
January 03 , 2019.
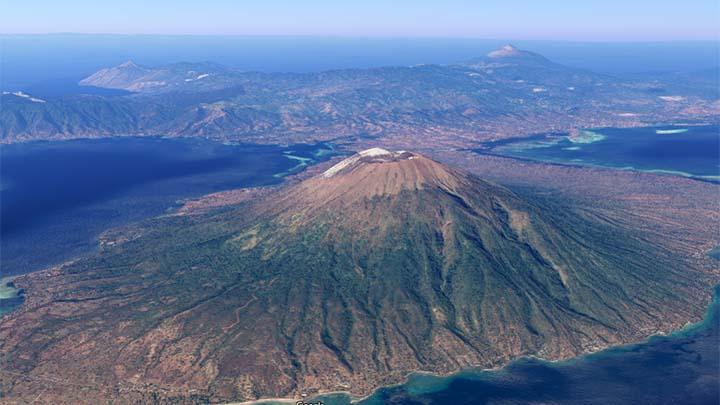
Indonesia , Lewotolok :
Seismicity, Ile Lewotolok Volcano on Alert Status .
The officers at the Ile Lewotolok Volcano Observation Post, Lembata regency, East Nusa Tenggara, set the status of the mountain to be in alert » WASPADA » after repeated seismic activity.
The Ile Lewotolok Volcano monitoring officer Yeremias Kristianto Pugel, in his report received by Antara in Kupang, Wednesday, January 2, said that the increase in status had occurred since Sunday, December 30.
“Until now, the status is still alert,” he said when contacted from Kupang.
Yeremias appealed to the public, visitors, climbers, and tourists around Ile Lewotolok Volcano not to be around the mountain area. At present, climbing activities have been banned. The residents were asked to be more than 2 kilometers from the summit or center of mountain activity.
The Head of the Regional Disaster Management Agency (BPBD) NTT Tini Thadeus said that he had received information about the status of the mountain.
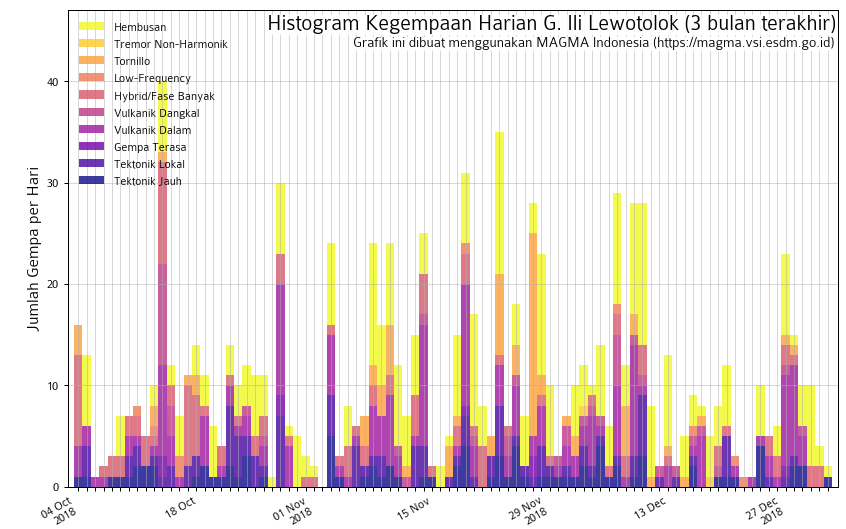
Tini said, since December 29, seismographs on Mount Lewotolok noted four earthquake gusts, one shallow earthquake, three times deep volcanic earthquakes, and two distant tectonic earthquakes.
Tini expects residents or visitors to follow the ban from mountain monitoring post officials.
“We also ask residents under the foot of the mountain to be more alert,” he said.
The Ile Lewotolok volcano, which has a height of 1423 meters, is a very active mountain.
The volcano observatory raised the alert status of the volcano to 2 (« Waspada » on the Indonesian 1-4 scale), as an increase of volcanic earthquakes and fumarolic activity had been observed during the past week.
The observatory reported a light steam / gas plume rising approx. 500 m above the summit crater of Lowotolok. Since 29 December, the seismic network detected 4 earthquake swarms, one shallow and 3 deeper volcanic earthquakes. This could indicate magma intrusions under the volcano, which could (but not must) lead to a new eruption of the volcano in a near to medium-term future (weeks to months).
Residents as well as visitors and climbers are advised to keep a safety distance of 2 km from the crater. At present, climbing activities have been banned, and residents should remain on alert.
Source : TEMPO.CO, Volcanodiscovery.
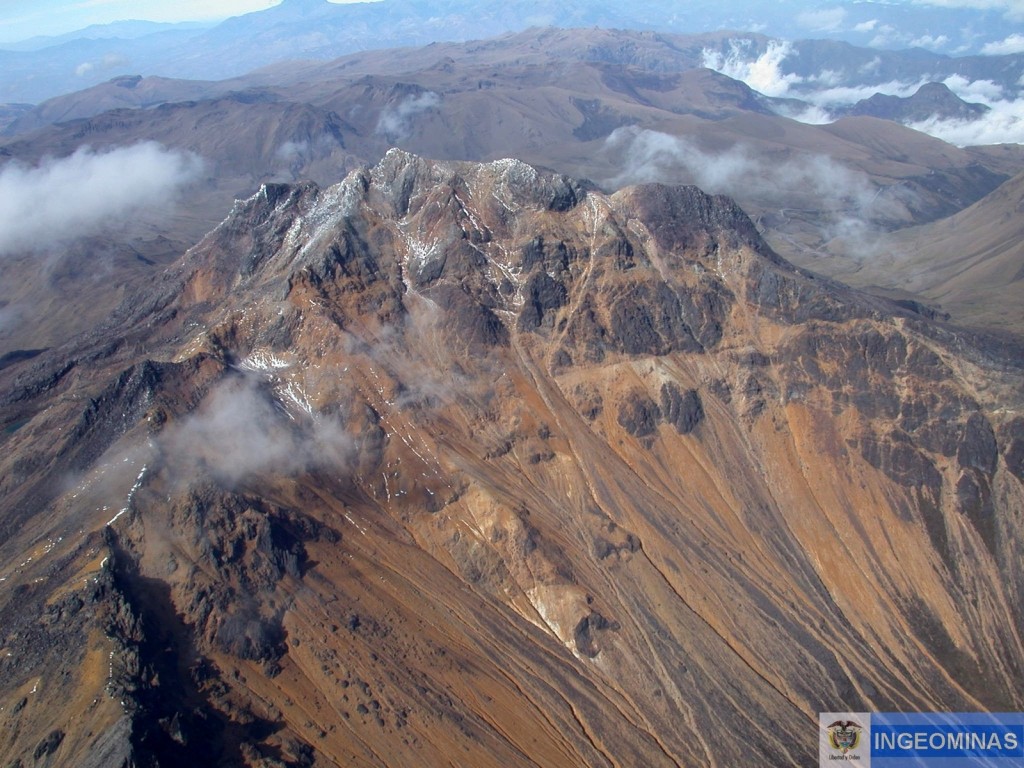
Colombia , Chiles / Cerro Negro :
Weekly activity bulletin of Chiles and Cerro Negro volcanoes
The level of activity of volcanoes continues at the level: YELLOW LEVEL ■ (III): CHANGES IN THE BEHAVIOR OF THE VOLCANIC ACTIVITY.
Following the activity of the VOLCANOES CHILE and CERRO NEGRO, the COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE (SGC) reports that:
Between 24 and 30 December 2018, seismic occurrence levels similar to those reported the previous week are maintained, with a total of 1,247 events, mostly associated with fractures of cortical material in the volcanic building. The hypocentres of these earthquakes are located southwest of the summit of the Chiles volcano, some of them located to the south-east, with epicentral distances of less than 9 km and depths of up to 10 km from the summit ( 4700 meters above sea level). The maximum local magnitude reached was 2.9 on the Richter scale.
The COLOMBIAN GEOLOGICAL SERVICE is attentive to the evolution of the volcanic phenomenon and will continue to inform in a timely manner of the observed changes.
Source : SGC
Photo : Ingeominas.
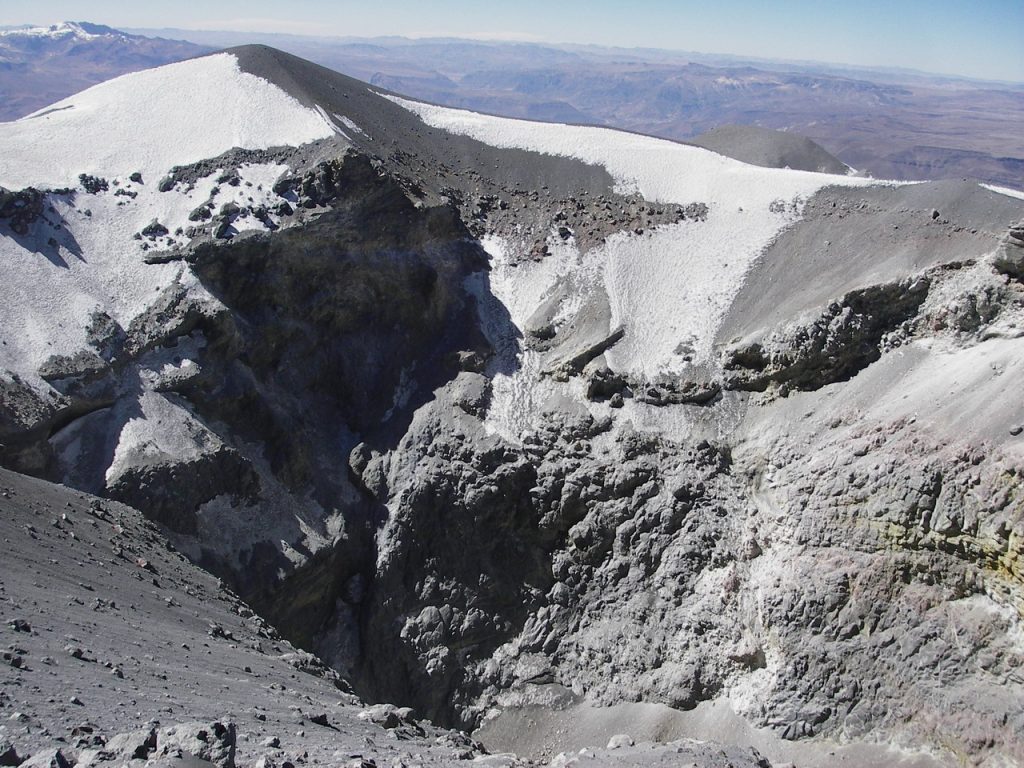
Peru , Sabancaya :
An average of 23 explosions / day was recorded. The activity associated with fluid movements (long-period types) continues to predominate. Earthquakes associated with the rise of magma (hybrid types) remain very few and low energy.
The columns of gas and eruptive ash reached a maximum height of 3300 m above the crater. The dispersion of these materials occurred within a radius of about 30 km, mainly to the Southeast, Northeast and West sectors.
The deformation of the surface of the volcanic building presents important changes.
The MIROVA satellite system recorded 2 thermal anomalies, with values between 1 MW and 3 MW VRP (Rayed Volcano Energy).
In general, eruptive activity maintains moderate levels. No significant changes are expected in the coming days.
Source : IGP Peru.
Photo :Unknown author.
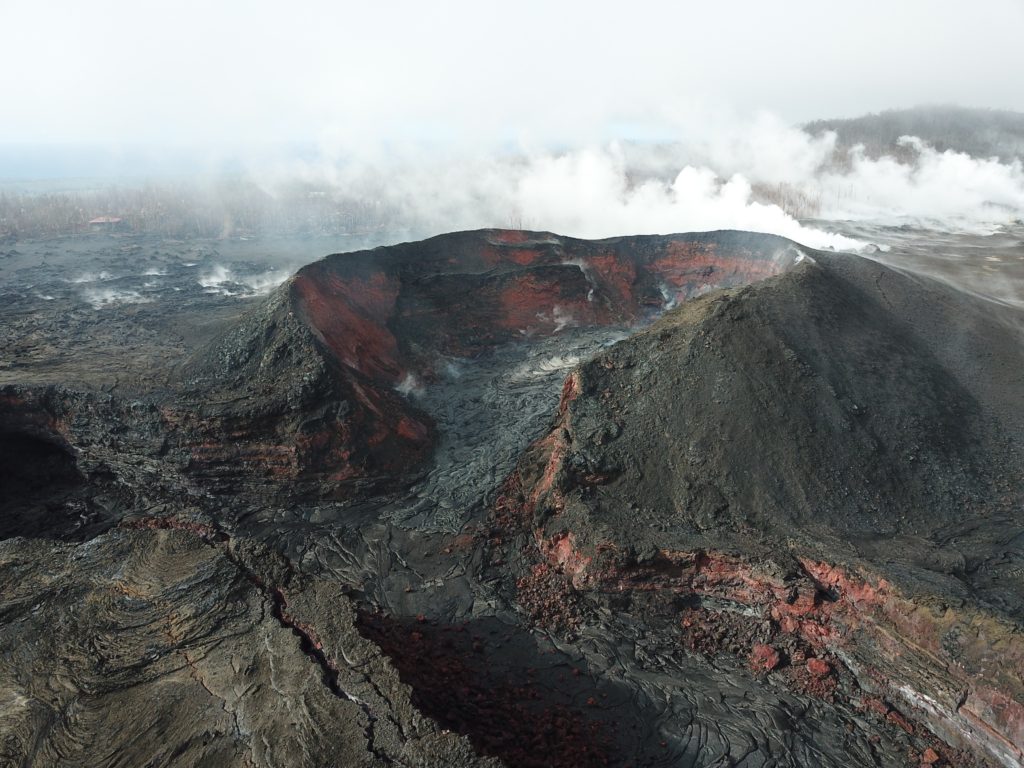
Kilauea , Hawaï :
19°25’16 » N 155°17’13 » W,
Summit Elevation 4091 ft (1247 m)
Current Volcano Alert Level: ADVISORY
Current Aviation Color Code: YELLOW
Activity Summary:
Kīlauea Volcano is not erupting. Rates of seismicity, deformation, and gas release have not changed significantly over the past week. Deformation signals are consistent with slow refilling of the middle East Rift Zone.
Observations:
HVO monitoring data during the past week showed no significant changes. Low rates of seismicity at the summit and East Rift Zone (ERZ) continue, with events occurring primarily in the summit and south flank regions. In the ERZ, tiltmeters showed little change over the last week. GPS stations continue to record minor inflation downrift of Puʻu ʻŌʻō. Sulfur dioxide emission rates have been below detection limits in the LERZ since early September, though minor amounts of volcanic gas are still present. Sulfur dioxide emission rates from the summit and Puʻu ʻŌʻō remain low.
Hazards remain in the LERZ eruption area and at the Kīlauea summit. Residents and visitors near recently active fissures and lava flows should heed Hawaii County Civil Defense and National Park warnings, and be prepared, if necessary, to self-evacuate in the unlikely event of renewed activity. Please note that Hawaii County maintains a closure of the entire lava flow field and vents and prohibits access unless authorized through Civil Defense.
The Hawaiian Volcano Observatory (HVO) continues to closely monitor Kīlauea’s seismicity, deformation, and gas emissions for any sign of reactivation, and maintains visual surveillance of the summit and the East Rift Zone. HVO will continue to issue a weekly update (every Tuesday) and additional messages as warranted by changing activity.
Source : HVO
Photo : Dane DuPont
Costa Rica , Poas / Rincon de la Vieja / Turrialba :
Daily report on the state of volcanoes. Date: January 1, 2019. Updated at: 11:19:00.
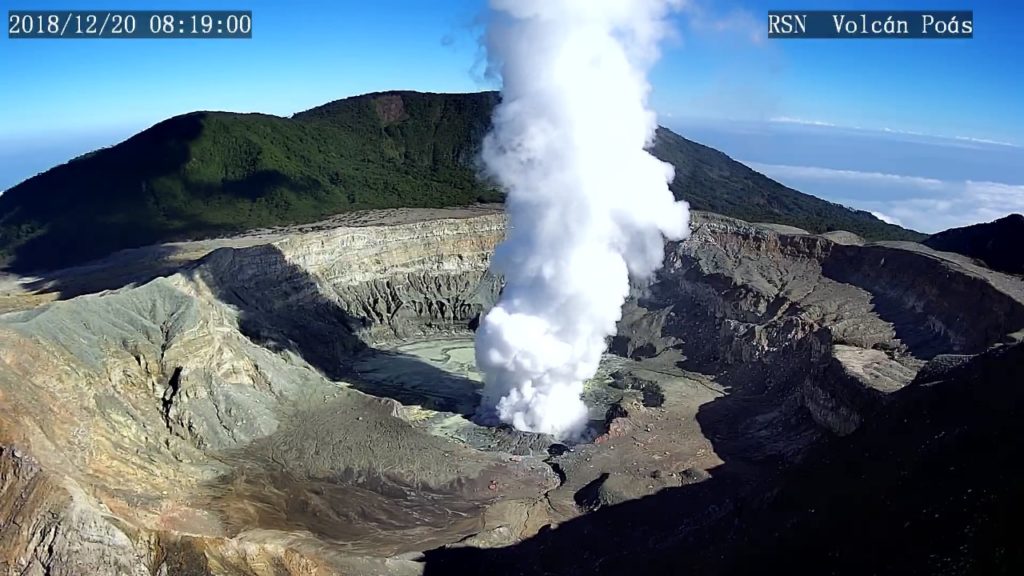
Poas Volcano:
On January 1, 2019, at 10:07 am local time, there was an eruption on the Poas volcano, with a column that rose 50 meters above crater height and 2758 meters above sea level. the sea (9046.24 ft).
Duration of the activity: 2 minutes.
The seismic activity is similar to that of yesterday.
At the time of this report, the winds blow towards the West.
The Poás volcano has frequent eruptions of water vapor, magmatic gases and fine sediments through the fumaroles of the Boca A (Boca Roja or old dome). Seismicity shows frequent low-frequency volcanic earthquakes and short, low-amplitude tremors associated with eruptions. The acidic lagoon continues to fall and appears with a milky gray color. Two fumaroles remain active, one under water and the other aerial. The CO2 / SO2 gas ratio is kept around 2 and the SO2 concentration remains low.
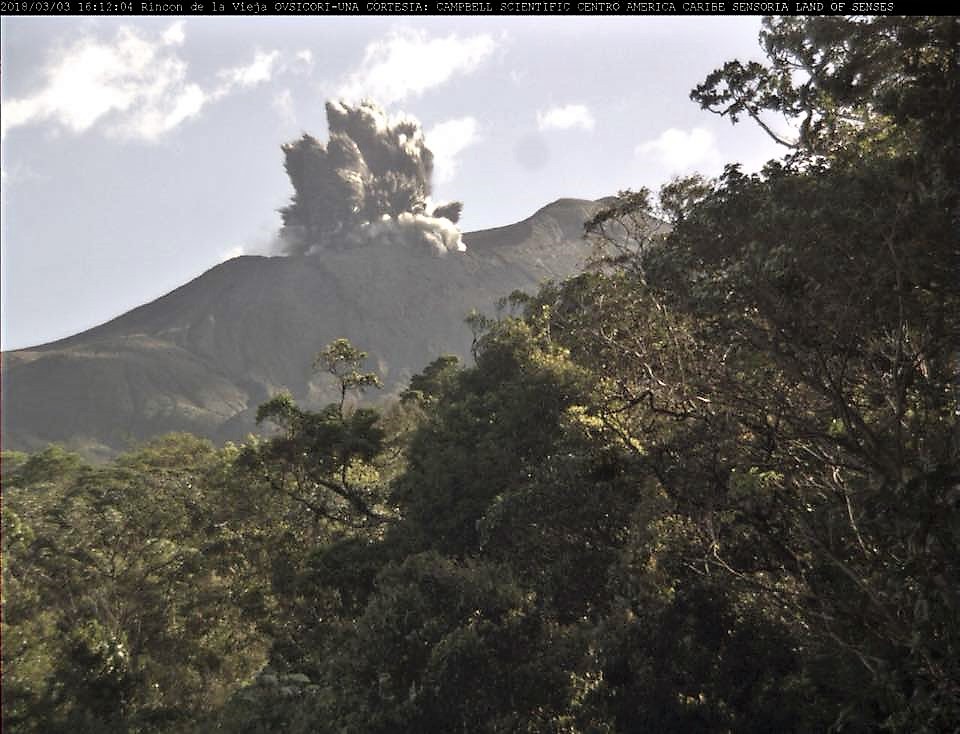
Rincon de la Vieja volcano:
On January 1, 2019, at 5:55 local time, there is an eruption on the Rincon de la Vieja volcano. The height reached by the column due to visibility conditions of the site is unknown.
Duration of the activity: 2 minutes.
The seismic activity is more important compared to yesterday.
At the time of this report, the winds blow towards the West.
After the small steam eruption at 05:55 this morning, the seismic recording, dominated until now by frequent tremors of low amplitude and short duration, becomes dominated by a continuous bottom tremor and low amplitude. The summit remains cloudy.
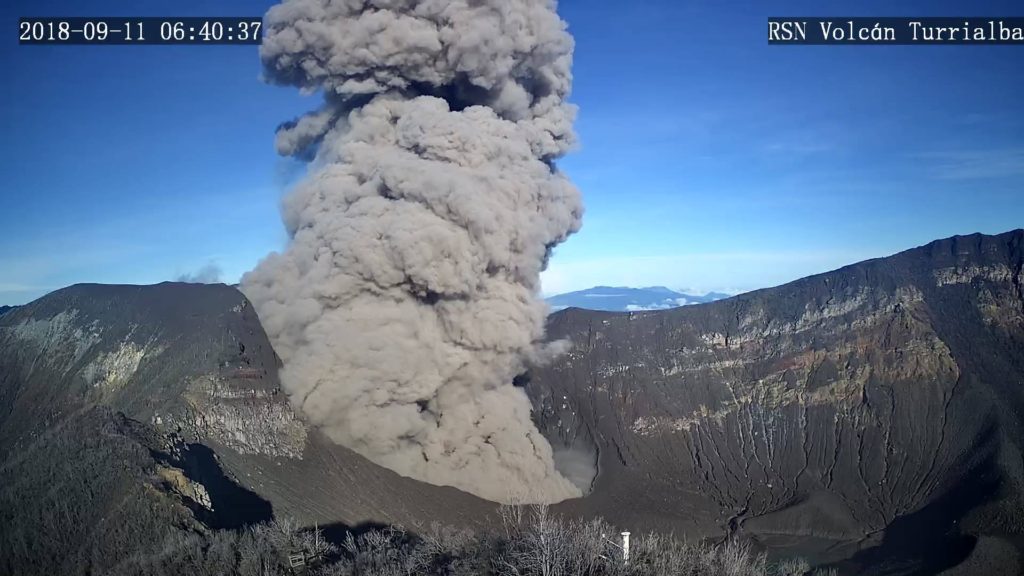
Turrialba Volcano:
On January 1, 2019, at 09:10 local time, there was an eruption on the Turrialba volcano, with a column that rose 200 meters above crater height and 3540 meters above sea level. from the sea. (11611.2 ft).
Duration of the activity: 1 hour and 30 minutes.
The seismic activity is similar to that of yesterday.
At the time of this report, the winds blow from the northwest.
The Turrialba volcano has a very weak and almost transparent plume of gas and aerosols. Ash emissions are prolonged and occur sporadically, with weak plumes and very diluted ash in the gas column. Seismic activity is characterized by small low frequency volcanic earthquakes and the absence of volcanic tremor. NASA’s IMO-AURA satellite imagery indicates a substantial reduction in the mass of gaseous sulfur dioxide, SO2, detected remotely between August and December 2018, compared to the previous months of 2018 and 2017. The glowing light due to gases and incandescent rocks in the western crater continue to be observed at night. At the time of writing, no falls of ash or sulfur odor have been reported.
Source : Ovsicori.
Photos : Archives RSN.










No comment yet, add your voice below!