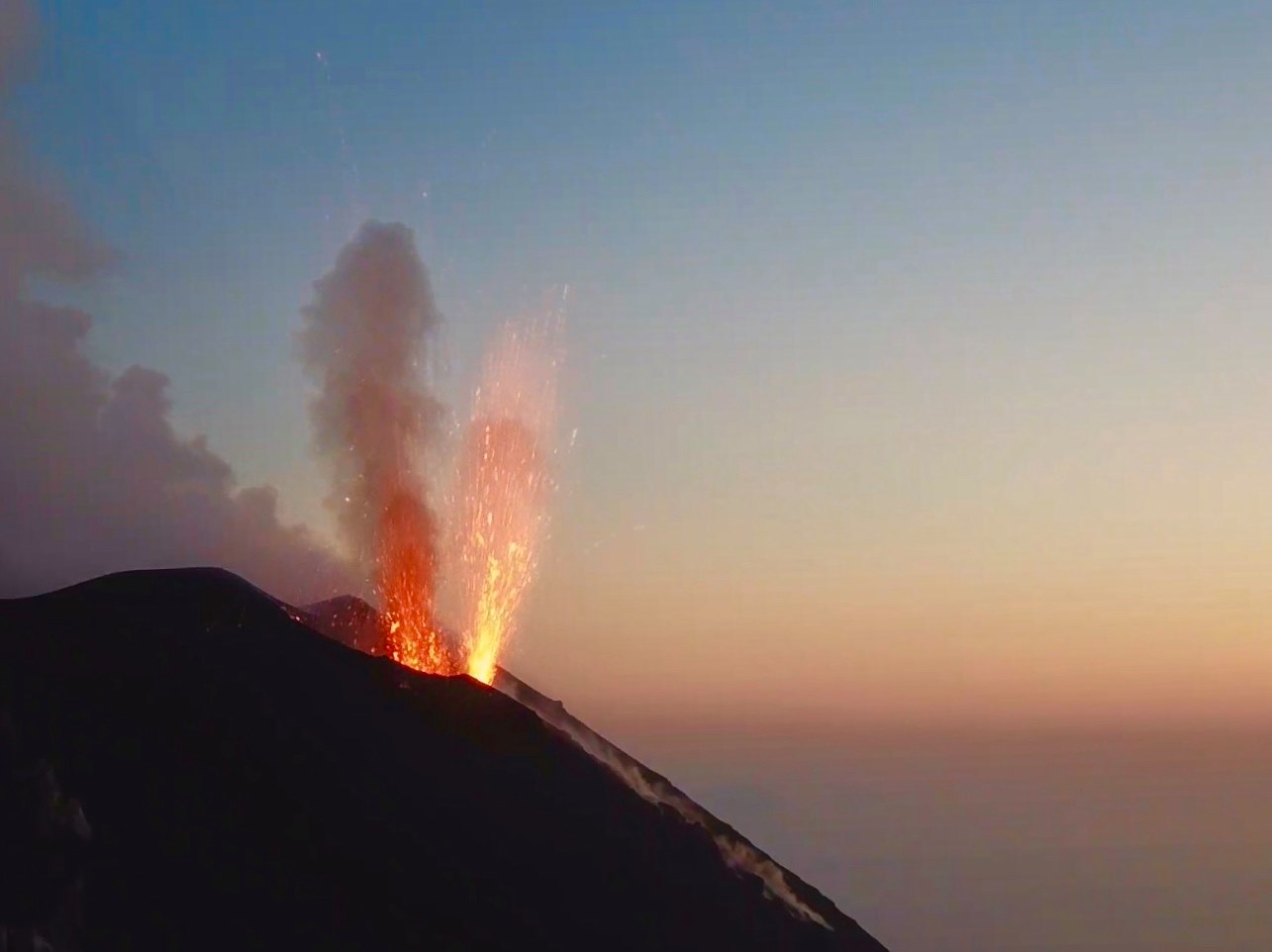

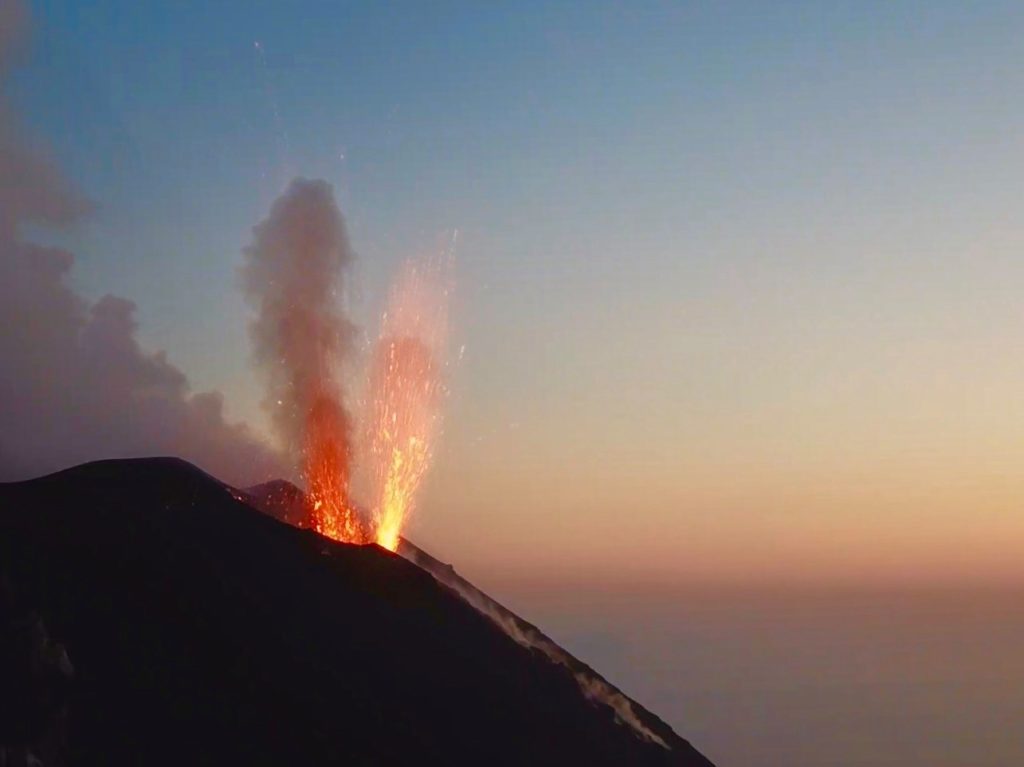
July 15 , 2020.
Italy , Stromboli :
Weekly bulletin, from July 06, 2020 to July 12, 2020, (issue date July 14, 2020)
SUMMARY OF ACTIVITY STATUS
In light of the monitoring data, it is emphasized:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: During this period, normal explosive activity of the Strombolian type was observed, accompanied by degassing and splashing activities. The total average daily hourly frequency of explosions fluctuated between average values between 10 and 16 events / h with an intensity of medium to low explosions in the areas of the North and Center-South crater.
2) SEISMOLOGY: The seismological parameters do not show significant variations.
4) DEFORMATIONS: The island’s soil deformation monitoring networks did not show any significant variation to report for the period considered.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: the flow of SO2 is at a medium-low level
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity in the upper zone is at a medium-low level.
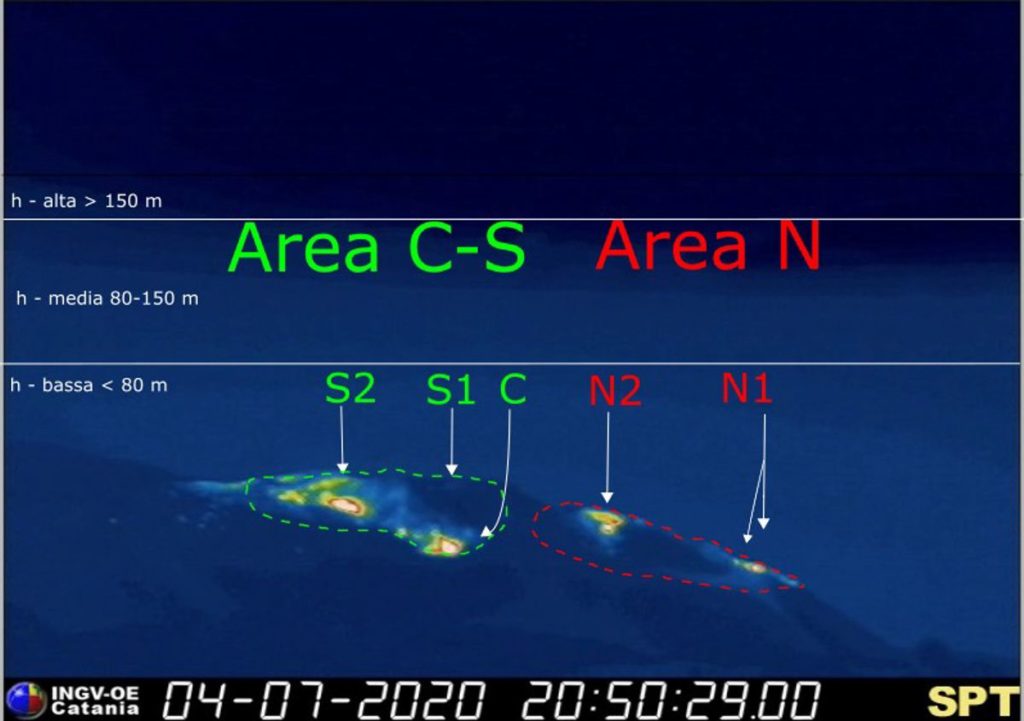
The crater terrace seen by the thermal camera located on Pizzo sopra la Fossa with the delimitation of the crater zones of the Center-South and North zones (ZONE N, ZONE C-S respectively).
Abbreviations and arrows indicate the names and locations of the active vents, the area above the crater terrace is divided into three height ranges related to the intensity of the explosions.
During the observation period, the eruptive activity of Stromboli was characterized by the analysis of images recorded by the INGV-OE surveillance cameras (Punta dei Corvi, altitude 190m, 400 m and Pizzo). The explosive activity was mainly produced by 3 (three) eruptive vents located in the area of the North crater and by 3 (three) eruptive vents located in the area of the Center-South crater. All the mouths are placed inside the depression which occupies the terrace of the crater. Due to the unfavorable weather conditions of July 6 and 7, the description of the explosive activity is limited.
Explosive activity in the North and Center-South zones produced moderate explosions of coarse material (lapilli and bombs) mixed with fine materials (ash) whose frequency and intensity of occurrence decreased during the week .
SEISMICITY:
Last week, 11 seismic signals were recorded which may be associated with small-scale landslides.
The amplitude of the volcanic tremor had medium-low values.
Source : INGV
Photos : INGV .
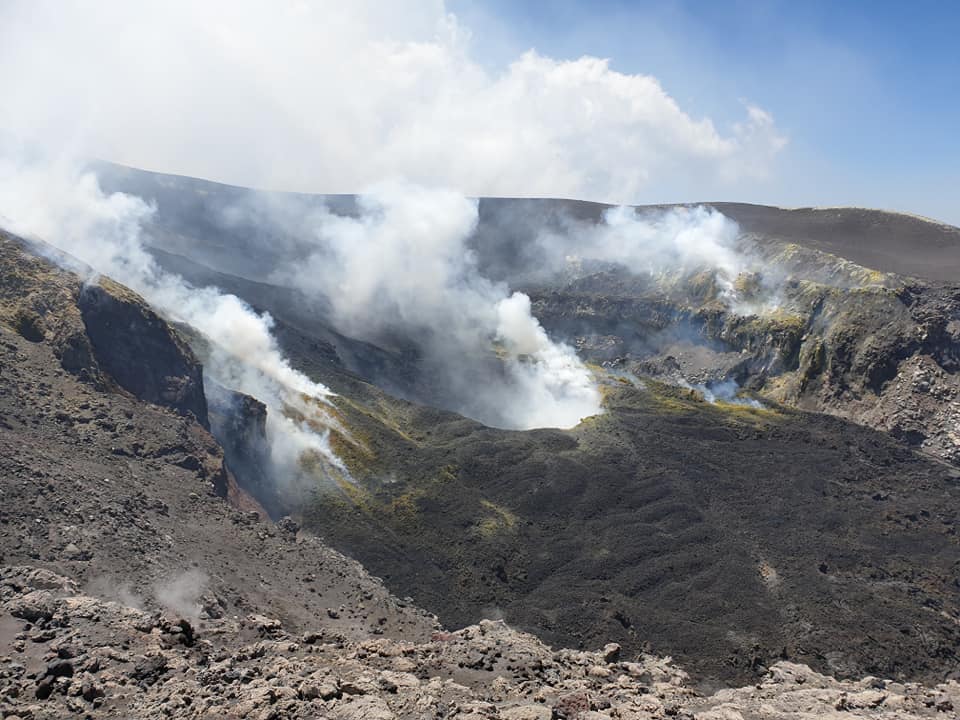
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
Weekly bulletin, from July 06, 2020 to July 12, 2020, (issue date July 14, 2020)
SUMMARY OF ACTIVITY STATUS
In light of the monitoring data, it is emphasized:
1) VOLCANOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS: Strombolian activity of the New Southeast Crater, of the Voragine Crater, with sporadic impulsive explosive activity with emission of ash and lithic material. Activity in the northeast crater was characterized by rapid and repeated gas emissions to the bottom of the crater. Finally, the Bocca Nuova presented a normal degassing.
2) SEISMOLOGY: Absence of seismic fracturing activity with Ml> = 2.0; decrease in the average amplitude of the volcanic tremor.
3) INFRASOUND: Modest infrasound activity.
4) DEFORMATIONS: The Etna soil deformation monitoring networks did not show any significant changes last week.
5) GEOCHEMISTRY: the flow of SO2 is at a medium-low level.
6) SATELLITE OBSERVATIONS: The thermal activity in the upper zone is at a medium-low level.
During the week, the volcanic activity of the upper craters of Etna was monitored by analyzing images from the network of surveillance cameras from the INGV section of Catania, Etneo Observatory (INGV-OE) and through inspections carried out by INGV-OE staff, from 8 to 10 July.
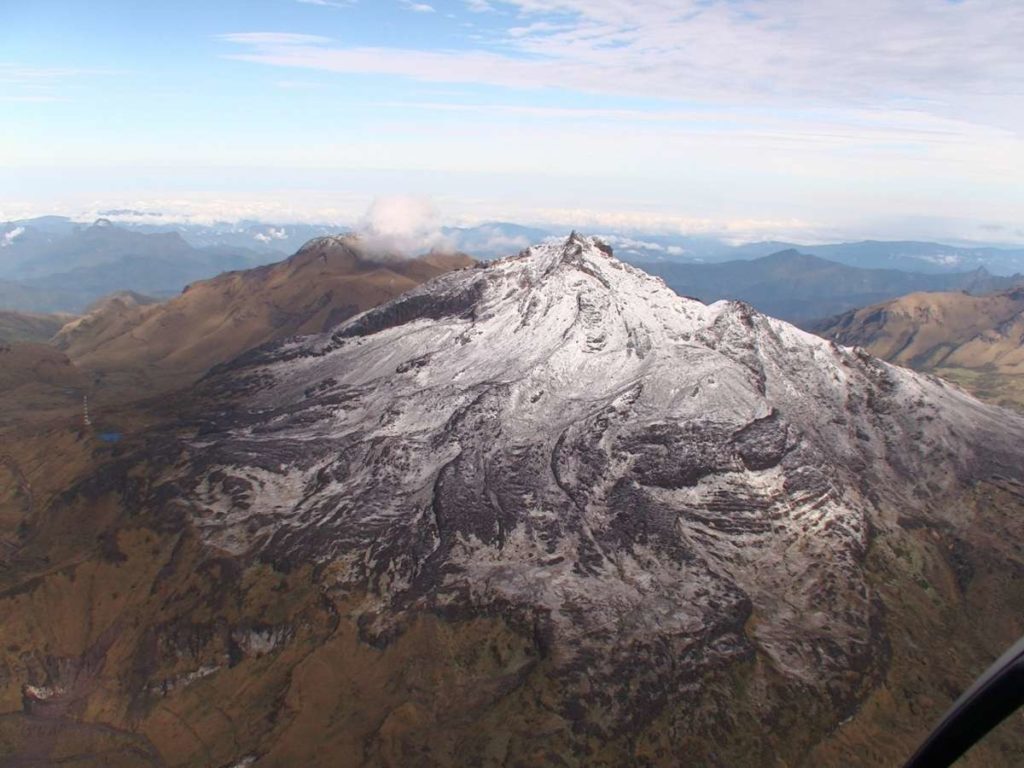
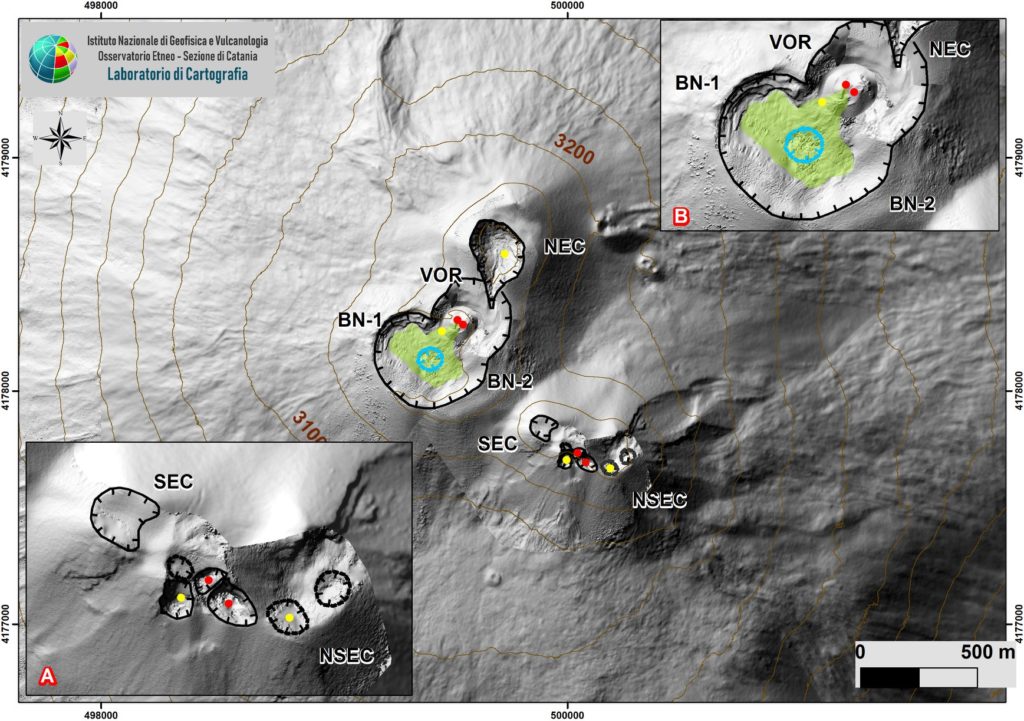
Map of the Etna summit area updated to May 9, 2020 by the drone group INGV-OE on DEM 2014, developed by the Air physics laboratory section Rome 2. System details are displayed SEC -NSEC (A) and craters BN and VOR (B). For the meaning of the symbols, see the text.
During the period under review, the upper craters were mainly characterized by degassing activities. Strombolian activity in the New Southeast Crater (NSEC) during this period increased with emissions of lava shreds which fell near the edge of the crater. In addition, observations made during the inspection from July 8 to 10 showed that a collapse crater formed at the center of the depression of the Bocca Nuova crater, affected by modest degassing from the bottom. Voragine sometimes presented a low ash emission with sporadic impulsive explosive activity with emissions of ash and lithic materials.
Finally, intra-crater activity was observed in the northeast crater with rapid and repeated gas emissions, audible from the edge of the crater.
Volcanic tremors:
During the week in question, the average amplitude of volcanic tremor remained at high levels until 10 p.m. UTC on July 8, when a drop caused the amplitude level to vary from high to medium. The sources of the volcanic tremor were located near the area of the New Southeast Crater at a depth of about 2900-3000 m above sea level
Source : INGV.
Photo : Cratère Central , Alessandro Bonforte et Emanuela De Beni.
Guatemala , Fuego :
SPECIAL VOLCANOLOGY BULLETIN, BEFGO # 45-2020.
Type of activity: Vulcanienne
Morphology: composite stratovolcano
Location: 14 ° 28’54˝Latitude N; 90 ° 52’54˝Longitude W.
Height: 3763 m above sea level.
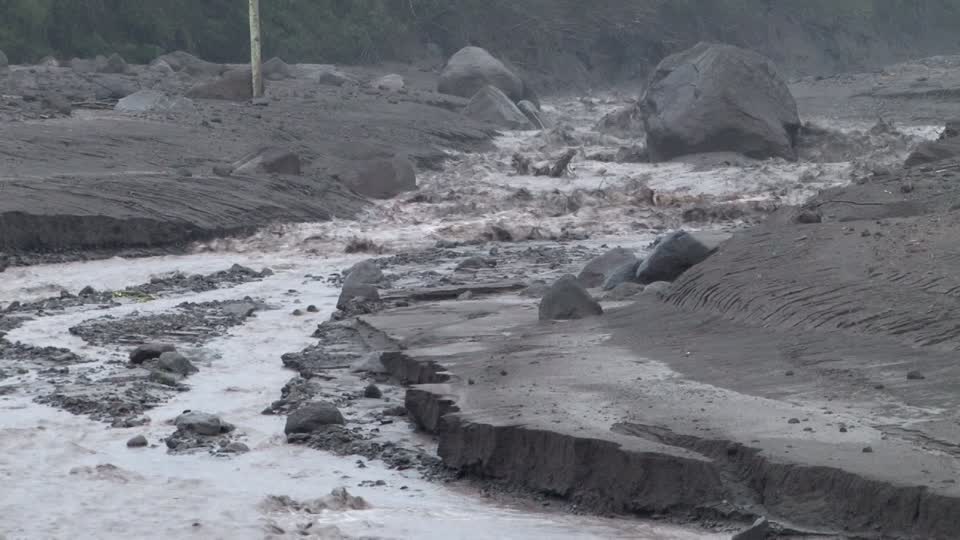
LAHAR IN HONDA AND CENIZA RAVINES.
The INSIVUMEH seismic network located on the Fuego Volcano records high-frequency seismic tremors, generated by volcanic materials which descend through the Honda and Ceniza ravines, located respectively in the Southeast and Southwest. These lahars have weak to moderate characteristics and are generated by the rain that is currently occurring near the volcanic building.
Heavy rains in the upper part of the volcanic complex can generate the descent of larger lahars in these volcano ravines or in others. Lahars can transport tree branches and volcanic materials such as ash and blocks 1 to 2 meters in diameter that vibrate the ground. If the rain persists, the generation of a greater number of lahars is not excluded. Pay particular attention to the canyons mentioned during the night and early morning.
Source : Insivumeh.
Colombia , Chiles / Cerro Negro :
Weekly activity bulletin of Chiles and Cerro Negro volcanoes
Volcanic activity continues at the YELLOW LEVEL ■ (III): CHANGES IN THE BEHAVIOR OF VOLCANIC ACTIVITY.
According to the monitoring of the activity of VOLCANS CHILE AND CERRO NEGRO, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE (SGC) reports that:
During the period evaluated between July 7 and July 13, 2020, the seismicity in the Chiles – Cerro Negro volcano region recorded an increase in both the number of events and their energy, compared to the previous period. The predominance of events associated with the fracture of the rock is maintained, which were located preferentially towards the South and the Southeast of the Chiles volcano, at distances up to 13 km, with depths less than 11 km compared to the height of its summit (4700 m) and a maximum local magnitude of 2.3 on the Richter scale.
An earthquake of ML 2.3 was recorded on July 10 at 10.38 am, at a distance of 13 km southeast of the Chiles volcano and at a depth of 8 km. No reports of felt earthquakes were received.
The changes recorded by one of the volcanic deformation sensors have continued since May 2019. The other volcanic monitoring parameters did not show significant variations and no manifestation of surface activity was observed.
Source : SGC.
Photo : hablemosdevolcanes.com.
Chile , Nevados of Chillan :
Special report of volcanic activity (REAV), Region of Ñuble, volcanic complex of Nevados de Chillán.
July 14, 2020 at 3:40 p.m. local time (mainland Chile).
The National Geological and Mining Service of Chile (Sernageomin) publishes the following PRELIMINARY information, obtained thanks to the surveillance teams of the National Volcanic Surveillance Network (RNVV), processed and analyzed at the South Andean Volcanological Observatory (Ovdas):
Yesterday Tuesday, July 14 at 3:17 p.m. local time (7:17 p.m. UTC), the monitoring stations installed near the Nevados de Chillán Volcanic Complex recorded an earthquake associated with rock fracturing (Volcano-Tectonics).
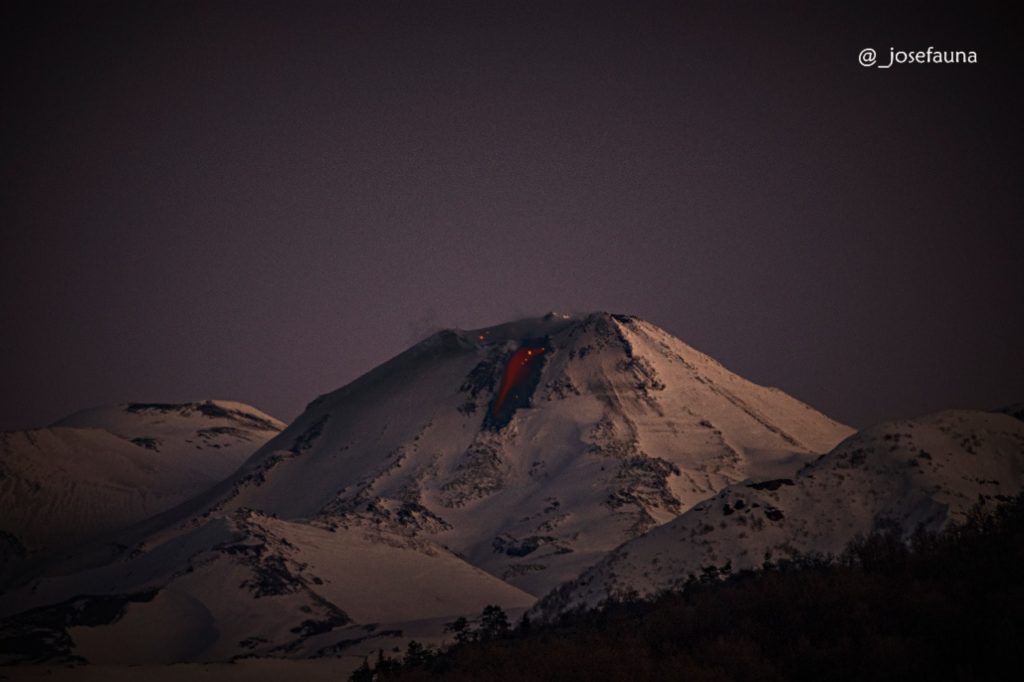
View from the Caracol sector, San Fabián de Alico, Ñuble.
Long exposure photograph captured at approximately 8:30 p.m., where the flow of incandescent lava is observed which continues to descend slowly along the north slope of the volcanic building, at a rate or a speed of the order of 0.2 m3 / s, as indicated by the Sernageomin.
The characteristics of the earthquake after its analysis are as follows:
TIME OF ORIGIN: 3:17 p.m. local time (7:17 p.m. UTC)
LATITUDE: 36 874 ° S
LENGTH: 71,406 ° W
DEPTH: 2.7 km
LOCAL MAGNITUDE: 3.2 (ML)
OBSERVATIONS:
No surface activity related to the reported event is recorded. At the time of publication of this report, no opinion had been given by neighboring communities on the perception of this earthquake.
The volcanic technical alert remains at the YELLOW level.
Source : Sernageomin .
Photo : Josefauna.









No comment yet, add your voice below!