank eruption of Nyiragongo, DRCongo. Interestingly, these source flows, cracks and vents are similarly aligned with the rift zone of the 2002 eruption. Created by the Volcano Disaster Assistance Program.
Seismic data during 22-24 May showed events seemingly propagating from the summit area to the S into Lake Kivu. Several strong earthquakes shook buildings in Goma, causing some to collapse and injure people; a news article noted that tremor was felt about every 30 minutes beginning around noon on 23 May. Both airports in Goma closed for security reasons. A M 5.1 earthquake with a hypocenter beneath Lake Kivu was recorded at 1037 on 24 May. The VAAC noted that ashfall around the volcano and in surrounding towns was visible in satellite data. Cracks a few 10s of centimeters wide opened in different parts of the city on 25 May. The cracks stretched for several hundred meters from the northern city limit down to the lake, and were nearly 100 m long near the airport. Some cracks were hot and emitting gasses, and some were flaming. Ash plumes rose to 6.1 km (20,000 ft) a.s.l. and drifted S; ground-based reports indicated ash in the atmosphere above Goma. Seismicity remained intense on 25 May with more than 130 earthquakes between M 2 and 5 recorded in a 24-hour period. News reports indicated hundreds of damaged buildings in neighboring Rwanda.
May 28 , 2021 : Current seismicity and ground deformation data continue to indicate the presence of magma under the urban area of Goma with an extension under Lake Kivu. In the last 24 hours, seismicity, although less felt by the population, remains high, with hundreds of events per day still being detected by the OVG. In view of these results, we can expect the tremors to continue in the coming days. The location of these events seems to have stopped its progression towards the South but remains localized under Lake Kivu. Surface deformations are still recorded by the GPS network. These observations are consistent with the presence of magma at depth. Ash fallout may occur as a result of the collapse of parts of the crater. Data on the stability of Lake Kivu currently show no significant change.
Source : GVP , Georiska .
Photo : MONUSCO @MONUSCO / twitter / OVG , Volcano Disaster Assistance Program ,
Video : Anthony Caere
Alaska , Great Sitkin :
52°4’35 » N 176°6’39 » W,
Summit Elevation 5709 ft (1740 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
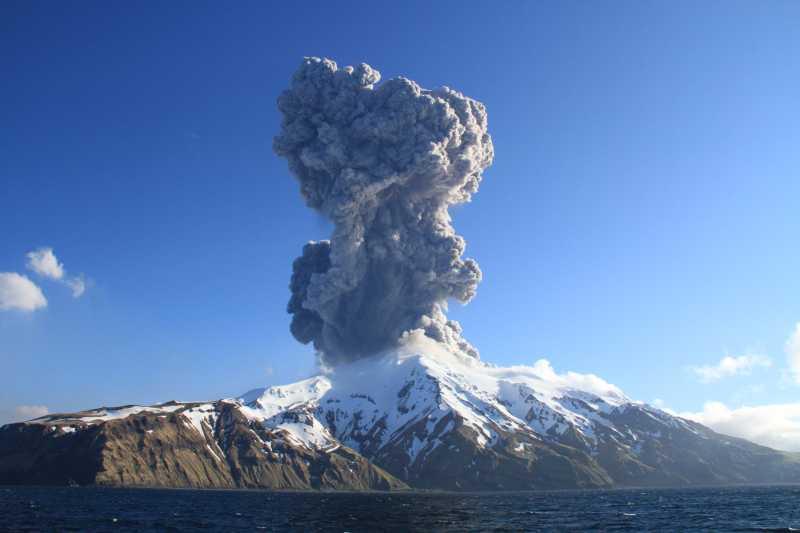
A short-duration explosive event occurred on May 25 AKDT (May 26 UTC) following a day-long increase in local seismic activity. The Aviation Color Code and Volcano Alert Level was increased to ORANGE/WATCH on May 25 at 7:43 PM AKDT (03:43 UTC on May 26) in response to the elevated seismic activity as well as observations of robust steaming, sulfur dioxide gas emissions, and elevated surface temperatures observed the previous week. A 1–2 minute-long explosive event occurred on May 25 at 9:04 PM AKDT (05:04 UTC on May 26) and the Aviation Color Code and Volcano Alert Level were increased to RED/WARNING. The ash cloud rose to an altitude of ~15,000 ft above sea level and drifted eastward over the Bering Sea. This event did not result in ashfall on local communities. Following the explosion, seismic activity decreased greatly, and satellite observations showed no additional ash emissions. As a result of this marked decrease in activity the Aviation Color Code and Volcano Alert Level were decreased to ORANGE/WATCH on May 26 at 8:31 AM AKDT (16:31 UTC) and to YELLOW/ADVISORY on May 27 at 12:58 PM AKDT (20:58 UTC). Seismicity remains at low levels and satellite observations show no additional activity.
Eruption plume of Great Sitkin volcano captured by Lauren Flynn (USFWS) from the R/V Tiglax on the evening of May 25, 2021 at 2106 HADT.
The prognosis for renewed eruptive activity is uncertain. Additional explosive events, the eruption of lava, or a return to non-eruptive behaviors are all possible. AVO will report on significant changes and observations in monitoring data should they occur.
Great Sitkin is monitored with a local real-time seismic network, which will typically allow AVO to detect changes in unrest that may lead to an explosive eruption. Rapid detection of an ash-producing eruption would be accomplished using a combination of seismic, infrasound, lightning, and satellite data.
Source : AVO.
Photo : Flynn, Lauren
Saint Vincent , Soufrière Saint Vincent :
La Soufriere Volcano – SCIENTIFIC UPDATE May 27 , 2021 , 6:00PM .
– Seismic activity at La Soufrière, St Vincent has remained low since the tremor associated with the explosion and ash venting on 22 April.
– In the last 24 hours, only a few long-period and volcano-tectonic earthquakes have been recorded.
– Persistent steaming is observable from the observatory once the cloud cover is high enough and thermal anomalies continue to be detected by the NASA FIRMS alert system. These have been persistent since the 22 April explosion.
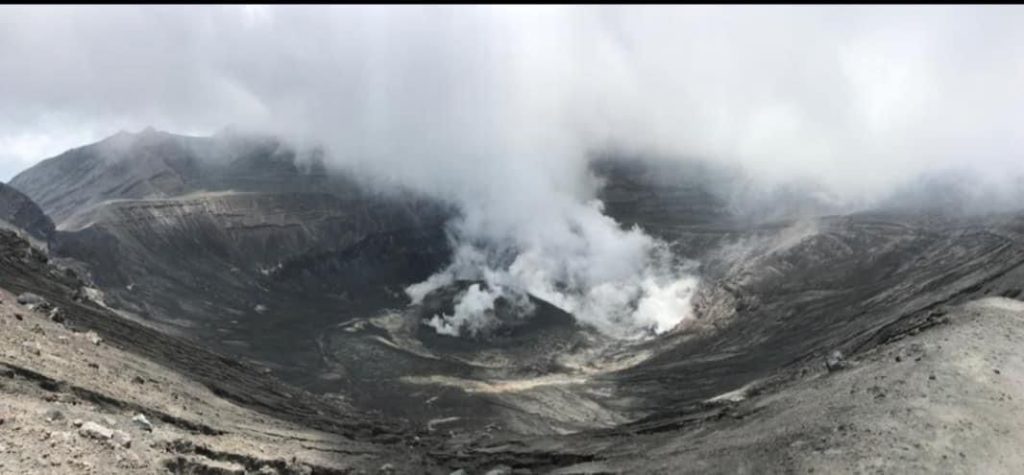

– Thermal anomalies indicate that there is a source of heat within the crater and are most likely from a small body of magma left over, close to the floor of the Summit Crater.
– Measurements of the sulphur dioxide(SO2) flux at La Soufrière were carried out by boat off the west coast on 25 May and 27 May.
– Several traverses were completed and yielded an average SO2 flux of 464 and 242 tons per day, respectively. SO2 can be an indicator that fresh magma from a deeper source is being degassed.
– The volcano continues to be in a state of unrest. Escalation in activity can still take place with little or no warning.
– The volcano is at alert level ORANGE.
Source et photo : UWI
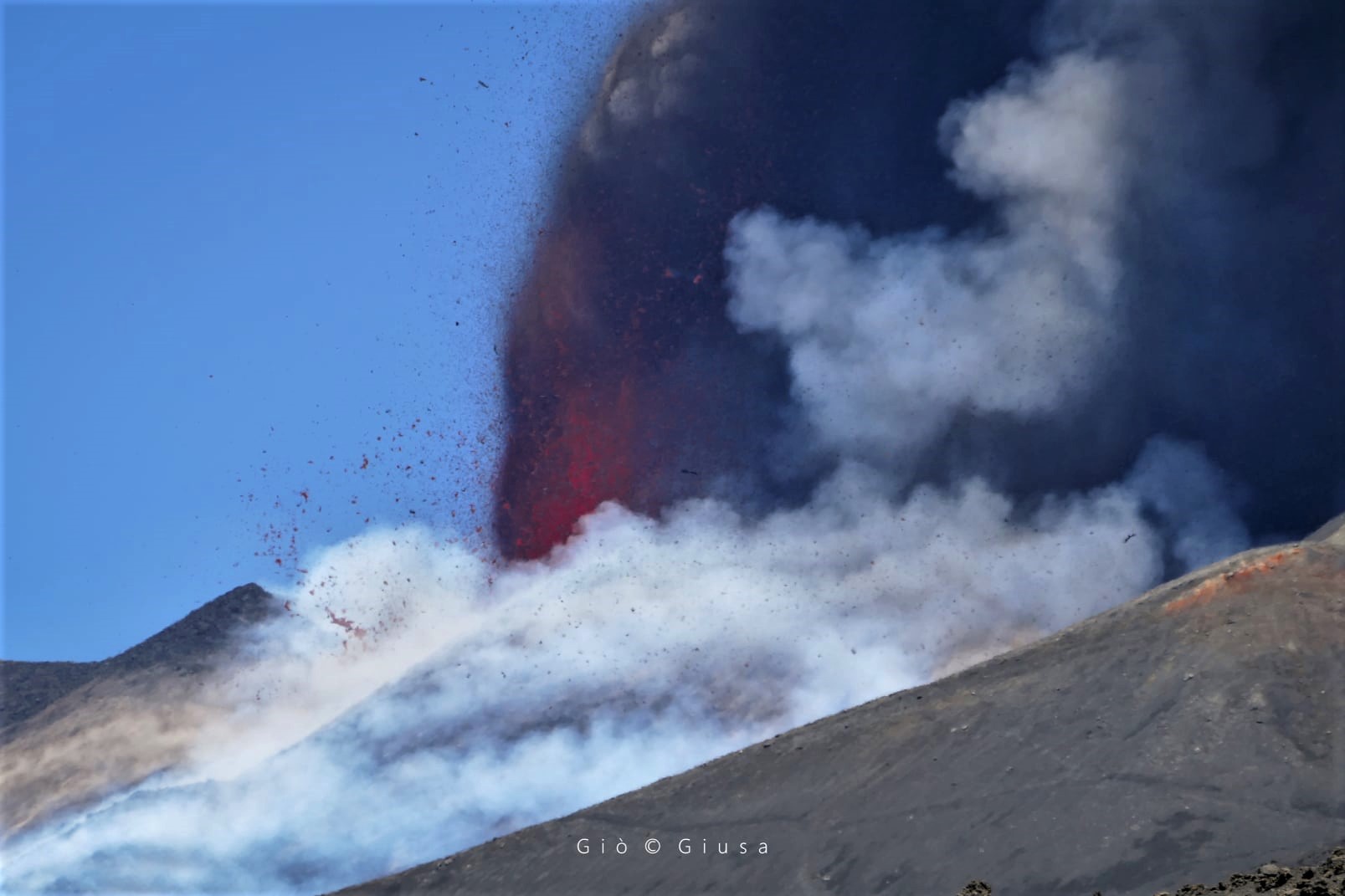
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
Press release on ETNA’s activity, May 30, 2021, 06:00 (04:00 UTC):
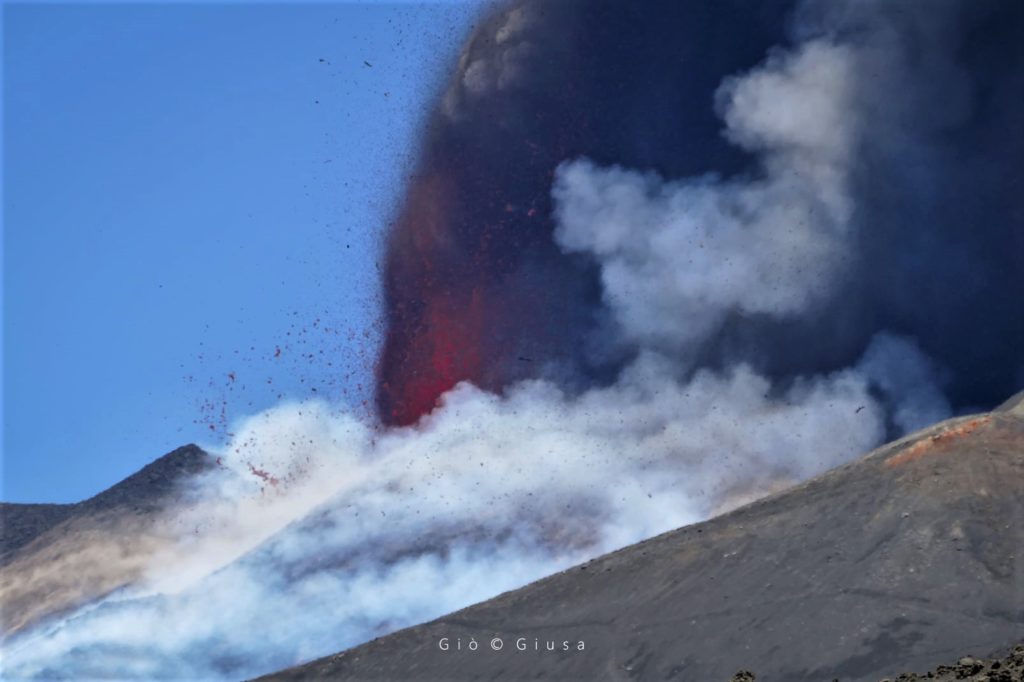
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Osservatorio Etneo, announces that from 03:45 UTC we observe a resumption of Strombolian activity at the Southeast Crater.
From around 01:10 UTC, there is a gradual increase in the average amplitude of the volcanic tremor whose values reached high levels around 03:30 UTC. The center of gravity of the sources of the volcanic tremor is located in the region of the Southeast Crater at an altitude of about 2900 m s.l.m.
From approximately 03:40 UTC, an increase in infrasonic activity is observed.
Analysis of the soil deformation data shows the onset of a very weak disturbance at some stations of the inclinometric network around 03:30 UTC. No significant modifications to the stations of the GNSS network.
Press release on ETNA’s activity, May 30, 2021, 06:40 (04:40 UTC):
The National Institute of Geophysics and Volcanology, Etneo Observatory, announces that a lava fountain is underway in the Southeast Crater. Based on the forecast model, the eruptive cloud produced by the current activity disperses to the Southeast.
The amplitude of the volcanic tremor has reached very high levels and, at the same time, we observe the appearance of infrasound tremor, both located in the area of the Southeast Crater.
The analysis of the deformations of the ground shows, from 04:00, an increase in the disturbance of the inclinometric signals. There are no significant changes to the GNSS network.
Further updates will be communicated shortly
Source : INGV.
Photo : Gio Giusa (26/05) .
Chile , Nevados of Chillan :
Special Report on Volcanic Activity (REAV), Ñuble region, Nevados de Chillán volcanic complex, May 27, 2021, 1:30 p.m. local time (Continental Chile).
The National Service of Geology and Mines of Chile (Sernageomin) publishes the following PRELIMINARY information, obtained thanks to the monitoring equipment of the National Volcanic Monitoring Network (RNVV), processed and analyzed in the Volcanological Observatory of the Southern Andes ( Ovdas):
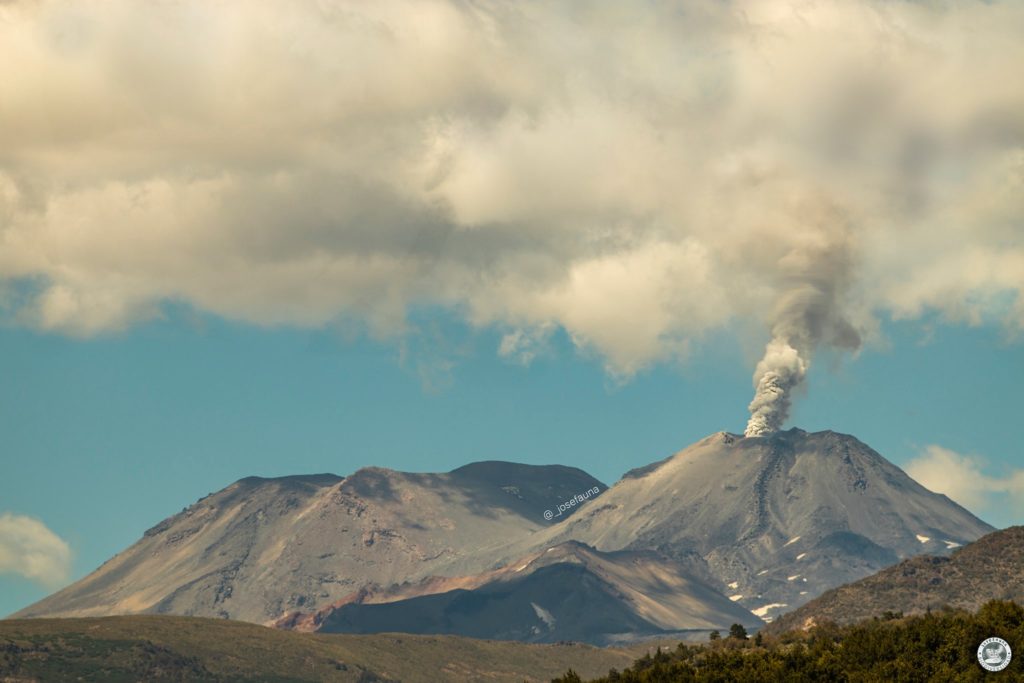
On Thursday, May 27, at 1:10 p.m. local time (5:10 p.m. UTC), monitoring stations installed near the Nevados de Chillán volcanic complex recorded an explosion associated with fluid dynamics in the volcanic system, with gas emission and projections particulate.
The characteristics of the earthquake after its analysis are as follows:
TIME OF ORIGIN: 1:10 p.m. local time (5:10 p.m. UTC)
LATITUDE: 36.867 ° S
LONGITUDE: 71.372 ° W
DEPTH: 1.1 km
REDUCED DISPLACEMENT: 530 (cm2)
ACOUSTIC SIGNAL: 4.4 Pa reduced to 1 km.
The characteristics associated with surface activity are as follows:
MAXIMUM HEIGHT OF THE COLUMN: 260 m above the point of emission.
DIRECTION OF DISPERSAL: East-South-East.
The volcanic technical alert remains at the Yellow level.
Source : Sernageomin .
Photo : Josefauna.








No comment yet, add your voice below!