
December 28 , 2018.
Italy / Sicily , Etna :
Deepening and updating of the seismic and volcanic activity in the region of Etna.
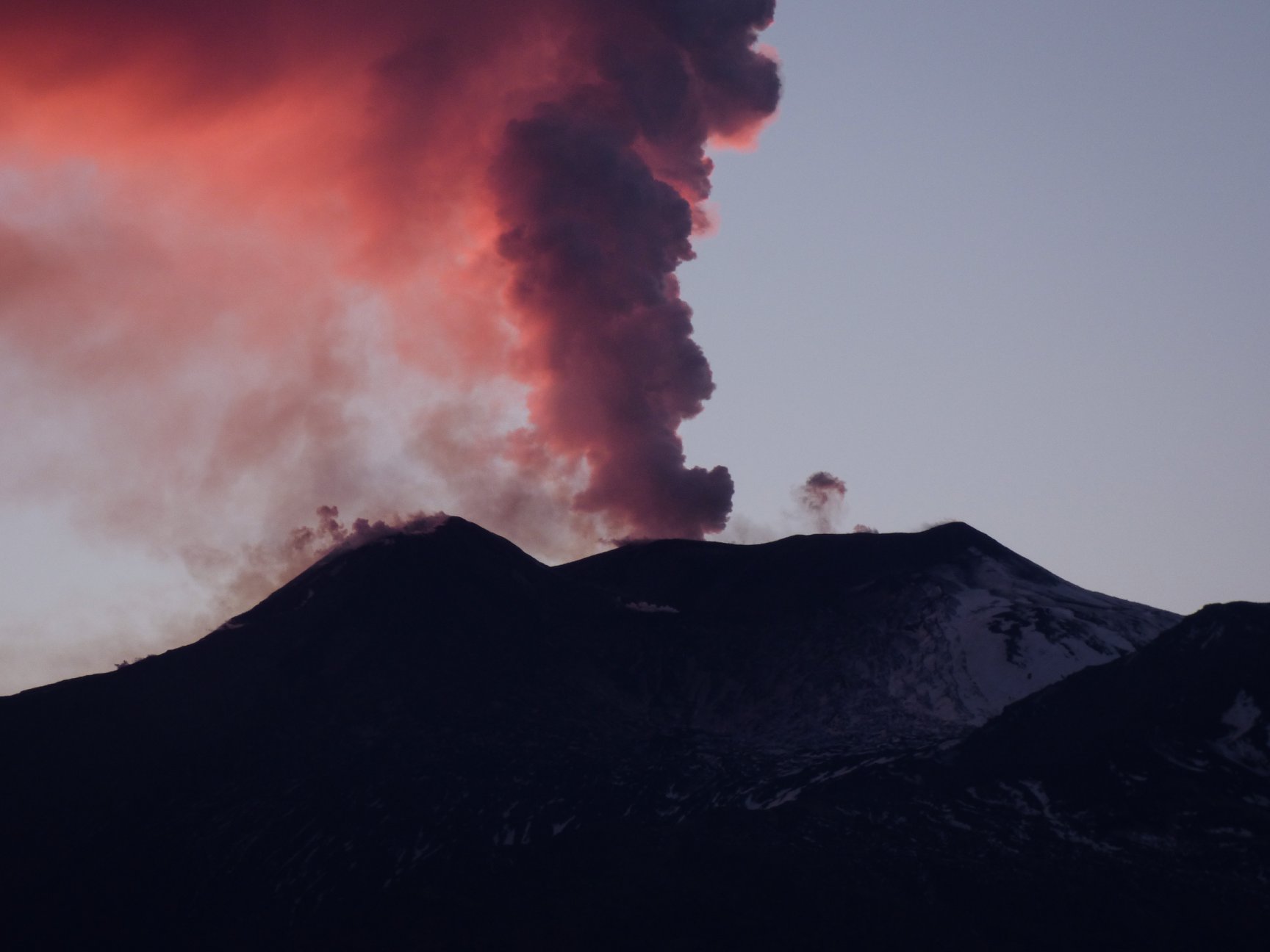
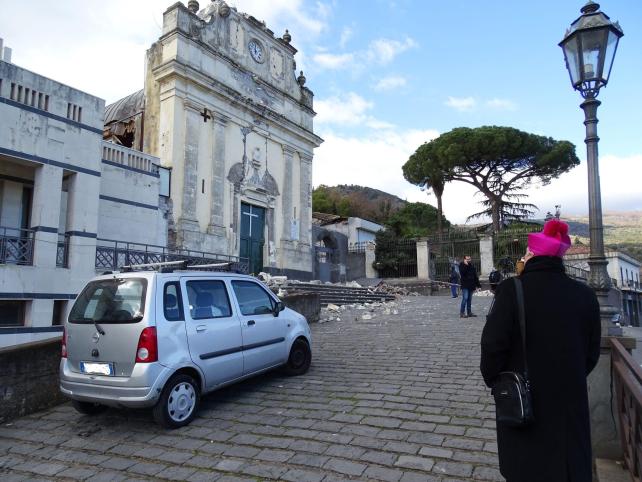
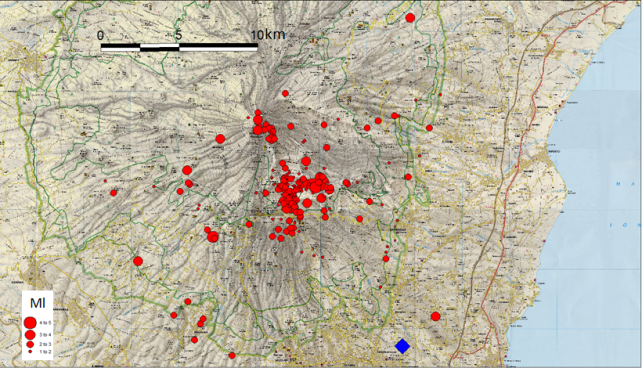
At 3:19 am today, December 26, 2018, at the bottom of the southeast flank of Mount Etna, one of the most energetic earthquakes occurred on the volcano. The seismic event, with a magnitude Ml equal to 4.8, 4.9 Mw, was located 1 km south of the city of Lavinaio (CT), at a depth of about 1 km below the level of The earthquake was widely felt by people in almost the entire Catania region, causing damage and injury to areas near the epicenter.
Figure 1 – Fleri: Damage to Maria Santissima del Rosario Church (Foto INGV).
A few hours earlier, at 1:09, the earthquake had been anticipated by another earthquake of magnitude Ml 3.3 located a little further north-east and at the same depth.
The 3:19 earthquake is probably related to the activation of the Fiandaca fault and the Pennisi fault, two of the southernmost structures of Timpe’s tectonic system. In fact, the greatest damage is distributed along these volcano-tectonic structures, as well as the superficial fault effects associated with the seismic event. The distribution of the damage and the extension of the faults are very similar to those reported by historical sources for the earthquake of 8 August 1894 (Int 899 max EMS, Mw 4.6), which broke the Fiandaca fault for the first time on all its length.
Other historical events documented by the historical seismic catalog took place in 1875, 1907, and 1984, but were less energetic and due to activation of some parts of the Fiandaca fault.
The night’s earthquake took place on the third day since the start of the ongoing volcanic eruption at Etna, which touches the highest parts of the volcano and Valle del Bove. In particular, an open eruption crack at the base of the New Southeast Crater on the morning of December 24th, which produced a cloud of ash re falling mainly in the vicinity of Zafferana Etnea (CT) and a pouring lava flow in the Valle del Bove having crossed its western wall (figures 2 and 3).
Figure 2. – The new eruptive fissure and mouths that fed and still feed weakly the lava flows (Photo INGV).
Figure 3. – Lava flows progressing in Valle del Bove (Foto INGV).
This volcanic phenomenon was preceded by a few hours and is still accompanied today by significant deformation and seismic activity, which generated about 1 100 earthquakes, about 60 of which exceed 2.5 magnitude ( Fig. 4); in addition, a significant increase in the average amplitude of volcanic tremors was recorded during the day of December 24 and currently, although decreasing, the values remain above the norm.
Figure 4. – Epicentral map of the most energetic earthquakes recorded on December 24, 2018. The earthquake recorded at 3:19 am, with a magnitude of 4.8 ml, is reported with the blue diamond.
During the last three days, recorded seismicity has affected several areas of the volcano: in particular, in the early hours of December 24, it was recorded in the area of the summit coinciding with the eruptive theater, surface up to 2 km below sea level. Subsequently, it positioned itself along the western and southern walls of Valle del Bove, at a depth of 4 to 5 km below sea level.
It should be noted that the earthquake of today is not generated by the magmatic mass movements present in the epicentral region, but is probably the fragile response of the eastern flank of the volcano to a stress induced by the magmatic system that is causing eruption. In fact, the intrusion of a magma dyke often transfers stress to surrounding tectonic structures, causing earthquakes, even of high magnitude.
The current eruptive situation does not deviate much from the most well-known cases for effusive ethnic eruptions, during which a transfer of stress from the intrusive masses to the more superficial parts of the flanks of the volcano can generate the triggering of earthquakes, even at several kilometers away from the eruptive centers.
On the basis of current eruptive manifestations, problems are currently excluded from populations and major infrastructure: in fact, the lava effusion has produced runoff from the base of the New Southeast Crater in the vast desert of the Valle del Bove. However, although the more superficial volcanological evidences indicate a decrease of the general eruptive activity, the information obtained from the geophysical signals does not make it possible to exclude a possible feeding, still in progress, of the dyke and its intrusion. On the basis of the current seismicity distribution, this dyke could affect a sector other than the current eruptive theater, with the opening of new eruptive fractures at altitudes below 2400 meters, coinciding with the western and southern walls of the Valle del Bove. .
The INGV Etneo Observatory continuously monitors the evolution of phenomena in close contact with the Department of Civil Protection (DPC) and all civil protection authorities.
Source : INGV.
Read the article : https://ingvterremoti.wordpress.com/2018/12/26/approfondimento-e-aggiornamento-sullattivita-sismica-e-vulcanica-in-area-etnea/
Vanuatu Archipelago , Ambrym :
16°15’00”S 168°07’00”E
Summit Elevation 4377ft (1334m)
Current Vanuatu Volcano Alert Level: Level 3
Eruptive activity at Ambrym is continuing in the minor eruption state. The Volcanic Alert Level remains at Level 3 .
The volcanic eruption at Ambrym is continuing in the minor eruption. The Danger Zone for life safety remains at the Danger Zone B which is about 2 km around Benbow and 4 km around Marum craters (including Maben-Mbwelesu, Niri-Mbwelesu and Mbwelesu) . The additional area of risk is within 3 km from major cracks in the South East of Ambrym .
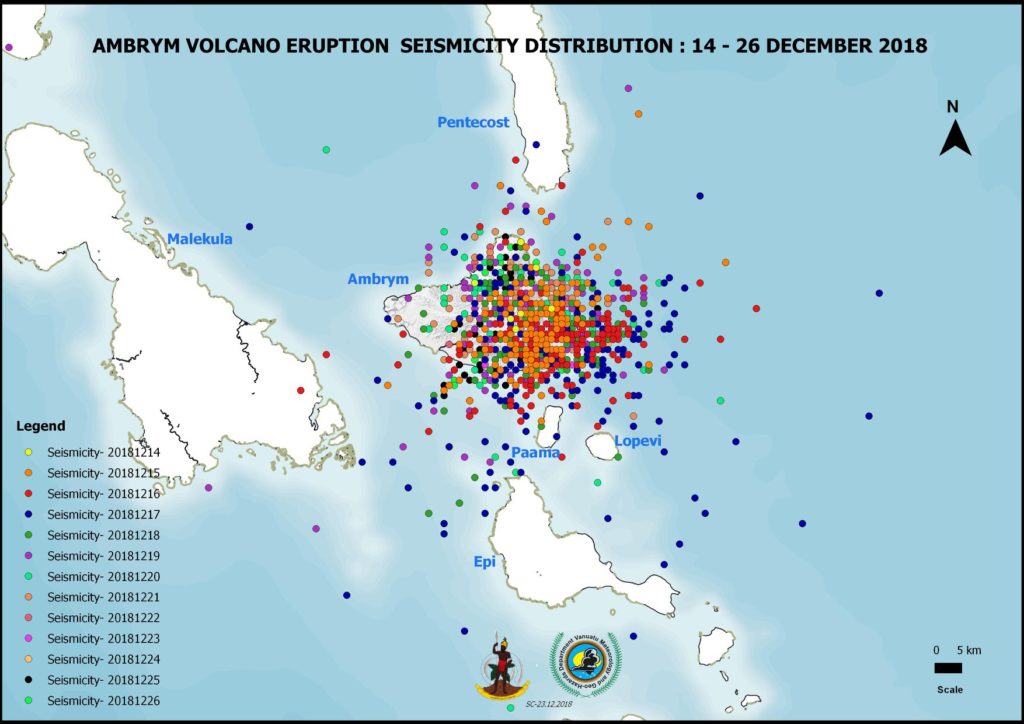
Though people are not feeling strong earthquakes compare to the past few days, current observations and analysis of seismic data recorded from the monitoring network confirm an ongoing seismicity. This is related to the current volcano eruption. This seismicity may continue to affect the existing cracks, especially in the South East Ambrym area. Latest satellite imagery analysis confirm a remarquable land deformation on Ambrym island, therefore people from Ambrym and neighboring islands may continue to expect earthquakes.
The Alert Level for Ambrym volcano has been at the Level 2 since 7 December 2017. The current activity show that Ambrym volcano is undergoing a small scale eruption. This is consistent with the Alert Level 3 activity. Level 3 indicates ‘Minor eruption; Danger is now at 2 km around Benbow and 4 km around Marum with areas exposed to prevailing winds and in major cracked areas in the south eastern part of Ambrym’ . The possibility that the Ambrym volcano activity escalate to the level of moderate eruption (Level 4) is low for now.
The Ambrym Volcano-Seismic Activity was updated by the Vanuatu Meteorological and Geoavailability Department on December 26, 2018 at 5:30 pm:
Since December 14, 2018, the national volcano monitoring network has detected more than 4,500 earthquakes related to the activity of Ambrym volcano at level 3 (minor eruption), of which 1,378 have been located (see seismic map of Ambrym above).
Source : Geohazard .
Video : John Tasso Zulu
Indonesia , Anak Krakatau :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION – VONA:
Issued: December 27 , 2018
Volcano: Anak Krakatau (262000)
Current Aviation Colour Code: RED
Previous Aviation Colour Code: orange
Source: Anak Krakatau Volcano Observatory
Notice Number: 2018KRA127
Volcano Location: S 06 deg 06 min 07 sec E 105 deg 25 min 23 sec
Area: Lampung, Indonesia
Summit Elevation: 1082 FT (338 M)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
Continuing eruption and ash emission.
Volcanic Cloud Height:
Best estimate of ash-cloud top is around 23482 FT (7338 M) above sea level, may be higher than what can be observed clearly. Source of height data: ground observer.
Other Volcanic Cloud Information:
Ash-cloud moving to northeast.
Remarks:
Seismic activity is characterized by volcanic tremor with 25mm amplitude.
Contacts:
Ministry of Energy and Mineral Resources
Geological Agency
Center for Volcanology and Geological Hazard Mitigation (CVGHM)
Tel: +62-22-727-2606
Facsimile: +62-22-720-2761
Email : vsi@vsi.esdm.go.id
Next Notice:
A new VONA will be issued if conditions change significantly or the colour code is changes.
Latest Volcanic information is posted at VONA | MAGMA Indonesia Website
Link : https://magma.vsi.esdm.go.id/vona/
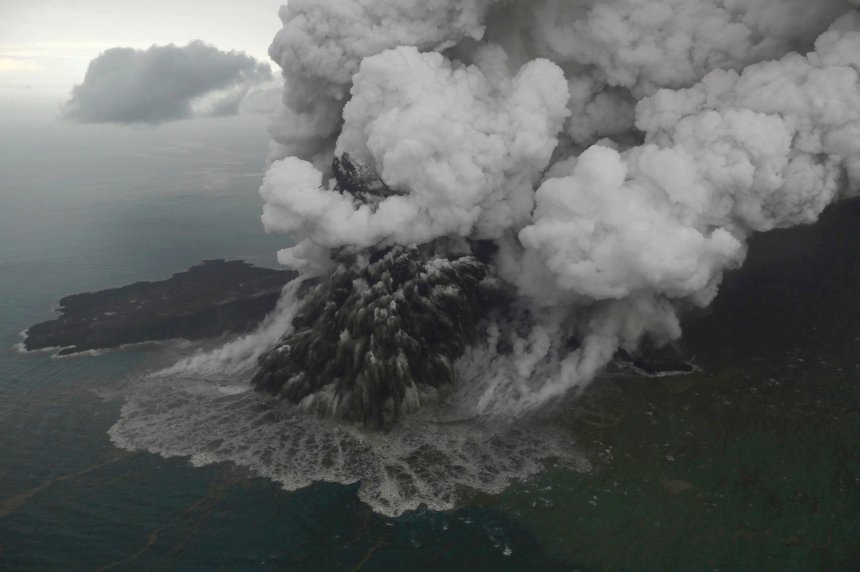
Level of activity level III (SIAGA) since December 27, 2018. The Anak Krakatau volcano (338 m above sea level) has increased its volcanic activity since June 18, 2018.
Since yesterday and until this morning, the volcano was clearly visible then covered with fog. The crater smoke is observed at a height of about 2,500 meters above the peak, black in color and thick in intensity. The wind is blowing weakly to the north and east.
By the seismographs, on December 27, 2018 it was recorded:
Continuous tremor with amplitude 8 to 35 mm, dominant 25 mm
1 distant tectonic earthquake
Recommendation:
People / tourists are not allowed to approach the crater within 5 km.
Source : Magma Indonesia , PVMBG.
Photo : Nurul Hidayat/Bisnis Indonesia
Video : NolkilometeƦ via Sherine France
Kamchatka , Sheveluch :
VOLCANO OBSERVATORY NOTICE FOR AVIATION (VONA).
Issued: December 27 , 2018
Volcano:Sheveluch (CAVW #300270)
Current aviation colour code: ORANGE
Previous aviation colour code:orange
Source:KVERT
Notice Number:2018-132
Volcano Location:N 56 deg 38 min E 161 deg 18 min
Area:Kamchatka, Russia
Summit Elevation:10768.24 ft (3283 m), the dome elevation ~8200 ft (2500 m)
Volcanic Activity Summary:
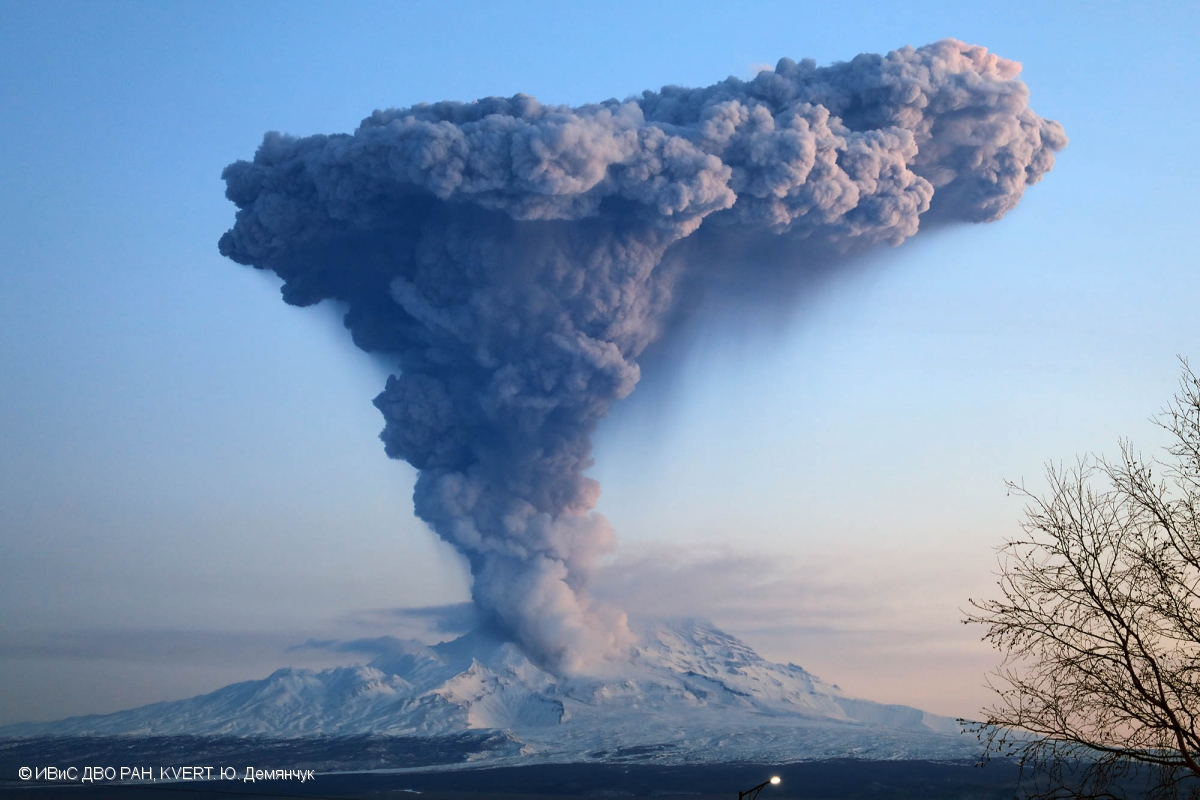
An eruptive activity of the volcano continues. Satellite data show an ash plume extended about 40 km to the north-west from the volcano.
Explosive-extrusive eruption of the volcano continues. Ash explosions up to 26,200-49,200 ft (8-15 km) a.s.l. could occur at any time. Ongoing activity could affect international and low-flying aircraft.
Explosions sent ash up to 10 km a.s.l. on 04 December, 2017, ash plume is extending to the northeast from the volcano.
Volcanic cloud height:
16400 ft (5000 m) AMSL Time and method of ash plume/cloud height determination: 20181227/2200Z – Himawari-8
Other volcanic cloud information:
Distance of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: 25 mi (40 km)
Direction of drift of ash plume/cloud of the volcano: NW / azimuth 313 deg
Time and method of ash plume/cloud determination: 20181227/2200Z – Himawari-8
The meteorological conditions (cyclones) in the northern part of Kamchatka caused a strong increased in gas-steam activity of the volcano, on the background of which, on December 26-27, explosive events repeatedly occurred with ash emission up to 6-9 km a.s.l. According to videodata, strong explosions sent ash up to 9 km a.s.l. on 26 December. Satellite data by KVERT showed ash clouds drifted for about 300 km to the north-west from the volcano; a thermal anomaly over the volcano was noting all week.
Source : Kvert.
Photo : Yu. Demyanchuk, IVS FEB RAS, KVERT









No comment yet, add your voice below!